-
缓存
- 用途
- 经常使用的数据,查询后加入缓存,再次查询不需要从数据库获取
- 一次性使用的数据,用完删除,比如发送短信验证码
- Java caching的核心接口(jsr107)
- CachingProvider: 缓存提供者.创建,配置,获取,管理,控制CacheManager
- CacheManager: 缓存管理器.创建,配置,获取,管理,控制Cache
- Cache: 缓存.一个类似Map的数据结构
- Entry: 缓存条目.一个存储在Cache中的key-value对
- Expiry: 缓存条目过期时间.存储在Cache中的条目的有效期
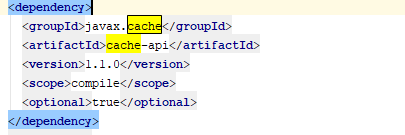
- 使用jsr107需要导入该包
- spring缓存抽象
- Cache: 缓存接口,有RedisCache,ConcurrentMapCache等实现
- CacheManager: 缓存管理器,管理Cache组件
- @Cacheable: 增加缓存,可使用spEL表达式
- @CacheEvict: 清除缓存
- @CachePut: 修改缓存
- @EnableCaching: 开启基于注解的缓存
- keyGenerator: 缓存的key的生成策略
- serialize: 缓存的value的序列化策略
- @Caching是@Cacheable,@CachePut,@CacheEvict的组合注解
- @CacheConfig抽取公共配置
- @Cacheable/@CachePut/@CacheEvict的主要参数
- cacheNames/value: 指定缓存组件的名字,是一个数组
- key: 指定缓存的key值,默认是参数的值
- KenGenerator: key值生成器,key/keyGenerator二选一
- CacheManager: 指定缓存管理器,或cacheResolver指定缓存解析器
- condition: 满足条件缓存
- unless: 否定条件缓存(异步模式不支持)
- sync: 使用异步模式
- 缓存原理
- CacheAutoConfiguration: 自动配置类

- 默认SimpleCacheConfiguration生效
- 给容器中注入了一个ConcurrentMapCacheManager组件
- 创建和获取一个ConcurrentMapCache类型的组件
- 运行流程
- 查询语句运行之前,先获取Cache组件(CacheManager.getCache()),如果没有获取到,则创建一个并放入CurrentMap中
- 查询Cache(缓存组件),按照cacheNames指定的名字获取
- key默认使用SimpleKeyGenerator生成
- 没有查到缓存,调用目标方法,将结果加入缓存
- 查到缓存,直接返回,不调用目标方法
- 整合redis缓存
- 导入redis的启动器
- 操作五大数据类型(redisTemplate,stringRedisTemplate)
- stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue();
- stringRedisTemplate.opsForList();
- stringRedisTemplate.opsForHash();
- stringRedisTemplate.opsForSet();
- stringRedisTemplate.opsForZSet();
- 通过CacheManager获取
@Autowired private RedisCacheManager redisCacheManager; Cache cache = redisCacheManager.getCache("com.version.controller.DriverInfoController"); cache.put("name", "jiyu"); cache.get("name");
- CacheAutoConfiguration: 自动配置类
- 用途
-
消息队列
- 重要概念:消息代理和目的地,当消息发送者发送消息后,由消息代理接管,保证消息送达指定目的地
- 目的地形式
- 队列(queue): 点对点通信.一个消息只有一个发送者和接收者
- 主题(topic): 发布(publish)/订阅(subscribe)消息.一个消息只有一个发送者,但可以有多个接收者
- 用途
- 异步处理: 注册完毕后,立即返回消息,发送邮件,统计数据等操作先写入消息队列,稍后读取
- 应用解耦: 订单和库存之间使用微服务解耦,下单时订单模块向消息队列写入消息,然后库存模块读取消息
- 秒杀任务: 定长消息,先抢占位置,再执行实际操作
- 服务协议
- JMS(Java message service): Java消息服务,基于jvm消息代理规范.有ActiveMQ等实现
- AMQP(Advanced Message Queuing Protocol): 高级消息队列.有RabbitMQ等实现
- 比较
JMS AMQP 定义 Java API 网络级协议 跨语言跨平台 否 是 model peer-2-peer(点对点)
pub/sub(发布/订阅)
direct exchange(点对点)
fanout exchange(发布/订阅)
topic exchange(发布/订阅)
headers exchange(发布/订阅)
system exchange(发布/订阅)
支持消息类型 TextMessage
MapMessage
BytesMessage
StreamMessage
ObjectMessage
Message(只有消息头和属性)
byte[]
消息需要序列化后发送
- spring支持
- spring-jms提供了对jms的支持
- spring-rabbit提供了对amqp的支持
- 需要ConnectionFactory的实现来连接消息队列
- 提供JmsTemplate和RabbitTemplate来发送消息
- 在方法上使用注解@JmsListener,@RabbitListener监听消息代理发布的消息
- @EnableJms,@EnableRabbit开启消息队列支持
- JmsAutoConfiguration, RabbitAutoConfiguration自动配置类
- rabbit简介
- 核心概念
- Message: 消息.消息是不具名的,由消息头消息体组成.消息体是不透明的(程序根据需要自定义的),消息头由一系列可选属性组成,这些属性包括routing-key(路由键),priority(优先权),delivery-mode(消息是否需要持久化存储)等
- Publisher: 消息发送者.向交换器发(Exchange)送消息(Message)的客户端程序
- Exchange: 交换器.接收消息发送者(Publish)发送的消息并将这些消息路由给服务器中的队列(Queue).有四种交换器
- direct(默认): 消息的路由键和绑定中的绑定键完全一致才能接收消息(单播模式)
- fanout: 交换器收到消息时,会给绑定该交换器的消息队列都发消息(广播模式)
- topic: 按照匹配模式转发消息到消息队列.以路由键和绑定键的字符串切分单词,使用逗号分隔.#匹配0个或多个单词,*匹配一个单词
- headers: 和direct一致,性能较差,基本不用
- Queue: 消息队列.用来保存消息直到发给消费者.它是消息的容器,也是消息的终点,一个消息可以投入一个或多个队列
- Binding: 绑定.用于关联队列(Queue)和交换器(Exchange).一个绑定就是基于路由键将交换器和消息队列连接起来的路由规则,可以将交换器理解为一个有绑定(Binging)构成的路由表.Exchange和Queue可以是多对多关系
- Connection: 网络连接,比如一个tcp连接
- Channel: 信道.多路复用连接中的一条独立的双向数据流通道,信道是建立在真实的tcp连接内的虚拟连接.AMQP命令都是通过信道发出去的,因为tcp的建立和销毁开销较大,所以引入信道(Channel)复用一条tcp连接
- Consumer: 消息消费者.从消息队列(Queue)中取出消息的客户端程序
- VirtualHost: 虚拟主机,每个虚拟主机都是一个迷你版的RabbitMQ服务器,拥有自己的消息队列,交换器,绑定和权限机制,vhost是amqp的基础,必须在连接时指定.默认是的vhost是/
- Broker: 消息队列服务器实体
- 关系图

- springboot整合rabbitmq
- 导入starter启动器
- RabbitAutoConfiguration自动配置类
- CachingConnectionFactory自动部署连接工厂
- RabbitProperties绑定rabbitmq的配置
- RabbitTemplate给rabbitmq发送和接收消息
- AmqpAdmin系统功能管理组件,新建交换器,消息队列等
- 核心概念
-
elasticsearch
- 类比关系型数据库
mysql elasticsearch 数据库(database) 索引(index)(名词,动词索引是存储数据的意思) 数据表(table) 类型(type) 记录(record) 文档(document) 字段(field) 属性(property) - 整合springboot项目
- springdata方式(默认方式)
- Client节点信息clusterNodes,clusterName
- ElasticsearchTemplate
- 编写ElasticsearchRepository的子接口操作es数据库
- jest方式
- 导入jest工具包(io.searchbox.client.JestClient)
- springdata方式(默认方式)
- 类比关系型数据库
-
任务调度
- 异步任务:使用@EnableAsync开启异步任务,在需要异步的方法上加@Async注解
- 定时任务: 使用@EnableScheduling开启异步任务,在需要异步的方法上加@Scheduled(cron = "0 * 1/24 * * ?")注解
- cron表达式

- cron表达式
- 邮件任务
-
spring-security
- 引入启动器
- 编写配置文件
@EnableWebSecurity public class CustomerSecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter { } - 控制请求访问权限
-
整合springcloud服务发现
- spring cloud是一个分布式的整体解决方案,能够快速构建应用,对接云平台资源
- 配置管理
- 服务发现
- 熔断
- 路由
- 微代理
- 控制总线
- 一次性token验证
- 全局锁
- leader选举
- 分布式session管理
- 集群状态
- spring cloud五大组件
- 服务发现--netflix eureka
- 客户端负载均衡--netflix ribbon
- 断路器--netflix hystrix
- 服务网关--netflix zuul
- 分布式配置--spring cloud config
- 监控管理,加入actuator的启动器即可,通过在项目的/actuator/**下访问
{GET /actuator/archaius, produces [application/vnd.spring-boot.actuator.v2+json || application/json]} {GET /actuator/auditevents, produces [application/vnd.spring-boot.actuator.v2+json || application/json]} {GET /actuator/beans, produces [application/vnd.spring-boot.actuator.v2+json || application/json]} {GET /actuator/caches/{cache}, produces [application/vnd.spring-boot.actuator.v2+json || application/json]} {GET /actuator/caches, produces [application/vnd.spring-boot.actuator.v2+json || application/json]} {DELETE /actuator/caches/{cache}, produces [application/vnd.spring-boot.actuator.v2+json || application/json]} {DELETE /actuator/caches} {GET /actuator/health, produces [application/vnd.spring-boot.actuator.v2+json || application/json]} {GET /actuator/health/{component}, produces [application/vnd.spring-boot.actuator.v2+json || application/json]} {GET /actuator/health/{component}/{instance}, produces [application/vnd.spring-boot.actuator.v2+json || application/json]} {GET /actuator/conditions, produces [application/vnd.spring-boot.actuator.v2+json || application/json]} {GET /actuator/configprops, produces [application/vnd.spring-boot.actuator.v2+json || application/json]} {GET /actuator/env, produces [application/vnd.spring-boot.actuator.v2+json || application/json]} {GET /actuator/env/{toMatch}, produces [application/vnd.spring-boot.actuator.v2+json || application/json]} {POST /actuator/env, consumes [application/vnd.spring-boot.actuator.v2+json || application/json], produces [application/vnd.spring-boot.actuator.v2+json || application/json]} {DELETE /actuator/env, produces [application/vnd.spring-boot.actuator.v2+json || application/json]} {GET /actuator/info, produces [application/vnd.spring-boot.actuator.v2+json || application/json]} {GET /actuator/loggers, produces [application/vnd.spring-boot.actuator.v2+json || application/json]} {GET /actuator/loggers/{name}, produces [application/vnd.spring-boot.actuator.v2+json || application/json]} {POST /actuator/loggers/{name}, consumes [application/vnd.spring-boot.actuator.v2+json || application/json]} {GET /actuator/heapdump, produces [application/octet-stream]} {GET /actuator/threaddump, produces [application/vnd.spring-boot.actuator.v2+json || application/json]} {GET /actuator/metrics/{requiredMetricName}, produces [application/vnd.spring-boot.actuator.v2+json || application/json]} {GET /actuator/metrics, produces [application/vnd.spring-boot.actuator.v2+json || application/json]} {GET /actuator/scheduledtasks, produces [application/vnd.spring-boot.actuator.v2+json || application/json]} {GET /actuator/httptrace, produces [application/vnd.spring-boot.actuator.v2+json || application/json]} {GET /actuator/mappings, produces [application/vnd.spring-boot.actuator.v2+json || application/json]} {POST /actuator/refresh, produces [application/vnd.spring-boot.actuator.v2+json || application/json]} {GET /actuator/features, produces [application/vnd.spring-boot.actuator.v2+json || application/json]} {POST /actuator/service-registry, consumes [application/vnd.spring-boot.actuator.v2+json || application/json], produces [application/vnd.spring-boot.actuator.v2+json || application/json]} {GET /actuator/service-registry, produces [application/vnd.spring-boot.actuator.v2+json || application/json]} {GET /actuator, produces [application/vnd.spring-boot.actuator.v2+json || application/json]} - 健康指示器: 实现HealthIndicator接口的xxxHealthIndicator类加入到容器中
- spring cloud是一个分布式的整体解决方案,能够快速构建应用,对接云平台资源






















 747
747











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








