LinkedList的几大特点
- ArrayList是一个有序数组
- ArrayList线程不安全
- ArrayList可以存放空值
官网介绍,linkedList是一个双向链表
/**
* Doubly-linked list implementation of the {@code List} and {@code Deque}
* interfaces. Implements all optional list operations, and permits all
* elements (including {@code null}).
*/
public class LinkedList<E>
extends AbstractSequentialList<E>
implements List<E>, Deque<E>, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable{
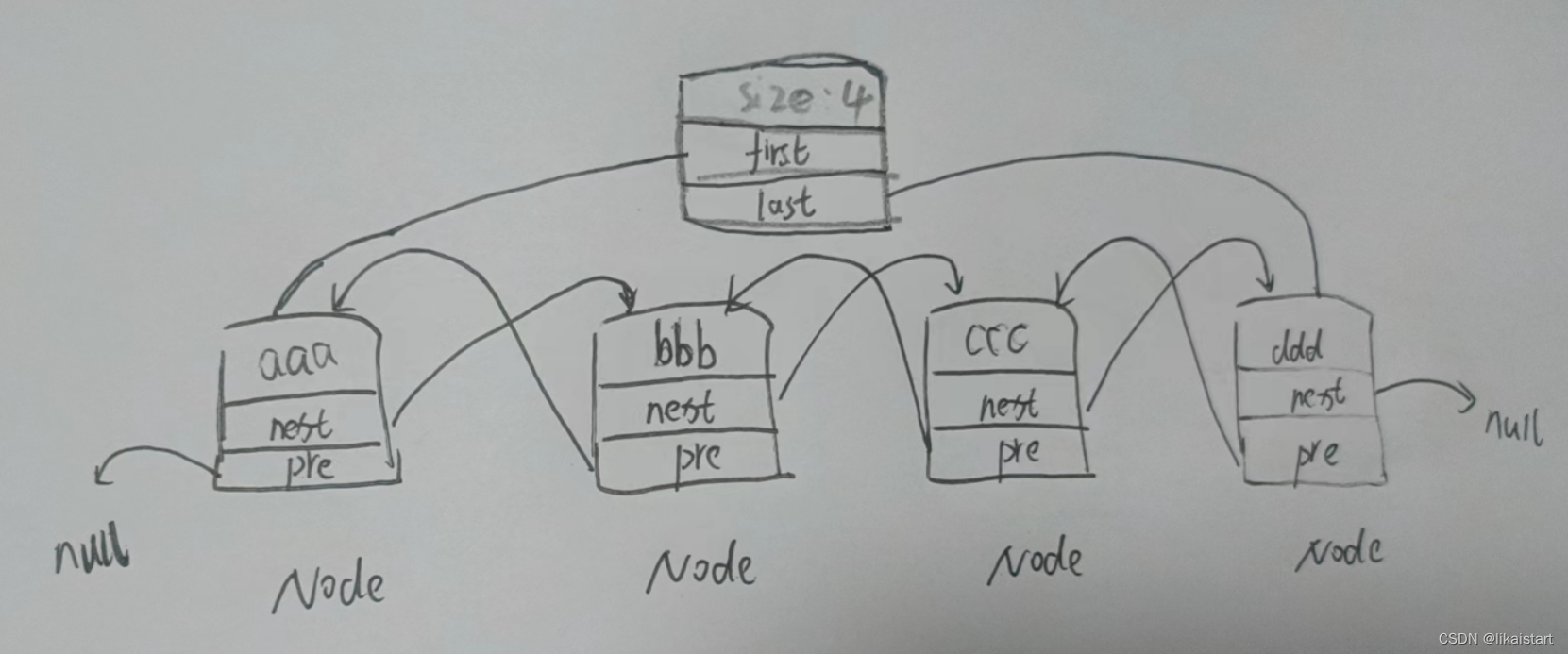
}大概结构如下图所示
transient int size = 0;
/**
* Pointer to first node.
* Invariant: (first == null && last == null) ||
* (first.prev == null && first.item != null)
*/
transient Node<E> first;
/**
* Pointer to last node.
* Invariant: (first == null && last == null) ||
* (last.next == null && last.item != null)
*/
transient Node<E> last;
//LinkedList每个节点对应的字段
private static class Node<E> {
E item;
Node<E> next;
Node<E> prev;
Node(Node<E> prev, E element, Node<E> next) {
this.item = element;
this.next = next;
this.prev = prev;
}
}
根据类元素以及节点构造函数,确定LinkedList结构(先熟悉LinkedList结构再看源码,能达到事半功倍效果)
添加操作源码分析
List<String> linkedList = new LinkedList<>();
linkedList.add("aaa");
linkedList.add("bbb");
linkedList.add("ccc");
linkedList.add("ddd");
添加元素ddd
- 首先校验pre链接
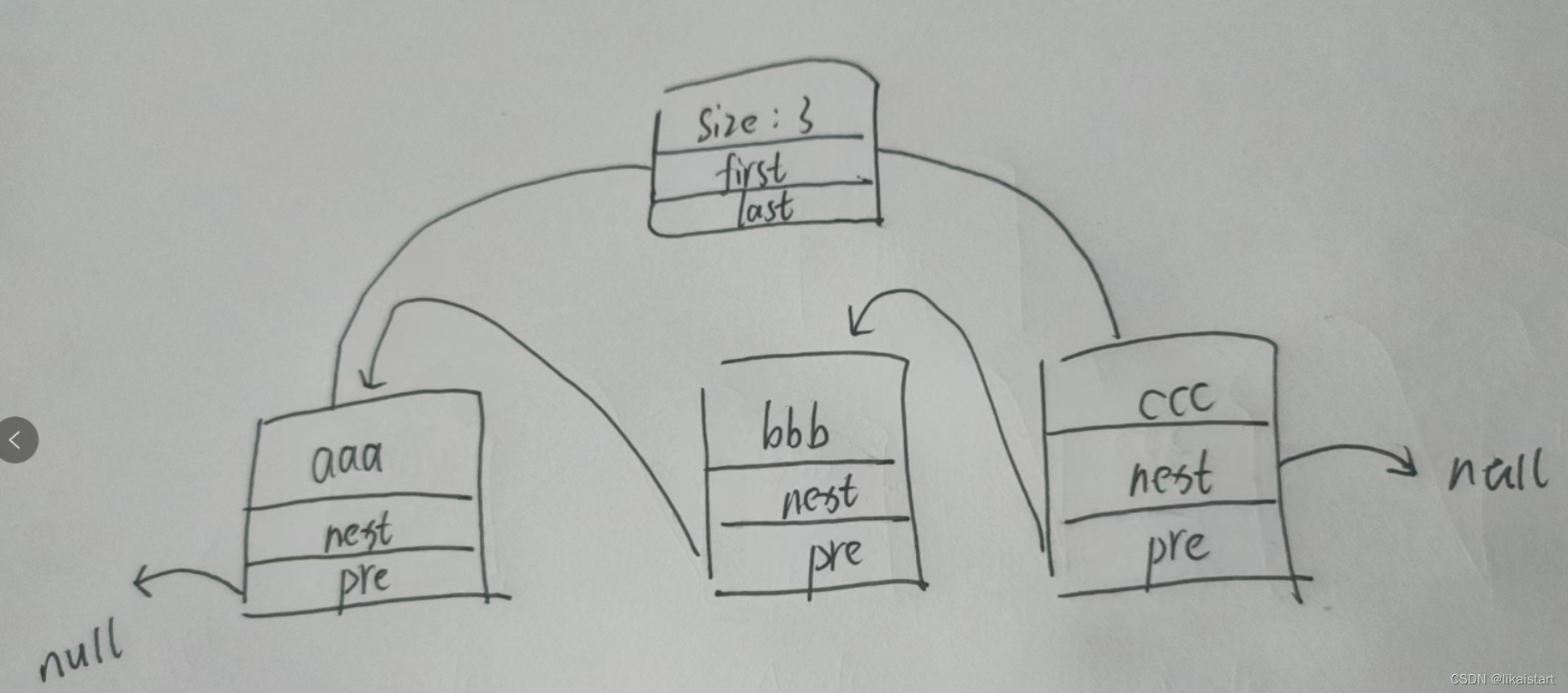
具体结构类似下图
- ccc所在节点,pre指向前bbb所在的节点;同理bbb所在的节点pre向前指向aaa所在的节点
- ccc所在的节点next指向null
- 继续校验next链接
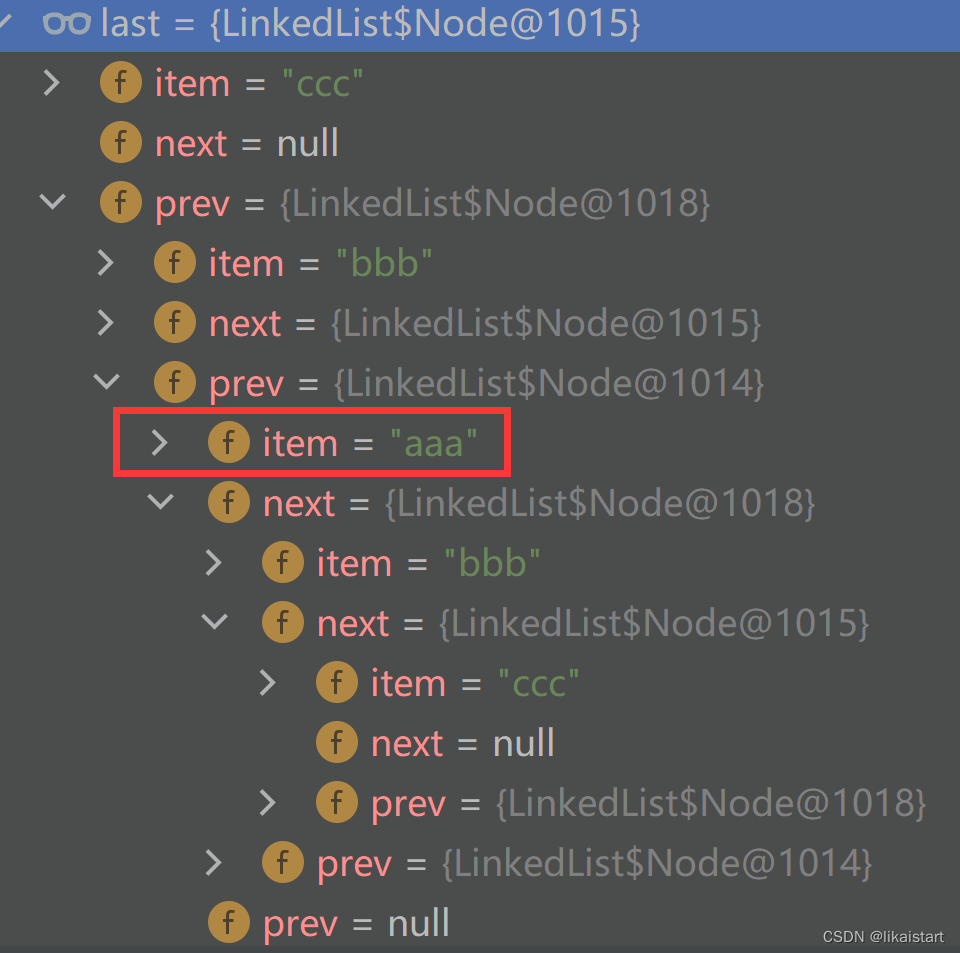
具体结构类似下图
- aaa所在节点,next指向后bbb所在的节点;同理bbb所在的节点next向后指向ccc所在的节点
- aaa所在的节点,pre指向空
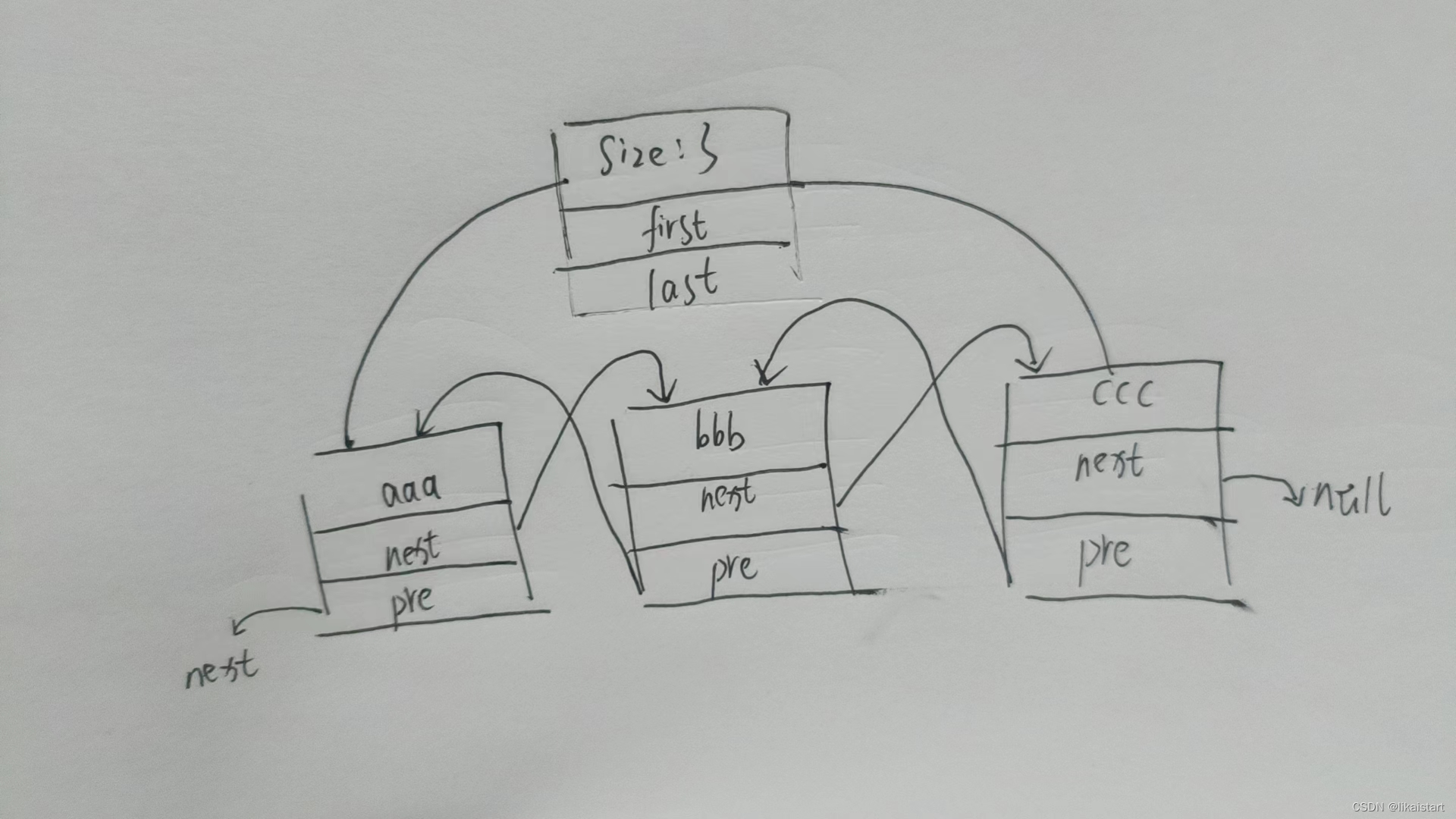
综上所述,linkedList大致数据结构与手工图相似
源码分析
/**
* Appends the specified element to the end of this list.
*
* <p>This method is equivalent to {@link #addLast}.
*
* @param e element to be appended to this list
* @return {@code true} (as specified by {@link Collection#add})
*/
public boolean add(E e) {
linkLast(e); //338
return true;
}
/**
* Links e as last element.
*/
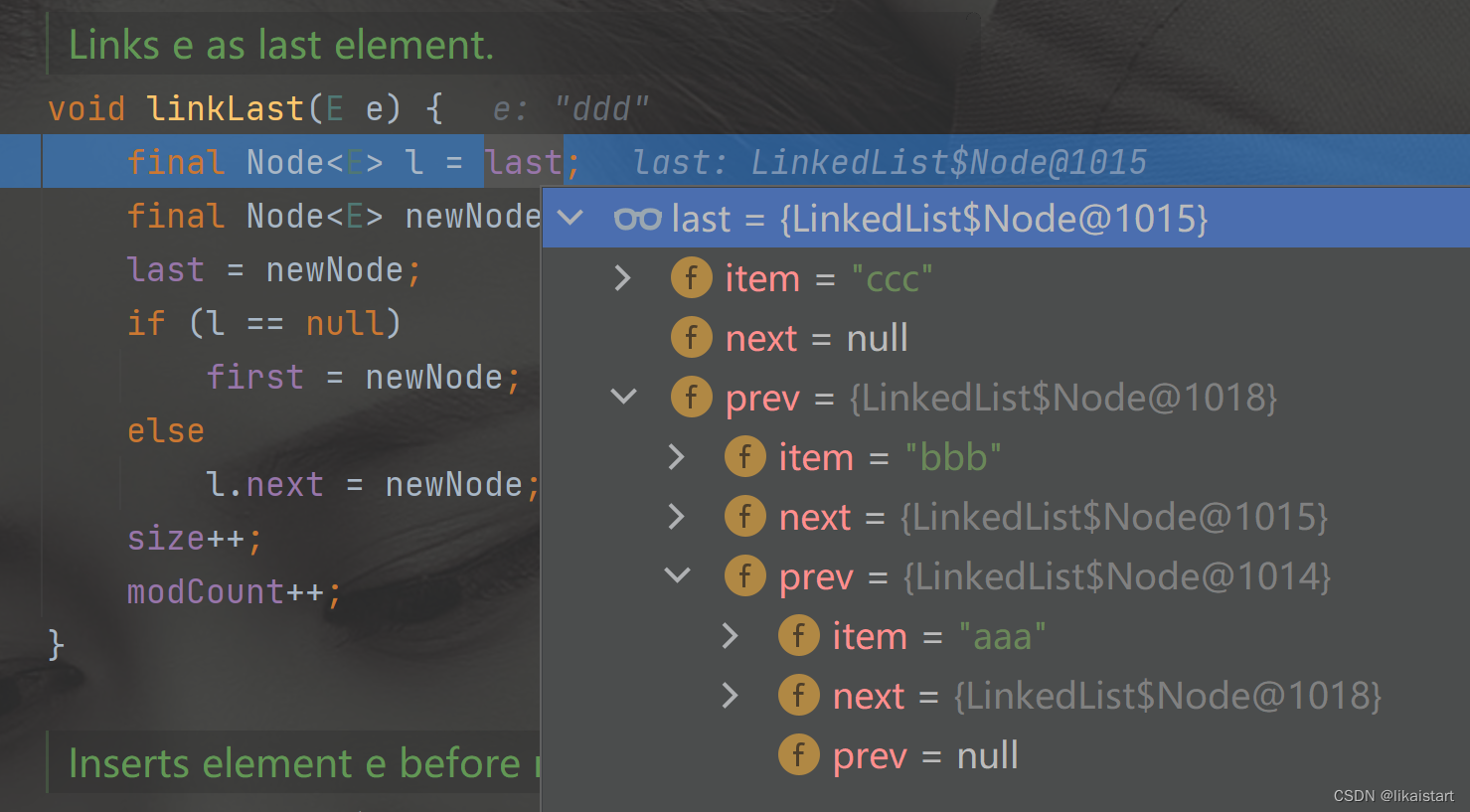
void linkLast(E e) {
final Node<E> l = last; //141
final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(l, e, null); //142
last = newNode; //143
if (l == null) //144
first = newNode; //145
else
l.next = newNode; //146
size++; //147
modCount++; //148
}- 步骤一
- 添加操作338行转linkLast方法
- 步骤二
- 141行,将新增前最后末尾元素 数据只给l,等待使用(说明:即将新增的元素追加到末尾,因此新增的元素的pre指向的就是当前l)
- 步骤三
- 142行,141行获得的值l,当做新元素的pre
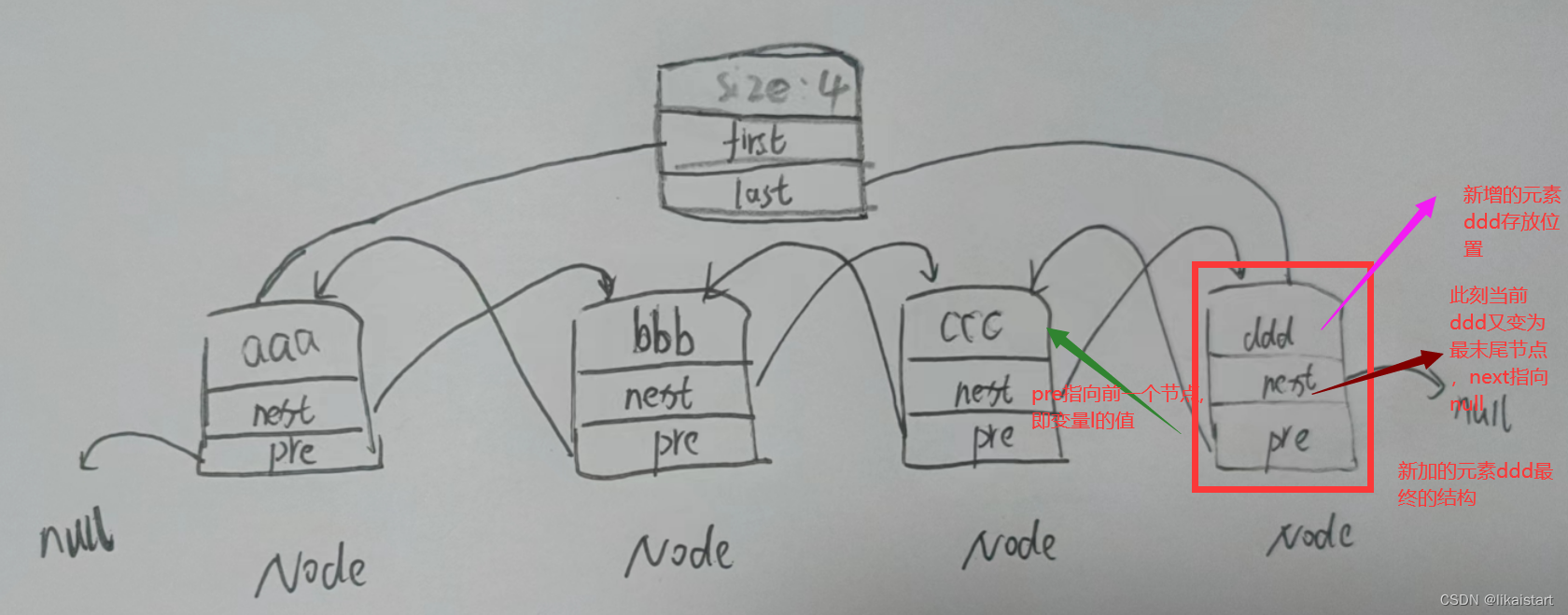
-
步骤四
-
此刻最末尾元素已经变为,ddd坐在的节点 需要更新last
-
-
步骤五
-
145行,如果是首次添加元素需要走145
-
-
步骤六
-
非首次增加元素,新增加的元素是由ccc替换的,ccc的next之前是指向null,此刻已经指向ddd所在的节点,即ccc.next指向新节点
-
-
步骤七
-
前6个步骤结束,元素ddd已经成功加到集合中了,集合长度自增1,且当前数据结构变化自增1
-
查询操作源码分析
/**
* Returns the element at the specified position in this list.
*
* @param index index of the element to return
* @return the element at the specified position in this list
* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc}
*/
public E get(int index) {
checkElementIndex(index); //476
return node(index).item; //477
}
/**
* Returns the (non-null) Node at the specified element index.
*/
Node<E> node(int index) { //566
// assert isElementIndex(index); //567
if (index < (size >> 1)) { //569
Node<E> x = first; //570
for (int i = 0; i < index; i++) //571
x = x.next; //572
return x; //573
} else { //574
Node<E> x = last; //575
for (int i = size - 1; i > index; i--) //576
x = x.prev; //577
return x; //578
}
}
- 步骤一
- 476行校验元素有没有越界
- 步骤二
- 477行跳转到方法node(int index)
- 步骤三
- 569行如果查询的index小于总长度的一半(奇数向下取整),从头开始查找
- 否则从,末尾开始查找
修改操作源码分析
/**
* Replaces the element at the specified position in this list with the
* specified element.
*
* @param index index of the element to replace
* @param element element to be stored at the specified position
* @return the element previously at the specified position
* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc}
*/
public E set(int index, E element) {
checkElementIndex(index); //490
Node<E> x = node(index); //491
E oldVal = x.item; //492
x.item = element; //493
return oldVal; //494
}- 步骤一 490行,校验待修改的数组元素有没有越界
- 步骤二 491行,获取到原待删除的 节点(具体看查询源码分析)
- 步骤三 根据Node<E>内部类可知,具体元素保存在item字段上,以此将element赋值到节点x的item上
- 步骤四 返回旧数据
删除操作源码分析
linkedList.add("aaa");
linkedList.add("bbb");
linkedList.add("ccc");
linkedList.add("bbb");
linkedList.remove("bbb");
linkedList.remove(1);
log.info("打印日志:{}", JSONObject.toJSON(linkedList));
LinkedList支持两种方式的删除,通过索引删除以及通过待删除的元素值进行删除
/**
* 根据元素值删除
*/
public boolean remove(Object o) {
if (o == null) { //356
for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; x = x.next) { //357
if (x.item == null) { //358
unlink(x); //359
return true; //360
}
}
} else {
for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; x = x.next) { //364
if (o.equals(x.item)) { //365
unlink(x); //366
return true; //367
}
}
}
return false; //371
}
/**
* 根据索引删除
*/
public E remove(int index) { //524
checkElementIndex(index); //525
return unlink(node(index)); //526
} /**
* Unlinks non-null node x.
*/
E unlink(Node<E> x) {
// assert x != null; //210
final E element = x.item; //211
final Node<E> next = x.next; //212
final Node<E> prev = x.prev; //213
if (prev == null) { //215
first = next; //216
} else { //217
prev.next = next; //218
x.prev = null; //219
}
if (next == null) { //222
last = prev; //223
} else { //224
next.prev = prev; //225
x.next = null; //226
}
x.item = null; //229
size--; //230
modCount++; //231
return element; //232
}根据元素删除
- 步骤一(图一)
- 356行,若删除的元素为null,遍历集合,查找有没有等于null的元素,若存在调用unlink(x)进行删除操作
- 364行,若删除的元素不为null,查找有没有与待删除元素相等的值,若存在调用unlink(x)进行删除操作
- 步骤二(图二)
- 针对相关的三个数组进行操作
- 待删除的数组x
- 后一个数组next
- 以及前一个数组prev
- 215行---219行
- 将前一个节点next与后一个节点进行关联,即aaa.next与ccc节点做关联
- 将当前节点的prev指向null,即bbb.prev=null
- 222行---226行
- 将后一个节点prev与前一个节点进行关联,即ccc.pre与aaa节点做关联
- 将当前节点的next指向null,即bbb.next=null
- 针对相关的三个数组进行操作
- 步骤三
- 229行,将节点值也改为null,此刻节点bbb等待GC
- 步骤四
- size自减1,modCount自增1,返回要删除的元素值
根据索引删除
- 步骤一:525行校验有没有越界
- 步骤二:526行node(index)首先是根据索引找到对应的节点
- 步骤三:执行删除操作





















 212
212











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








