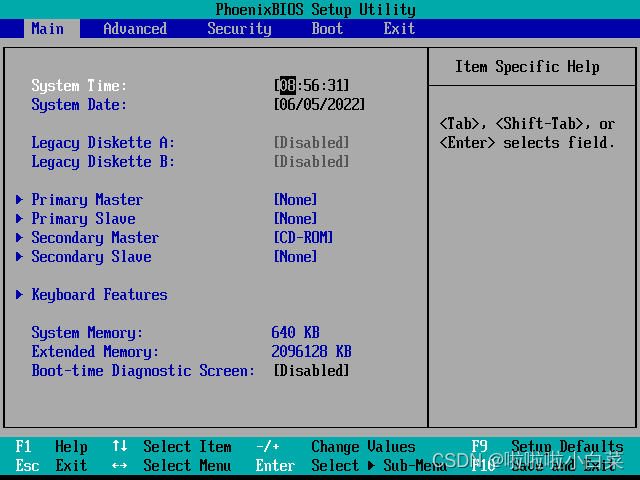
关于系统时间的,系统存在一个人硬件时间和软件的时间,以我使用的Rocky(Linux)系统为例子,在开机的时候按下F2键,弹出BIOS界面,在这里我们可以看到
启动好后我们使用命令clock也可以获取他的硬件时间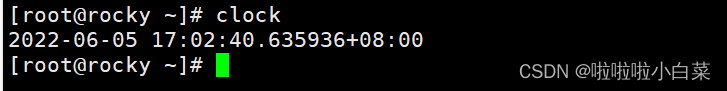
我们用date则是获取他的软件时间,这两者是有区别的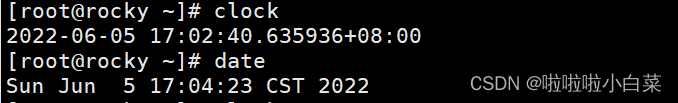
现在我们模拟下改下时间date +月日小时分年.秒(即2020/10/30 08:30:30)
现在的硬件时间可以用clock
现在我们把硬件时间为基准修改错误的软件时间使用clock -s 命令即可修正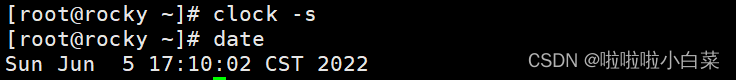
把软件时间为基准修改错误的硬件时间使用clock -w命令即可修正![]()
使用 cal 2022命令可以看到2022年整年的日历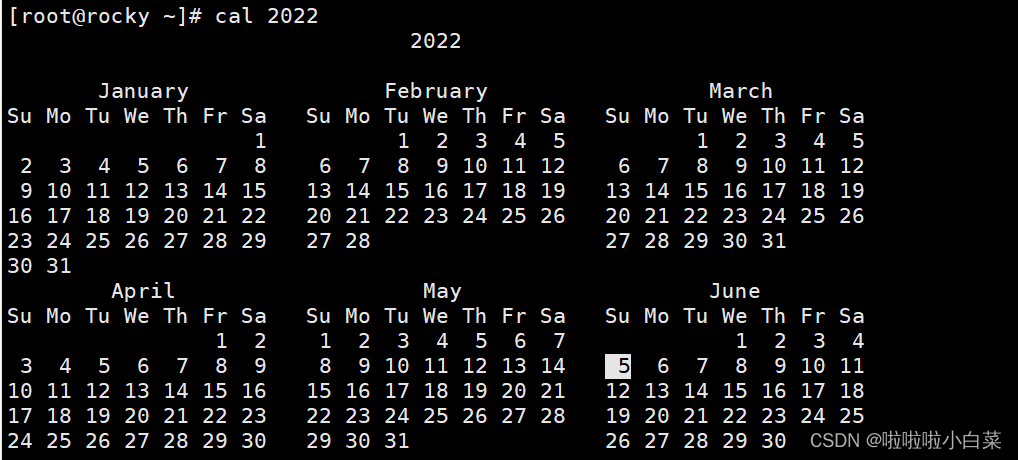
补充小知识:用cal 9 1752查看的时候发现中间消失了11天。(有兴趣可以看下)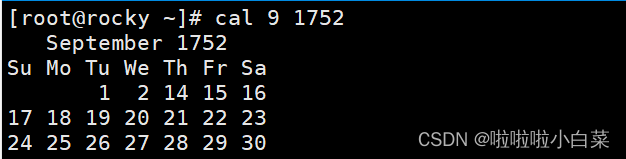






















 106
106











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










