前言
异步调用是处理高并发项目、减少程序处理时间的利器,我们可以通过开启多个线程、调用线程池等方式进行异步任务的处理,下面介绍一种注解方式实现异步调用的方法。
同步调用
既然有异步调用,那么对应的肯定是同步调用,我们先来看下同步调用
package com.example.test.async;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import java.util.Random;
/**
* @author zy
* @version 1.0.0
* @ClassName AsyncTest.java
* @Description TODO
* @createTime 2022/12/26
*/
@Component
public class AsyncTest {
public static Random random = new Random();
public void taskOne() throws Exception{
System.out.println("任务一开始");
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
Thread.sleep(random.nextInt(10000));
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("任务一耗时:"+(end-start)+"ms");
}
public void taskTwo() throws Exception{
System.out.println("任务二开始");
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
Thread.sleep(random.nextInt(10000));
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("任务二耗时:"+(end-start)+"ms");
}
public void taskThree() throws Exception{
System.out.println("任务三开始");
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
Thread.sleep(random.nextInt(10000));
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("任务三耗时:"+(end-start)+"ms");
}
}
@Test
void test() throws Exception{
asyncTest.taskOne();
asyncTest.taskTwo();
asyncTest.taskThree();
}
经过测试,三个方法依次执行

异步调用
上面的方法虽然执行起来没问题,但是执行时间比较长,若这三个任务本身之间不存在依赖关系,可以并发执行的话,同步调用在执行效率方面就比较差,可以考虑通过异步调用的方式来并发执行。只需要加上@Async注解即可将它们设置成异步方法,当然,需要在启动类上加上@EnableAsync注解
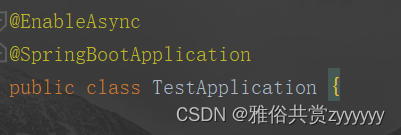
package com.example.test.async;
import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.Async;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import java.util.Random;
/**
* @author zy
* @version 1.0.0
* @ClassName AsyncTest.java
* @Description TODO
* @createTime 2022/12/26
*/
@Component
public class AsyncTest {
public static Random random = new Random();
@Async
public void taskOne() throws Exception{
System.out.println("任务一开始");
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
Thread.sleep(random.nextInt(10000));
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("任务一耗时:"+(end-start)+"ms");
}
@Async
public void taskTwo() throws Exception{
System.out.println("任务二开始");
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
Thread.sleep(random.nextInt(10000));
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("任务二耗时:"+(end-start)+"ms");
}
@Async
public void taskThree() throws Exception{
System.out.println("任务三开始");
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
Thread.sleep(random.nextInt(10000));
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("任务三耗时:"+(end-start)+"ms");
}
}
反复执行单元测试,可能会有不同结果:
- 没有任何任务相关的输出
- 有部分任务相关的输出
- 乱序的任务相关的输出
因为目前三个方法都是异步执行,主程序不会理会这三个任务是否主席给你完成,这就导致了输出不完整的情况。
注:@Async所修饰的函数不要定义为static类型,这样异步调用不会生效
异步回调
如果我们想要知道异步方法是否都执行完成了该怎么做呢?这就需要使用Future来返回异步结果。
package com.example.test.async;
import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.Async;
import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.AsyncResult;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import java.util.Random;
import java.util.concurrent.Future;
/**
* @author zy
* @version 1.0.0
* @ClassName AsyncTest.java
* @Description TODO
* @createTime 2022/12/26
*/
@Component
public class AsyncFutureTest {
public static Random random = new Random();
@Async
public Future<String> taskOne() throws Exception{
System.out.println("任务一开始");
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
Thread.sleep(random.nextInt(10000));
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("任务一耗时:"+(end-start)+"ms");
return new AsyncResult<>("任务一完成");
}
@Async
public Future<String> taskTwo() throws Exception{
System.out.println("任务二开始");
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
Thread.sleep(random.nextInt(10000));
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("任务二耗时:"+(end-start)+"ms");
return new AsyncResult<>("任务二完成");
}
@Async
public Future<String> taskThree() throws Exception{
System.out.println("任务三开始");
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
Thread.sleep(random.nextInt(10000));
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("任务三耗时:"+(end-start)+"ms");
return new AsyncResult<>("任务三完成");
}
}
void Test() throws Exception{
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
Future<String>task1 = asyncFutureTest.taskOne();
Future<String>task2 = asyncFutureTest.taskTwo();
Future<String>task3 = asyncFutureTest.taskThree();
for(;;){
if(task1.isDone() && task2.isDone() && task3.isDone()){
break;
}
Thread.sleep(100);
}
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("全部任务执行完成,耗时:"+(end-start)+"ms");
}
执行单元测试,结果如下

可以很清晰的看到,执行任务总耗时是小于三个任务顺序执行耗时的。






















 1万+
1万+











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










