第2章 不要小瞧数组
2-1 数组基础

创建数组以及访问、修改数组元素
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = new int[10];
for(int i = 0 ; i < arr.length ; i ++)
arr[i] = i;
int[] scores = new int[]{100, 99, 66};
for(int i = 0 ; i < scores.length ; i ++)
System.out.println(scores[i]);
for(int score: scores)
System.out.println(score);
scores[0] = 96;
for(int i = 0 ; i < scores.length ; i ++)
System.out.println(scores[i]);
}
}
- 数组最大的优点:快速查询,如:scores[2]
-数组最好应用于“索引有语意”的情况 - 并非所有有语意的索引都适用于数组
- 身份证号
- 数组也可以处理索引没有语意的情况
- 我们大部分情况都是处理索引没有语意的情况
2-2 制作属于我们自己的数组类
- 索引没有语意,如何表示没有元素?
- 如何添加元素?如何删除元素?
基于Java的数组,二次封装我们自己的数组类
Java的数组是静态的,我们自己制作的数组是动态的

我们自己制作的数组类名称为Array,在这个类中封装一个Java的数组名为data,其中capacity为数组的最大容量,size表示数组实际的大小(也表示数组中第一个没有元素的位置)。两个属性都设置为私有的,防止用户自己修改。
public class Array {
private int[] data;
private int size;
// 构造函数,传入数组的容量capacity构造Array
public Array(int capacity){
data = new int[capacity];
size = 0;
}
// 无参数的构造函数,默认数组的容量capacity=10
public Array(){
this(10);
}
// 获取数组的容量
public int getCapacity(){
return data.length;
}
// 获取数组中的元素个数
public int getSize(){
return size;
}
// 返回数组是否为空
public boolean isEmpty(){
return size == 0;
}
}
2-3 向数组中添加元素
添加元素的思路主要为:先将要添加的元素的位置之后的元素全部向后移动一个单位(从最后的元素移动,否则会修改原数组中的值),再将数组长度加1。
// 向所有元素后添加一个新元素
public void addLast(int e){
add(size, e);
}
// 在所有元素前添加一个新元素
public void addFirst(int e){
add(0, e);
}
// 在index索引的位置插入一个新元素e
public void add(int index, int e){
if(size == data.length)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Add failed. Array is full.");
if(index < 0 || index > size)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Add failed. Require index >= 0 and index <= size.");
for(int i = size - 1; i >= index ; i --)
data[i + 1] = data[i];
data[index] = e;
size ++;
}
2-3数组中查询和修改元素
保证要查找的元素的索引值合理即可。
// 获取index索引位置的元素
public int get(int index){
if(index < 0 || index >= size)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Get failed. Index is illegal.");
return data[index];
}
// 修改index索引位置的元素为e
public void set(int index, int e){
if(index < 0 || index >= size)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Set failed. Index is illegal.");
data[index] = e;
}
2-4 包含、搜索和删除
需要注意的是删除指定的元素时,所实现的方法只删除了一个指定元素,如果数组中存在多个相同元素的也是如此,可以针对这个问题进行优化(如删除所有的指定元素),这个问题其实也反映了我们之前写的find()方法存在的问题(可以根据这个设计一个findAll()方法)。
// 从数组中删除index位置的元素, 返回删除的元素
public int remove(int index){
if(index < 0 || index >= size)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Remove failed. Index is illegal.");
int ret = data[index];
for(int i = index + 1 ; i < size ; i ++)
data[i - 1] = data[i];
size --;
return ret;
}
// 从数组中删除第一个元素, 返回删除的元素
public int removeFirst(){
return remove(0);
}
// 从数组中删除最后一个元素, 返回删除的元素
public int removeLast(){
return remove(size - 1);
}
// 从数组中删除元素e
public void removeElement(int e){
int index = find(e);
if(index != -1)
remove(index);
}
2-6 使用泛型
让我们的数据结构可以存放“任意”类型(包括用户自定义)的数据
- Java中的泛型不可以是基本数据类型,只能是类对象
boolean、byte、char、short、int、long、float、double - 每个基本数据类型都有对应的包装类
Boolean、Byte、Char、Short、Int、Long、Float、Double - 自动装箱、拆箱
注意改造代码时几个问题:
- 在原来的构造方法中由于Java不支持通过new关键字来实例化泛型数组,所以在使用泛型实例数组时需要先实例出一个Object数组再强制转换为泛型类型的数组
- 在使用改造完后的Array类时,在实例化数组时需要指定数组类型
(如Array arr = new Array<>(20);)
public class Array<E> {
private E[] data;
private int size;
// 构造函数,传入数组的容量capacity构造Array
public Array(int capacity){
data = (E[])new Object[capacity];//注意这里Java不支持直接new一个泛型数组
size = 0;
}
// 无参数的构造函数,默认数组的容量capacity=10
public Array(){
this(10);
}
// 获取数组的容量
public int getCapacity(){
return data.length;
}
// 获取数组中的元素个数
public int getSize(){
return size;
}
// 返回数组是否为空
public boolean isEmpty(){
return size == 0;
}
// 在index索引的位置插入一个新元素e
public void add(int index, E e){
if(size == data.length)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Add failed. Array is full.");
if(index < 0 || index > size)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Add failed. Require index >= 0 and index <= size.");
for(int i = size - 1; i >= index ; i --)
data[i + 1] = data[i];
data[index] = e;
size ++;
}
// 向所有元素后添加一个新元素
public void addLast(E e){
add(size, e);
}
// 在所有元素前添加一个新元素
public void addFirst(E e){
add(0, e);
}
// 获取index索引位置的元素
public E get(int index){
if(index < 0 || index >= size)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Get failed. Index is illegal.");
return data[index];
}
// 修改index索引位置的元素为e
public void set(int index, E e){
if(index < 0 || index >= size)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Set failed. Index is illegal.");
data[index] = e;
}
// 查找数组中是否有元素e
public boolean contains(E e){
for(int i = 0 ; i < size ; i ++){
if(data[i].equals(e))
return true;
}
return false;
}
// 查找数组中元素e所在的索引,如果不存在元素e,则返回-1
public int find(E e){
for(int i = 0 ; i < size ; i ++){
if(data[i].equals(e))
return i;
}
return -1;
}
// 从数组中删除index位置的元素, 返回删除的元素
public E remove(int index){
if(index < 0 || index >= size)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Remove failed. Index is illegal.");
E ret = data[index];
for(int i = index + 1 ; i < size ; i ++)
data[i - 1] = data[i];
size --;
data[size] = null; // loitering objects != memory leak
return ret;
}
// 从数组中删除第一个元素, 返回删除的元素
public E removeFirst(){
return remove(0);
}
// 从数组中删除最后一个元素, 返回删除的元素
public E removeLast(){
return remove(size - 1);
}
// 从数组中删除元素e
public void removeElement(E e){
int index = find(e);
if(index != -1)
remove(index);
}
@Override
public String toString(){
StringBuilder res = new StringBuilder();
res.append(String.format("Array: size = %d , capacity = %d\n", size, data.length));
res.append('[');
for(int i = 0 ; i < size ; i ++){
res.append(data[i]);
if(i != size - 1)
res.append(", ");
}
res.append(']');
return res.toString();
}
}
2-7 动态数组
扩容方法:实例出一个新数组,将原数组中的每一个元素依次放入新数组中,再替换原数组。
// 将数组空间的容量变成newCapacity大小
private void resize(int newCapacity){
E[] newData = (E[])new Object[newCapacity];
for(int i = 0 ; i < size ; i ++)
newData[i] = data[i];
data = newData;
}
在插入元素时判断如果这个数组满了就扩容,给出的代码是扩充为当前数组元素个数的二倍,Java中ArrayList扩充为1.5倍。
- 扩容大小与元素个数有关,有助于提高动态数组的效率
//修改add()方法中的判断语句
if(size == data.length)
resize(2 * data.length);
对于删除元素的操作也可以根据删除后的元素个数缩小数组
//修改remove()方法中的判断语句
if(size == data.length / 2)
resize(data.length / 2);
2-8 简单的复杂度分析
- O(1),O(n),O(logn),O(nlogn),O(n^2)
- 大O描述的是算法的运行时间和输入数据之间的关系
- 渐进时间复杂度,描述的是n趋近于无穷的情况

| 方法 | 时间复杂度 |
|---|---|
| addLast(e) | O(1) |
| addFirst(e) | O(n) |
| add(index, e) | O(n/2)=O(n) |
| removeLast(e) | O(1) |
| removeFirst(e) | O(n) |
| remove(index, e) | O(n/2)=O(n) |
| set(index, e) | O(1) |
| get(index) | O(1) |
| contains(e) | O(n) |
| find(e) | O(n) |
总结
| 操作名 | 时间复杂度 |
|---|---|
| 增 | O(n) |
| 删 | O(n) |
| 改 | 已知索引O(1); 未知索引O(n) |
| 查 | 已知索引O(1); 未知索引O(n) |
2-9 均摊复杂度和防止复杂度的震荡
-
均摊复杂度
resize() O(n)
假设当前capacity = 8, 并且每一次添加操作都使用addLast
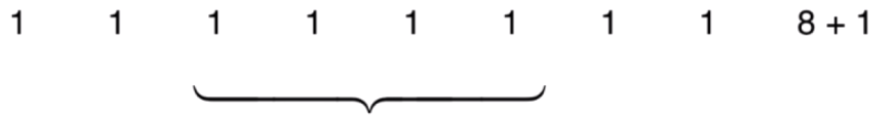
9次addLast操作,触发resize,总共进行了17此基本操作
平均,每次addLast操作进行2次基本操作
推广:
假设capacity = n, n+1次addLast,触发resize,总共进行2n+1次基本操作
平均,每次addLast操作进行2次基本操作
这样均摊计算,时间复杂度为O(1)
在这个例子中,这样均摊计算比计算最坏情况有意义。
同理,removeLast操作,均摊复杂度也为O(1) -
复杂度震荡
当我们同时看addLast和removeLast操作:假如添加元素时正好需要resize但添加完后立即进行删除操作又执行了一次resize,这时均摊复杂度为O(n)- 出现问题的原因:removeLast时resize过于着急(Eager)
- 解决方案:Lazy
当size == capacity /4 时,才将capacity 减半
//修改remove方法
if(size == data.length / 4 && data.length / 2 != 0)





















 7454
7454











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








