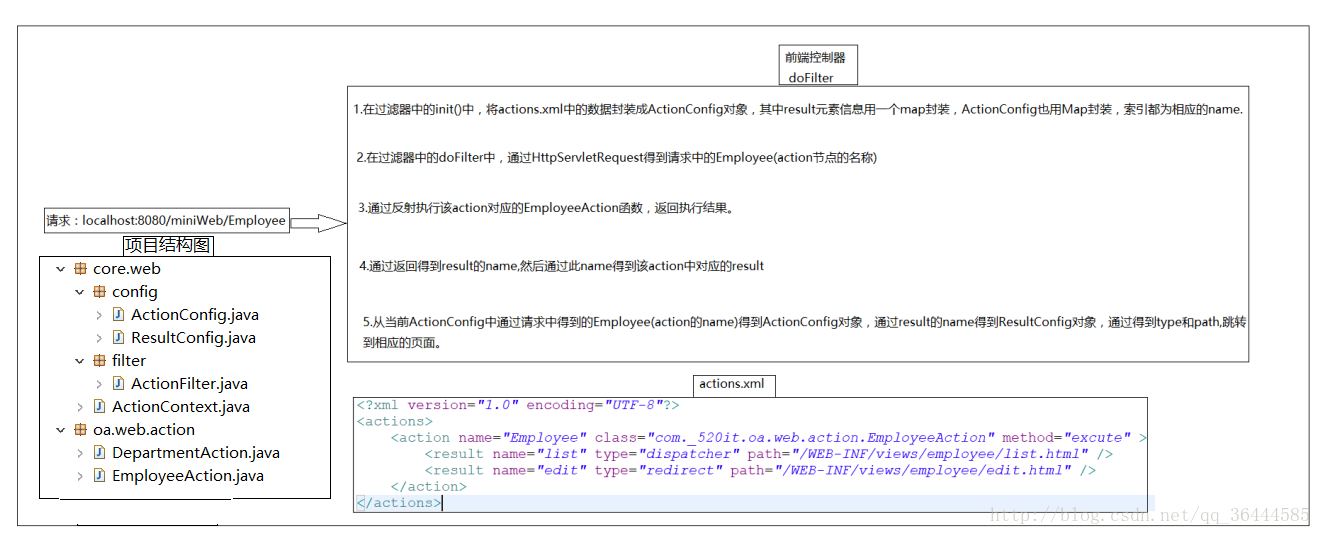
miniMVC流程和项目结构:
1:创建oa.web.action包,并在其中编写两个对象的action,如:EmployeeAction和DepartmentAction:
package com._520it.oa.web.action;
public class EmployeeAction {
public void excute(){
System.out.println("员工的列表");
}
}
package com._520it.oa.web.action;
public class DepartmentAction {
public void excute(){
System.out.println("部门列表");
}
}2.1:在源文件夹resources中编写actions.xml文件,为action节点配置name,class,method属性,代表每次请求时需要执行的对象方法:
<!-- actions.xml -->
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<actions>
<action name="Employee" class="com._520it.oa.web.action.EmployeeAction" method="excute" />
<action name="Department" class="com._520it.oa.web.action.DepartmentAction" method="excute" />
</actions>
2.2:在包web.core.config中编写ActionConfig类,用来封装每一个actions.xml中action节点的信息(以后只需在actions.xml中添加action节点即可):
package com._520it.core.web.config;
//使用lombok完成get/set/toString
@Data
public class ActionConfig {
private String name;
private String className;
private String method;
public ActionConfig(String name, String className, String method) {
this.name = name;
this.className = className;
this.method = method;
}
}
2.3:在包filter中编写处理请求的过滤器:
//1.解析actions.xml文件,将actions.xml中的action节点封装成对象,在过滤器中的init中封装成ActionConfigMap
//2.在doFilter中根据请求中的信息,取出ActionConfigMap中的ActionConfig对象,利用反射创建对象并执行函数
package com._520it.core.web.filter;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import javax.servlet.Filter;
import javax.servlet.FilterChain;
import javax.servlet.FilterConfig;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.ServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.ServletResponse;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import javax.xml.parsers.DocumentBuilder;
import javax.xml.parsers.DocumentBuilderFactory;
import org.w3c.dom.Document;
import org.w3c.dom.Element;
import org.w3c.dom.NodeList;
import com._520it.core.web.config.ActionConfig;
/**
* @author lq
*
*/
@SuppressWarnings("all")
public class ActionFilter implements Filter {
//将action对象的配置信息封装成对象,并装在Map中,获取时方便用请求名索引
private Map<String, Object> actionConfigMap = new HashMap<>();
public void init(FilterConfig filterConfig) throws ServletException {
//1.获取文档对象
Document doc = getDocument();
//2.获取文档中所有action节点的节点集合
NodeList nodeList = doc.getElementsByTagName("action");
for (int i = 0; i < nodeList.getLength(); i++) {
//3.获取每个节点中的属性信息,并封装成配置对象
Element actionEl = (Element) nodeList.item(i);
String actionName = actionEl.getAttribute("name");
String actionClassName = actionEl.getAttribute("class");
String actionMethod = actionEl.getAttribute("method");
//4.创建配置文件对象,并放入配置文件对象映射中
ActionConfig actionConfig = new ActionConfig(actionName, actionClassName, actionMethod);
actionConfigMap.put(actionName, actionConfig);
}
}
public void doFilter(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response,
FilterChain chain) throws IOException, ServletException {
try {
//1.在过滤器中对请求和相应对象强强转成Http类型,方便处理Http请求相关操作
HttpServletRequest req = (HttpServletRequest) request;
HttpServletResponse resp = (HttpServletResponse) response;
//2.得到请求中的最后一个/请求的名称
String requestUri = req.getRequestURI();
String actionName = requestUri.substring(requestUri
.lastIndexOf("/") + 1);
//3.判断配置对象映射中是否含有当前请求的信息
if (!actionConfigMap.containsKey(actionName)) {
chain.doFilter(req, resp);
}
//4.获取当前请求操作的配置对象
ActionConfig actionConfig = (ActionConfig) actionConfigMap.get(actionName);
//5.通过反射执行请求对象中的函数
Class clz = Class.forName(actionConfig.getClassName());
Object actionObj = clz.newInstance();
Method method = clz.getMethod(actionConfig.getMethod());
method.invoke(actionObj);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public void destroy() {
}
//返回文档对象
public Document getDocument() {
DocumentBuilderFactory db = DocumentBuilderFactory.newInstance();
try {
DocumentBuilder builder = db.newDocumentBuilder();
return builder.parse(Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader()
.getResourceAsStream("actions.xml"));
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
throw new RuntimeException("解析action.xml文件失败!");
}
}
3.1:如何在对象Action中得到请求中的参数信息,写一个函数ActionContext,用来封装HttpServletRequest和HttpServletResponse:
//1.含HttpServletRequest和HttpServletResponse参数的构造器,方便构造函数。
//2.既然有了这个构造器,已上两个参数就不需要setter方法了。
//3.设置一个静态私有的ActionContext对象:
静态目的就是方便该类的静态方法getContext()能调用它,
私有目的:其他类不能直接调用该变量
package com._520it.core.web;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
public class ActionContext {
private HttpServletRequest req;
private HttpServletResponse resp;
//虽然此变量是静态的,但是是私有的,和getContext的static不重复
private static ActionContext mContext;
public ActionContext(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) {
this.req = req;
this.resp = resp;
}
public static void setContext(ActionContext context){
mContext = context;
}
public static ActionContext getContext(){
return mContext;
}
//因为构造器中已经有传req和resp得ActionContext对象,此处创建get即可
public HttpServletRequest getReq() {
return req;
}
public HttpServletResponse getResp() {
return resp;
}
}3.2:在过滤器中,将当前的环境变量存储到ActionContext对象中,方便在其他对象中操作请求的信息:
ActionContext context = new ActionContext(req, resp);
context.setContext(context);3.3:在对象Action中调用ActionContext对象,以得到请求中的参数信息:
public class EmployeeAction {
public void excute(){
System.out.println("员工的列表");
ActionContext context = ActionContext.getContext();
String username = context.getReq().getParameter("username");
System.out.println("username=" + username);
}
}
4.但此时在对象ActionContext中有线程不安全情况:
public class EmployeeAction {
public void excute(){
System.out.println("员工的列表");
try {
Thread.sleep(8000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
ActionContext context = ActionContext.getContext();
String username = context.getReq().getParameter("username");
System.out.println("username=" + username);
}
}
4.1:问题:最后一次请求中的参数值会覆盖前面请求中的参数,主要原因是ActionContext中每次请求使用的是同一个该类中的ActionContext对象成员变量
4.2:解决:
为容易发生线程不安全的变量使用ThreadLocal,ThreadLocal又称为“线程局部变量”,它为每一个使用该变量的线程都提供一个变量值的副本,使每一个线程都可以独立地改变自己的副本,而不会和其他线程的副本冲突(好比每一个线程都使用的是一个新的变量),相应ActionContext的变化:
private static ThreadLocal<ActionContext> threadLocal = new ThreadLocal<>();
public static void setContext(ActionContext context){
threadLocal.set(context);
}
public static ActionContext getContext(){
return threadLocal.get();
}
5.在执行完action对象中的函数后跳转到一个页面中:
5.1:在actions.xml中的action节点展开并配置result节点,包含name,type,path,页面名字,请求类型,路径:
<actions>
<action name="Employee" class="com._520it.oa.web.action.EmployeeAction" method="excute" >
<result name="list" type="dispatcher" path="/WEB-INF/views/employee/list.html" />
<result name="edit" type="redirect" path="/WEB-INF/views/employee/edit.html" />
</action>
</actions>5.2:在core.web.config中创建ResultConfig对象,封装result节点的属性信息:
package com._520it.core.web.config;
@Data
public class ResultConfig {
private String name;
private String type;
private String path;
public ResultConfig(String name, String type, String path) {
this.name = name;
this.type = type;
this.path = path;
}
}5.3:在ActionConfig类中添加成员变量:
private Map<String, ResultConfig> resultConfigMap = new HashMap<>();并提供getter和setter方法,用于封装action节点中result节点属性信息。
5.4:在过滤器中,解析actions.xml时,在每个action节点迭代时,迭代得出result属性:
//将action对象的配置信息封装成对象,并装在Map中,获取时方便用请求名索引
private Map<String, ActionConfig> actionConfigMap = new HashMap<>();
private Map<String, ResultConfig> resultConfigMap = new HashMap<>();
public void init(FilterConfig filterConfig) throws ServletException {
//1.获取文档对象
Document doc = getDocument();
//2.获取文档中所有action节点的节点集合
NodeList nodeList = doc.getElementsByTagName("action");
for (int i = 0; i < nodeList.getLength(); i++) {
//3.获取每个节点中的属性信息,并封装成配置对象
Element actionEl = (Element) nodeList.item(i);
String actionName = actionEl.getAttribute("name");
String actionClassName = actionEl.getAttribute("class");
String actionMethod = actionEl.getAttribute("method");
//4.创建配置文件对象,并放入配置文件对象映射中
ActionConfig actionConfig = new ActionConfig(actionName, actionClassName, actionMethod);
actionConfigMap.put(actionName, actionConfig);
//5.获取文档中所有result节点的节点集合
resultConfigMap = new HashMap<>();
NodeList resultNode = actionEl.getElementsByTagName("result");
for (int j = 0; j < resultNode.getLength(); j++) {
Element resultEl = (Element) resultNode.item(j);
String resultName = resultEl.getAttribute("name");
String resultType = resultEl.getAttribute("type");
String resultPath = resultEl.getAttribute("path");
ResultConfig resultConfig = new ResultConfig(resultName, resultType, resultPath);
resultConfigMap.put(resultName, resultConfig);
//6.将该action中所有result节点组成的map对象封装到actionConfig对象中
actionConfig.setResultConfigMap(resultConfigMap);
}
}
}5.5:在doFilter中,执行完函数后,得到函数返回值(result的名称),由请求得到action的名称,得到对应ActionConfig对象,由函数返回值得到ActionConfig对象中对应的ResultConfig对象,然后根据请求类型和资源路径跳转到相应界面:
public void doFilter(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response,
FilterChain chain) throws IOException, ServletException {
try {
//1.在过滤器中对请求和相应对象强强转成Http类型,方便处理Http请求相关操作
HttpServletRequest req = (HttpServletRequest) request;
HttpServletResponse resp = (HttpServletResponse) response;
//2.将当前的环境变量存储到ActionContext对象中,方便在其他对象中操作请求的信息
ActionContext context = new ActionContext(req, resp);
context.setContext(context);
//3.得到请求中的最后一个/请求的名称
String requestUri = req.getRequestURI();
String actionName = requestUri.substring(requestUri
.lastIndexOf("/") + 1);
//4.判断配置对象映射中是否含有当前请求的信息
if (!actionConfigMap.containsKey(actionName)) {
chain.doFilter(req, resp);
}
//5.获取当前请求操作的配置对象
ActionConfig actionConfig = (ActionConfig) actionConfigMap.get(actionName);
//6.通过反射执行请求对象中的函数
Class clz = Class.forName(actionConfig.getClassName());
Object actionObj = clz.newInstance();
Method method = clz.getMethod(actionConfig.getMethod());
String action = (String) method.invoke(actionObj);
System.out.println("acton=" + action);
//7.通过执行函数返回的result的name,得到该action中确切的ResultConfig对象
ResultConfig resultConfig = actionConfigMap.get(actionName).getResultConfigMap().get(action);
String type = resultConfig.getType();
String path = resultConfig.getPath();
if("dispatcher".equals(type)){
req.getRequestDispatcher(path).forward(req, resp);
System.out.println(path);
}else if("redirect".equals(type)){
resp.sendRedirect(path);
System.out.println(path);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
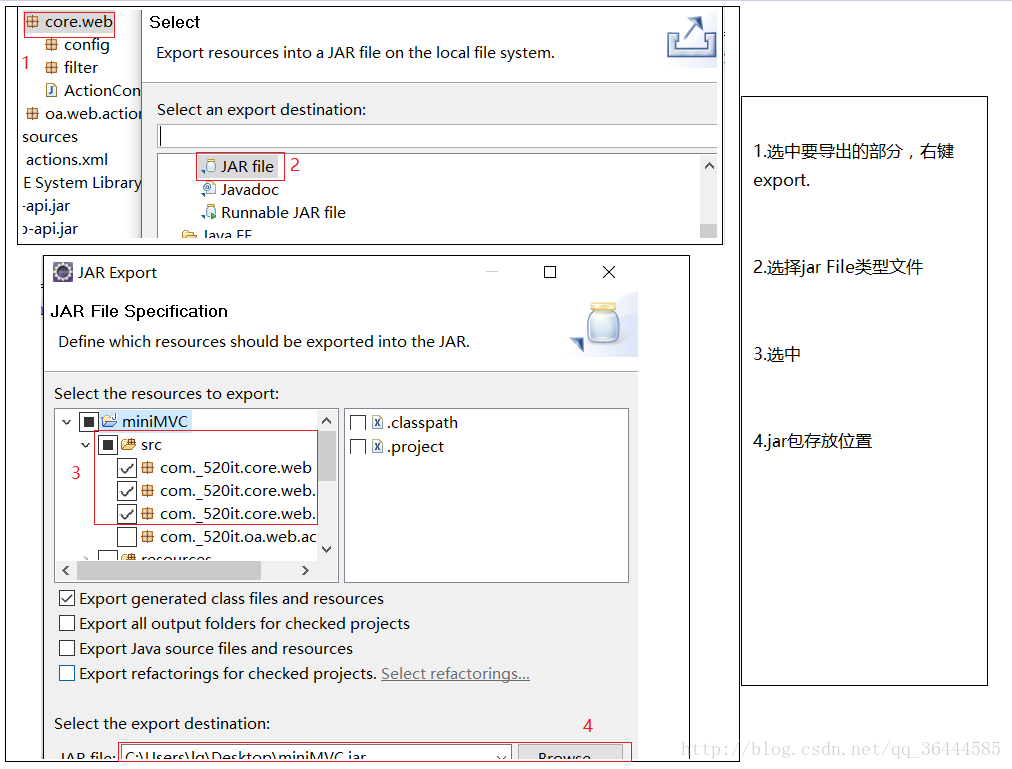
6.导出miniMVC框架:
7.使用jar包:
7.1:导入jar包并buildpath.
7.2:在web.xml中配置ActionFilter前端控制器:
<filter>
<filter-name>ActionFilter</filter-name>
<filter-class>com._520it.core.web.filter.ActionFilter</filter-class>
</filter>
<filter-mapping>
<filter-name>ActionFilter</filter-name>
<url-pattern>/*</url-pattern>
</filter-mapping>
7.3:书写自己的Action函数,如Product:
package A.B.C;
public class Product {
public String execute(){
System.out.println("Product.execute()");
return "welcome";
}
}7.4:在resources源文件夹中新建actions.xml文件,并配置:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<actions>
<action name="Product" class="A.B.C.Product" method="execute">
<result name="welcome" type="redirect" path="/abc.html" />
</action>
</actions>7.5:然后在webapp中随便写个html页面,如abc.html
7.6:访问格式:http://localhost:8080/miniMVC/Product;
miniMVC:tomcat根/config/server.xml中context元素属性path的值
Product:应该和action中的name向对应;
Product中的execute返回值应与result元素中的name相对应






















 463
463











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








