文章目录
IO流
1. File类
- java.io.File类:文件和文件目录路径的抽象表示,与平台无关
- File可以新建、删除、重命名文件和目录,但是不能访问文件本身的内容。如果需要访问文件本身的内容,则需要使用IO流
1.1 File类的常用构造器
- public File(String pathname)
- public File(String parent, String child)
- public File(File parent, String child)
1.2 路径分隔符
路径分隔符和系统有关:
- 在winodws和dos系统中,使用\来分割
- UNIX和URL使用/来表示
因此,为了解决这个隐患,可以使用File类提供的一个常量File.separator。根据操作系统,动态的提供分隔符。
1.3 常用方法1
-
public String getAbsolutePath()
-
public String getPath()
-
public String getName()
-
public String getParent()
-
public long length()
获取文件的长度,单位为字节。不能读取目录的长度
-
public long lastModified()
获取最后一次的修改时间,单位毫秒值。可以用new Date()来现实具体时间
-
public String[] list()
获取指定目录下所有文件或文件夹的名称数组
-
public File[] listFiles()
获取指定目录下所有文件或文件夹的File数组
1.4 常用方法2
-
public boolean isDirectory()
-
public boolean isFile()
-
public boolean exisits()
-
public boolean canRead()
-
public boolean canWrite()
-
public boolean isHidden()
-
public boolean createNewFile()
创建文件。如果文件存在,则不创建,返回false
-
public boolean mkdir()
创建文件目录。如果上级目录不存在,则创建失败并返回false
-
public boolean mkdirs()
创建文件目录。如果上级目录不存在,则一并创建
-
public boolean delete()
删除文件或文件目录。不经过回收站
-
public boolean renameTo(File file)
重命名(移动文件)。file1.renameTo(file2) 要求file2在硬盘中不存在。
2. I/O流
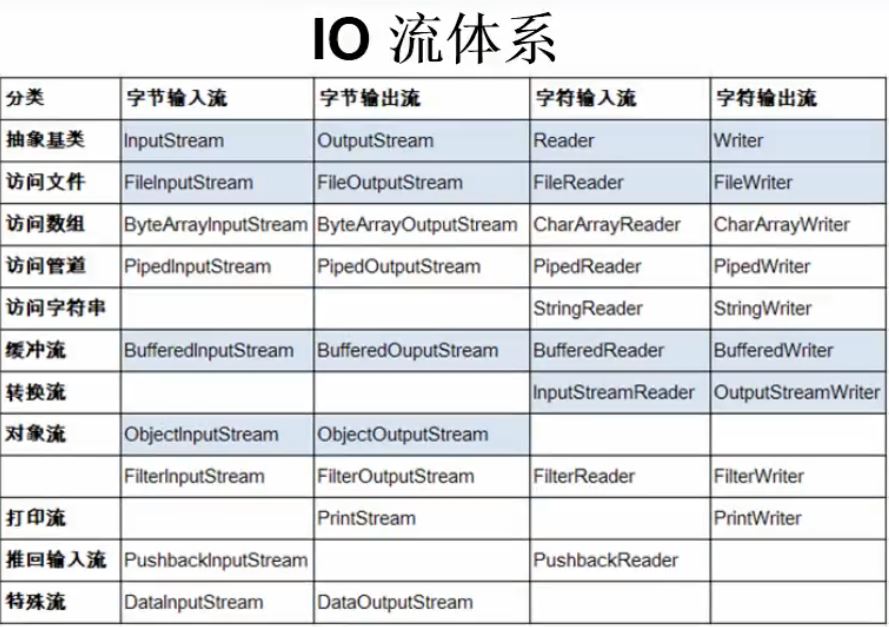
2.1 流的分类
-
按操作数据单位不同分为:字节流(8 bit) 和 字符流(16 bit)
对于非文本,如图片、视频则一般使用字节流。文本使用字符流
-
按数据流的流向不同分为:输入流 和 输出流
-
按流的角色的不同分为:节点流 和 处理流
| 抽象基类 | 字节流 | 字符流 |
|---|---|---|
| 输入流 | InputStream | Reader |
| 输出流 | OutputStream | Writer |
JAVA的IO流都是从这4个抽象基类派生出来的。子类命名通常是在基类前面加名称。如FileReader
2.3 FileReader
2.3.1 read() 读取单个字符
fr.read()用于读取单个字符。如果达到文件末尾,则返回-1
public class IOLearning {
@Test
public void testFileReader() {
FileReader fr = null;
try {
File file = new File("hello.txt");
fr = new FileReader(file);
int data;
// fr.read()用于读取单个字符。如果达到文件末尾,则返回-1
while ((data = fr.read()) != -1) {
System.out.print((char) data);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
if (fr != null) {
fr.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
2.3.2 read(char[] cbuf)
fr.read(char[]) 返回每次读取的字符个数。如果达到文件末尾,则返回-1
public class IOLearning {
@Test
public void testFileReader2() {
FileReader fr = null;
try {
File file = new File("hello.txt");
fr = new FileReader(file);
int len;
char[] cbuf = new char[5];
// fr.read(cbuf)返回每次读取的字符个数。如果达到文件末尾,则返回-1
while ((len = fr.read(cbuf)) != -1) {
String str = new String(cbuf, 0, len);
System.out.print(str);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
if (fr != null) {
fr.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
2.4 FileWriter
如果文件不存在,则会自动创建。
new FileWriter(File file, boolean append)
- 若append为true, 则不会覆盖原有的内容,会在末尾增加内容。
- 若append为false或者不指定,则会覆盖原有内容。
public class IOLearning {
@Test
public void testFileWriter() {
FileWriter fw = null;
try {
File file = new File("output.txt");
fw = new FileWriter(file, false);
fw.write("hello world123");
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
if (fw != null) {
fw.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
2.4.1 实现文件的复制
public class IOLearning {
@Test
public void copy() {
FileReader fr = null;
FileWriter fw = null;
try {
File sourceFile = new File("hello.txt");
File targetFile = new File("output2.txt");
fr = new FileReader(sourceFile);
fw = new FileWriter(targetFile);
int len;
char[] cbuf = new char[5];
while ((len = fr.read(cbuf)) != -1) {
fw.write(cbuf, 0, len);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
if (fw != null) {
fw.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
try {
if (fr != null) {
fr.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
2.5 FileInputStream和FileOutputStream
使用字节流处理文件时,如果包含中文,则有可能出现乱码。
所以字节流一般用于非文本文件的处理,如图片、视频等。
public class IOLearnig {
@Test
public void testFileInputStream() {
FileInputStream fis = null;
try {
File file = new File("hello.txt");
fis = new FileInputStream(file);
int len;
byte[] buffer = new byte[5];
while ((len = fis.read(buffer)) != -1) {
String str = new String(buffer, 0, len);
System.out.print(str);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
if (fis != null) {
fis.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
2.6 缓冲流–开发过程中一般使用缓冲流
BufferInputStream BufferReader
BufferOutputStream BufferWriter
缓冲流其实就是在FileInputStream、FileReader外面再包装一层。
当关闭资源时,只需要关闭缓冲流即可,剩下的内部流会自动关闭
使用BufferedReader时,可以是按行读取。br.readLine()
@Test
public void testBufferedStream() {
BufferedReader br = null;
BufferedWriter bw = null;
try {
File srcFile = new File("hello.txt");
File destFile = new File("output.txt");
FileReader fr = new FileReader(srcFile);
FileWriter fw = new FileWriter(destFile);
br = new BufferedReader(fr);
bw = new BufferedWriter(fw);
int len;
char[] cbuf = new char[1024];
while ((len = br.read(cbuf)) != -1) {
String str = new String(cbuf, 0, len);
bw.write(str);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
if (br != null) {
br.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
try {
if (bw != null) {
bw.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
2.7 转换流
- InputStreamReader: 将一个字节的输入流转换为字符的输入流
- OutputStreamReader: 将一个字节的输出流转换为字符的输出流
public class IOLearning {
@Test
public void testInputStreamReader() {
InputStreamReader isr = null;
try {
File file = new File("hello.txt");
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(file);
isr = new InputStreamReader(fis, "UTF-8");
int len;
char[] cbuf = new char[1024];
while ((len = isr.read(cbuf)) != -1) {
String str = new String(cbuf, 0, len);
System.out.print(str);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
if (isr != null) {
isr.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
2.8 对象流与序列化
-
序列化: 将内存中的Java对象保存到磁盘中或通过网络传输出去。使用ObjectOutputStream.writeObject()方法
-
反序列化:从磁盘或网络中读取Java对象。使用ObjectInputStream.readObject()方法
-
要想将自定义的对象序列化,则必须继承Serializable接口,且必须提供一个全局常量serialVersionUID。要求类中的所有属性,都是可以序列化的。(基本数据类型默认可以序列化)
-
static和transient修饰的成员变量无法序列化
public class Person implements Serializable { private static final long serialVersionUID = 421234123213L; private Integer id; private String name; private Integer age; // 构造器 getter setter方法省略。。 }
public class IOLearning {
@Test
public void testObjectOutputStream() {
ObjectOutputStream oos = null;
try {
oos = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("object.dat"));
Person person = new Person("xxx",15);
oos.writeObject(person);
oos.flush();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
if (oos != null) {
oos.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
2.9 随机访问文件
- RandomAccessFile直接继承于java.lang.Object类,实现了DataInput和DataOutput接口
- RandomAccessFile既可以作为一个输入流,又可以作为一个输出流
3. NIO
NIO中引入了Path,Path可以看成是File类的升级。Paths可以操作文件或文件目录
File file = new File("test.txt");
Path path = Paths.get("test.txt"); // 两句语句是等价的
File file = path.toFile();
Path newPath = file.toPath(); // file和path的相互转换
4. 第三方开源IO包
Apache的commons-io
5. URL网络编程
5.1 URL的基本结构
<传输协议>://<主机名>:<端口号>/<文件名>#片段名?参数列表
5.2 URL类中的方法
- public String getProtocol()
- public String getHost()
- public String getPort()
- public String getPath()
- public String getFile()
- public String getQuery()
5.3 下载资源
// 实际开发中,不要抛出异常,使用try/catch捕获
public class urlTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
URL url = new URL("http://localhost:8080/examples/sample.jpg");
HttpURLConnection urlConnection = (HttpURLConnection) url.openConnection();
urlConnection.connect(); // 获取连接
InputStream is = urlConnection.getInputStream();
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("E:\\sample.jpg");
byte[] buffer = new byte[1024];
int len;
while((len = is.read(buffer)) != -1) {
fos.write(buffer, 0, len);
}
is.close;
fos.close;
urlConnection.disconnect();
}
}






















 268
268











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








