原文链接: tf.py_func 操作tensor 增强 拓展 tensorflow灵活性
上一篇: tf 图像随机变换
下一篇: ros 自定义action
tf.py_func
本质功能是将流经tensor的真实数据传递给包装函数,将函数返回值包装成tensor后返回,所以需要返回值类型
参考: https://blog.csdn.net/tiankongtiankong01/article/details/80568311
它的具体功能描述是 包装一个 普通的 Python 函数, 这个函数 接受 numpy 的数组作为输入和输出 , 让这个函数可以作为 TensorFlow 计算图上 的计算节点 OP 来使用 。
py_func(
func,
inp,
Tout,
stateful=True,
name=None
)
参数:
- func : 一个 Python 函数, 它接受 NumPy 数组作为输入和输出,并且数组的类型和大小必须和输入和输出用来衔接的 Tensor 大小和数据类型相匹配.
- inp : 输入的 Tensor 列表.
- Tout : 输出 Tensor 数据类型 的列表或元祖.
- stateful : 状态,布尔值.
- name : 节点 OP 的名称.
关于stateful : operation分为有状态的与无状态的operation, 无状态的operation主要进行数学计算,比如矩阵乘法,加法等,如果给该 OP 同一个输入,那么将会得到同一个输出;
有状态的 operation(stateful operation)分为variable以及queue,variable负责保存机器学习模型的模型参数,queue提供更加复杂的模型架构,给定同一个输入,可能会得到不同的输出。
common subexpression elimination (CSE) 公共子表达式消除 只会在无状态的节点 OP 上执行。
tf.py_func的核心是一个 func函数 (由用户自己定义),该函数接收numpy array作为输入,并返回numpy array类型的输出。看到这里,大家应该能够明白为什么建议使用py_func, 因为在func函数中,可以对转化成numpy array的tensor进行np.运算,这就大大扩展了程序的灵活性。
在使用tf.py_func的过程中,主要核心是使用前三个参数。

第一个参数 func ,也是 最重要的 ,是一个用户自定制的函数,输入numpy array,输出也是numpy array,在该函数中,可以自由使用np.操作。
第二个参数 inp ,是func函数接收的输入,是一个 列表 。
第三个参数 Tout ,指定了func函数返回的numpy array转化成tensor后的格式,如果是返回 多 个值,就是一个 列表或元组 ;如果只有 一 个返回值,就是一个 单独的dtype类型 (当然也可以用列表括起来)。
最后来看看tf.py_func的输出:

输出是一个tensor列表或单个tensor。
到这里,tf.py_func的原理也就逐渐明晰了。 首先,tf.py_func接收的是tensor,然后将其转化为numpy array送入func函数,最后再将func函数输出的numpy array转化为tensor返回。
在使用过程中,有两个需要注意的地方, 第一就是func函数的返回值类型一定要和Tout指定的tensor类型一致。第二就是,如下图所示,tf.py_func中的func是脱离Graph的。在func中不能定义可训练的参数参与网络训练(反传)。
简单代码示例:
def my_func(x):
return np.sinh(x)
inp = tf.placeholder(tf.float32)
y = tf.py_func(my_func, [inp], tf.float32)
缺点:
- 这个被包装过的的计算函数的内部部分不会被序列化到 GraphDef 里面去,所以,如果你要序列化存储和恢复模型,就不能使用该函数。
- 这个被包装的计算节点 OP 与调用它的 Python 程序必须运行在同一个物理设备上,也就是说,如果使用分布式TensorFlow,必须使用 tf.train.Server 和 with tf.device(): 来保证二者在同一个服务器内。
tf.py_func在定义多输出函数时,输出变量类型需要用[ ]框起来;
tf.py_func在定义单输出函数时,输出变量类型不能再用[ ]框起来;
使用tf.py_func获得未知tensor维度。
直接使用内置函数会报错
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
def main():
a = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, shape=[1, 2], name="tensor_a")
b = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, shape=[None, 2], name="tensor_b")
tile_a = tf.tile(a, [b.get_shape()[0], 1])
sess = tf.Session()
array_a = np.array([[1., 2.]])
array_b = np.array([[3., 4.], [5., 6.], [7., 8.]])
feed_dict = {a: array_a, b: array_b}
tile_a_value = sess.run(tile_a, feed_dict=feed_dict)
print(tile_a_value)
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
TypeError: Failed to convert object of type <class 'list'> to Tensor. Contents: [Dimension(None), 1]. Consider casting elements to a supported type.
使用拓展函数成功
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
def tile_tensor(tensor_a, tensor_b):
tile_tensor_a = tf.py_func(_tile_tensor, [tensor_a, tensor_b], tf.float32)
return tile_tensor_a
def _tile_tensor(a, b):
tile_a = np.tile(a, (b.shape[0], 1))
return tile_a
def main():
a = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, shape=[1, 2], name="tensor_a")
b = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, shape=[None, 2], name="tensor_b")
tile_a = tile_tensor(a, b)
sess = tf.Session()
array_a = np.array([[1., 2.]])
array_b = np.array([[3., 4.], [5., 6.], [7., 8.]])
feed_dict = {a: array_a, b: array_b}
tile_a_value = sess.run(tile_a, feed_dict=feed_dict)
# [[1. 2.]
# [1. 2.]
# [1. 2.]]
print(tile_a_value)
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
在tf.py_func中对tensor的值作出判断
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
def main():
a = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, shape=[1], name="tensor_a")
b = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, shape=[1, 2], name="tensor_b")
tile_b = b
if a[0] == 1.:
tile_b = tf.tile(b, [4, 1])
sess = tf.Session()
array_a = np.array([1.])
array_b = np.array([[2., 3.]])
feed_dict = {a: array_a, b: array_b}
tile_b_value = sess.run(tile_b, feed_dict=feed_dict)
print(tile_b_value)
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
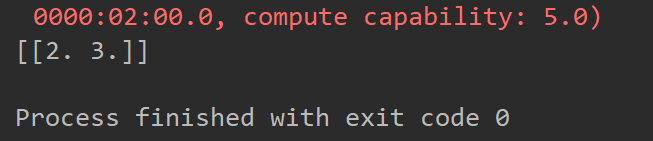
大家可以看到,由于在if语句执行时,tensor a里面是空的。因此, 不会执行if中的语句 。尽管在feed_dict中a被填充了1.0,并且程序不报错,可是没有达到预想的目标。
如何解决这个问题?稍微改写一下上述代码,让判值进行tensor扩张在tf.py_func中执行:
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
def tile_b(tensor_a, tensor_b):
tile_tensor_b = tf.py_func(_tile_b, [tensor_a, tensor_b], tf.float32)
return tile_tensor_b
def _tile_b(a, b):
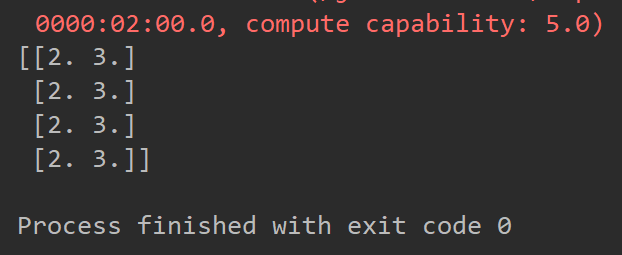
if a[0] == 1.:
tile_b = np.tile(b, (4, 1))
else:
tile_b = b
return tile_b
def main():
a = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, shape=[1], name="tensor_a")
b = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, shape=[1, 2], name="tensor_b")
tile_tensor_b = tile_b(a, b)
sess = tf.Session()
array_a = np.array([1.])
array_b = np.array([[2., 3.]])
feed_dict = {a: array_a, b: array_b}
tile_b_value = sess.run(tile_tensor_b, feed_dict=feed_dict)
print(tile_b_value)
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()





















 8708
8708

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








