1.IOC&DI
IOC(Inversion ofControl):其思想是反转资源获取的方向.容器主动地将资源推送给它所管理的组件, 组件所要做的仅是选择一种合适的方式来接受资源. 这种行为也被称为查找的被动形式。
DI(DependencyInjection) — IOC 的另一种表述方式:即组件以一些预先定义好的方式(例如: setter 方法)接受来自如容器的资源注入。
2.在 Spring 的 IOC 容器里配置 Bean(xml、注解)
在 xml 文件中通过 bean 节点来配置 bean
id:Bean 的名称。在 IOC 容器中必须是唯一的
Bean 的配置方式:通过全类名(反射)、[通过工厂方法(静态工厂方法 & 实例工厂方法)、FactoryBean]
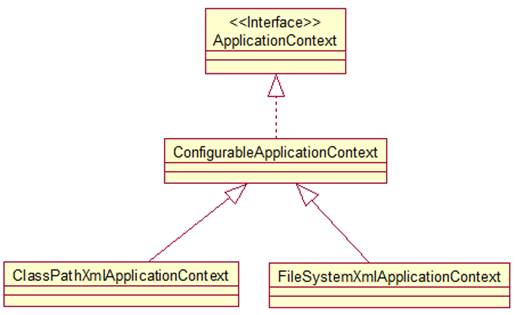
3.两种类型的 IOC 容器(BeanFactory & ApplicationContext)实现.
只有在容器实例化后, 才可以从 IOC容器里获取 Bean 实例并使用。
BeanFactory: IOC 容器的基本实现.
ApplicationContext: 提供了更多的高级特性. 是 BeanFactory 的子接口.
3.1ApplicationContext
ConfigurableApplicationContext 扩展于 ApplicationContext,新增加两个主要方法:refresh() 和 close(), 让 ApplicationContext 具有启动、刷新和关闭上下文的能力
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext:从 类路径下加载配置文件
FileSystemXmlApplicationContext: 从文件系统中加载配置文件
3.2获取Bean
调用 ApplicationContext 的 getBean() 方法
4. 3种依赖注入的方式
4.1属性注入
属性注入即通过 setter 方法注入Bean的属性值或依赖的对象
属性注入使用 <property> 元素, 使用 name 属性指定 Bean 的属性名称,value 属性或 <value> 子节点指定属性值
属性注入是实际应用中最常用的注入方式
4.2构造器注入
通过构造方法注入Bean 的属性值或依赖的对象,它保证了 Bean 实例在实例化后就可以使用。
构造器注入在 <constructor-arg> 元素里声明属性, <constructor-arg> 中没有 name 属性
按索引或类型匹配参数
4.3工厂方法注入(很少使用,不推荐)
5.注入属性值细节
5.1字面值
可用字符串表示的值,可以通过 <value> 元素标签或 value 属性进行注入。
基本数据类型及其封装类、String 等类型都可以采取字面值注入的方式
若字面值中包含特殊字符,可以使用 <![CDATA[]]> 把字面值包裹起来。
5.2引用其他Bean
组成应用程序的 Bean 经常需要相互协作以完成应用程序的功能. 要使 Bean 能够相互访问, 就必须在Bean 配置文件中指定对 Bean 的引用
在 Bean 的配置文件中, 可以通过<ref> 元素或 ref 属性为 Bean 的属性或构造器参数指定对Bean 的引用.
也可以在属性或构造器里包含 Bean 的声明, 这样的 Bean 称为内部 Bean
5.3内部bean
当 Bean 实例仅仅给一个特定的属性使用时, 可以将其声明为内部 Bean. 内部 Bean 声明直接包含在 <property> 或 <constructor-arg> 元素里, 不需要设置任何 id 或 name 属性
内部 Bean 不能使用在任何其他地方
可以使用专用的 <null/> 元素标签为 Bean 的字符串或其它对象类型的属性注入 null 值
5.4集合属性
在 Spring中可以通过一组内置的 xml 标签(例如: <list>, <set> 或 <map>) 来配置集合属性.
配置 java.util.List 类型的属性, 需要指定 <list> 标签, 在标签里包含一些元素. 这些标签可以通过 <value> 指定简单的常量值, 通过 <ref> 指定对其他 Bean 的引用. 通过<bean> 指定内置 Bean 定义. 通过<null/> 指定空元素. 甚至可以内嵌其他集合.
数组的定义和 List 一样, 都使用<list>
配置 java.util.Set 需要使用 <set> 标签, 定义元素的方法与 List 一样.
Java.util.Map通过<map> 标签定义, <map> 标签里可以使用多个 <entry> 作为子标签. 每个条目包含一个键和一个值.
必须在 <key> 标签里定义键
因为键和值的类型没有限制, 所以可以自由地为它们指定 <value>, <ref>,<bean> 或 <null> 元素.
可以将 Map 的键和值作为 <entry> 的属性定义: 简单常量使用 key 和 value来定义; Bean 引用通过 key-ref 和 value-ref 属性定义
使用 <props> 定义 java.util.Properties, 该标签使用多个 <prop> 作为子标签. 每个 <prop> 标签必须定义 key 属性.
5.6导入util命名空间配置独立的集合bean
使用 util schema 里的集合标签定义独立的集合 Bean.
5.7使用 p 命名空间
使用 p 命名空间后,基于 XML 的配置方式将进一步简化
6.示例
Main
package com.spring.beans;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
import com.spring.beans.collections.DataSource;
import com.spring.beans.collections.NewPerson;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/* //1.创建HelloWorld的一个对象
HelloWorld helloWorld = new HelloWorld();
//2.为name属性赋值
helloWorld.setName("World");
*/
//1.创建SpringIOC容器
//ApplicationContext代表IOC容器
//ClassPathXmlApplicationContext:是ApplicationContext接口的实现类,从类路径下加载配置文件。
ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
//2.从IOC容器通过id获取Bean示例
//利用id定位IOC容器中的Bean
HelloWorld helloWorld = (HelloWorld)ac.getBean("helloWorld");
//利用类型返回IOC中的Bean,但要求容器中只能有一个该类型的Bean
// HelloWorld helloWorld = ac.getBean(HelloWorld.class);
//3.调用hello方法
helloWorld.Hello();
Car c1 = (Car)ac.getBean("car1");
System.out.println(c1);
Car c2 = (Car)ac.getBean("car2");
System.out.println(c2);
Person p1 = (Person)ac.getBean("person1");
System.out.println(p1);
Person p2 = (Person)ac.getBean("person2");
System.out.println(p2);
com.spring.beans.collections.Person p3 =
(com.spring.beans.collections.Person) ac.getBean("person3");
System.out.println(p3);
NewPerson np = (NewPerson)ac.getBean("newPerson");
System.out.println(np);
DataSource d = (DataSource)ac.getBean("dataSource");
System.out.println(d);
com.spring.beans.collections.Person p4 = (com.spring.beans.collections.Person) ac.getBean("person4");
System.out.println(p4);
com.spring.beans.collections.Person p5 = (com.spring.beans.collections.Person)ac.getBean("person5");
System.out.println(p5);
}
}
/*
Hello World's Constructor
setName:Spring
Hello:Spring
Car [brand=Audi, crop=shanghai, price=444555.0, maxSpeed=2000]
Car [brand=Baoma, crop=<shanghai>, price=0.0, maxSpeed=240]
Person [name=p1, age=12, car=Car [brand=Ford, crop=changan, price=111222.0, maxSpeed=0]]
Person [name=Jerry, age=20, car=Car [brand=Audi, crop=shanghai, price=444555.0, maxSpeed=2000]]
Person [name=Mike, age=20, cars=[Car [brand=Audi, crop=shanghai, price=444555.0, maxSpeed=2000],
Car [brand=Baoma, crop=<shanghai>, price=0.0, maxSpeed=240], Car [brand=Ford, crop=changan, price=111222.0, maxSpeed=0]]]
Person [name=Rose, age=22, cars={c1=Car [brand=Audi, crop=shanghai, price=444555.0, maxSpeed=2000],
c2=Car [brand=Baoma, crop=<shanghai>, price=0.0, maxSpeed=240]}]
DataSource [properties={passWord=1234, jdbcurl=jdbc:mysql:///test, driverClass=com.mysql.jdbdc.driver, user=root}]
Person [name=Jack, age=23, cars=[Car [brand=Audi, crop=shanghai, price=444555.0, maxSpeed=2000],
Car [brand=Baoma, crop=<shanghai>, price=0.0, maxSpeed=240]]]
*/applicationContext.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:util="http://www.springframework.org/schema/util"
xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/util
http://www.springframework.org/schema/util/spring-util-4.3.xsd">
<!--属性注入
配置bean
class:bean 的全类名,通过反射方式在IOC中创建Bean,所以要求Bean中必须有无参数的构造器
id:标识容器中的Bean,id唯一
-->
<bean id = "helloWorld" class = "com.spring.beans.HelloWorld">
<property name = "name" value = "Spring"></property>
</bean>
<!-- 通过构造方法配置Bean的属性 -->
<bean id = "car1" class = "com.spring.beans.Car">
<constructor-arg value = "Audi" index = "0"></constructor-arg>
<constructor-arg value = "shanghai" index = "1"></constructor-arg>
<constructor-arg value = "444555" type = "double"></constructor-arg>
</bean>
<!-- 使用构造器注入属性值可以指定参数索引和类型,以区分重载的构造方法 -->
<bean id = "car2" class = "com.spring.beans.Car">
<constructor-arg value = "Baoma" type = "java.lang.String"></constructor-arg>
<!-- 字面值包含特殊字符可使用<![DATA[]]>进行包裹 -->
<!-- 属性值可以使用value子节点进行配置 -->
<constructor-arg type = "String">
<value><![CDATA[<shanghai>]]></value>
</constructor-arg>
<constructor-arg type = "int">
<value>240</value>
</constructor-arg>
</bean>
<!-- 可随意使用property的ref属性建立bean之间的引用关系 -->
<bean id = "person1" class = "com.spring.beans.Person">
<property name="name" value = "p1"></property>
<property name="age" value = "12"></property>
<!--<property name="car" ref = "car1"></property> -->
<!--<property name="car">
<ref bean ="car2"/>
</property>
-->
<!-- 内部Bean,不能被外部引用,只能在内部使用 -->
<property name="car">
<bean id = "car3" class = "com.spring.beans.Car">
<constructor-arg value = "Ford" type = "String"></constructor-arg>
<constructor-arg value = "changan" type = "String"></constructor-arg>
<constructor-arg value = "111222" type = "double"></constructor-arg>
</bean>
</property>
</bean>
<bean id = "person2" class = "com.spring.beans.Person">
<constructor-arg value = "Jerry" ></constructor-arg>
<constructor-arg value = "20"></constructor-arg>
<!--
<constructor-arg ref = "car1"></constructor-arg>
-->
<!-- 测试NULL值 -->
<!--
<constructor-arg><null/></constructor-arg>
-->
<constructor-arg ref = "car1"></constructor-arg>
<!-- 为级联属性赋值 和struts2不同,属性初始化才能为级联属性赋值-->
<property name="car.maxSpeed" value = "2000"></property>
</bean>
<bean id = "person3" class = "com.spring.beans.collections.Person">
<property name="name" value = "Mike"></property>
<property name="age" value = "20"></property>
<property name = "cars">
<!-- 使用List节点 -->
<list>
<ref bean = "car1"/>
<ref bean = "car2"/>
<bean class = "com.spring.beans.Car">
<constructor-arg value = "Ford" type = "String"></constructor-arg>
<constructor-arg value = "changan" type = "String"></constructor-arg>
<constructor-arg value = "111222" type = "double"></constructor-arg>
</bean>
</list>
</property>
</bean>
<!-- 配置Map属性 -->
<bean id = "newPerson" class = "com.spring.beans.collections.NewPerson">
<property name="name" value = "Rose"></property>
<property name="age" value = "22"></property>
<property name="cars">
<!-- 使用Map节点及property子节点配置Map类型的子节点 -->
<map>
<entry key="c1" value-ref="car1"></entry>
<entry key="c2" value-ref="car2"></entry>
</map>
</property>
</bean>
<!--配置Properties属性 -->
<bean id = "dataSource" class = "com.spring.beans.collections.DataSource">
<property name="properties" >
<!-- 使用props和prop子节点为Properties属性赋值 -->
<props>
<prop key="user">root</prop>
<prop key="passWord">1234</prop>
<prop key="jdbcurl">jdbc:mysql:///test</prop>
<prop key="driverClass">com.mysql.jdbdc.driver</prop>
</props>
</property>
</bean>
<!-- 配置独立的集合bean,以供多个bean进行引用,需要导入util命名空间 -->
<util:list id = "cars">
<ref bean = "car1"/>
<ref bean = "car2"/>
</util:list>
<bean id = "person4" class = "com.spring.beans.collections.Person">
<property name="name" value="Jack"></property>
<property name="age" value="23"></property>
<property name="cars" ref="cars"></property>
</bean>
<!-- 通过p命名空间为bean的属性赋值,需要先导入p命名空间 ,相对于传统配置方式更为简洁-->
<bean id="person5" class="com.spring.beans.collections.Person" p:age="30"
p:name="ZhangSan" p:cars-ref="cars"></bean>
</beans>HelloWorld
package com.spring.beans;
public class HelloWorld {
private String name;
public HelloWorld() {
System.out.println("Hello World's Constructor");
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
System.out.println("setName:"+getName());
}
public void Hello() {
System.out.println("Hello:"+getName());
}
}
Car
package com.spring.beans;
public class Car {
String brand;
String crop;
double price;
int maxSpeed;
public Car(String brand, String crop, double price) {
super();
this.brand = brand;
this.crop = crop;
this.price = price;
}
public Car(String brand, String crop, int maxSpeed) {
super();
this.brand = brand;
this.crop = crop;
this.maxSpeed = maxSpeed;
}
public String getBrand() {
return brand;
}
public void setBrand(String brand) {
this.brand = brand;
}
public String getCrop() {
return crop;
}
public void setCrop(String crop) {
this.crop = crop;
}
public double getPrice() {
return price;
}
public void setPrice(double price) {
this.price = price;
}
public int getMaxSpeed() {
return maxSpeed;
}
public void setMaxSpeed(int maxSpeed) {
this.maxSpeed = maxSpeed;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Car [brand=" + brand + ", crop=" + crop + ", price=" + price + ", maxSpeed=" + maxSpeed + "]";
}
}
Person
package com.spring.beans;
public class Person {
private String name;
private int age;
private Car car;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public Car getCar() {
return car;
}
public void setCar(Car car) {
this.car = car;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Person [name=" + name + ", age=" + age + ", car=" + car + "]";
}
public Person() {
super();
}
public Person(String name, int age, Car car) {
super();
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.car = car;
}
}
package com.spring.beans.collections;
import java.util.List;
import com.spring.beans.Car;
public class Person {
private String name;
private int age;
private List<Car> cars;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public List<Car> getCars() {
return cars;
}
public void setCars(List<Car> cars) {
this.cars = cars;
}
public Person() {
super();
}
public Person(String name, int age, List<Car> cars) {
super();
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.cars = cars;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Person [name=" + name + ", age=" + age + ", cars=" + cars + "]";
}
}
package com.spring.beans.collections;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import com.spring.beans.Car;
public class NewPerson {
private String name;
private int age;
private Map<String,Car> cars;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public Map<String, Car> getCars() {
return cars;
}
public void setCars(Map<String, Car> cars) {
this.cars = cars;
}
public NewPerson() {
super();
}
public NewPerson(String name, int age, Map<String, Car> cars) {
super();
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.cars = cars;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Person [name=" + name + ", age=" + age + ", cars=" + cars + "]";
}
}
package com.spring.beans.collections;
import java.util.Properties;
public class DataSource {
private Properties properties;
public Properties getProperties() {
return properties;
}
public void setProperties(Properties properties) {
this.properties = properties;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "DataSource [properties=" + properties + "]";
}
}






















 318
318

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








