转载自:http://blog.csdn.net/harvic880925/article/details/50085595
在上篇中,我们简单给大家讲解了如何利用反射来获取普通类型的类的使用,今天给大家讲解下,有关如何使用反射来获取泛型中的信息。提前提个醒,本篇文章内容稍难,大家可能需要多看几篇。
这篇文章将大量用到泛型的知识,如果对泛型声明及填充不太了解的同学,请先看完夯实JAVA之泛型详解一代龙套篇
一、获取泛型超类和接口的相信信息
在这部分内容中,我们将讲述如何获取泛型的超类和接口,把上篇中遗留下来的两个函数先讲完。1、获取泛型超类相信信息
上篇中,我们讲了,要获取泛型类型的超类,要用到一个函数:下面我们就先看看这个函数怎么用,我们依然以上篇中的Point类以及它的派生类PointImpl为例:
从上面的代码中,我们可以看到,Point类是一个泛型类,具有一个泛型变量T;而PointImpl派生自Point并且在派生时,将Point进行填充为Point,即将Point中的泛型变量填充为Integer类型。
下面, 我们将通过反射获取PointImpl的父类的类型,以及PointImpl的填充类型
我们在没看代码之前,我们先看看结果,我们知道PointImpl的父类类型是Point,而PointImpl的填充类型应该是Integer.
然后我们再看看代码:
相信上面这段代码,大家肯定是很不懂的。。。。因为确实狠复杂,不管那些,我们先看看结果:

从结果中,我们可以看到,先获得到的是PointImpl在填充父类时的类型Integer,然后获得的是PointImpl的父类类型。
下面先看如何获取当前类在填充父类时的填充类型的:
对应代码是这一块:
下面我们对这块分块讲解:
(1)、获取泛型超类
在这段代码中,我们通过clazz.getGenericSuperclass()获取PointImpl.class的超类。由于我们知道PointImpl.class的父类是泛型,所以我们只能使用clazz.getGenericSuperclass()来获取。但获取出来的类型确是很让人捉急。一个Type类型,下面我们先间断下,讲讲这个Type类型是个什么鬼。(2)、Type类型
我们先看看Type的源码,看他自己是怎么说的:Type是一个接口,这里意思是它是Java所有类型都会继承这个接口。但通过源码会发现String,Integer,Double这些类都没有继承这个接口,就连Object也没继承!
这就有点坑爹了,再仔细查代码会出现,Class继承了这个接口:
所以说,这个Type类型是泛型所特有的。那它用是来做什么的呢?
他就是用来标识,当前Class中所填充的类型的。意思是,当我们在填充一个泛型时,比如上面我们的:
这个填充类型就会放在Type的保存起来,当需要用到的时候再取出来。那问题又来了,我们这里填充的是Integer类型,那如果我们填充的是数组泛型呢,比如Point<ArrayList>,再假如我们填充的是一个通配符呢?这Type要怎么识别呢?
为了解决这个问题,Java的开发者,在Type的基础上派生了另外几个接口,分别来保存不同的类型,他们分别是:
- ParameterizedType:这就是上面我们代码中用到的,他代表的是一个泛型类型,比如Point,它就是一个泛型类型。
我们在代码中,利用:
获得PointImpl.class的父类,而它的父类是Point,这明显是一个泛型类型,所以它对应的类型就是ParameterizedType; - TypeVariable:这个代表的就是泛型变量,例如Point,这里面的T就是泛型变量,而如果我们利用一种方法获得的对象是T,那它对应的类型就是TypeVariable;(这个类型的应用后面会细讲)
- WildcardType:上面的TypeVariable对应的是泛型变量,而如果我们得到不是泛型变量,而是通配符比如:? extends Integer,那它对应的类型就是WildcardType;
- GenericArrayType:如果我们得到的是类似String[]这种数组形式的表达式,那它对应的类型就是GenericArrayType,非常值得注意的是如果type对应的是表达式是ArrayList这种的,这个type类型应该是ParameterizedType,而不是GenericArrayType,只有类似Integer[]这种的才是GenericArrayType类型。
- 虽然我们后面会对TypeVariable,WildcardType进行讲解,这里还是先对他们三个类型对应的意义先总结一下,比如我们这里的clazz.getGenericSuperclass(),得到的Type对应的是完整的泛型表达式即:Point,那它对应的类型就是ParameterizedType,如果我们得到的Type对应的表达式,仅仅是Point中用来填充泛型变量T的Integer,那这个Type对应的类型就是TypeVariable,如果我们得到的是依然是填充泛型变量T的填充类型,这而个填充类型却是通配符?,那这个Type对应的类型就是WildcardType。这一段看不大明白也没关系,后面还会再讲。
(3)、ParameterizedType
上面我们已经提到当获取的Type类型,对应的是一个完整泛型表达式的时候,比如,我们这里获取到的PointImpl.class的父类:这时的type对应的完整表达式就是:Point
在ParameterizedType中有两个极有用的函数:
- getActualTypeArguments():用来返回当前泛型表达式中,用来填充泛型变量的真正值的列表。像我们这里得到的Point,用来填充泛型变量T的是Integer类型,所以这里返回的Integer类型所对应的Class对象。(有关这一段,下面会补充,这里先看getRawType)
- getRawType():我们从我们上面的代码中,也可以看到,它返回的值是com.harvic.blog_reflect_2.Point,所以它的意义就是声明当前泛型表达式的类或者接口的Class对象。比如,我们这里的type对应的是Point,而声明Point这个泛型的当然是Point类型。所以返回的是Point.Class
下面我们再回过来看看getActualTypeArguments():
我们上面说到,这个函数将返回用来填充泛型变量真实参数列表。像我们这里的是Point,将返回Integer对应的Class对象。而并不是所有的每次都会返回填充类型对应的Class对象。我们知道我们在填充一个泛型时,是存在各种可能的,比如Point,Point<? extends Number>,Point<ArrayList>,Point<ArrayList<? extend Number>>,等等
虽然我们没办法穷举可能填充为哪些类型,但我们知道Type类型是用来表示填充泛型变量的类型的,而继承Type接口只有下面五个:Class,ParameterizedType,TypeVariable,WildcardType,GenericArrayType!
所以这也是Type[] getActualTypeArguments();中Type[]数组的所有可能取值!
好了,现在我们再回来看看我们的代码
我们在Type type = clazz.getGenericSuperclass();之后,得到的type的值对应的是:Point,所以我们知道,type对应的是ParameterizedType,所以我们用
来识别,然后将type变量强转为ParameterizedType变量:
然后到了最重要的两句:
然后,先利用parameterizedType.getActualTypeArguments()获取当前泛型变量的填充列表,我们知道Point中泛型变量T被填充为Integer,所以我们得到的数组Type[]里,只有一个值,它对应的就是Integer.Class。
然后我们将得到的Type进行强转成Class类型,所以parameterArgClass对应的值就是Integer.Class。所以我们利用parameterArgClass.getName():java.lang.Integer
(5)、getRawType()
最后,我们再来看看getRawType的用法:我们知道,parameterizedType对应的值是Point,而parameterizedType.getRawType()得到的就是声明这个泛型的类的Class对象。所以这里的type1对应的值就是Point.Class。所以我们将其转换成Class对象,通过class22.getName()得到的值是:com.harvic.blog_reflect_2.Point
2、获取所继承泛型接口的相关信息
上泛我们也说到,获取普通类所继承的接口使用的是Class.getInterfaces()函数,如果要获取泛型接口的对象需要用到:这里提前强调一点:大家需要注意是getGenericInterfaces()数与Class.getInterfaces()函数一样,都只能获取此类直接继承的接口列表!
这里得到的一个Type数组,因为我们一个类可以继承多个接口,所以这里的每一个type对应的就是我们所继承的一个接口类型。
下面我们举个例子来看这个接口的用法:
首先,生成一个泛型接口:
可以看到,我们这个泛型接口里有两个泛型变量,这个接口里我们没有定义任何的方法,因为我们这里只会获取填充泛型接口的实际类型,不会用到它的方法,所以就没有必要生成了,写个空接口即可。
然后,我们直接使用前面的PointImpl来继承好了,就不再另写其它类了:
从这里可以看出,我们在生成PointImpl时将 PointInterface<T,U>填充为PointInterface<String,Double>
下面我们来看如何来获取PointImpl所继承的泛型接口的信息:
依然是一长段让人受不了的代码,我们一点点来分析。
首先,是获得PointImpl.class所继承接口的数组
因为我们知道,我们的PointImpl只继承了一个接口:PointInterface<String,Double>,所以此时的Type[]中只有一个元素,即代表着PointInterface<String,Double>的type
然后是利用for…each循环遍历types中的每一个元素。
因为我们知道,我们这里的type代表的是PointInterface<String,Double>,明显它是一个泛型,所以它对应的type类型应该是ParameterizedType!下面的代码就与上面获取泛型超类的一样了,即通过parameterizedType.getActualTypeArguments()获取到它的参数数组
因为我们知道,PointInterface<T,U>被PointImpl填充为PointInterface<String,Double>,所以它的真实的参数类型应该是String和Double, 我们前面说过Type只有五种类型:Class,ParameterizedType,TypeVariable,WildcardType,GenericArrayType。而ParameterizedType代表完整的泛型表达式,TypeVariable代表泛型变量的符号即T,U等,WildcardType代表通配符,GenericArrayType代表数组类型,而Class则表示派生于Object的所有Class类,明显这里的String和Double是Class类型的。
所以我们将它们强转为Class类型,然后通过parameterArgClass.getName()得到它们的完整路径名。
最后通过parameterizedType.getRawType()获取声明PointInterface<String,Double>的接口类类型,虽然这里得到的是Type,但我们声明接口的是PointInterface.Class所以,也是Class类型,直接将其强转为Class即可。最后通过Class.getName()获取其完整的路径名。
好了,到这里,有关泛型超类和继承接口的信息获取到这就结束了,下面我们再来看看上面另外提到的另外三个Type类型:TypeVariable,WildcardType,GenericArrayType
二、Type的五种类型
上面说们说过,Type接口是用来保存当前泛型被填充的类型的,它总共有五种类型:Class,ParameterizedType,TypeVariable,WildcardType,GenericArrayType在这上面的例子中,我们用到了Class,ParameterizedType;当type所代表的表达式是一个完整泛型时,比如Point,那这个Type类型就是ParameterizedType;如果type所代表的是一个确定的类,比如Integer,String,Double等,那这个type所对应的类型就是Class;强转之后,得到的就是他们所对应的Class对象,即Integer.Class,String.Class,Double.Class等
前面我们说过,如果type对应的是一个泛型变量,即类似于T,或U这种还没有被填充的泛型变量,那它的类型就是TypeVariable;而如果type对应的是一个通配符表达式,比如? extends Num,或者仅仅是一个通配符?,类似这种有通符符的类型就是WildcardType;
而如果type对应的类型是类似于String[]的数组,那它的类型就是GenericArrayType;
下面我们就来分别看看TypeVariable、WildcardType和GenericArrayType的用法
1、TypeVariable
我们上面说了,当type代表的类型是一个泛型变量时,它的类型就是TypeVariable。TypeVariable有两个函数:- getName:就是得到当前泛型变量的名称;
- getBounds:返回表示此类型变量上边界的 Type 对象的数组。如果没有上边界,则默认返回Object;
我们依然在PointInterface泛型接口上做文章:
这里,我们在PointInterface的基础上,重写一个类PointGenericityImpl,与上面直接在类中填充不同的是,它是一个泛型类,首先,将PointInterface<T,U>填充为PointInterface<T,Integer>,即第一个参数依然是一个泛型,而第二个参数填充为Integer;而我们也给PointGenericityImpl中的泛型变量T添加了限定:T extends Number&Serializable,给它添加了extends限定(上边界):指定T必须派生自Number类和Serializable类。
我们再看一下如何获取信息:
先看看结果:
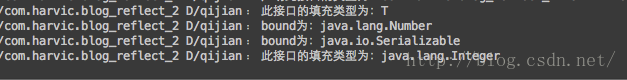
依然是一坨复杂得像翔一样的代码,我们逐段来分析下;
首先,获取PointGenericityImpl直接继承的的泛型接口数组
我们知道PointGenericityImpl只直接继承了一个接口:PointInterface<T,Integer>,其中T的限定为:<T extends Number&Serializable>;所以types中只有一个元素,这个type元素代表的是PointInterface<T,Integer>,明显它是一个泛型,所以这个type的类型是ParameterizedType。所以,我们下面虽然用了for …each进行了列举了types中的所有元素,但我们知道它只有一个元素。
然后我们将这个元素强转为ParameterizedType,然后利用parameterizedType.getActualTypeArguments()得到PointInterface<T,U>中T和U被填充的真实类型对应的Type数组。
我们知道,PointInterface<T,U>被真实填充为了PointInterface<T,Integer>,其中T的限定为:<T extends Number&Serializable>;所以这个Type[]数组包含两个变量,一个是T,一个是Integer;
我们知道T是一个泛型变量,所以对应的类型应该是TypeVariable
而Integer则是一个具体的类,它对应的类型应该是Class
针对T:
我们知道T对应的type是TypeVariable,所以将它强转为TypeVariable变量。然后用typeVariable.getName()获取这个填充的泛型变量的名字,得到的值为:
然后,利用typeVariable.getBounds()得到T的限定条件:上边界的数组。上边界的意思就是extends关键字后面的限定条件。“上”的意思就是能取到的最大父类。最大父类当然是用extends关键字来限定的。我们知道这里的T的限定条件是:<T extends Number&Serializable>,所以 Type[] typebounds = typeVariable.getBounds();所得到typebounds有两个变量,一个是Number,一个是Serializable;这两个都是具体的类型,所以我们可以直接将它们转换为Class类型,然后利用Class.getName()获取它们完整的路径名,结果如下:(有关上下边界的意义下面在讲WildcardType时会有图文讲解)
针对Integer:
再来看下代码:因为PointInterface<T,U>被真实填充为了PointInterface<T,Integer>,上面我们讲完了T的获取,在
中第一个类型是type类型对应的是T,第二个type类型则是Integer类型。明显Integer是一个Class类型,所以我们直接将它强转为Class即可
结果为:

2、GenericArrayType
上面我们说过,当type对应的类型是类似于String[]、Integer[]等的数组时,那type的类型就是GenericArrayType;这里要特别说明的如果type对应的是类似于ArrayList、List这样的类型,那type的类型应该是ParameterizedType,而不是GenericArrayType,因为ArrayList是一个泛型表达式。所以当且仅当type对应的类型是类似于String[]、Integer[]这样的数组时,type的类型才是GenericArrayType!我们先看看GenericArrayType的函数:
getGenericComponentType:这是GenericArrayType仅有一个函数,由于getGenericComponentType所代表的表达是String[]这种的数组,所以getGenericComponentType获取的就是这里的数组类型所对应的Type,比如这里的String[]通过getGenericComponentType获取到的Type对应的就是String.
好了,下面我们就举个例子来看看GenericArrayType的用法
我们重新生成一个泛型接口PointSingleInterface:
这个泛型接口,只有一个泛型变量
然后生成一个类继承这个接口:
在PointArrayImpl中,我们填充PointSingleInterface中泛型变量T的是Integer[],一个Integer数组!
下面我们来看看如何获取PointArrayImpl的接口信息:
先看执行结果:

依然看起来有点复杂,我们一点点来分析:
首先,通过clazz.getGenericInterfaces()获取PointArrayImpl.class的接口对应的type列表
然后利用for…each对interfaces数组进行逐个列表,但我们知道它只有一个元素,代表的表达式是PointSingleInterface<Integer[]>;然后用
得到表达式中PointSingleInterface<Integer[]>的参数列表,显然参数只有一个,即Integer[],所以actualArgs中只有一个元素,这个type元素对应的表达式是Integer[];
我们知道当type对应的表达式是Integer[]时,这个type的类型就是GenericArrayType
我们将arg强转为GenericArrayType类型的变量arrayType,然后利用arrayType.getGenericComponentType()得到数组的类型,因为我们这里的数组是Integer[],所以得到的类型是Integer,明显这是一个确切的类,所以它的类型就是Class,所以我们直接将comType进行强制转换为Class<?> typeClass,最后利用typeClass.getName()得到Integer的具体类名。
好了,到这里,我们已经讲完了三种类型,下面开始讲解最后一个也是最难的一种类型WildcardType!
3、WildcardType
(1)、概述
我们前面说过,当type所代表的表达式是类型通配符相关的表达式时,比如<? extends Integer>,<? super String>,或者<?>等,这个type的类型就是WildcardType!我们先来看看WildcardType的函数:
- getUpperBounds:获取上边界对象列表,上边界就是使用extends关键定所做的的限定,如果没有默认是Object;
- getLowerBounds:获取下边界对象列表,下边界是指使用super关键字所做的限定,如果没有,则为Null
<? extends Integer>:这个通配符的上边界就是Integer.Class,下边界就是null
<? super String>:这个通配符的下边界是String,上边界就是Object;
有关上下边界,大家可能很不好记,我画个图来给大家解释下,上下边界的含义:

看到这个类继承图,大家应该很容易就明白了,类继承图中,根结点始终是在祖先类,而且在继承图的上方,所以上方的就是上界,而子类是在下方,下方的就是下界。
而表现在代码上,上界是继承的关系,所以是<? extends Object>,而下界的则是<? super Double>
(2)、有关通配符的使用范围
我们在 《夯实JAVA基本之一——泛型详解(2)》 讲过,通配符只是泛型变量的填充类型的一种,不能做为泛型变量使用。在 《夯实JAVA基本之一——泛型详解(2)》 中我们多次强调:通配符?只能出现在Box<?> box;中,其它位置都是不对的。
即只能出现在生成泛型实例时使用,其它位置都是不可以的。
尤其像下面这两个,直接用来填充类中的泛型变量:
但下面这样却是允许的:
因为,这里的通配符Comparable<? extends Number>,只有来生成Comparable对象的,所以是允许使用的!大家一定要注意,通配符只能用来填充泛型类来生成对象。其它用途一概是错误的!
(3)、举个例子
同样,我们使用上面的PointSingleInterface泛型接口:然后我们生成一个类来继承这个接口:
接下来就看看我们是怎么得到的PointWildcardImpl信息的:(代码比较长,后面会细讲)
执行结果为:

看到这一大段代码,估计尿血的感觉都出来了。我们对它逐段分析:
首先获取PointWildcardImpl.class所直接继承的接口
然后将type强转成ParameterizedType的变量,利用parameterizedType.getActualTypeArguments()获取PointSingleInterface的填充参数:Comparable<? extends Number>
所以此时的actualTypes也仅有一个元素,它代表的表达式是Comparable<? extends Number>,明显这依然是一个泛型,所以还得继续往下剥
所以继续将其中的actualType进行强转,然后再得到它的填充参数:
此时的compareArgs列表中也仅有一个元素,这个元素代表的表达式是:<? extends Number>
这就是一个WildcardType类型了,然后是得到这个WildcardType的上下边界信息了:
完整获取上下边界的代码如下:(后面会分开讲)
我们讲到,下边界使用的是super关键字来做限定的,我们这里的表达式是:<? extends Number>,所以下边界是Null,虽然写了代码,也不会执行到里面去。
然后再看看如何得到上边界:
我们知道,<? extends Number>的下边界就是Number.Class,所以Type[] upperBounds数组中只有一个元素,这个type对应的是Number.Class,所以将它强转为Class对象,然后通过boundClass.getName()得到它的完整对象名。
结果如下:

好了,到这里,所有有关type的类型就讲完了,但我们上面是逐个分析当前type应该强转为哪种类型的,如果我们稍微疏忽分析错了,或者,我们根本不知道它当前是哪种类型,这要怎么办,我们必须能写出来一个统一的转换函数出来!我们知道type所有的类型总共五种:Class,ParameterizedType,TypeVariable,WildcardType,GenericArrayType;所以我们利用递规的方法来写一个通用类型转换函数出来。
4、Demo:写一个通用类型转换函数
我们这节就要写一个通用的类型转换函数了,1、实现parseClass(Class<?> c)函数
先写一个parseClass的入口函数,用来得到他所直接继承的泛型接口:然后再来实现它其中的parseTypeParameters函数,来解析type[]数组:
这段代码也很简单,对types进行枚举,利用parseTypeParameter(type)对每一个type进行分析,我们看看parseTypeParameter(type)是如何对每一个函数进行分析的:
这段代码很长,我们先不管它是怎么写出来的,下面再细讲,我们先看看如何使用我们写出来的parseClass(Class<?> c)函数来解析的;
2、使用parseClass(Class<?> c)
首先,我们还用上面用PointWildcardImpl类:然后我们调用parseClass(Class<?> c)对它进行分析:
结果为:
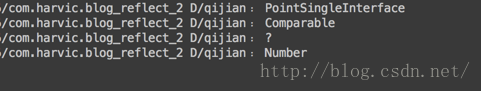
可以看到,打印出了每一个字段的名字。
好了,我们再回过头来看看,parseTypeParameter(Type type)是怎么写的。
3、parseClass(Class<?> c)实现详解
在parseClass(Class<?> c)中,最关键的部分是parseTypeParameter(Type type)函数,所以我们直接对parseTypeParameter(Type type)进行分析。我们知道,type总共有五种类型:Class,ParameterizedType,TypeVariable,WildcardType,GenericArrayType,所以我们在解析type时分别对它的每种类型进行判断,然后分别解析即可:
如果type是Class类型,则说明type是一个确切的类了,不会再有下一层的泛型参数填充了,所以直接打印出它的名字。
如果type是一个泛型变量,即类似于T,U这些代表泛型变量的字母,我们先打印出这个字母,然后由于泛型变量还有边界,tv.getBounds()可以得到它的所有上边界。所以利用parseTypeParameters(tv.getBounds());分析它的所有上边界type
如果type类型是WildcardType,即上面最难的通配符,因为只要是WildcardType,肯定是有问号的,但WildcardType是没有getName()函数来获取问号的标识的,所以我们只有手动输出一个问号标识了Log.d(TAG, “?”);同样通配符也是有上下边界的,比如<? extends xxx>,<? super xxx>,所以利用parseTypeParameters()分别来分析它的上边界type数组和下边界的type数组
如果type的类型是ParameterizedType,那type代表的表达式肯定是一个泛型,类似于我们上面的Comparable<? extends Number>,我们利用pt.getRawType()得到声明这个类的类型,比如这里的Comparable<? extends Number>,得到的将是Comparable.Class。然后利用getActualTypeArguments()得到这个泛型的具体填充参数列表。同样利用parseTypeParameter()和parseTypeParameters()再次分析。
最后,是GenericArrayType类型,如果type代表的表达式是类似于String[],Integer[]这种数组的话,那type就是GenericArrayType类型。GenericArrayType只有一个函数getGenericComponentType(),得到这个数组的类型。同样将返回的type值传给parseTypeParameter(t)再次分析。
好了,有关反射中相关泛型的部分就结束了,下面再总结一下,本篇文章中所涉及到的所有函数。
5、本文涉及函数:
ParameterizedType相关TypeVariable相关
GenericArrayType相关
WildcardType相关
到这里整篇文章也就结束了,泛型相关的这部分东西也真是太难讲了,相当复杂而且不易理解,大家有用到的话就多看几遍吧,下篇我们将会讲到如何利用反射得到类的内部信息。
有关ParameterizedType.getOwnerType()的用法参考 《ParameterizedType.getOwnerType() 函数怎么用?》
如果本文有帮到你,记得加关注哦
本文所涉及源码下载地址:http://download.csdn.net/detail/harvic880925/9306441


























 2731
2731

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








