快读和快写
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
PrintWriter pw = new PrintWriter(new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(System.out)));
}
}
class Read{
StreamTokenizer st = new StreamTokenizer(new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in)));
BufferedReader bf = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
public int nextInt() throws IOException {
st.nextToken();
return (int)st.nval;
}
public String nextString() throws IOException {
return bf.readLine();
}
}递归的概念:自己调用自己
所有递归都可以转为一个递归搜素树
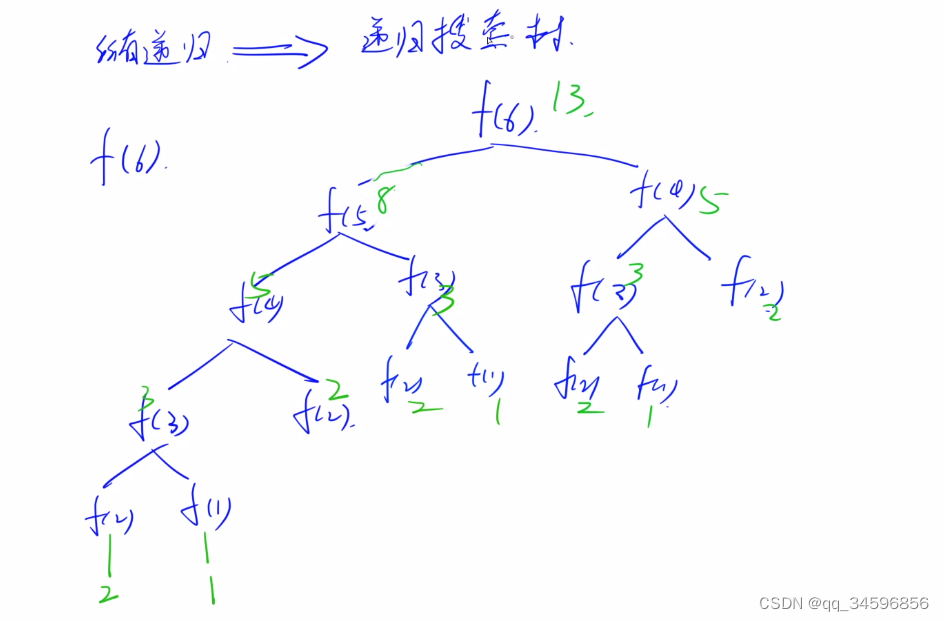
递归类型1:指数型枚举
![]()

import java.util.*;
class Main{
private static int n;
private static int[] arr;//0表示初始,1表示选,2表示不选
public static void dfs(int u) {
if (u == n) {
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (arr[i] == 1) {
System.out.printf("%d ",i + 1);
}
}
System.out.println();
return;
}
//递归
arr[u] = 1;
dfs(u + 1);
arr[u] = 0;
arr[u] = 2;
dfs(u + 1);
arr[u] = 0;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
n = sc.nextInt();
arr = new int[n];
dfs(0);
}
}
类型2:排列型枚举
字典序:A = 123 B = 121 , 按字典序比较就是先比较1,在比较2,最后比较 3 和 1,可知B < A


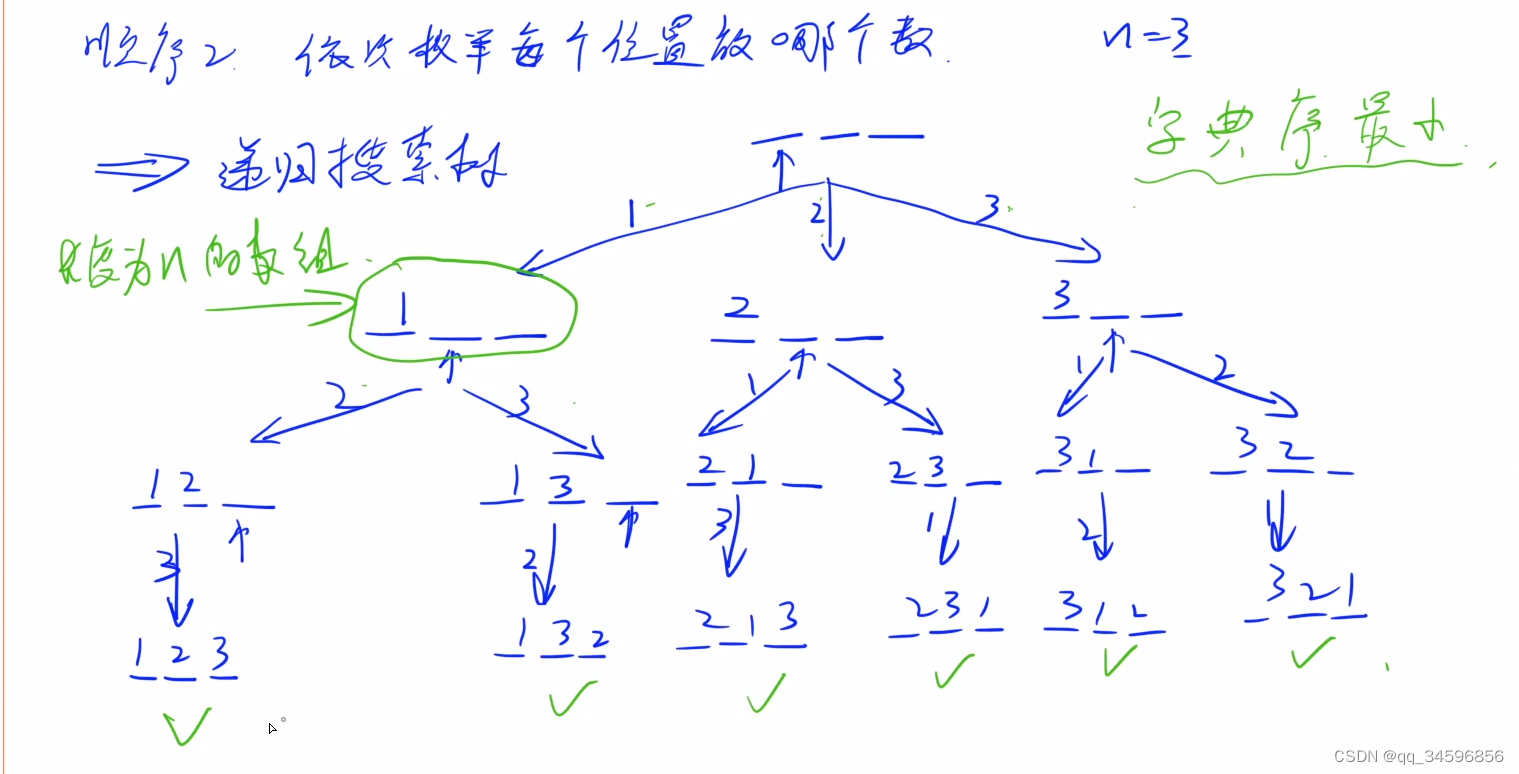
import java.util.*;
class Main{
static int N = 10;
static int n = 0;
static int[] st = new int[N]; // 表示放什么数
static boolean[] used = new boolean[N]; // 表示当前数有没有用过
public static void main(String[] args){
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
n = sc.nextInt();
dfs(0);
}
public static void dfs(int u){
if (u == n){
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++){
System.out.print(st[i]+" ");
}
System.out.println();
return;
}
// 进行枚举
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++){
if(!used[i+1]){
st[u] = i+1; // u位置放的是i数
used[i+1] = true; // 表示i数已经用过
dfs(u+1);
st[u] = 0;
used[i+1] = false;
}
}
}
}
类型3:组合型枚举
首先排列数有序,组合数无序
也就是说 3 2 1 = 3 1 2 = 1 2 3 = 1 3 2 = 2 1 3 = 2 3 1
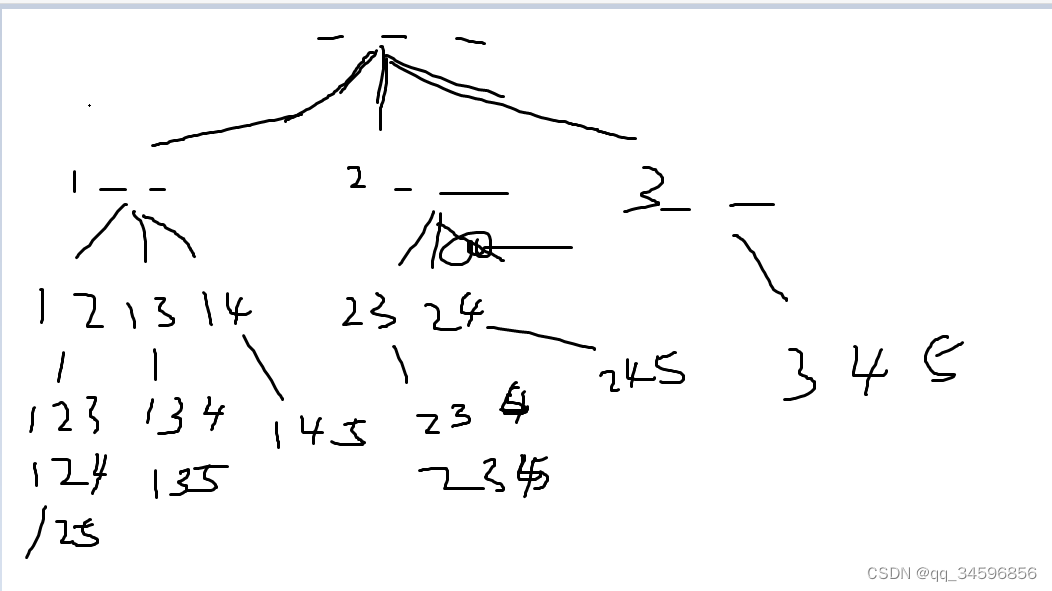
由上图可知,我们求出组合数需要三个量,第一个是保存方案数的ways数组,第二个是当前遍历到哪一个数的开头的层数,第三个数是从哪一个数开始遍历
import java.util.*;
class Main{
static int N = 26;
static int n = 0;
static int m = 0; // 这是那一层
static int[] st = new int[N]; // 表示当前位置放的数
public static void main(String[] args){
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
n = sc.nextInt();
m = sc.nextInt();
dfs(1,1);
}
// start 表示这一层从什么开始
public static void dfs(int u,int start){
if (u > m){
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++){
System.out.print(st[i] + " ");
}
System.out.println();
return;
}
for (int i = start; i <= n; i++){
st[u] = i;
dfs(u+1,i+1);
st[u] = 0;
}
}
}递推:先求子问题,在用子问题去计算原问题

import java.util.*;
class Main{
public static void main(String[] args){
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = sc.nextInt();
int[] f = new int[46];
f[1] = 0;
f[2] = 1;
for (int i = 3; i <= n; i++){
f[i] = f[i - 1] + f[i - 2];
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
System.out.print(f[i] +" ");
}
}
}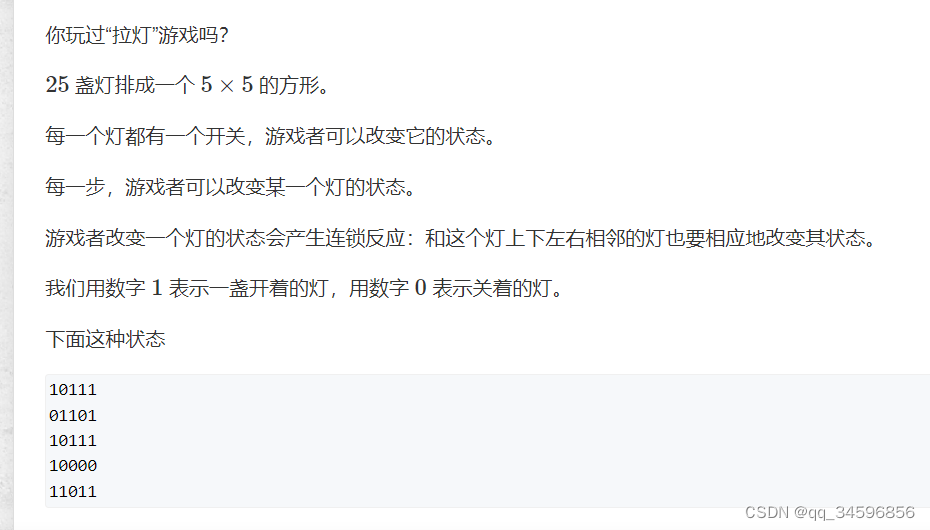
利用2进制与十进制的关系确定第一行的所有状态

技巧 : 查看 数字 i 的第 k 位是否为 1
i >> k & 1
技巧: 用偏移量转换坐标的上下左右
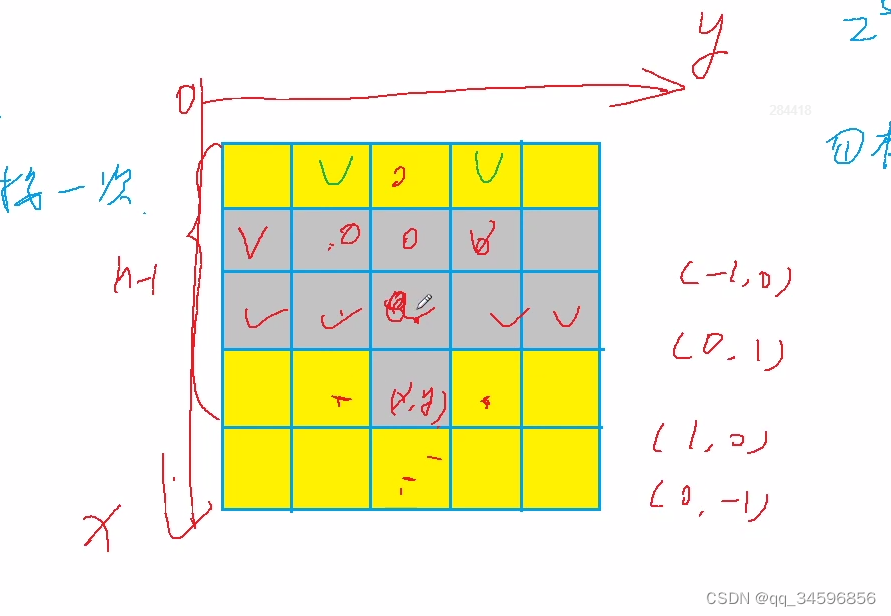
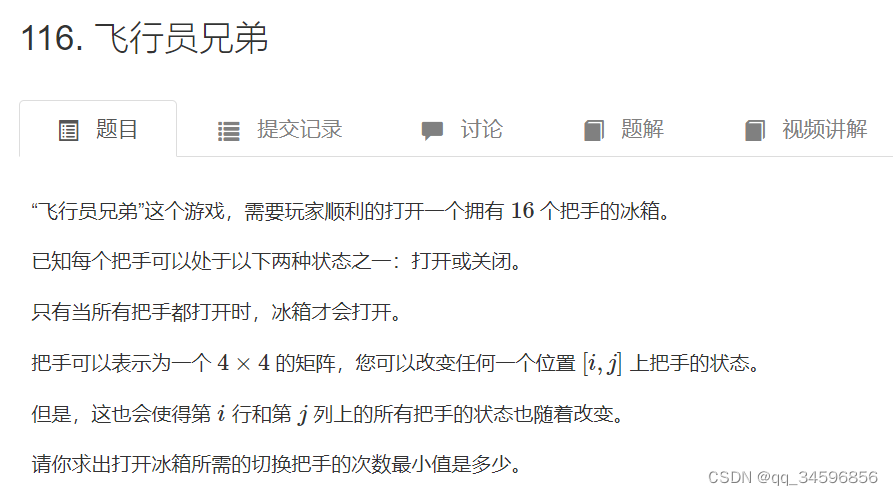
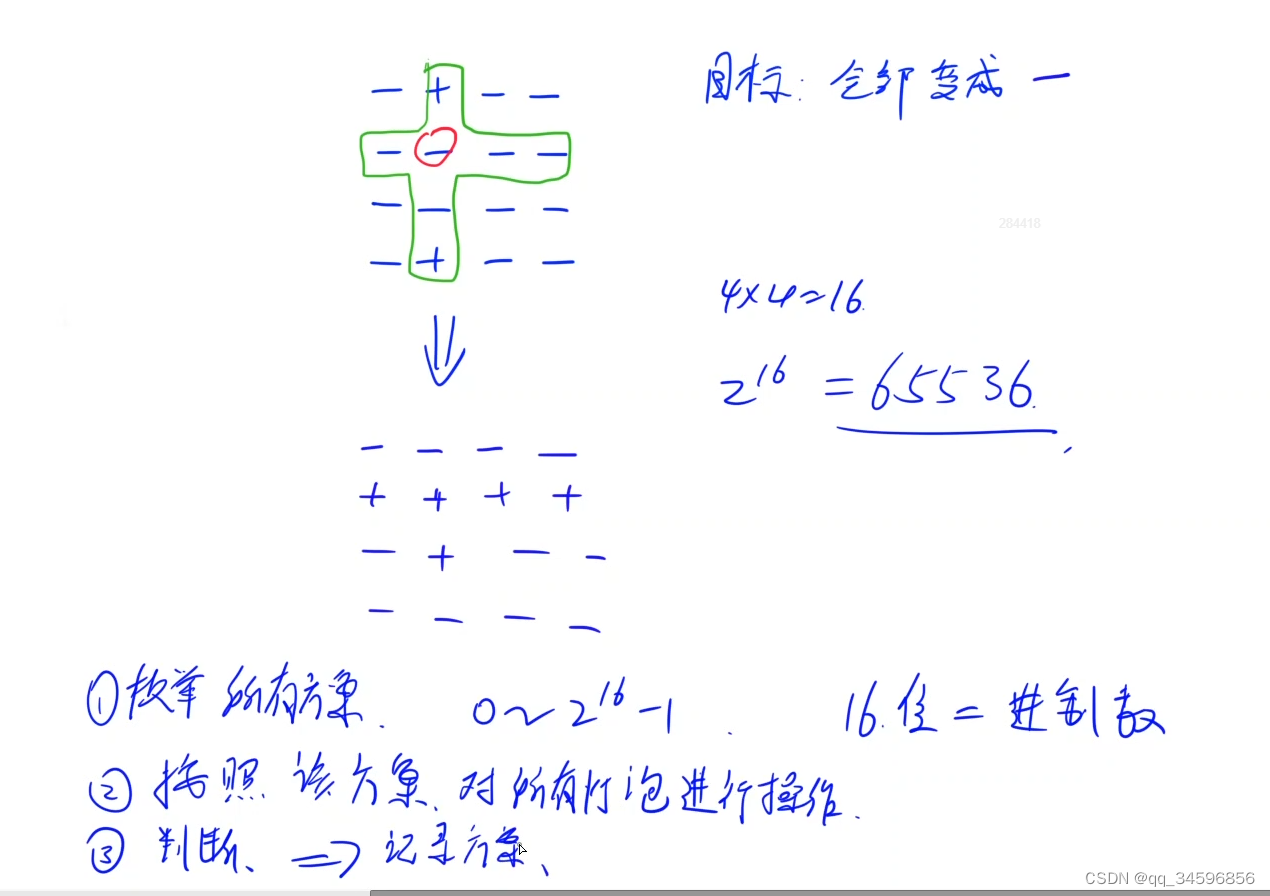
技巧:n*n的二维求x行y列的数, n * x + y ,如 4 * 4 的盘中, 0行0列的数就是0,1行1列的数是5
import java.io.*;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class Main{
static BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
static PrintWriter out = new PrintWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(System.out));
static int N = 4;
static int[][] change = new int[N][N];
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//预处理,改变当前数组中该位置的把手,则该行该列的把手也要更改
for (int i = 0; i < N; i ++)
for (int j = 0; j < N; j ++) {
for (int k = 0; k < N; k ++)
change[i][j] += (1 << get(i, k)) + (1 << get(k, j)); //加上该行N列,加上该列N行
change[i][j] -= 1 << get(i, j); //该点被加了两次
}
int state = 0; // 用来存储初始的状态
for (int i = 0; i < N; i ++) { //开始存储
String line = in.readLine();
for (int j = 0; j < N; j ++)
if (line.charAt(j) == '+')
state += 1 << get(i, j); //该二进制位有1为'+',就是没有打开
} //存储完毕
List<PII> path = new ArrayList<>(); //用来存储变换过的把手的坐标
for (int i = 0; i < 1 << 16; i ++) { //二进制存储所有的操作方法
int now = state; //备份初始的状态
List<PII> temp = new ArrayList<>();
for (int j = 0; j < 16; j ++)
if ((i >> j & 1) == 1) {
int x = j / 4, y = j % 4;
now ^= change[x][y];
temp.add(new PII(x, y));
}
//如果本次操作让now为0,也就是打开了冰箱门和(如果用来存储总操作的path为空或者path存的步数多于新的) 更新path
if (now == 0 && (path.isEmpty() || path.size() > temp.size()))
path = temp;
}
out.println(path.size());
for (PII p : path)
out.println(p.x + 1 + " " + (p.y + 1));
out.flush();
}
public static int get(int x, int y) { //根据在数组中的下标得到线性的大小
return N * x + y;
}
}
class PII {
int x, y;
public PII(int a, int b) {
x = a;
y = b;
}
}







 文章介绍了Java编程中递归、递归搜索树、两种类型的枚举(排列型和组合型)以及递推的概念。通过实例展示了如何使用DFS进行深度优先搜索,并运用2进制与十进制关系解决特定问题。
文章介绍了Java编程中递归、递归搜索树、两种类型的枚举(排列型和组合型)以及递推的概念。通过实例展示了如何使用DFS进行深度优先搜索,并运用2进制与十进制关系解决特定问题。














 294
294











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








