题目描述
编一个程序,读入用户输入的一串先序遍历字符串,根据此字符串建立一个二叉树(以指针方式存储)。 例如如下的先序遍历字符串: ABC##DE#G##F### 其中“#”表示的是空格,空格字符代表空树。建立起此二叉树以后,再对二叉树进行中序遍历,输出遍历结果。
输入描述:
输入包括1行字符串,长度不超过100。输出描述:
可能有多组测试数据,对于每组数据,
输出将输入字符串建立二叉树后中序遍历的序列,每个字符后面都有一个空格。
每个输出结果占一行。示例1
输入
复制
abc##de#g##f###
输出
复制
c b e g d f a
#include <stdio.h>
#include <cstdio>
#include <string>
#include <string.h>
#include <math.h>
#include <algorithm>
#include <iostream>
#include <stack>
using namespace std;
typedef struct Node{
Node *lchild,*rchild;
char data;
}TreeNode;
bool BuildTree(TreeNode *&root)
{
char a;
a=getchar();
if(a==EOF)
return false;
if(a=='#')
return NULL;
else
{
root=(TreeNode *)malloc(sizeof(TreeNode));
root->data=a;
BuildTree(root->lchild);
BuildTree(root->rchild);
}
return true;
}
void InOrder(Node *T){
if(T->lchild!=NULL){
InOrder(T->lchild);
}
if(T)
printf("%c ",T->data);
if(T->rchild!=NULL){
InOrder(T->rchild);
}
}
int main(){
TreeNode *root=NULL;
while(BuildTree(root)){
InOrder(root);
printf("\n");
getchar();
}
}
题目描述
1
/ \
2 3
/ \ / \
4 5 6 7
/\ /\ /\ /\
如上图所示,由正整数 1, 2, 3, ...组成了一棵无限大的二叉树。从某一个结点到根结点(编号是1的结点)都有一条唯一的路径,比如从5到根结点的路径是(5, 2, 1),从4到根结点的路径是(4, 2, 1),从根结点1到根结点的路径上只包含一个结点1,因此路径就是(1)。对于两个结点x和y,假设他们到根结点的路径分别是(x1, x2, ... ,1)和(y1, y2,...,1),那么必然存在两个正整数i和j,使得从xi 和yj 开始,有xi = yj,xi + 1 = yj + 1,xi + 2 = yj + 2,...
现在的问题就是,给定x和y,要求他们的公共父节点,即xi(也就是 yj)。
输入描述:
输入包含多组数据,每组数据包含两个正整数x和y(1≤x, y≤2^31-1)。输出描述:
对应每一组数据,输出一个正整数xi,即它们的首个公共父节点。示例1
输入
复制
10 4输出
复制
2#include <stdio.h>
#include <cstdio>
#include <string>
#include <string.h>
#include <math.h>
#include <algorithm>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main(){
long long x,y;
while(scanf("%lld %lld",&x,&y)!=EOF)
{
long long a,b;
a=x;
b=y;
if(a==b)
{
printf("%lld\n",a);
}
else
{
while(a!=b)
{
if(a>b)
a=a/2;
else if(a<b)
b=b/2;
}
printf("%lld\n",a);
}
}
}
题目描述
二叉排序树,也称为二叉查找树。可以是一颗空树,也可以是一颗具有如下特性的非空二叉树: 1. 若左子树非空,则左子树上所有节点关键字值均不大于根节点的关键字值; 2. 若右子树非空,则右子树上所有节点关键字值均不小于根节点的关键字值; 3. 左、右子树本身也是一颗二叉排序树。 现在给你N个关键字值各不相同的节点,要求你按顺序插入一个初始为空树的二叉排序树中,每次插入后成功后,求相应的父亲节点的关键字值,如果没有父亲节点,则输出-1。
输入描述:
输入包含多组测试数据,每组测试数据两行。
第一行,一个数字N(N<=100),表示待插入的节点数。
第二行,N个互不相同的正整数,表示要顺序插入节点的关键字值,这些值不超过10^8。输出描述:
输出共N行,每次插入节点后,该节点对应的父亲节点的关键字值。示例1
输入
复制
5
2 5 1 3 4
输出
复制
-1
2
2
5
3
#include <stdio.h>
#include <cstdio>
#include <string>
#include <string.h>
#include <math.h>
#include <algorithm>
#include <iostream>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
typedef struct TreeNode
{
int data;
struct TreeNode *lchild,*rchild;
}TreeNode;
TreeNode* insert(struct TreeNode *root,int x,int &f)
{
if(root==NULL)
{
root=(TreeNode *)malloc(sizeof(TreeNode));
root->data=x;
root->lchild=NULL;
root->rchild=NULL;
return root;
}
else if(root->data>x)
{
f=root->data;
root->lchild=insert(root->lchild,x,f);
}
else if(root->data<x)
{
f=root->data;
root->rchild=insert(root->rchild,x,f);
}
return root;
}
int main(){
int n;
while(scanf("%d",&n)!=EOF)
{
struct TreeNode *root=NULL;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
int f=-1;
int x;
scanf("%d",&x);
root=insert(root,x,f);
printf("%d\n",f);
}
}
}
题目描述
输入一系列整数,建立二叉排序树,并进行前序,中序,后序遍历。
输入描述:
输入第一行包括一个整数n(1<=n<=100)。
接下来的一行包括n个整数。输出描述:
可能有多组测试数据,对于每组数据,将题目所给数据建立一个二叉排序树,并对二叉排序树进行前序、中序和后序遍历。
每种遍历结果输出一行。每行最后一个数据之后有一个空格。
输入中可能有重复元素,但是输出的二叉树遍历序列中重复元素不用输出。示例1
输入
复制
5
1 6 5 9 8
输出
复制
1 6 5 9 8
1 5 6 8 9
5 8 9 6 1
#include <stdio.h>
#include <cstdio>
#include <string>
#include <string.h>
#include <math.h>
#include <algorithm>
#include <iostream>
#include <queue>
#include <stack>
using namespace std;
typedef struct TreeNode{
int data;
TreeNode *lchild,*rchild;
}TreeNode;
TreeNode * Insert(struct TreeNode *root,int x)
{
if(root==NULL)
{
root=(TreeNode *)malloc(sizeof(TreeNode));
root->data=x;
root->lchild=root->rchild=NULL;
return root;
}
else if(x<root->data)
root->lchild=Insert(root->lchild, x);
else if(x>root->data)
root->rchild=Insert(root->rchild, x);
return root;
}
void PreOrder(struct TreeNode *Root)
{
if(Root)
{
printf("%d ",Root->data);
PreOrder(Root->lchild);
PreOrder(Root->rchild);
}
}
void InOrder(struct TreeNode *Root)
{
if(Root)
{
InOrder(Root->lchild);
printf("%d ",Root->data);
InOrder(Root->rchild);
}
}
void PostOrder(struct TreeNode *Root)
{
if(Root)
{
PostOrder(Root->lchild);
PostOrder(Root->rchild);
printf("%d ",Root->data);
}
}
int main(){
int n;
int x;
struct TreeNode *root;
while(scanf("%d",&n)!=EOF)
{
root=NULL;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
scanf("%d",&x);
root=Insert(root,x);
}
PreOrder(root);
printf("\n");
InOrder(root);
printf("\n");
PostOrder(root);
printf("\n");
}
}
1064 Complete Binary Search Tree (30 分)
A Binary Search Tree (BST) is recursively defined as a binary tree which has the following properties:
- The left subtree of a node contains only nodes with keys less than the node's key.
- The right subtree of a node contains only nodes with keys greater than or equal to the node's key.
- Both the left and right subtrees must also be binary search trees.
A Complete Binary Tree (CBT) is a tree that is completely filled, with the possible exception of the bottom level, which is filled from left to right.
Now given a sequence of distinct non-negative integer keys, a unique BST can be constructed if it is required that the tree must also be a CBT. You are supposed to output the level order traversal sequence of this BST.
Input Specification:
Each input file contains one test case. For each case, the first line contains a positive integer N (≤1000). Then N distinct non-negative integer keys are given in the next line. All the numbers in a line are separated by a space and are no greater than 2000.
Output Specification:
For each test case, print in one line the level order traversal sequence of the corresponding complete binary search tree. All the numbers in a line must be separated by a space, and there must be no extra space at the end of the line.
Sample Input:
10
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 0
Sample Output:
6 3 8 1 5 7 9 0 2 4
通过中根序列“左中右”的顺序重建整棵树:先将给定的序列从小到大排序,然后对按完全二叉树的数组存储方式存储的整棵树进行中序遍历,遍历过程中将数字从小到大填入数组,最后就能得到一棵完全二叉查找树。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <cstdio>
#include <string>
#include <string.h>
#include <math.h>
#include <algorithm>
#include <iostream>
#include <queue>
#include <vector>
#include <stack>
#include <map>
#include <set>
using namespace std;
int tree[10001];
int a[10001];
int n,position=0;
void InOrder(int root)
{
if(root>n)
return;
InOrder(root*2);
tree[root]=a[position++];
InOrder(root*2+1);
}
int main(){
scanf("%d",&n);
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
scanf("%d",&a[i]);
}
sort(a,a+n);
InOrder(1);
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
if(i==1)
printf("%d",tree[i]);
else
printf(" %d",tree[i]);
}
}
1099 Build A Binary Search Tree (30 分)
A Binary Search Tree (BST) is recursively defined as a binary tree which has the following properties:
- The left subtree of a node contains only nodes with keys less than the node's key.
- The right subtree of a node contains only nodes with keys greater than or equal to the node's key.
- Both the left and right subtrees must also be binary search trees.
Given the structure of a binary tree and a sequence of distinct integer keys, there is only one way to fill these keys into the tree so that the resulting tree satisfies the definition of a BST. You are supposed to output the level order traversal sequence of that tree. The sample is illustrated by Figure 1 and 2.
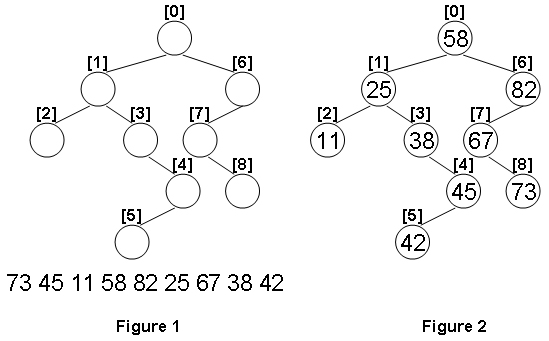
Input Specification:
Each input file contains one test case. For each case, the first line gives a positive integer N (≤100) which is the total number of nodes in the tree. The next N lines each contains the left and the right children of a node in the format left_index right_index, provided that the nodes are numbered from 0 to N−1, and 0 is always the root. If one child is missing, then −1 will represent the NULL child pointer. Finally N distinct integer keys are given in the last line.
Output Specification:
For each test case, print in one line the level order traversal sequence of that tree. All the numbers must be separated by a space, with no extra space at the end of the line.
Sample Input:
9
1 6
2 3
-1 -1
-1 4
5 -1
-1 -1
7 -1
-1 8
-1 -1
73 45 11 58 82 25 67 38 42
Sample Output:
58 25 82 11 38 67 45 73 42
#include <stdio.h>
#include <cstdio>
#include <string>
#include <string.h>
#include <math.h>
#include <algorithm>
#include <iostream>
#include <queue>
#include <vector>
#include <stack>
#include <map>
#include <set>
using namespace std;
int key[101];
typedef struct node //考察树的静态写法
{
int data,lchild=-1,rchild=-1;
}node;
vector<node>tree(1005);
void insert(int root,int &index) //插入函数是重点!!!中根遍历!!
{
if(root==-1)
return;
insert(tree[root].lchild,index);
tree[root].data=key[index++];
insert(tree[root].rchild,index);
}
void levelTraval(int root)
{
queue<int>q;
q.push(root);
int flag=0;
while(!q.empty())
{
int tmp=q.front();
q.pop();
if(flag==0)
{
printf("%d",tree[tmp].data);
flag=1;
}
else{
printf(" %d",tree[tmp].data);
}
if(tree[tmp].lchild!=-1)
q.push(tree[tmp].lchild);
if(tree[tmp].rchild!=-1)
q.push(tree[tmp].rchild);
}
}
int main(){
int n;
scanf("%d",&n);
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
int a,b;
scanf("%d %d",&a,&b);
if(a!=-1)
tree[i].lchild=a;
if(b!=-1)
tree[i].rchild=b;
}
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
scanf("%d",&key[i]);
}
sort(key,key+n);
int root=0,index=0;
insert(root,index);
levelTraval(root);
}
题目描述
判断两序列是否为同一二叉搜索树序列
输入描述:
开始一个数n,(1<=n<=20) 表示有n个需要判断,n= 0 的时候输入结束。 接下去一行是一个序列,序列长度小于10,包含(0~9)的数字,没有重复数字,根据这个序列可以构造出一颗二叉搜索树。 接下去的n行有n个序列,每个序列格式跟第一个序列一样,请判断这两个序列是否能组成同一颗二叉搜索树。
输出描述:
如果序列相同则输出YES,否则输出NO
示例1
输入
复制
2 567432 543267 576342 0
输出
复制
YES NO
#include <stdio.h>
#include <cstdio>
#include <string>
#include <string.h>
#include <math.h>
#include <algorithm>
#include <iostream>
#include <queue>
#include <vector>
#include <stack>
#include <map>
#include <set>
using namespace std;
typedef struct TreeNode
{
char data;
TreeNode *lchild,*rchild;
}TreeNode;
vector<char>v1,v2[1001];
TreeNode *insert(struct TreeNode *root,char x)
{
if(root==NULL)
{
root=(TreeNode*)malloc(sizeof(TreeNode));
root->data=x;
root->lchild=root->rchild=NULL;
return root;
}
else if(x<root->data)
{
root->lchild=insert(root->lchild,x);
}
else if(x>root->data)
{
root->rchild=insert(root->rchild,x);
}
return root;
}
void LayerTraval(struct TreeNode *root,vector<char> &v)
{
queue<TreeNode*>q;
q.push(root);
while(!q.empty())
{
TreeNode *t=q.front();
v.push_back(t->data);
//printf("%c",t->data);
q.pop();
if(t->lchild)
q.push(t->lchild);
if(t->rchild)
q.push(t->rchild);
}
}
int main(){
int n;
while(scanf("%d",&n)!=EOF)
{
if(n==0)
break;
char str1[1001]; //能用char[]尽量不用string,否则容易过不了测试点
scanf("%s",str1);
struct TreeNode *root=NULL;
for(int i=0;i<strlen(str1);i++)
root=insert(root,str1[i]);
LayerTraval(root,v1);
char str[1001][1001];
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
scanf("%s",str[i]);
struct TreeNode *root1=NULL;
for(int j=0;j<strlen(str[i]);j++)
{
root1=insert(root1,str[i][j]);
}
LayerTraval(root1,v2[i]);
int flag=0;
for(int j=0;j<v1.size();j++)
{
//printf("%d\n",v2[i][j]);
if(v1[j]!=v2[i][j])
{
printf("NO\n");
flag=1;
break;
}
}
if(flag==0)
printf("YES\n");
}
}
}





















 400
400











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








