【Cute】MMA抽象代码理解
导读:
阅读本文前建议先读上面reed大神的数篇文章,文本逻辑主要是针对具体的代码,记录一下自己学习过程中的理解与注释。
code
reference: https://github.com/reed-lau/cute-gemm/blob/main/gemm-simple.cu#L80-L86
using mma_op = SM80_16x8x16_F16F16F16F16_TN;
using mma_traits = MMA_Traits<mma_op>;
using mma_atom = MMA_Atom<mma_traits>;
using MMA = decltype(make_tiled_mma(mma_atom{},
make_layout(Shape<_2, _2, _1>{}),
make_layout(Shape<_1, _2, _1>{})));
mma_op
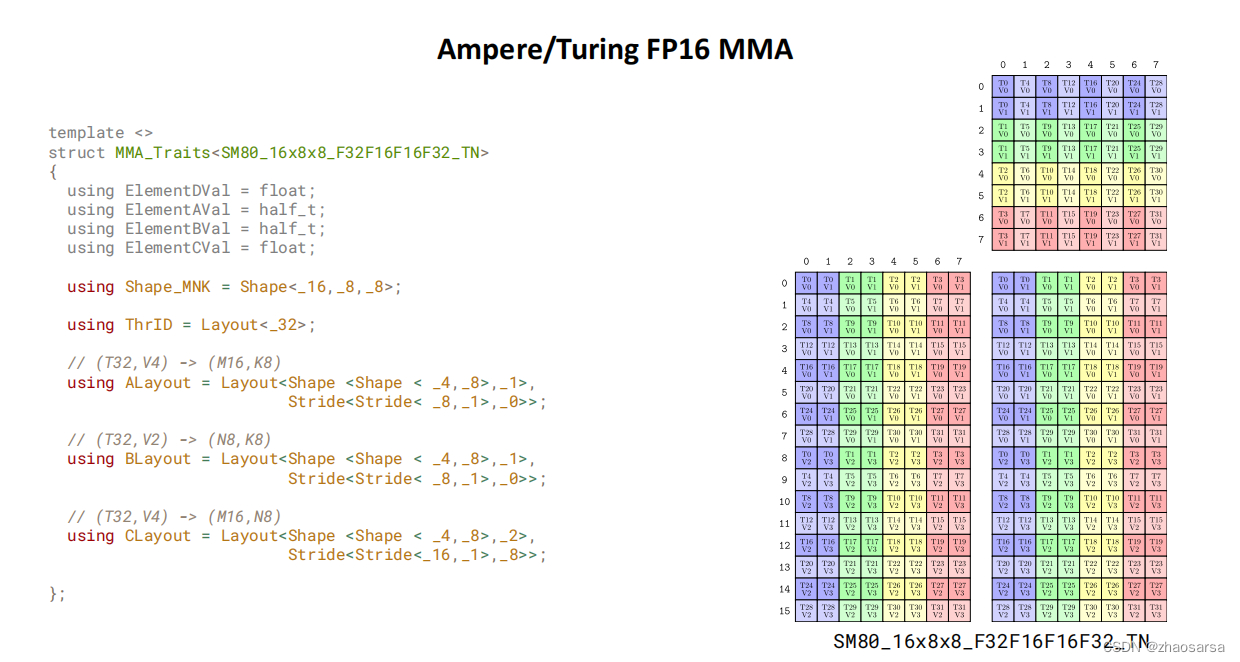
这是一个示例图,但是有点区别,它的A是F32的;tid(logical thread id), vid(logical value id);
这是矩阵乘法的一个最小原子,内部是怎么计算以后再说,先搞清楚,这一个原子它解决A:(16,8),B:(8,8)的计算,最后输出C:(16,8);
对应到上面给出的代码,就是A:(16,16),B:(16,8),C:(16,8);通常矩阵大这个原子也会设的大一点,会让每个并行的计算量多一点。

tile
MMA_Traits和MMA_Atom根据MMA_op补全部分计算的属性。具体的涉及一些概念可以参考之前的文章。
这里主要讲一下atom tile和value tile,在之前的cutlass定义中atom tile又叫thr_layout,value tile叫val_layout。
atom tile主要是指上述的op原子计算在M和N方向上各自拓展多少次,在tensor core中,每个op都是一个warp,即有32个线程;M和N方向各拓展两次,就有4个warp,128个线程,所以也叫thr_layout;
value tile主要是指拓展后的atom,在M和N方向上继续重复多少次计算,因为是重复,内部是loop操作,所以不会占用更多的线程,只会扩大处理的矩阵大小。
图

最下面就是最小的tensor core指令—-MMA_Atom(16816),小框是元素级别的计算(这个可以先不关注,或者结合最上面的图来看,实际上是线程计算过程中的图示)。
中间就是刚才说到的拓展,实线是atom的warp级拓展,即M轴拓展2次,N轴拓展2次,一共4个,每个warp固定32个线程,一共128个;虚线是value layout级别的重复计算,不会增大线程数。在这个基础上就可以定义出TiledMMA,每个TiledMMA处理 A:(32,16),B(16, 32),C:(32,32)的大小。
最后虽然我们抽象定义的是block层面的计算,但cuda在每次执行时都是到thread层面的,所以要通过下面的代码去把当前thread对应计算所需要的元素抠出来,也就是最上面的图示
TiledMMA tiled_mma;
auto thr_mma = tiled_mma.get_slice(threadIdx.x);
auto tAgA = thr_mma.partition_A(gA); // (MMA, MMA_M, MMA_K, num_tile_k)
auto tBgB = thr_mma.partition_B(gB); // (MMA, MMA_N, MMA_K, num_tile_k)
auto tCgC = thr_mma.partition_C(gC); // (MMA, MMA_M, MMA_N)
到这里基本应该清楚了MMA的整个计算逻辑和流程,下面这幅图更清晰的阐述了每个thread的计算

在slice-k模式下,k维度的计算就是通过循环完成的,循环是在同一个thread内部做的。
reference:https://github.com/reed-lau/cute-gemm/blob/main/gemm-simple.cu#L40-L49
int num_tile_k = size<2>(gA);
#pragma unroll 1
for(int itile = 0; itile < num_tile_k; ++itile) {
cute::copy(tAgA(_, _, _, itile), tArA);
cute::copy(tBgB(_, _, _, itile), tBrB);
cute::gemm(tiled_mma, tCrC, tArA, tBrB, tCrC);
}
不断累加即可。
cutlass3.4
reference: https://github.com/reed-lau/cute-gemm/blob/main/gemm-multi-stage.cu#L244-L262
using mma_op = SM80_16x8x16_F16F16F16F16_TN;
using mma_traits = MMA_Traits<mma_op>;
using mma_atom = MMA_Atom<mma_traits>;
static constexpr int kMmaEURepeatM = 2;
static constexpr int kMmaEURepeatN = 2;
static constexpr int kMmaEURepeatK = 1;
using mma_atom_shape = mma_traits::Shape_MNK;
static constexpr int kMmaPM = 1 * kMmaEURepeatM * get<0>(mma_atom_shape{});
static constexpr int kMmaPN = 2 * kMmaEURepeatN * get<1>(mma_atom_shape{});
static constexpr int kMmaPK = 1 * kMmaEURepeatK * get<2>(mma_atom_shape{});
using MMA_EU_RepeatT = decltype(make_layout(make_shape(
Int<kMmaEURepeatM>{}, Int<kMmaEURepeatN>{}, Int<kMmaEURepeatK>{})));
using MMA_P_T = Tile<Int<kMmaPM>, Int<kMmaPN>, Int<kMmaPK>>;
using MMA = decltype(make_tiled_mma(mma_atom{}, MMA_EU_RepeatT{}, MMA_P_T{}));
在cutlass3.4版本中,对上面所述的value layout的输入进行了一定的更新;
在这里MMA_P_T和之前<_1,_2,_1>的功能是完全一致的。之前是定义重复逻辑,现在直接定义最终布局,并且还可以指定更精细的布局方式。
具体可以参见:
https://github.com/NVIDIA/cutlass/discussions/1345
简单来讲就是又拓展了布局的能力,新的布局不仅支持之前的value layout,还支持通过更精细的布局控制,以使tv划分模式更易于管理/直观,并有效地交错各个mma(不过现在原子级的tv我还没怎么搞明白。。)























 7998
7998

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








