本教程是跟着 Data Binding Guide 学习过程中得出的一些实践经验,同时修改了官方教程的一些错误,每一个知识点都有对应的源码,争取做到实践与理论相结合。
Data Binding 解决了 Android UI 编程中的一个痛点,官方原生支持 MVVM 模型可以让我们在不改变既有代码框架的前提下,非常容易地使用这些新特性。其实在此之前,已经有些第三方的框架(RoboAndroid) 可以支持 MVVM 模型,无耐由于框架的侵入性太强,导致一直没有流行起来。
准备
Android Studio 更新到 1.3 版本
打开 Preferences,找到 Appearances & Behavior 下的 Updates 选项,把 Automatically Check updates for 修改成 Canary Channel。
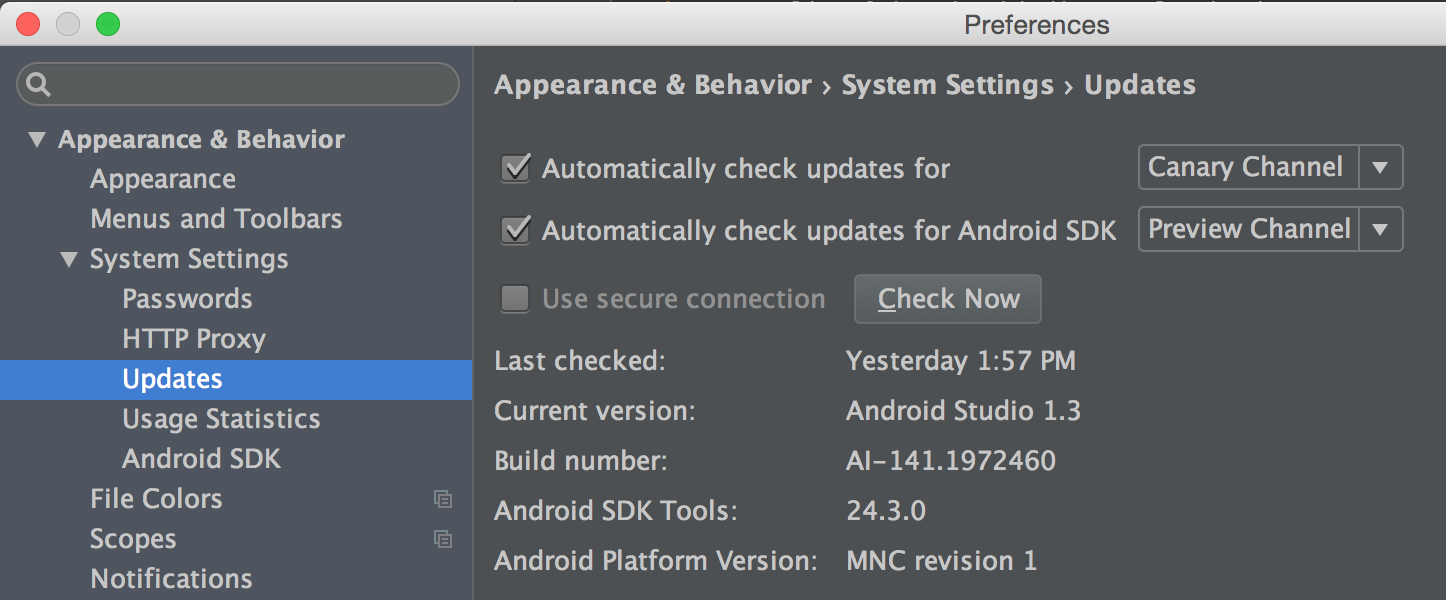
注意
Data Binding 是一个 support 包,因此与 android M 没什么关系,可以不用下载 Android MNC Preview 的 SDK。
新建一个 Project
修改 Project 的 build.gradle,为 build script 添加一条依赖,Gradle 版本为 1.2.3。
- 1
- 2
- 1
- 2
为用到 Data Binding 的模块添加插件,修改对应的 build.gradle。
- 1
- 1
注意
如果 Module 用到的 buildToolsVersion 高于 22.0.1,比如 23 rc1,那com.android.databinding:dataBinder 的版本要改为 1.3.0-beta1,否则会出现如下错误:

基础
工程创建完成后,我们通过一个最简单的例子来说明 Data Binding 的基本用法。
布局文件
使用 Data Binding 之后,xml的布局文件就不再单纯地展示 UI 元素,还需要定义 UI 元素用到的变量。所以,它的根节点不再是一个 ViewGroup,而是变成了 layout,并且新增了一个节点 data。
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
要实现 MVVM 的 ViewModel 就需要把数据与UI进行绑定,data 节点就为此提供了一个桥梁,我们先在data 中声明一个 variable,这个变量会为 UI 元素提供数据(例如 TextView 的 android:text),然后在Java 代码中把”后台”数据与这个 variable 进行绑定。
如果要用一个表格来展示用户的基本信息,用 Data Binding 应该怎么实现呢?
数据对象
添加一个 POJO 类 - User,非常简单,四个属性以及他们的 getter 和 setter。
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
稍后,我们会新建一个 User 类型的变量,然后把它跟布局文件中声明的变量进行绑定。
定义 Variable
再回到布局文件,在 data 节点中声明一个变量 user。
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 1
- 2
- 3
其中 type 属性就是我们在 Java 文件中定义的 User 类。
当然,data 节点也支持 import,所以上面的代码可以换一种形式来写。
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
然后我们刚才在 build.gradle 中添加的那个插件 - com.android.databinding会根据xml文件的名称Generate 一个继承自 ViewDataBinding 的类。
例如,这里 xml 的文件名叫 activity_basic.xml,那么生成的类就是 ActivityBasicBinding。
注意
java.lang.* 包中的类会被自动导入,可以直接使用,例如要定义一个 String 类型的变量:
- 1
- 1
绑定 Variable
修改 BasicActivity 的 onCreate 方法,用 DatabindingUtil.setContentView() 来替换掉setContentView(),然后创建一个 user 对象,通过 binding.setUser(user) 与 variable 进行绑定。
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
注意
ActivityBasicBinding 类是自动生成的,所有的 set 方法也是根据 variable 名称生成的。例如,我们定义了两个变量。
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
那么就会生成对应的两个 set 方法。
- 1
- 2
- 1
- 2
使用 Variable
数据与 Variable 绑定之后,xml 的 UI 元素就可以直接使用了。
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
至此,一个简单的数据绑定就完成了,可参考完整代码
高级用法
使用类方法
首先为类添加一个静态方法
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
然后在 xml 的 data 节点中导入:
- 1
- 1
使用方法与 Java 语法一样:
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
类型别名
如果我们在 data 节点了导入了两个同名的类怎么办?
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 1
- 2
- 3
这样一来出现了两个 User 类,那 user 变量要用哪一个呢?不用担心,import 还有一个 alias 属性。
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 1
- 2
- 3
Null Coalescing 运算符
- 1
- 1
就等价于
- 1
- 1
属性值
通过 ${} 可以直接把 Java 中定义的属性值赋值给 xml 属性。
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
使用资源数据
这个例子,官方教程有错误,可以参考Android Data Binder 的一个bug,完整代码在此。
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
-
顶
- 23




















 3468
3468











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








