C++的函数
1. 函数
1.1 函数概述
① 函数作用:将一段经常使用的代码封装起来,减少重复代码。
② 一个较大的程序,一般分为若干个程序块,每个模块实现特定的功能。
1.2 函数定义
① 函数的定义主要有5个部分:
- 返回值类型:一个函数可以返回一个值。
- 函数名:给函数起个名称。
- 参数列表:使用该函数时,传入的数据。
- 函数体语句:花括号内的代码,函数内需要执行的语句。
- return表达式:和返回值类型挂钩,函数执行完后,返回相应的数据。
② 语法格式如下所示:
返回值类型 函数名 (参数列表)
{
函数体语句
return 表达式
}
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
//函数的定义
//语法:返回值类型 函数名 (参数列表) { 函数体语句 return表达式 }
//加法函数,实现两个整型相加,并且将相加的结果进行返回
int add(int num1, int num2)
{
int sum = num1 + num2;
return sum;
}
int main()
{
system("pause"); //按任意键继续
return 0;
}
1.3 函数调用
① 功能:使用定义好的函数
② 语法:函数名(参数)
② 函数定义里小括号内称为形参,函数调用时传入的参数称为实参
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
//函数的定义
//语法:
//返回值类型 函数名 (参数列表) { 函数体语句 return表达式 }
//定义加法函数
//函数定义的时候,num1和num2并不是真实数据
//它们只是一个形式上的参数,简称形参
int add(int num1, int num2)
{
int sum = num1 + num2;
return sum;
}
int main()
{
//main函数中调用add函数
int a = 10;
int b = 20;
//函数调用语法:函数名称:(参数)
//a和b称为 实际参数,简称实参
//当调用函数的时候,实参的值会传递给形参
int c = add(a, b);
cout << "c = " << c << endl;
system("pause"); //按任意键继续
return 0;
}
运行结果:
- c = 30
- 请按任意键继续. . .
1.4 函数值传递
① 所谓值传递,就是函数调用时实参将数值传入给形参。
② 值传递时,如果形参发生改变,并不影响实参。
③ 在下面代码例子中,实参传进去时,新参会产生新的内存空间赋值,对num1、num2的操作并不会改变实参a、b的值。
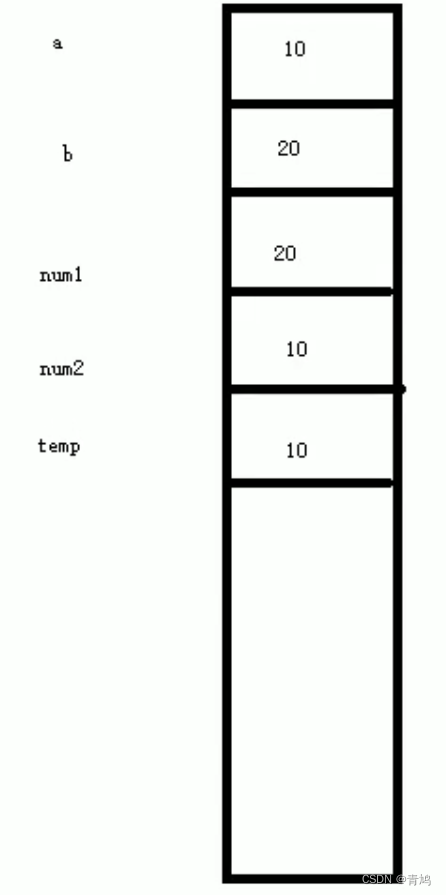
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
//值传递
//定义函数,实现两个数字进行交换函数
//如果函数不需要返回值,声明的时候可以写void
void swap(int num1, int num2)
{
cout << "交换前:" << endl;
cout << "num1= " << num1 << endl;
cout << "num2= " << num2 << endl;
int temp = num1;
num1 = num2;
num2 = temp;
cout << "交换后:" << endl;
cout << "num1= " << num1 << endl;
cout << "num2= " << num2 << endl;
return; //前面写了void,所以不需要返回值。返回值不需要的时候,也可以不写return。
}
int main()
{
//main函数中调用add函数
int a = 10;
int b = 20;
cout << "a = " << a << endl;
cout << "b = " << b << endl;
//当我们把值传递的时候,函数的形参发生发生改变,并不会影响实参
swap(a, b);
cout << "a = " << a << endl;
cout << "b = " << b << endl;
system("pause"); //按任意键继续
return 0;
}
运行结果:
- a = 10
- b = 20
- 交换前:
- num1= 10
- num2= 20
- 交换后:
- num1= 20
- num2= 10
- a = 10
- b = 20
1.5 函数常见样式
① 常见的函数样式有四种
- 无参无返
- 有参无返
- 无参有返
- 有参有返
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
//函数常见样式
//1、无参无返
void test01()
{
cout << "this is test01" << endl;
}
//2、有参无返
void test02(int a)
{
cout << "this is test 02 a = " << a << endl;
}
//3、无参有返
int test03()
{
cout << "this is test 03 " << endl;
return 1000;
}
//4、有参有返
int test04(int a )
{
cout << "this is test 04 a = " << a << endl;
return a;
}
int main()
{
//无参无返函数调用
test01();
//有参无返函数调用
test02(100);
//无参有返函数调用
int num1 = test03();
cout << "num1 = " << num1 << endl;
//有参有返函数调用
int num2 = test04(10000);
cout << "num2 = " << num2 << endl;
system("pause"); //按任意键继续
return 0;
}
运行结果:
- this is test01
- this is test 02 a = 100
- this is test 03
- num1 = 1000
- this is test 04 a = 10000
- num2 = 10000
1.6 函数声明
① 作用:告诉编译器函数名称及如何调用函数。函数的实际主体可以单独定义。
② 函数的声明可以多次,但是函数的定义只能有一次。
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
//函数的声明
//比较函数,实现两个整型数字进行比较,返回较大的值。
//提前告诉编译器函数的存在,可以利用函数的声明
//函数的声明
//声明可以写多次,但是定义只能有一次
int max(int a, int b);
int max(int a, int b);
int max(int a, int b);
int main()
{
int a = 10;
int b = 20;
cout << max(a, b) << endl;
system("pause"); //按任意键继续
return 0;
}
//函数定义在main函数之后,必须要在main函数之前写函数的声明
int max(int a, int b)
{
return a > b ? a : b;
}
运行结果:
- 20
1.7 函数分文件编写
① 作用:让代码结构更加清晰。
② 函数分文件编写一般有4个步骤:
- 创建后缀名为.h的头文件。
- 创建后缀名为.cpp的源文件。
- 在头文件中写函数的声明。
- 在源文件中写函数的定义。
1.7.1 swap.h头文件
//这个是swap.h头文件
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
//函数的声明
void swap(int a, int b);
### 1.7.2 swap.pp源文件
//这个是swap.pp源文件
#include "swap.h"
//函数的定义
void swap(int a, int b)
{
int temp = a;
a = b;
b = temp;
cout << "a = " << a << endl;
cout << "b = " << b << endl;
}
1.7.3 主文件 .cpp文件
//主文件,调用函数分文件
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#include "swap.h" //包含要调用的函数的头文件,双引号表示我们自己写的头文件
int main()
{
int a = 10;
int b = 20;
cout << max(a, b) << endl;
system("pause"); //按任意键继续
return 0;
}
1.8 函数默认参数
① 在C++中,函数的形参列表中的形参是可以有默认值的。
② 语法:返回值类型 函数名 (参数 = 默认值) {}
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
//函数默认参数
//如果我们自己传入数据,就用自己的数据,如果没有,那么永默认值
//语法:返回值类型 函数名(形参 = 默认值)
int func01(int a,int b,int c)
{
return a + b + c;
}
//注意事项
//1、如果某个位置以及有了默认参数,那么从这个位置往后,从左到右都必须有默认值
int func02(int a, int b = 40, int c = 50)
{
return a + b + c;
}
//2、如果函数声明有默认参数,函数实现就不能有默认参数
//例如,函数定义为 int func03(int a = 20, int b = 20){return a + b;},而函数声明为int func03(int a = 10, int b = 10);那么编译器不知道按照哪个默认参数来运行
//声明和实现只能有一个有默认参数
int func03(int a = 10, int b = 10);
//这个是函数的实现
int func03(int a , int b)
{
return a + b;
}
int main()
{
cout << func01(10, 20, 30) << endl;
cout << func02(10) << endl;
cout << func02(10, 20) << endl;
cout << func02(10, 20,30) << endl;
cout << func03() << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
运行结果:
- 60
- 100
- 80
- 60
- 20
- 请按任意键继续. . .
1.9 函数占位参数
① C++中函数的形参列表里可以有占位参数,用来做占位,调用函数时必须填补该位置。
② 语法:返回值类型 函数名 (数据类型) {}
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
//占位参数
//返回值类型 函数名(数据类型){}
//目前,占位参数还用不到,后面会用到
void func01(int a,int)
{
cout << "this is func01" << endl; //函数内部无法调用第二个参数,无法像a+b这样调用第二个参数
}
//占位参数,还可以有默认参数
void func02(int a, int = 10)
{
cout << "this is func02" << endl;
}
int main()
{
func01(10, 20);
func02(10); //有默认参数,可以只输入一个参数
system("pause");
return 0;
}
运行结果:
- this is func01
- this is func02
- 请按任意键继续. . .
2. 函数重载
2.1 函数重载条件
① 作用:函数名可以相同,提高复用性。
② 函数重载满足条件:
- 同一个作用域下。
- 函数名称相同。
- 函数参数类型不同 或者 个数不同 或者 顺序不同。
③ 函数的返回值不可以作为函数重载的条件。
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
//函数重载
//可以让函数名相同,提高复用性
//函数重载的满足条件
//1、同一作用域下
//2、函数名称相同
//3、函数参数类型不同,或者个数不同,或者顺序不同
void func()
{
cout << "func 的调用" << endl;
}
void func(int a)
{
cout << "func (int a) 的调用" << endl;
}
void func(double a)
{
cout << "func (double a) 的调用" << endl;
}
void func(double a, int b)
{
cout << "func (double a, int b) 的调用" << endl;
}
void func(int a, double b)
{
cout << "func (int a, double b) 的调用" << endl;
}
/*
注意事项
函数的返回值不可以作为函数重载的条件
int func(int a, double b)
//调用func(3.14,3)时,编译器不知道是调用int func(int a, double b){}还是调用void func(int a, double b){}
{
cout << "func (int a, double b) 的调用" << endl;
}
*/
int main()
{
func(); // 根据传入参数的个数不同,调用不同的函数
func(10);
func(3.14); // 根据传入参数的类型不同,调用不同的函数
func(3,3.14); // 根据传入参数的顺序不同,调用不同的函数
func(3.14,3); // 根据传入参数的顺序不同,调用不同的函数
system("pause");
return 0;
}
运行结果:
- func 的调用
- func (int a) 的调用
- func (double a) 的调用
- func (int a, double b) 的调用
- func (double a, int b) 的调用
- 请按任意键继续. . .
2.2 函数重载注意事项
① 引用作为重载条件。
② 函数重载碰到函数默认参数。
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
//函数重载的注意事项
//1、引用作为重载的条件
void fun(int& a) // int &a = 10; 不合法,所以fun(10);无法调用
{
cout << "func(int &a)调用" << endl;
}
// const int &a = 10; 合法
void fun(const int& a) //语法是可以的,const引用和普通引用属于类型不同,fun(10)可以调用
{
cout << "func(const int &a)调用" << endl;
}
//2、函数重载碰到默认参数
void func2(int a,int b = 20)
{
cout << "func2(int a,int b = 20) 的调用" << endl;
}
void func2(int a)
{
cout << "func2(int a) 的调用" << endl;
}
int main()
{
int a = 10;
//变量可读可写,所以调用变量时,是调用可读可写的引用函数,const int a = 10的fun(a);调用func(const int &a)调用
fun(a);
fun(10);
//既可以调用void func2(int a,int b = 20),也可以调用void func2(int a)
//func2(10); //当函数重载碰到默认参数,出现二义性,报错,尽量避免这种情况
func2(10,20); //不会出现二义性
system("pause");
return 0;
}
运行结果:
- func(int &a)调用
- func(const int &a)调用
- func2(int a,int b = 20) 的调用
- 请按任意键继续. . .






















 99
99











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








