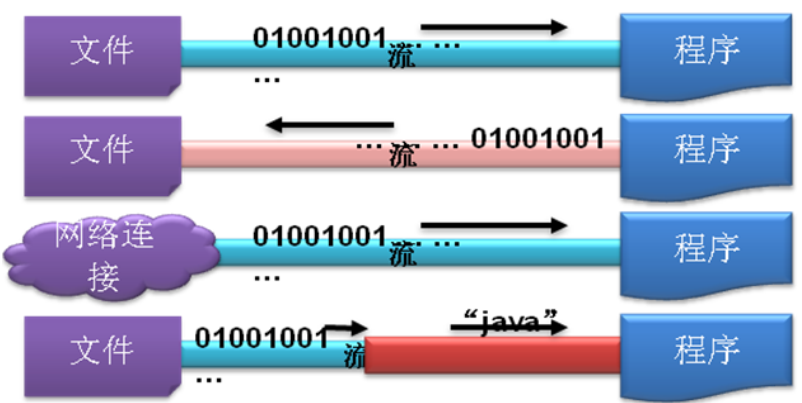
IO流
IO指的是Input/Output,IO流:输入输出流。 统称为数据流。(IO Stream)
在Java程序中,对于数据的输入 / 输出操作以流的方式进行;流是从起源到接收的有序数据。JDK提供了各种各样的流类,用以获取不同种类的数据;
流的作用
对文件进行读写操作
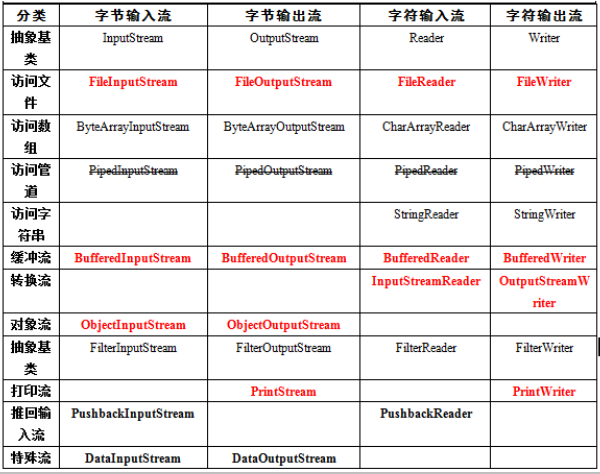
流的分类
按流向分
输入流
读取数据的流输出流
写入数据的流
按功能分
节点流
直接操作目标的流处理流
是对一个已存在的流的连接和封装,通过对数据的处理为程序提供更为强大、灵活的读写功能。
按数据传输单位分
字节流
以字节作为单位传输的流字符流
以字符作为单位传输的流
字节输入流
InputStream
常用子类:FileInputStream
InoutStreamDemo.java
public class InputStreamDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
File file = new File("f:/a.txt");
FileInputStream fis = null;
try {
fis = new FileInputStream(file);
int data = -1;
while ((data = fis.read()) != -1) {
System.out.print((char) data);
}
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if (fis != null) {
try {
fis.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
Demo2.java
public class Demo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// File file = new File("f:/a.txt");
File file = new File("src/com/rair/Demo2.java");
FileInputStream fis = null;
try {
fis = new FileInputStream(file);
byte[] buf = new byte[1024];
int len = -1;
while ((len = fis.read(buf)) != -1) {
String msg = new String(buf, 0, len);
System.out.println(msg);
}
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if (fis != null) {
try {
fis.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
字节输出流
OutputStream
常用子类:FileOutputStream
Demo3.java
public class Demo3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 文件不存在会自动创建,文件夹不存在无法自动创建,true表示后面追加,默认是覆盖写入
FileOutputStream fos = null;
try {
fos = new FileOutputStream("f:/a.txt", true);
fos.write(97);
byte[] buf = { 98, 99, 100 };
fos.write(buf);
String msg = "文件字节输出流";
byte[] bytes = msg.getBytes();// 字符转字节
fos.write(bytes);
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if (fos != null) {
try {
fos.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
混合使用实现文件复制:
public class CopyFile {
public static void main(String[] args) {
File file = new File("f:/a.txt");
File desDir = new File("c:/");
copyFile(file, desDir);
}
private static void copyFile(File file, File desDir) {
// jdk1.7新增自动关流;写在try()里
// try(FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(file);FileOutputStream
// fos = new FileOutputStream(new File(desDir,file.getName()));)
FileInputStream fis = null;
FileOutputStream fos = null;
try {
fis = new FileInputStream(file);
fos = new FileOutputStream(new File(desDir, file.getName()));
byte[] buf = new byte[1024];
int len = -1;
int count = 0;
while ((len = fis.read(buf)) != -1) {
fos.write(buf, 0, len);
count += len;
System.out.println("正在复制..." + count + "字节");
}
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
fis.close();
fos.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
字节缓冲流
缓冲流是建立在相应的节点流之上,对读写的数据提供了缓冲的功能,提高了读写的效率,还增加了一些新的方法。
字节缓冲分输入缓冲和输出缓冲。
1、 缓冲字节输入流:BufferedInputStream。BufferedInputStream 为另一个输入流添加一些功能,即缓冲输入以及支持 mark 和 reset 方法的能力。
2、 缓冲字节输出流:BufferedOutputStream。 输出字节时,先把要输出的字节输出到缓冲区,当手动调用flush()方法或者缓冲区满或者流关闭时才会把数据输出到结点流。
3、 字节缓冲输入流的缓冲区默认大写为8k字节。也可以指定缓冲区大小。
BufferedInputStream
复制一张图片
public class BufferredInputStreamDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
File file = new File("f:/img.png");
File dir = new File("c:/");
copyFile(file, dir);
}
private static void copyFile(File file, File dir) throws IOException {
BufferedInputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream(
file));
BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(
new FileOutputStream(new File(dir, file.getName())));
byte[] buf = new byte[16];
int len = -1;
int count = 0;
while ((len = bis.read(buf)) != -1) {
bos.write(buf, 0, len);
System.out.println(count += len);
}
bos.close();
}
}
BufferedOutputSteam
读一个TXT文件
public class BufferedDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("c:/a.txt"));
String line = null;
while ((line = reader.readLine()) != null) {
System.out.println(line);
}
reader.close();
}
}






















 2307
2307

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








