Spring boot实现基于注解的aop面向切面编程
背景
从最开始使用Spring,AOP和IOC的理念就深入我心。正好,我需要写一个基于注解的AOP,被这个注解修饰的参数和属性,就会被拿到参数并校验参数。
一,引入依赖
当前spring boot版本为2.7.18,我引入的aspectjweaver版本为1.9.5。
<dependency>
<groupId>org.aspectj</groupId>
<artifactId>aspectjweaver</artifactId>
<version>1.9.5</version>
</dependency>
二,写注解
这个注解用来修饰方法,相当于一个切点,加上这个注解,这个方法就被被aop执行。
@Target({ElementType.METHOD})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface ParamInterceptor {
boolean checkParam() default true;
}
这个注解是用来修饰参数和属性的。被修饰的参数和属性在aop中会通过反射取出数据并判断
@Target({ElementType.PARAMETER, ElementType.FIELD})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface VerifyParam {
int min() default -1;
int max() default -1;
boolean required() default false;
VerifyRegexEnum regex() default VerifyRegexEnum.NO;
}
这个是用到的VerifyRegexEnum 枚举类
@AllArgsConstructor
@Getter
public enum VerifyRegexEnum {
NO("", "不校验"),
IP("^((25[0-5]|2[0-4]\\d|1\\d\\d|[1-9]?\\d)(\\.(25[0-5]|2[0-4]\\d|1\\d\\d|[1-9]?\\d)){3})$", "ip地址"),
POSITIVE_INTEGER("^\\d+$", "正整数"),
NUMBER_LETTER_UNDER_LINE("\\w+$", "数字字母下划线"),
PHONE("^1[3-9]\\d{9}$", "手机号"),
EMAIL("^\\w+([-+.]\\w+)*@\\w+([-.]\\w+)*\\.\\w+([-.]\\w+)*$", "邮箱"),
ID_CARD("^\\d{17}(\\d|x|X)$", "身份证"),
PASSWORD("^[a-zA-Z0-9]{6,20}$", "密码"),
MONEY("^\\d+(\\.\\d+)?$", "金额"),
;
private String regex;
private String desc;
public static boolean isMatch(String regex, String str) {
return str.matches(regex);
}
}
三,编写切面aspect
该切面类就实现了,对参数和属性的校验。
@Aspect
@Component
@Slf4j
public class CdesAspect {
@Before("@annotation(com.cdes.annotation.ParamInterceptor)")
public void before(JoinPoint point) {
Object[] args = point.getArgs();
Method method = ((MethodSignature) point.getSignature()).getMethod();
log.info("参数校验,方法名:{}",method.getName());
ParamInterceptor paramInterceptor = method.getAnnotation(ParamInterceptor.class);
if (paramInterceptor == null ) {
return;
}
if(!paramInterceptor.checkParam()){
return;
}
try{
checkParam(method,args);
}catch (BizException e){
throw new BizException("400",e.getErrorMsg());
}catch (Exception e){
throw new BizException("400",e.getMessage());
}
}
private void checkParam(Method method, Object[] args) throws IllegalAccessException {
Parameter[] parameters = method.getParameters();
for (int i = 0; i < parameters.length; i++) {
Parameter parameter = parameters[i];
Object paramValue = args[i];
VerifyParam paramAnnotation = parameter.getAnnotation(VerifyParam.class);
//取方法参数上的注解,如果有,则校验参数,如果没有,取该参数的属性,看是否有该注解
if (paramAnnotation != null) {
if(paramAnnotation.required() && paramValue == null){
throw new BizException( "400",parameter.getName()+":参数不能为空");
}
if(paramAnnotation.max() != -1){
if (paramValue.toString().length() > paramAnnotation.max()) {
throw new BizException( "400",parameter.getName()+":参数长度不能超过"+paramAnnotation.max());
}
}
if(paramAnnotation.min() != -1){
if (paramValue.toString().length() < paramAnnotation.min()) {
throw new BizException( "400",parameter.getName()+":参数长度不能小于"+paramAnnotation.min());
}
}
if(paramAnnotation.regex() != null && paramAnnotation.regex() != VerifyRegexEnum.NO){
if(!VerifyRegexEnum.isMatch(paramAnnotation.regex().getRegex(),paramValue.toString())){
throw new BizException( "400",parameter.getName()+":参数不符合正则表达式");
}
}
}else{
//取属性上的注解,看是否需要校验
Field[] fields = paramValue.getClass().getDeclaredFields();
if(fields == null || fields.length == 0){
continue;
}
for (Field field : fields) {
field.setAccessible(true);
VerifyParam ann = field.getAnnotation(VerifyParam.class);
if(ann == null){
continue;
}
Object filedValue = field.get(paramValue);
if(ann.required() && filedValue == null){
throw new BizException( "400",field.getName()+":属性不能为空");
}
if(ann.max() != -1){
if (filedValue.toString().length() > ann.max()) {
throw new BizException( "400",field.getName()+":属性长度不能超过"+ann.max());
}
}
if(ann.min() != -1){
if (filedValue.toString().length() < ann.min()) {
throw new BizException( "400",field.getName()+":属性长度不能小于"+ann.min());
}
}
if(ann.regex() != null && ann.regex() != VerifyRegexEnum.NO){
if(!VerifyRegexEnum.isMatch(ann.regex().getRegex(),filedValue.toString())){
throw new BizException( "400",field.getName()+":属性不符合正则表达式");
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
四,使用
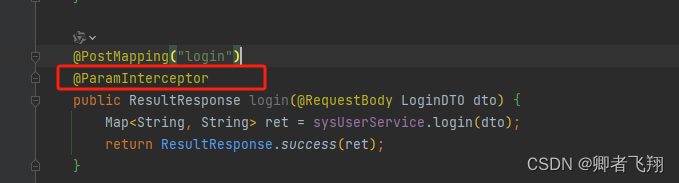
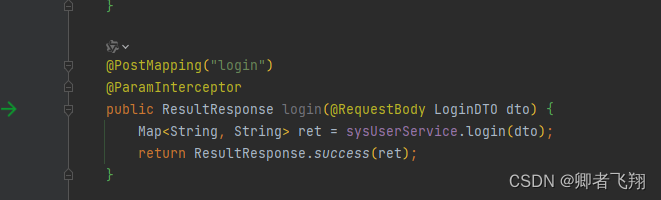
controller中的login方法加上了ParamInterceptor注解,然后这个方法的入参LoginDTO中的属性加上了VerifyParam注解
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
public class LoginDTO {
@VerifyParam(regex = VerifyRegexEnum.PHONE)
private String phone;
@VerifyParam(regex = VerifyRegexEnum.PASSWORD)
private String password;
@VerifyParam(required = true)
private String verifyCode;
@VerifyParam(required = true)
private String codeId;
}
总结
经过测试,校验参数功能正常。可以看到,spring boot的aop功能使用起来还是相当简单的。






















 8400
8400

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








