前情提示:
Mac 10.14
MySQL8.0官方下载安装
PS:
无论是homebrew等方式,在Mac下都是不会生成my.cnf文件,因为已经使用了最优默认值,如果需要也可以自行新建或配置/etc/my.cnf
加载my.cnf位置顺序查看:
mysql --verbose --help | grep my.cnf![]()
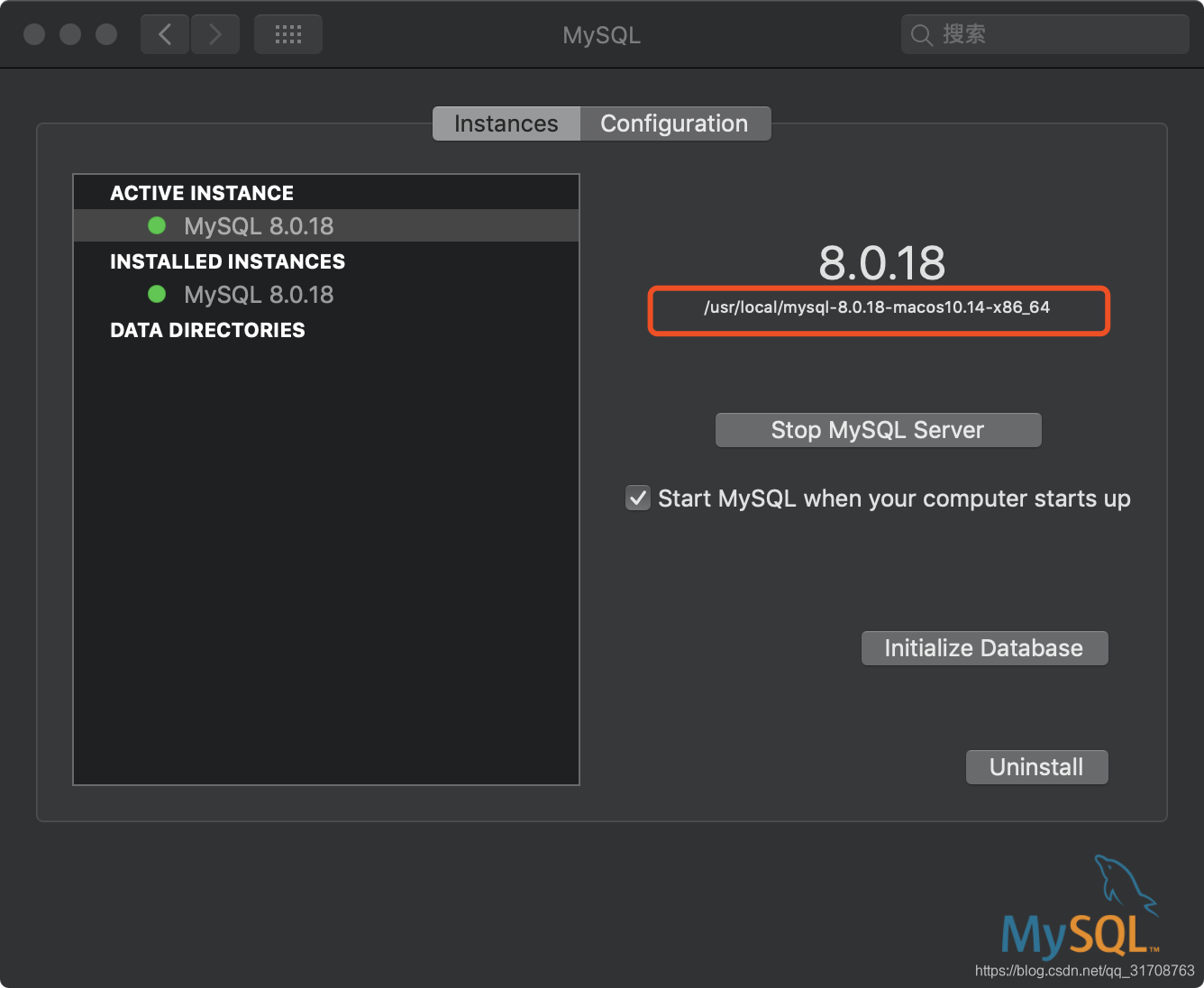
默认安装位置:/usr/local/mysql
补充:
(Mac)这里实际安装位置为mysql8.0-mac-xxx类似这种格式的,只是引用了快捷方式,在偏好设置里可以看到,而且也可以看到mysql文件夹左下角有个快捷键头。
一般情况下/usr/local/mysql/support-files/下不会有示例文件,如果有可以执行以下命令:
cd /usr/local/mysql/support-files/
sudo cp my-huge.cnf /etc/my.cnf如果没有,也可以手动创建my.cnf文件:
#
# FromDual configuration file template for MySQL, Galera Cluster, MariaDB and Percona Server
# Location: %MYCNF%
# This template is intended to work with MySQL 5.7 and newer and MariaDB 10.0 and newer
# Get most recent updated from here:
# https://www.fromdual.com/mysql-configuration-file-sample
#
[client]
port = %PORT% # default 3306
socket = %SOCKET% # Use mysqld.sock on Ubuntu, conflicts with AppArmor otherwise
[mysql]
no_auto_rehash
max_allowed_packet = 16M
prompt = '\u@\h [\d]> ' # 'user@host [schema]> '
default_character_set = utf8 # Possibly this setting is correct for most recent Linux systems
[mysqldump]
max_allowed_packet = 16M
[mysqld_safe] # Becomes sooner or later obsolete with systemd
open_files_limit = 8192 # You possibly have to adapt your O/S settings as well
user = mysql
log-error = %INSTANCEDIR%/log/%UNAME%_%INSTANCE%_error.log # Adjust AppArmor configuration: /etc/apparmor.d/local/usr.sbin.mysqld
[mysqld]
# Connection and Thread variables
port = %PORT% # default 3306
socket = %SOCKET% # Use mysqld.sock on Ubuntu, conflicts with AppArmor otherwise
basedir = %BASEDIR%
datadir = %DATADIR%
# tmpdir = '%INSTANCEDIR%/tmp'
# innodb_tmpdir = '%INSTANCEDIR%/tmp' # MySQL 5.7
max_allowed_packet = 16M
default_storage_engine = InnoDB
# explicit_defaults_for_timestamp = 1 # MySQL 5.6, test carefully! This can have an impact on application.
# disable_partition_engine_check = true # Since MySQL 5.7.17 to 5.7.20. To get rid of nasty message in error log
# character_set_server = utf8mb4 # For modern applications, default in MySQL 8.0
# collation_server = utf8mb4_general_ci
max_connections = 151 # Values < 1000 are typically good
max_user_connections = 145 # Limit one specific user/application
thread_cache_size = 151 # Up to max_connections makes sense
# Query Cache (does not exist in MySQL 8.0 any more!)
# query_cache_type = 1 # Set to 0 to avoid global QC Mutex
# query_cache_size = 32M # Avoid too big (> 128M) QC because of QC clean-up lock!
# Session variables
sort_buffer_size = 2M # Could be too big for many small sorts
tmp_table_size = 32M # Make sure your temporary results do NOT contain BLOB/TEXT attributes
read_buffer_size = 128k # Resist to change this parameter if you do not know what you are doing
read_rnd_buffer_size = 256k # Resist to change this parameter if you do not know what you are doing
join_buffer_size = 128k # Resist to change this parameter if you do not know what you are doing
# Other buffers and caches
table_definition_cache = 1400 # As big as many tables you have
table_open_cache = 2000 # connections x tables/connection (~2)
table_open_cache_instances = 16 # New default in 5.7
# MySQL error log
log_error = %INSTANCEDIR%/log/%UNAME%_%INSTANCE%_error.log # Adjust AppArmor configuration: /etc/apparmor.d/local/usr.sbin.mysqld
# log_timestamps = SYSTEM # MySQL 5.7, equivalent to old behaviour
log_warnings = 2 # MySQL 5.6, equivalent to log_error_verbosity = 3
# log_error_verbosity = 3 # MySQL 5.7, equivalent to log_warnings = 2, MariaDB does NOT support this!
innodb_print_all_deadlocks = 1
# wsrep_log_conflicts = 1 # for Galera only!
# Slow Query Log
slow_query_log_file = %INSTANCEDIR%/log/%UNAME%_%INSTANCE%_slow.log # Adjust AppArmor configuration: /etc/apparmor.d/local/usr.sbin.mysqld
slow_query_log = 0
log_queries_not_using_indexes = 0 # Interesting on developer systems!
long_query_time = 0.5
min_examined_row_limit = 100
# General Query Log
general_log_file = %INSTANCEDIR%/log/%UNAME%_%INSTANCE%_general.log # Adjust AppArmor configuration: /etc/apparmor.d/local/usr.sbin.mysqld
general_log = 0
# Performance Schema
# performance_schema = ON # for MariaDB 10 releases
performance_schema_consumer_events_statements_history_long = ON # MySQL 5.6/MariaDB 10 and newer
# Binary logging and Replication
server_id = %SERVERID% # Must be set on MySQL 5.7 and newer if binary log is enabled!
log_bin = %INSTANCEDIR%/binlog/%UNAME%_%INSTANCE%_binlog # Locate outside of datadir, adjust AppArmor configuration: /etc/apparmor.d/local/usr.sbin.mysqld
# master_verify_checksum = ON # MySQL 5.6
binlog_cache_size = 1M
binlog_stmt_cache_size = 1M
max_binlog_size = 128M # Make bigger for high traffic to reduce number of files
sync_binlog = 1 # Set to 0 or higher to increase write performance
expire_logs_days = 5 # We will survive easter holidays
binlog_format = ROW # Use MIXED if you want to experience some troubles
# binlog_row_image = MINIMAL # Since 5.6
# auto_increment_increment = 2 # For Master/Master set-ups use 2 for both nodes
# auto_increment_offset = 1 # For Master/Master set-ups use 1 and 2
# Slave variables
log_slave_updates = 1 # Use if Slave is used for Backup and PiTR
read_only = 0 # Set to 1 to prevent writes on Slave
# super_read_only = 0 # Set to 1 to prevent writes on Slave for users with SUPER privilege. Since 5.7, not in MariaDB
# skip_slave_start = 1 # To avoid start of Slave thread
# relay_log = %UNAME%_%INSTANCE%_relay-bin
# relay_log_info_repository = table # MySQL 5.6
# master_info_repository = table # MySQL 5.6
# slave_load_tmpdir = '%INSTANCEDIR%/tmp'
# Crash-safe replication Master
# binlog_checksum = CRC32 # default
# sync_binlog = 1 # default since 5.7.6, but slow!
# innodb_support_xa = 1 # default, depracted since 5.7.10
# Crash-safe replication Slave
# master_info_repository = TABLE
# relay_log_info_repository = TABLE
# relay_log_recovery = 1
# sync_relay_log_info = 1
# relay_log_purge = 1 # default
# slave_sql_verify_checksum = 1 # default
# GTID replication
# gtid_mode = ON # Master and Slave
# enforce_gtid_consistency = 1 # Master and Slave
# log_bin = %INSTANCEDIR%/binlog/%UNAME%_%INSTANCE%_binlog # In 5.6 also on Slave
# log_slave_updates = 1 # In 5.6 also on Slave
# Security variables
# local_infile = 0 # If you are security aware
# secure_auth = 1 # If you are security aware
# sql_mode = TRADITIONAL,ONLY_FULL_GROUP_BY,NO_ENGINE_SUBSTITUTION,STRICT_ALL_TABLES,NO_ZERO_IN_DATE,NO_ZERO_DATE,ERROR_FOR_DIVISION_BY_ZERO,NO_AUTO_CREATE_USER # Be careful changing this afterwards
# skip_name_resolve = 0 # Set to 1 if you do not trust your DNS or experience problems
# secure_file_priv = '%INSTANCEDIR%/tmp' # chmod 750, adjust AppArmor configuration: /etc/apparmor.d/local/usr.sbin.mysqld
# MyISAM variables
key_buffer_size = 8M # Set to 25 - 33 % of RAM if you still use MyISAM
myisam_recover_options = 'BACKUP,FORCE'
# disabled_storage_engines = 'MyISAM,MEMORY' # MySQL 5.7, do NOT during/before mysql_upgrade, good for Galera!
# MEMORY variables
max_heap_table_size = 64M # Should be greater or equal to tmp_table_size
# InnoDB variables
innodb_strict_mode = ON
# innodb_file_format_check = 1 # Desupported in MySQL 8.0
# innodb_file_format = Barracuda # For dynamic and compressed InnoDB tables, default in 5.7
innodb_buffer_pool_size = 128M # Go up to 80% of your available RAM
innodb_buffer_pool_instances = 8 # Bigger if huge InnoDB Buffer Pool or high concurrency
innodb_file_per_table = 1 # Is the recommended way nowadays
# innodb_flush_method = O_DIRECT # O_DIRECT is sometimes better for direct attached storage
# innodb_write_io_threads = 8 # If you have a strong I/O system or SSD
# innodb_read_io_threads = 8 # If you have a strong I/O system or SSD
# innodb_io_capacity = 1000 # If you have a strong I/O system or SSD
innodb_flush_log_at_trx_commit = 2 # 1 for durability, 0 or 2 for performance
innodb_log_buffer_size = 8M # Bigger if innodb_flush_log_at_trx_commit = 0
innodb_log_file_size = 256M # Bigger means more write throughput but longer recovery time
# Since MariaDB 10.0 and MySQL 5.6
innodb_monitor_enable = all # Overhead < 1% according to PeterZ/Percona
# Galera specific MySQL parameter
# default_storage_engine = InnoDB # Galera only works with InnoDB
# innodb_flush_log_at_trx_commit = 2 # Durability is achieved by committing to the Group
# innodb_autoinc_lock_mode = 2 # For parallel applying
# binlog_format = row # Galera only works with RBR
# query_cache_type = 0 # Use QC with Galera only in a Master/Slave set-up
# query_cache_size = 0
# WSREP parameter
# wsrep_on = on # Only MariaDB >= 10.1
# wsrep_provider = /usr/lib/galera/libgalera_smm.so # Location of Galera Plugin on Ubuntu ?
# wsrep_provider = /usr/lib64/galera-3/libgalera_smm.so # Location of Galera Plugin on CentOS 7
# wsrep_provider = none # Start mysqld without Galera
# wsrep_provider_options = 'gcache.size = 1G' # Depends on you workload, WS kept for IST
# wsrep_cluster_name = "My cool Galera Cluster" # Same Cluster name for all nodes
# wsrep_cluster_address = "gcomm://192.168.0.2,192.168.0.3" # Start other nodes like this
# wsrep_node_name = "Node A" # Unique node name
# wsrep_node_address = 192.168.0.1 # Our address where replication is done
# wsrep_node_incoming_address = 10.0.0.1 # Our external interface where application comes from
# wsrep_sync_wait = 1 # If you need realy full-synchronous replication (Galera 3.6 and newer)
# wsrep_slave_threads = 16 # 4 - 8 per core, not more than wsrep_cert_deps_distance
# wsrep_sst_method = rsync # SST method (initial full sync): mysqldump, rsync, rsync_wan, xtrabackup-v2
# wsrep_sst_auth = sst:secret # Username/password for sst user
# wsrep_sst_receive_address = 192.168.2.1 # Our address where to receive SST
# Group Replication parameter
# default_storage_engine = InnoDB # Group Replication only works with InnoDB
# server_id = %SERVERID% # Should be different on all 3 nodes
# log_bin = %INSTANCEDIR%/binlog/%UNAME%_%INSTANCE%_binlog # Locate outside of datadir, adjust AppArmor configuration: /etc/apparmor.d/local/usr.sbin.mysqld
# binlog_format = ROW
# binlog_checksum = NONE # not default!
# gtid_mode = ON
# enforce_gtid_consistency = ON
# master_info_repository = TABLE
# relay_log_info_repository = TABLE
# log_slave_updates = ON
# slave_parallel_workers = <n> # 1-2/core, max. 10
# slave_preserve_commit_order = ON
# slave_parallel_type = LOGICAL_CLOCK
# transaction_write_set_extraction = XXHASH64
# loose-group_replication_group_name = "$(uuidgen)" # Must be the same on all nodes
# loose-group_replication_start_on_boot = OFF
# loose-group_replication_local_address = "192.168.0.1"
# loose-group_replication_group_seeds = "192.168.0.1,192.168.0.2,192.168.0.3" # All nodes of Cluster
# loose-group_replication_bootstrap_group = OFF
# loose-group_replication_single_primary_mode = FALSE # = multi-primary8.0配置文件,仅参考:
参考1:
[client]
port = 3306
socket = /tmp/mysql.sock
[mysqld]
#Mysql服务的唯一编号 每个mysql服务Id需唯一
server-id = 1
#服务端口号 默认3306
port = 3306
#mysql安装根目录
basedir = /usr/local/mysql
#mysql数据文件所在位置
datadir = /usr/local/mysql/data
#pid
pid-file = /usr/local/mysql/mysql.pid
#设置socke文件所在目录
socket = /tmp/mysql.sock
#设置临时目录
tmpdir = /tmp
# 用户
user = mysql
# 允许访问的IP网段
bind-address = 0.0.0.0
# 跳过密码登录
#skip-grant-tables
#主要用于MyISAM存储引擎,如果多台服务器连接一个数据库则建议注释下面内容
skip-external-locking
#只能用IP地址检查客户端的登录,不用主机名
skip_name_resolve = 1
#事务隔离级别,默认为可重复读,mysql默认可重复读级别(此级别下可能参数很多间隙锁,影响性能)
transaction_isolation = READ-COMMITTED
#数据库默认字符集,主流字符集支持一些特殊表情符号(特殊表情符占用4个字节)
character-set-server = utf8mb4
#数据库字符集对应一些排序等规则,注意要和character-set-server对应
collation-server = utf8mb4_general_ci
#设置client连接mysql时的字符集,防止乱码
init_connect='SET NAMES utf8mb4'
#是否对sql语句大小写敏感,1表示不敏感
lower_case_table_names = 1
#最大连接数
max_connections = 400
#最大错误连接数
max_connect_errors = 1000
#TIMESTAMP如果没有显示声明NOT NULL,允许NULL值
explicit_defaults_for_timestamp = true
#SQL数据包发送的大小,如果有BLOB对象建议修改成1G
max_allowed_packet = 128M
#MySQL连接闲置超过一定时间后(单位:秒)将会被强行关闭
#MySQL默认的wait_timeout 值为8个小时, interactive_timeout参数需要同时配置才能生效
interactive_timeout = 1800
wait_timeout = 1800
#内部内存临时表的最大值 ,设置成128M。
#比如大数据量的group by ,order by时可能用到临时表,
#超过了这个值将写入磁盘,系统IO压力增大
tmp_table_size = 134217728
max_heap_table_size = 134217728
#禁用mysql的缓存查询结果集功能
#后期根据业务情况测试决定是否开启
#大部分情况下关闭下面两项
query_cache_size = 0
query_cache_type = 0
#数据库错误日志文件
log_error = error.log
#慢查询sql日志设置
slow_query_log = 1
slow_query_log_file = slow.log
#检查未使用到索引的sql
log_queries_not_using_indexes = 1
#针对log_queries_not_using_indexes开启后,记录慢sql的频次、每分钟记录的条数
log_throttle_queries_not_using_indexes = 5
#作为从库时生效,从库复制中如何有慢sql也将被记录
log_slow_slave_statements = 1
#慢查询执行的秒数,必须达到此值可被记录
long_query_time = 8
#检索的行数必须达到此值才可被记为慢查询
min_examined_row_limit = 100
#mysql binlog日志文件保存的过期时间,过期后自动删除
expire_logs_days = 5
参考2
[client]
port = 3306
socket = /usr/local/lnmp/mysql-8.0.12/mysql.sock
[mysqld]
#设置mysql 8.0 的加密方式为 mysql_native_password (默认为:caching_sha2_password)
default_authentication_plugin=mysql_native_password
basedir = /usr/local/lnmp/mysql-8.0.12
datadir = /usr/local/lnmp/mysql-8.0.12/data
port = 3306
server_id = 1
socket = /usr/local/lnmp/mysql-8.0.12/mysql.sock
#二进制日志目录
log-bin = /usr/local/lnmp/mysql-8.0.12/mysql-bin
#自动删除过期日志的天数
expire_logs_days = 10
#限制单个文件大小
max_binlog_size = 100M
#查询日志
general_log = 1
#查询日志文件位置
general_log_file = /usr/local/lnmp/mysql-8.0.12/query.log
#慢查询日志
slow_query_log = 1
#慢日志文件位置
slow_query_log_file = /usr/local/lnmp/mysql-8.0.12/slow-query.log
#超过2秒记录
long_query_time = 2
#错误日志
log-error = /usr/local/lnmp/mysql-8.0.12/error.log
sql_mode=NO_ENGINE_SUBSTITUTION,STRICT_TRANS_TABLES参考3:(实际使用)
# For advice on how to change settings please see
# http://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/5.6/en/server-configuration-defaults.html
# *** DO NOT EDIT THIS FILE. It's a template which will be copied to the
# *** default location during install, and will be replaced if you
# *** upgrade to a newer version of MySQL.
[mysqld]
# Remove leading # and set to the amount of RAM for the most important data
# cache in MySQL. Start at 70% of total RAM for dedicated server, else 10%.
# innodb_buffer_pool_size = 128M
# Remove leading # to turn on a very important data integrity option: logging
# changes to the binary log between backups.
# log_bin
# These are commonly set, remove the # and set as required.
# basedir = .....
# datadir = .....
# port = .....
# server_id = .....
# socket = .....
#服务端口号 默认3306
port = 3306
server_id = 1
# mysql安装根目录
basedir = /usr/local/mysql
# mysql数据文件所在位置
datadir = /usr/local/mysql/data
# pid
pid-file = /usr/local/mysql/data/mysql.pid
# 设置socke文件所在目录
socket = /usr/local/mysql/data/mysql.sock
# 跳过密码登录
# skip-grant-tables
# 数据库默认字符集,主流字符集支持一些特殊表情符号(特殊表情符占用4个字节)
# character-set-server = utf8mb4
# 数据库字符集对应一些排序等规则,注意要和character-set-server对应
# collation-server = utf8mb4_general_ci
# 设置client连接mysql时的字符集,防止乱码
# init_connect='SET NAMES utf8mb4'
# 是否对sql语句大小写敏感,1表示不敏感,8.0需要在初始化时候设置
# lower_case_table_names = 1
# 最大连接数
max_connections = 1000
#最大错误连接数
max_connect_errors = 1200
# wait_timeout = 1814400
# Remove leading # to set options mainly useful for reporting servers.
# The server defaults are faster for transactions and fast SELECTs.
# Adjust sizes as needed, experiment to find the optimal values.
# join_buffer_size = 128M
# sort_buffer_size = 2M
# read_rnd_buffer_size = 2M
# 二进制日志目录
log_bin = /usr/local/mysql/logs/mysql-bin
# 自动删除过期日志的天数
expire_logs_days = 10
# 限制单个文件大小
max_binlog_size = 100M
# 查询日志
general_log = 1
# 查询日志文件位置
general_log_file = /usr/local/mysql/logs/query.log
# 数据库错误日志文件
log_error = /usr/local/mysql/logs/error.log
# sql_mode=NO_ENGINE_SUBSTITUTION,STRICT_TRANS_TABLES
sql_mode=STRICT_TRANS_TABLES,NO_ZERO_IN_DATE,NO_ZERO_DATE,ERROR_FOR_DIVISION_BY_ZERO,NO_ENGINE_SUBSTITUTION5.7之后默认没了my.cnf和my.ini,新建配置文件:
sudo vim /etc/my.cnf:wq保存退出。
sudo chmod 664 /etc/my.cnfmysql的配置文件路径查找优先级为/etc/my.cnf,/etc/mysql/my.cnf,/usr/local/etc/my.cnf,通过Homebrew安装的my.cnf放在/usr/local/etc/中。重启MySQL服务;
注意:(在Mac下测试,当前登录为user1,非root)
配置logs目录,需要添加权限,看:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_31708763/article/details/104380553
要么使用Mac的系统偏好设置里的mysql启动与重启。要么使用命令行,但是要加上sudo。
额外:
Mac下MySQL的安装位置查看:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_31708763/article/details/104357564
https://www.fromdual.com/download
8.1手册:https://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/8.0/en/
5.7手册:https://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/5.7/en/server-configuration-defaults.html

























 524
524

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










