一、HashMap实现类
1.常用方法
增加:put(K key, V value)
删除:clear() remove(Object key)
修改:
查看:entrySet() get(Object key) keySet() size() values()
判断:containsKey(Object key) containsValue(Object value)
equals(Object o) isEmpty()
遍历方式:
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map<Integer,String> hm = new HashMap<>();
hm.put(12,"丽丽");
hm.put(7,"菲菲");
hm.put(19,"露露");
hm.put(12,"明明");
hm.put(6,"莹莹");
System.out.println("集合的长度:"+hm.size());
System.out.println("集合中内容查看:"+hm);
//遍历方式一:entrySet()迭代器
Iterator<Map.Entry<Integer, String>> entryIterator = hm.entrySet().iterator();
while (entryIterator.hasNext()){
Map.Entry<Integer, String> entry = entryIterator.next();
System.out.println("key="+entry.getKey()+"_value="+entry.getValue());
}
//方式二:keySet()迭代器
Iterator<Integer> keyIterator = hm.keySet().iterator();
while (keyIterator.hasNext()){
Integer key = keyIterator.next();
System.out.println(key);
System.out.println(hm.get(key));
}
//方式三:ForEach EntrySet
for (Map.Entry<Integer, String> entry : hm.entrySet()) {
System.out.println(entry.getKey());
System.out.println(entry.getValue());
}
//方式四:ForEach KeySet
for (Integer key : hm.keySet()) {
System.out.println(key);
System.out.println(hm.get(key));
}
//方式5:Lambda
hm.forEach((key, value) -> {
System.out.println(key);
System.out.println(value);
});
//方式6:Streams API 单线程
hm.entrySet().stream().forEach((entry) -> {
System.out.println(entry.getKey());
System.out.println(entry.getValue());
});
//方式7:Streams API 多线程
hm.entrySet().parallelStream().forEach((entry) -> {
System.out.println(entry.getKey());
System.out.println(entry.getValue());
});
原文参考,其中还有遍历方式的性能测试
https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/zQBN3UvJDhRTKP6SzcZFKw
这里记录一下文章性能测试结论和安全性结论:
性能测试结论:
- parallelStream 为多线程版本性能一定是最好的,除此外EntrySet 之所以比 KeySet 的性能高是因为,KeySet 在循环时使用了 map.get(key),而 map.get(key) 相当于又遍历了一遍 Map 集合去查询 key 所对应的值。为什么要用“又”这个词?那是因为在使用迭代器或者 for 循环时,其实已经遍历了一遍 Map 集合了,因此再使用 map.get(key) 查询时,相当于遍历了两遍。
- 而 EntrySet 只遍历了一遍 Map 集合,之后通过代码“Entry<Integer, String> entry = iterator.next()”把对象的 key 和 value 值都放入到了 Entry 对象中,因此再获取 key 和 value 值时就无需再遍历 Map 集合,只需要从 Entry 对象中取值就可以了。
- 所以,EntrySet 的性能比 KeySet 的性能高出了一倍,因为 KeySet 相当于循环了两遍 Map 集合,而 EntrySet 只循环了一遍。
安全性结论:
- 不能在遍历中使用集合 map.remove() 来删除数据,这是非安全的操作方式,但我们可以使用迭代器的 iterator.remove() 的方法来删除数据,这是安全的删除集合的方式。同样的我们也可以使用 Lambda 中的 removeIf 来提前删除数据,或者是使用 Stream 中的 filter 过滤掉要删除的数据进行循环,这样都是安全的,当然我们也可以在 for 循环前删除数据在遍历也是线程安全的。
我们应该尽量使用迭代器(Iterator)来遍历 EntrySet 的遍历方式来操作 Map 集合
2.JDK1.7和JDK1.8(jdk1.8.0_361)源码下(简要)
JDK1.7:数组+链表,链表数据添加用的头插法
public class HashMap<K,V>
extends AbstractMap<K,V> //【1】继承的AbstractMap中,已经实现了Map接口
//【2】又实现了这个接口,多余,但是设计者觉得没有必要删除,就这么地了
implements Map<K,V>, Cloneable, Serializable{
//【3】后续会用到的重要属性:先粘贴过来:
static final int DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY = 16;//哈希表主数组的默认长度
//定义了一个float类型的变量,以后作为:默认的装填因子,加载因子是表示Hsah表中元素的填满的程度
//太大容易引起哈西冲突,太小容易浪费 0.75是经过大量运算后得到的最好值
//这个值其实可以自己改,但是不建议改,因为这个0.75是大量运算得到的
static final float DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR = 0.75f;
transient Entry<K, V>[] table;//主数组,每个元素为Entry类型
transient int size;
int threshold;//数组扩容的界限值,门槛值 调用默认构造器时16*0.75=12
final float loadFactor;//用来接收装填因子的变量
//【4】查看构造器:内部相当于:this(16,0.75f);调用了当前类中的带参构造器
public HashMap() {
this(DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY, DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR);
}
//【5】本类中带参数构造器:--》作用给一些数值进行初始化的!
public HashMap(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor) {
//【6】给capacity赋值,capacity的值一定是 大于你传进来的initialCapacity 的 最小的 2的倍数
int capacity = 1;
while (capacity < initialCapacity)
capacity <<= 1;
//【7】给loadFactor赋值,将装填因子0.75赋值给loadFactor
this.loadFactor = loadFactor;
//【8】数组扩容的界限值,门槛值
threshold = (int) Math.min(capacity * loadFactor, MAXIMUM_CAPACITY + 1);
//【9】给table数组赋值,初始化数组长度为16
table = new Entry[capacity];
}
//【10】调用put方法:
public V put(K key, V value) {
//【11】对空值的判断
if (key == null)
return putForNullKey(value);
//【12】调用hash方法,获取哈希码
int hash = hash(key);
//【14】得到key对应在数组中的位置
int i = indexFor(hash, table.length);
//【16】如果你放入的元素,在主数组那个位置上没有值,e==null 那么下面这个循环不走
//当在同一个位置上放入元素的时候
for (Entry<K, V> e = table[i]; e != null; e = e.next) {
Object k;
//哈希值一样 并且 equals相比一样
//(k = e.key) == key 如果是一个对象就不用比较equals了
if (e.hash == hash && ((k = e.key) == key || key.equals(k))) {
V oldValue = e.value;
e.value = value;
e.recordAccess(this);
return oldValue;
}
}
modCount++;
//【17】走addEntry添加这个节点的方法:
addEntry(hash, key, value, i);
return null;
}
//【13】hash方法返回这个key对应的哈希值,内部进行二次散列,为了尽量保证不同的key得到不同的哈希码!
final int hash(Object k) {
int h = 0;
if (useAltHashing) {
if (k instanceof String) {
return sun.misc.Hashing.stringHash32((String) k);
}
h = hashSeed;
}
//k.hashCode()函数调用的是key键值类型自带的哈希函数,
//由于不同的对象其hashCode()有可能相同,所以需对hashCode()再次哈希,以降低相同率。
h ^= k.hashCode();
// This function ensures that hashCodes that differ only by
// constant multiples at each bit position have a bounded
// number of collisions (approximately 8 at default load factor).
/*
接下来的一串与运算和异或运算,称之为“扰动函数”,
扰动的核心思想在于使计算出来的值在保留原有相关特性的基础上,
增加其值的不确定性,从而降低冲突的概率。
不同的版本实现的方式不一样,但其根本思想是一致的。
往右移动的目的,就是为了将h的高位利用起来,减少哈西冲突
*/
h ^= (h >>> 20) ^ (h >>> 12);
return h ^ (h >>> 7) ^ (h >>> 4);
}
//【15】返回int类型数组的坐标
static int indexFor(int h, int length) {
//其实这个算法就是取模运算:h%length,取模效率不如位运算
return h & (length - 1);
}
//【18】调用addEntry
void addEntry(int hash, K key, V value, int bucketIndex) {
//【25】size的大小 大于 16*0.75=12的时候,比如你放入的是第13个,这第13个你打算放在没有元素的位置上的时候
if ((size >= threshold) && (null != table[bucketIndex])) {
//【26】主数组扩容为2倍
resize(2 * table.length);
//【30】重新调整当前元素的hash码
hash = (null != key) ? hash(key) : 0;
//【31】重新计算元素位置
bucketIndex = indexFor(hash, table.length);
}
//【19】将hash,key,value,bucketIndex位置 封装为一个Entry对象:
createEntry(hash, key, value, bucketIndex);
}
//【20】
void createEntry(int hash, K key, V value, int bucketIndex) {
//【21】获取bucketIndex位置上的元素给e
Entry<K, V> e = table[bucketIndex];
//【22】然后将hash, key, value封装为一个对象,然后将下一个元素的指向为e (链表的头插法)
//【23】将新的Entry放在table[bucketIndex]的位置上
table[bucketIndex] = new Entry<>(hash, key, value, e);
//【24】集合中加入一个元素 size+1
size++;
}
//【27】
void resize(int newCapacity) {
Entry[] oldTable = table;
int oldCapacity = oldTable.length;
if (oldCapacity == MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) {
threshold = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
return;
}
//【28】创建长度为newCapacity的数组
Entry[] newTable = new Entry[newCapacity];
boolean oldAltHashing = useAltHashing;
useAltHashing |= sun.misc.VM.isBooted() &&
(newCapacity >= Holder.ALTERNATIVE_HASHING_THRESHOLD);
boolean rehash = oldAltHashing ^ useAltHashing;
//【28.5】转让方法:将老数组中的东西都重新放入新数组中
transfer(newTable, rehash);
//【29】老数组替换为新数组
table = newTable;
//【29.5】重新计算
threshold = (int) Math.min(newCapacity * loadFactor, MAXIMUM_CAPACITY + 1);
}
//【28.6】
void transfer(Entry[] newTable, boolean rehash) {
int newCapacity = newTable.length;
for (Entry<K, V> e : table) {
while (null != e) {
Entry<K, V> next = e.next;
if (rehash) {
e.hash = null == e.key ? 0 : hash(e.key);
}
//【28.7】将哈希值,和新的数组容量传进去,重新计算key在新数组中的位置
int i = indexFor(e.hash, newCapacity);
//【28.8】头插法
e.next = newTable[i];//获取链表上元素给e.next
newTable[i] = e;//然后将e放在i位置
e = next;//e再指向下一个节点继续遍历
}
}
}
}
JDK1.8:数组+链表+红黑树,链表插入用的尾插法,红黑树部分阅读起来理解度不够,需要加强数据结构与算法的学习,后续再更新记录这部分
public class HashMap<K,V> extends AbstractMap<K,V>
implements Map<K,V>, Cloneable, Serializable {
//初始化数组长度16
static final int DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY = 1 << 4;
//最大长度2^30
static final int MAXIMUM_CAPACITY = 1 << 30;
//默认装填因子、负载因子0.75,经过验证的数字,时间和空间成本的折中
//0.5的话空间利用率不足,但是hash冲突少,不产生链表的话,那么查询效率很高-》时间好,空间不好
//1的话空间利用率满但是容易发生hash冲突并且查询效率低-》空间好,时间不好
static final float DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR = 0.75f;
///树化阈值,大于这个值,会将链表转化为红黑树,默认是8
static final int TREEIFY_THRESHOLD = 8;
红黑树转化回链表阈值,当某个红黑树上结点数目小于6,又会将红黑树转换回链表
static final int UNTREEIFY_THRESHOLD = 6;
//最小树化容量。当键值对个数没有超过这个值时,优先进行扩容,而不是转换成红黑树
static final int MIN_TREEIFY_CAPACITY = 64;
//主数组
transient Node<K,V>[] table;
//存储元素的集合
transient Set<Map.Entry<K,V>> entrySet;
//键值对个数
transient int size;
//修改次数。线程不安全的时候,启用fail-fast机制
transient int modCount;
//数组阀值,达到阀值开始计划扩容
int threshold;
//实际的装填因子、负载因子
final float loadFactor;
//内部类-节点类(hash-key-value-next)
static class Node<K,V> implements Map.Entry<K,V> {
final int hash;
final K key;
V value;
Node<K,V> next;
Node(int hash, K key, V value, Node<K,V> next) {
this.hash = hash;
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
this.next = next;
}
public final K getKey() { return key; }
public final V getValue() { return value; }
public final String toString() { return key + "=" + value; }
public final int hashCode() {
return Objects.hashCode(key) ^ Objects.hashCode(value);
}
public final V setValue(V newValue) {
V oldValue = value;
value = newValue;
return oldValue;
}
public final boolean equals(Object o) {
if (o == this)
return true;
if (o instanceof Map.Entry) {
Map.Entry<?,?> e = (Map.Entry<?,?>)o;
if (Objects.equals(key, e.getKey()) &&
Objects.equals(value, e.getValue()))
return true;
}
return false;
}
}
//无参构造器
public HashMap() {
//装填因子、负载因子 0.75
this.loadFactor = DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR;
}
//有参构造器,传初始化长度
public HashMap(int initialCapacity) {
this(initialCapacity, DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR);
}
//有参构造器,传初始化长度和填装(负载)因子
public HashMap(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor) {
//代码健壮性,异常值处理
if (initialCapacity < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal initial capacity: " +
initialCapacity);
if (initialCapacity > MAXIMUM_CAPACITY)
initialCapacity = MAXIMUM_CAPACITY;
if (loadFactor <= 0 || Float.isNaN(loadFactor))
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal load factor: " +
loadFactor);
this.loadFactor = loadFactor;
//阀值计算
this.threshold = tableSizeFor(initialCapacity);
}
//有参构造器,传Map接口实现类
public HashMap(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> m) {
this.loadFactor = DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR;
putMapEntries(m, false);
}
//将容量修正为2的n次幂
//例如cap=7,那么经过计算,最接近的是8=2^3
//cap=9,那么经过计算,最接近的是16=2^4
//cap=17,最接近的是32=2^5
static final int tableSizeFor(int cap) {
int n = cap - 1;
n |= n >>> 1;
n |= n >>> 2;
n |= n >>> 4;
n |= n >>> 8;
n |= n >>> 16;
return (n < 0) ? 1 : (n >= MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) ? MAXIMUM_CAPACITY : n + 1;
}
//put方法
public V put(K key, V value) {
return putVal(hash(key), key, value, false, true);
}
//hashmap的hash计算,扰动函数,用于降低哈希冲突
static final int hash(Object key) {
int h;
return (key == null) ? 0 : (h = key.hashCode()) ^ (h >>> 16);
}
//开始放置数据,传入hash-key-value-false-true
final V putVal(int hash, K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent,boolean evict) {
Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> p; int n, i;
//没有创建数组的时候,初始化数组长度
if ((tab = table) == null || (n = tab.length) == 0)
n = (tab = resize()).length;
//具体数组位置上没有数据时,插入数据
if ((p = tab[i = (n - 1) & hash]) == null)
tab[i] = newNode(hash, key, value, null);
else {
//具体数组位置上有数据时,产生冲突
Node<K,V> e; K k;
//插入数据和原数组数据key相同时,进行替换
if (p.hash == hash &&((k = p.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
//满足条件则把p地址赋值给e
e = p;
//p属于TreeNode类时,表示已经树化
else if (p instanceof TreeNode)
//添加到红黑树中
e = ((TreeNode<K,V>)p).putTreeVal(this, tab, hash, key, value);
else {
for (int binCount = 0; ; ++binCount) { //无限循环,遍历链表
if ((e = p.next) == null) {
//找到最后一个节点,插入数据,尾插法
p.next = newNode(hash, key, value, null);
if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD - 1) // -1 for 1st
//链表长度>=8时,尝试树化,REEIFY_THRESHOLD - 1=7,binCount从0开始
treeifyBin(tab, hash);
break;
}
// 如果存在相同key,则终止遍历
if (e.hash == hash &&
((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
break;
p = e;
}
}
//存在相同key时,替换里面的value,并返回原先value
if (e != null) {
V oldValue = e.value;
if (!onlyIfAbsent || oldValue == null)
e.value = value;
afterNodeAccess(e);
return oldValue;
}
}
//记录操作数
++modCount;
//当元素个数超过极限值时进行扩容
if (++size > threshold)
resize();
afterNodeInsertion(evict);
return null;
}
//扩容函数
final Node<K,V>[] resize() {
Node<K,V>[] oldTab = table;
int oldCap = (oldTab == null) ? 0 : oldTab.length;
int oldThr = threshold;
int newCap, newThr = 0;
if (oldCap > 0) {
//原先数组长度>= 2^30的话,数组阀值threshold = Integer.MAX_VALUE=2^31-1,返回原先数组
if (oldCap >= MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) {
threshold = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
return oldTab;
}
//新数组长度=oldCap*2,如果新数组长度< 2^30 && 老数组长度 >16,
else if ((newCap = oldCap << 1) < MAXIMUM_CAPACITY &&
oldCap >= DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY)
newThr = oldThr << 1; // 新阀值=老阀值*2
}
else if (oldThr > 0) // 调用有参构造器时传入了threshold
newCap = oldThr;
else { // 未初始化数组长度时,新建数组长度=16,新阀值=0.75*16=12
newCap = DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY;
newThr = (int)(DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR * DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY);
}
if (newThr == 0) { //新阀值=0时,进行赋值
float ft = (float)newCap * loadFactor;
newThr = (newCap < MAXIMUM_CAPACITY && ft < (float)MAXIMUM_CAPACITY ?
(int)ft : Integer.MAX_VALUE);
}
threshold = newThr;
@SuppressWarnings({"rawtypes","unchecked"})
//初始化数组
Node<K,V>[] newTab = (Node<K,V>[])new Node[newCap];
table = newTab;
if (oldTab != null) {
//遍历旧数组
for (int j = 0; j < oldCap; ++j) {
Node<K,V> e;
if ((e = oldTab[j]) != null) {
oldTab[j] = null;
//如果下一个元素为null,说明桶中只有一个元素,直接放入新数组中
if (e.next == null)
newTab[e.hash & (newCap - 1)] = e;
//如果元素是TreeNode,分解生成红黑树
else if (e instanceof TreeNode)
((TreeNode<K,V>)e).split(this, newTab, j, oldCap);
else { // 如果是链表节点
// 低位链表的头节点和尾节点
Node<K,V> loHead = null, loTail = null;
// 高位链表的头节点和尾节点
Node<K,V> hiHead = null, hiTail = null;
Node<K,V> next;
do {
next = e.next;
if ((e.hash & oldCap) == 0) {// 构建低位链表
if (loTail == null)
loHead = e;
else
loTail.next = e;
loTail = e;
}
else {// 构建高位链表
if (hiTail == null)
hiHead = e;
else
hiTail.next = e;
hiTail = e;
}
} while ((e = next) != null);
if (loTail != null) {// 低位链表放入新数组
loTail.next = null;
newTab[j] = loHead;
}
if (hiTail != null) {// 高位链表放入新数组
hiTail.next = null;
newTab[j + oldCap] = hiHead;
}
}
}
}
}
//返回数组
return newTab;
}
//创建节点
Node<K,V> newNode(int hash, K key, V value, Node<K,V> next) {
return new Node<>(hash, key, value, next);
}
//链表长度>8时尝试树化
final void treeifyBin(Node<K,V>[] tab, int hash) {
int n, index; Node<K,V> e;
//如果数组为null或者数组长度小于最64,不会进行树化,进行扩容
if (tab == null || (n = tab.length) < MIN_TREEIFY_CAPACITY)
resize();
//根据hash做与运算,得到下标,拿到首节点,如果不为空
else if ((e = tab[index = (n - 1) & hash]) != null) {
TreeNode<K,V> hd = null, tl = null;
//这里的dowhile循环会让单链表转为一个双向链表
do {
TreeNode<K,V> p = replacementTreeNode(e, null);
if (tl == null)
hd = p;
else {
p.prev = tl; //双向链表头尾相连
tl.next = p;
}
tl = p;
} while ((e = e.next) != null);
if ((tab[index] = hd) != null)
//树化,构建红黑树
hd.treeify(tab);
}
}
//返回新的树节点
TreeNode<K,V> replacementTreeNode(Node<K,V> p, Node<K,V> next) {
return new TreeNode<>(p.hash, p.key, p.value, next);
}
//
final void treeify(Node<K,V>[] tab) {
// 红黑树的根节点
TreeNode<K,V> root = null;
for (TreeNode<K,V> x = this, next; x != null; x = next) {
next = (TreeNode<K,V>)x.next;
x.left = x.right = null;
// 刚进入方法时,红黑树根节点此时一定为null,将链表的第一个节点作为根节点,颜色为黑色。
if (root == null) {
x.parent = null;// 根节点没有父节点
x.red = false;//黑色
root = x;//当前第一个节点给到root
}else {//这个分支说明已经有根节点了,与根节点的hash值进行比较
K k = x.key;// 此时的x是双向链表中的第二个节点
int h = x.hash;
Class<?> kc = null;
for (TreeNode<K,V> p = root;;) {
int dir, ph;
K pk = p.key;
if ((ph = p.hash) > h)
dir = -1; // 往树的左方向走
else if (ph < h)
dir = 1; // 往树的右方向走
else if ((kc == null &&
(kc = comparableClassFor(k)) == null) ||
(dir = compareComparables(kc, k, pk)) == 0)
//如果p的hash值与x的hash值相等,则比较key值。
//如果key没有实现comparable接口或者x的key值和p的值相等,则使用一套自定义的规则来比较节点x和节点p的大小,用来决定时向左走还是向右走。
dir = tieBreakOrder(k, pk);
TreeNode<K,V> xp = p;
// 判断插入左子树还是右子树 dir<0则左边插入,dir>0则右边插入,如果为null那么当前位置就是x的目标位置
if ((p = (dir <= 0) ? p.left : p.right) == null) {
x.parent = xp;
if (dir <= 0)
xp.left = x;
else
xp.right = x;
// 插入完成后,进行左旋右旋变色等操作,需要满足红黑树的特点。
root = balanceInsertion(root, x);
break;
}
}
}
}
moveRootToFront(tab, root);
}
}
这部分源码阅读的话可以自己写测试数据,“通话”和“重地”的hashcode是相同的,可以模拟出hash冲突,然后debug看看程序运行过程中变量变化,再自己画个图就能理解大部分数组+链表的过程,红黑树部分看不懂可以找资料或者视频加强学习。
public class TestMap {
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashMap<String, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("通话",10);
map.put("随便",20);
map.put("通话",40);
map.put("重地",40);
System.out.println("通话".hashCode());
System.out.println("重地".hashCode());
}
}
二、TreeMap实现类
1.常用方法
由于继承的AbstractMap父类,常用方法跟HashMap一样。
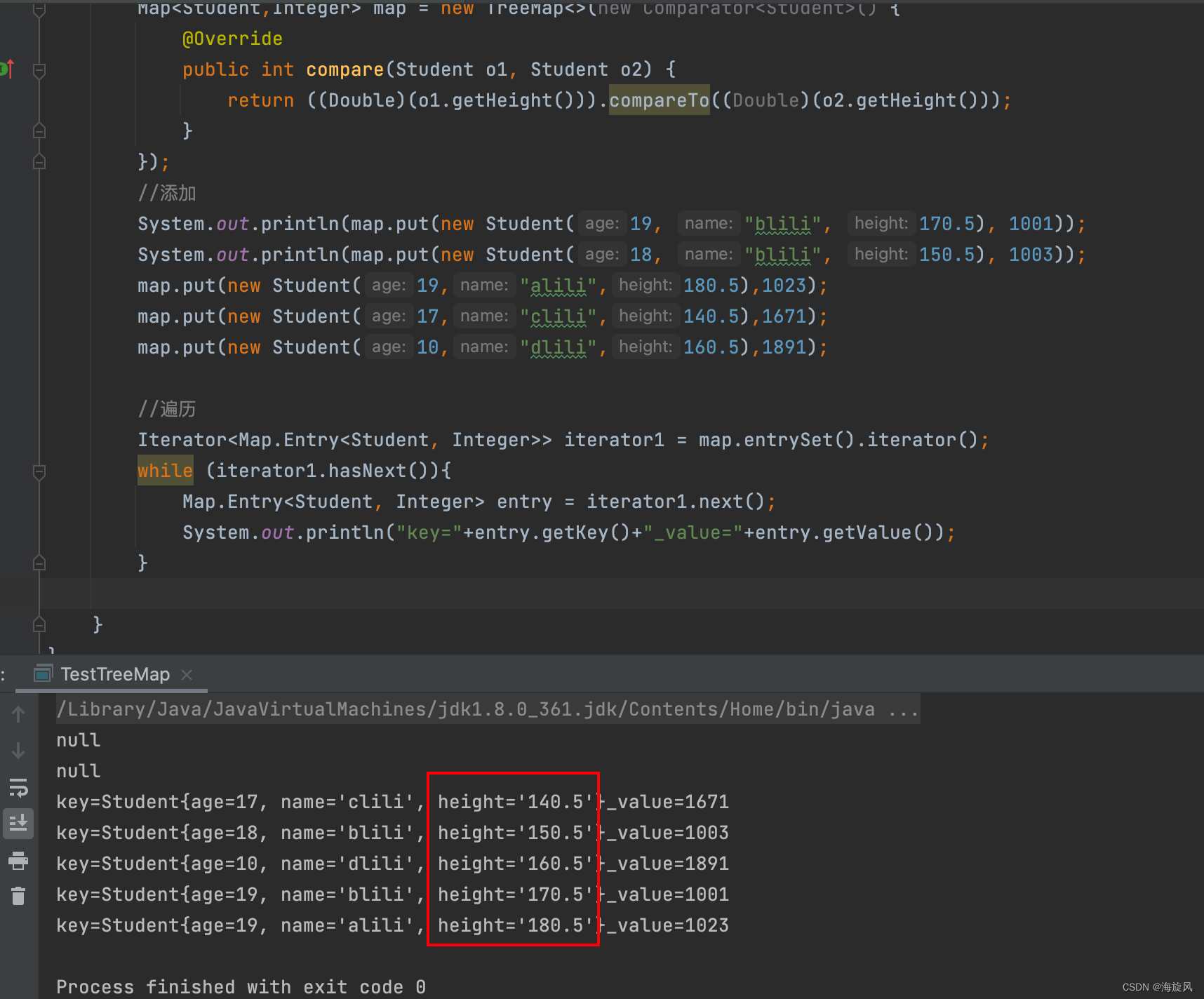
public class TestTreeMap {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map<Student,Integer> map = new TreeMap<>(new Comparator<Student>() {
@Override
public int compare(Student o1, Student o2) {
return ((Double)(o1.getHeight())).compareTo((Double)(o2.getHeight()));
}
});
//添加
System.out.println(map.put(new Student(19, "blili", 170.5), 1001));
System.out.println(map.put(new Student(18, "blili", 150.5), 1003));
map.put(new Student(19,"alili",180.5),1023);
map.put(new Student(17,"clili",140.5),1671);
map.put(new Student(10,"dlili",160.5),1891);
//遍历
Iterator<Student> iterator = map.keySet().iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()){
Student key = iterator.next();
System.out.println(key);
System.out.println(map.get(key));
}
Iterator<Map.Entry<Student, Integer>> iterator1 = map.entrySet().iterator();
while (iterator1.hasNext()){
Map.Entry<Student, Integer> entry = iterator1.next();
System.out.println("key="+entry.getKey()+"_value="+entry.getValue());
}
//删除
Integer blili = map.remove(new Student(19, "blili", 170.5));
System.out.println(map);
System.out.println(map.size()+"_"+blili);
}
}
2.JDK1.8(jdk1.8.0_361)源码下(简化)
理解了TreeMap后,TreeSet源码就好理解了。如果TreeSet存的是自定义类,自定义类必须要实现内部比较器Comparable接口或者创建外部比较器传给TreeSet有参构造器,否则TreeSet调用add方法就直接报错java.lang.ClassCastException无法强转了。
public class TreeMap<K,V>
extends AbstractMap<K,V>
implements NavigableMap<K,V>, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable
{
//成员变量
private final Comparator<? super K> comparator; //外部比较器
private transient Entry<K,V> root; //根结点
private transient int size = 0; //元素个数
private transient int modCount = 0; //操作次数
//构造器
//无参
public TreeMap() {
comparator = null;
}
//有参,传入外部比较器,另一篇文章Set接口中有说明内部比较器Comparable接口
//和外部比较器Comparator接口
public TreeMap(Comparator<? super K> comparator) {
this.comparator = comparator;
}
public TreeMap(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> m) {
comparator = null;
putAll(m);
}
//有参,多态,传SortedMap接口的实现类,例如TreeMap
//TreeMap类实现的接口之一NavigableMap,NavigableMap是继承extends SortedMap接口的
public TreeMap(SortedMap<K, ? extends V> m) {
comparator = m.comparator();
try {
buildFromSorted(m.size(), m.entrySet().iterator(), null, null);
} catch (java.io.IOException cannotHappen) {
} catch (ClassNotFoundException cannotHappen) {
}
}
//put 方法
public V put(K key, V value) {
Entry<K,V> t = root;
if (t == null) {
compare(key, key); //类型检查,判断有没有比较器以及key比较
//判断没有节点,创建根节点
root = new Entry<>(key, value, null);
size = 1;
modCount++;
return null;
}
int cmp;
Entry<K,V> parent;
// 外部比较器赋值
Comparator<? super K> cpr = comparator;
if (cpr != null) {
do {
parent = t;
//调用外部比较器,比较传入的key值和节点上的值哪个大,<0 >0 =0结果判断
//判断value是放节点左边还是节点右边,还是替换节点value值。
cmp = cpr.compare(key, t.key);
if (cmp < 0)
t = t.left;
else if (cmp > 0)
t = t.right;
else
return t.setValue(value);
} while (t != null);
}
else {
if (key == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
//没有外部比较器时,强转成内部比较器Comparable接口
//如果也没有实现内部比较器Comparable接口,会报错java.lang.ClassCastException无法强转
Comparable<? super K> k = (Comparable<? super K>) key;
do {
parent = t;
cmp = k.compareTo(t.key);
if (cmp < 0)
t = t.left;
else if (cmp > 0)
t = t.right;
else
return t.setValue(value);
} while (t != null);
}
//传入数据封装成节点
Entry<K,V> e = new Entry<>(key, value, parent);
//新节点插入
if (cmp < 0)
parent.left = e;
else
parent.right = e;
//重构红黑树
fixAfterInsertion(e);
size++;
modCount++;
return null;
}
final int compare(Object k1, Object k2) {
//如果传入的类没有实现外部比较器comparator接口的话,会强制换成内部比较器Comparable接口
//如果传入类也没有实现Comparable接口会直接报错java.lang.ClassCastException无法强转
return comparator==null ? ((Comparable<? super K>)k1).compareTo((K)k2)
: comparator.compare((K)k1, (K)k2);
}
//删除
public V remove(Object key) {
Entry<K,V> p = getEntry(key);
if (p == null)
return null;
V oldValue = p.value;
deleteEntry(p);
return oldValue;
}
//删除节点并重新平衡红黑树
private void deleteEntry(Entry<K,V> p) {
modCount++;
size--;
// If strictly internal, copy successor's element to p and then make p
// point to successor.
if (p.left != null && p.right != null) {
Entry<K,V> s = successor(p);
p.key = s.key;
p.value = s.value;
p = s;
} // p has 2 children
// Start fixup at replacement node, if it exists.
Entry<K,V> replacement = (p.left != null ? p.left : p.right);
if (replacement != null) {
// Link replacement to parent
replacement.parent = p.parent;
if (p.parent == null)
root = replacement;
else if (p == p.parent.left)
p.parent.left = replacement;
else
p.parent.right = replacement;
// Null out links so they are OK to use by fixAfterDeletion.
p.left = p.right = p.parent = null;
// Fix replacement
if (p.color == BLACK)
fixAfterDeletion(replacement);
} else if (p.parent == null) { // return if we are the only node.
root = null;
} else { // No children. Use self as phantom replacement and unlink.
if (p.color == BLACK)
fixAfterDeletion(p);
if (p.parent != null) {
if (p == p.parent.left)
p.parent.left = null;
else if (p == p.parent.right)
p.parent.right = null;
p.parent = null;
}
}
}
//返回EntrySet
public Set<Map.Entry<K,V>> entrySet() {
EntrySet es = entrySet;
return (es != null) ? es : (entrySet = new EntrySet());
}
//内部类EntrySet
class EntrySet extends AbstractSet<Map.Entry<K,V>> {
//返回迭代器EntryIterator类,需要获取到最左的叶子节点
public Iterator<Map.Entry<K,V>> iterator() {
return new EntryIterator(getFirstEntry());
}
public boolean contains(Object o) {
if (!(o instanceof Map.Entry))
return false;
Map.Entry<?,?> entry = (Map.Entry<?,?>) o;
Object value = entry.getValue();
Entry<K,V> p = getEntry(entry.getKey());
return p != null && valEquals(p.getValue(), value);
}
public boolean remove(Object o) {
if (!(o instanceof Map.Entry))
return false;
Map.Entry<?,?> entry = (Map.Entry<?,?>) o;
Object value = entry.getValue();
Entry<K,V> p = getEntry(entry.getKey());
if (p != null && valEquals(p.getValue(), value)) {
deleteEntry(p);
return true;
}
return false;
}
public int size() {
return TreeMap.this.size();
}
public void clear() {
TreeMap.this.clear();
}
public Spliterator<Map.Entry<K,V>> spliterator() {
return new EntrySpliterator<K,V>(TreeMap.this, null, null, 0, -1, 0);
}
}
//获取最左的叶子节点
final Entry<K,V> getFirstEntry() {
Entry<K,V> p = root;
if (p != null)
while (p.left != null)
p = p.left;
return p;
}
//迭代器类EntryIterator,继承父类PrivateEntryIterator
final class EntryIterator extends PrivateEntryIterator<Map.Entry<K,V>> {
EntryIterator(Entry<K,V> first) {
super(first);
}
public Map.Entry<K,V> next() {
//调用父类PrivateEntryIterator的方法
return nextEntry();
}
}
//迭代器父类PrivateEntryIterator
abstract class PrivateEntryIterator<T> implements Iterator<T> {
Entry<K,V> next;
Entry<K,V> lastReturned;
int expectedModCount;
PrivateEntryIterator(Entry<K,V> first) {
expectedModCount = modCount;
lastReturned = null;
next = first;
}
//判断当前节点,也就是最左叶子节点是否为空
public final boolean hasNext() {
return next != null;
}
//next方法,遍历结果是中序遍历:左根右
final Entry<K,V> nextEntry() {
Entry<K,V> e = next;
if (e == null)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
if (modCount != expectedModCount)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
//获取下次的节点
next = successor(e);
lastReturned = e;
//第一次循环返回的root最左叶子节点
return e;
}
final Entry<K,V> prevEntry() {
Entry<K,V> e = next;
if (e == null)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
if (modCount != expectedModCount)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
next = predecessor(e);
lastReturned = e;
return e;
}
public void remove() {
if (lastReturned == null)
throw new IllegalStateException();
if (modCount != expectedModCount)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
// deleted entries are replaced by their successors
if (lastReturned.left != null && lastReturned.right != null)
next = lastReturned;
deleteEntry(lastReturned);
expectedModCount = modCount;
lastReturned = null;
}
}
//传入的t默认是根节点最左节点,如果t不存在则返回 null
static <K,V> TreeMap.Entry<K,V> successor(Entry<K,V> t) {
if (t == null)
return null;
else if (t.right != null) {
//t如果有右边有节点就获取右节点下面最左叶子节点
//没有的话就返回t.right
Entry<K,V> p = t.right;
while (p.left != null)
p = p.left;
return p;
} else {
//中序遍历,getFirstEntry()获取的最左叶子节点传入进来
//左 根 右
Entry<K,V> p = t.parent;
Entry<K,V> ch = t;
while (p != null && ch == p.right) {
ch = p;
p = p.parent;
}
return p;
}
}
}
3.遍历结果说明(简图)
TreeMap遍历结果显示是中序遍历,左根右。
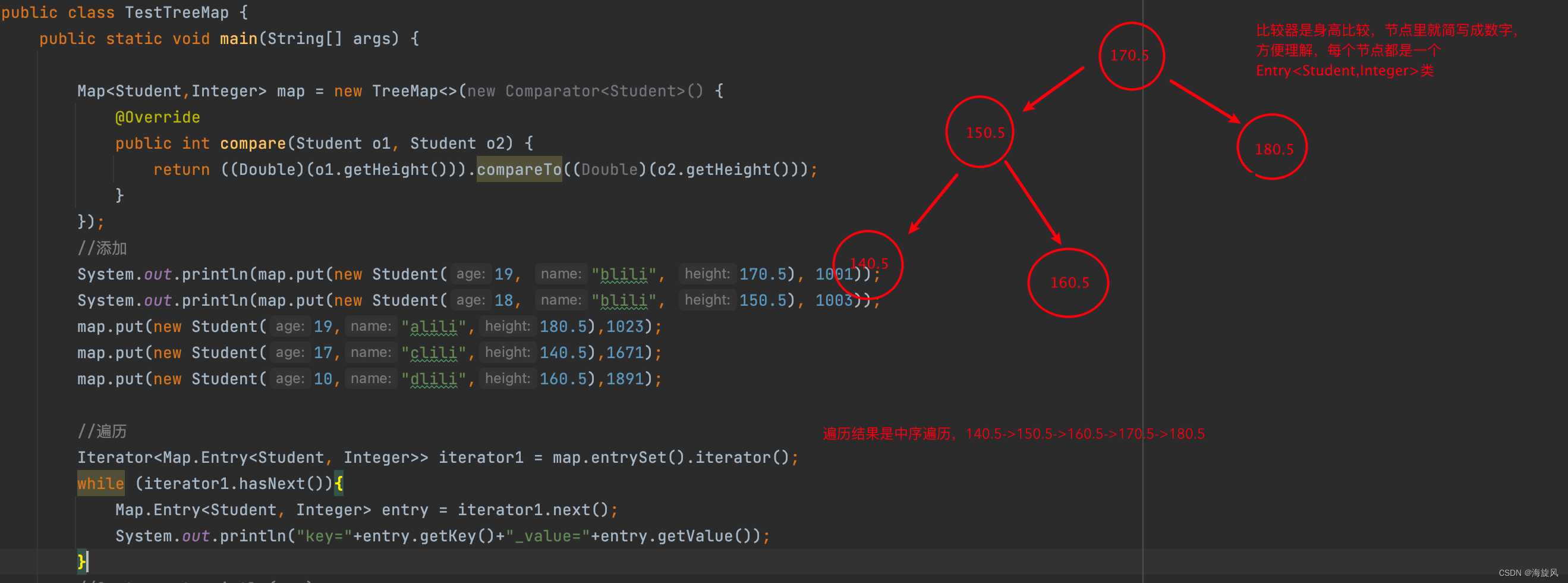
控制台打印结果





















 288
288

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








