08.13
4、弹窗蒙层
.pop{
width:600px;
height: 300px;
background: yellow;
margin: auto;
position: absolute;
top: 50%;
margin-top: -150px;
left: 50%;
margin-left: -300px;
}
.pop_mask{
position: fixed;
top: 0px;
background-color: #000;
opacity: 0.5;
width: 100%;
height: 100%;
}
<div class="pop_mask"></div>
<div class="pop">
test
</div>

3、使用css实现三角形
border
.circle{
margin:100px;
width: 0;
height: 0;
border: 50px solid;
border-color: transparent green transparent transparent;
}
<div class="circle"></div>

2、JS事件循环机制(event loop)之宏任务/微任务
JS是单线程,分同步/异步任务,异步也分执行时机,先执行微任务,再执行宏任务。
微任务:Promise、process.nextTick
宏任务:script、setTimeout、setInterval、setImmediate
setTimeout设置时间,是隔n秒后将任务插入到Event Queue中,如果前面没有任务,则立即执行,否则进入等待状态,所以setTimeout可能等待的时间不止n秒;设置为0秒情况,是不会立即执行的。
setTimeout(fn,0)的含义是,指定某个任务在主线程最早可得的空闲时间执行,意思就是不用再等多少秒了,只要主线程执行栈内的同步任务全部执行完成,栈为空就马上执行。
还有一个可能会被问到的ES7的异步方法async,async/await 是promise的语法糖。
console.log('script start') // 1️⃣
async function async1() { // 1️⃣
await async2() // 1️⃣
console.log('async1 end')
}
async function async2() {
console.log('async2 end')
}
async1()
setTimeout(function() {
console.log('setTimeout')
}, 0)
new Promise(resolve => { // 1️⃣
console.log('Promise') // 1️⃣
resolve()
})
.then(function() {
console.log('promise1')
})
.then(function() {
console.log('promise2')
})
console.log('script end') // 1️⃣
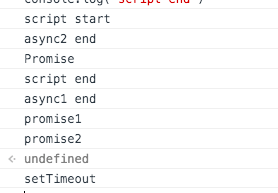
上图标记的1️⃣都是属于同步任务的,可能await async2()会有些疑问,转换成promise:
function async1() {
return new Promise((resolve, reject)=>{
async2()
resolve()
}).then(() => {
console.log('async1 end')
})
}
function async2() {
console.log('async2 end')
}
async1()
1、ES5/ES6 的继承除了写法以外还有什么区别
ES5以函数定义类,ES6用class关键字;ES5构造函数是function函数本身,ES6是constructor函数;
ES5 继承的实质是先创造子类的实例对象this,然后再将父类的方法添加到this上面(Parent.apply(this))。
借用构造函数:子类型构造函数调用父类型构造函数
function A(name) {
this.a = name;
this.arrA = ['a']
}
function B() {
// 绑定函数执行环境 传递参数
A.call(this, 'wsx')
}
var b1 = new B()
ES6通过class关键字定义类,类之间通过extends关键字实现继承。子类必须在constructor构造方法里调用super(),继承父类的this对象,得到与父类同样的实例属性和方法,然后再用子类的构造函数修改this。
class Square extends Rectangle {
constructor(length) {
// same as Rectangle.call(this, length, length)
super(length, length);
}
}























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








