一、JDBC概述
(一)什么是JDBC
JDBC全称Java DataBase Connectivity。Java数据库连接, 是Java语言中用来规范客户端程序如何来访问数据库的应用程序接口 ,提供了诸如查询和更新数据库中数据的方法。
(二)JDBC的由来
1.没有JDBC
在JDBC出现之前,Java语言要操作数据库,我们需要掌握具体的编程方式。而针对不同的数据库(MySQL、Oracle等),连接的方式会有较大差异,学习成本较高,数据库的切换也比较繁琐,改动较大。

2.使用JDBC
早期SUN公司的天才们想编写一套可以连接天下所有数据库的API,但是当他们刚刚开始时就发现这是不可完成的任务,因为各个厂商的数据库服务器差异太大了。后来SUN开始与数据库厂商们讨论,最终得出的结论是,由SUN提供一套访问数据库的规范(就是一组接口),并提供连接数据库的协议标准,然后各个数据库厂商会遵循SUN的规范提供一套访问自己公司的数据库服务器的API实现。SUN提供的规范命名为JDBC,而各个厂商提供的,遵循了JDBC规范的,可以访问自己数据库的API被称之为驱动!
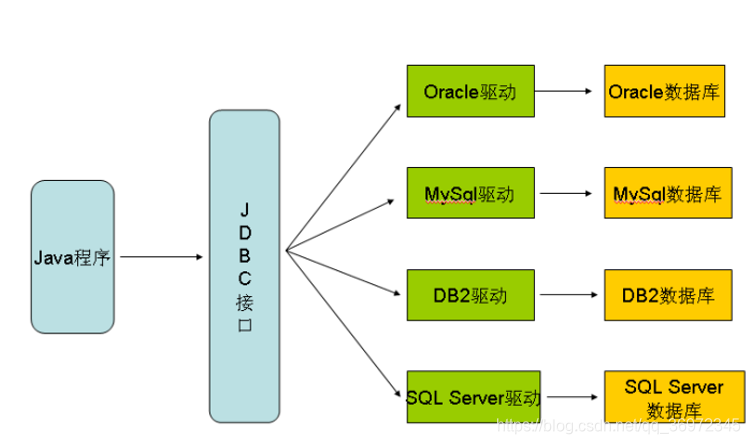
JDBC是接口,而JDBC驱动才是接口的实现,没有驱动无法完成数据库连接。每个数据库厂商都有自己的驱动,用来连接自己公司的数据库。
当然还有第三方公司专门为某一数据库提供驱动,这样的驱动往往不是开源免费的。
(三)JDBC核心类(接口)介绍
JDBC中的核心类(接口)有:DriverManager、Connection、Statement,和ResultSet(java.sql)。
1、DriverManager
DriverManger(驱动管理器)的作用有两个:
注册驱动:这可以让JDBC知道要使用的是哪个驱动。
获取Connection:如果可以获取到Connection,那么说明已经与数据库连接上了。
2、Connection
Connection对象表示连接,与数据库的通讯都是通过这个对象展开的。
Connection最为重要的一个方法就是用来获取Statement对象。
3、Statement
Statement是用来向数据库发送SQL语句的,这样数据库就会执行发送过来的SQL语句。
4、ResultSet
ResultSet对象表示查询结果集,只有在执行查询操作后才会有结果集的产生。结果集是一个二维的表格,有行有列。操作结果集要学习移动ResultSet内部的“行光标”,以及获取当前行上的每一列上的数据。
二、第一个JDBC程序
(一)数据准备
需求:查询出student表中的全部数据,展示在控制台上。
create table student(
id int primary key auto_increment,
name varchar(20),
age int,
birthday date
)
insert into student values(null,'张三',21,'2000-1-2');
insert into student values(null,'李四',22,'1999-2-3');
insert into student values(null,'王五',23,'1998-3-4');
insert into student values(null,'赵六',24,'1997-4-5');
(二)开发步骤
1.下载驱动jar包
下载地址:https://dev.mysql.com/downloads/connector/j/
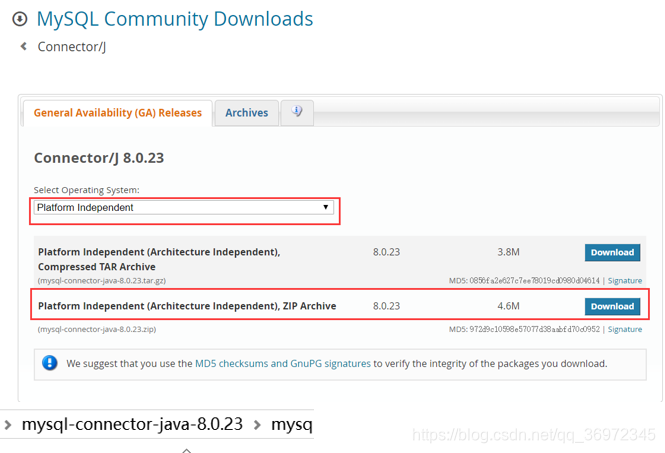
2.创建项目导入驱动
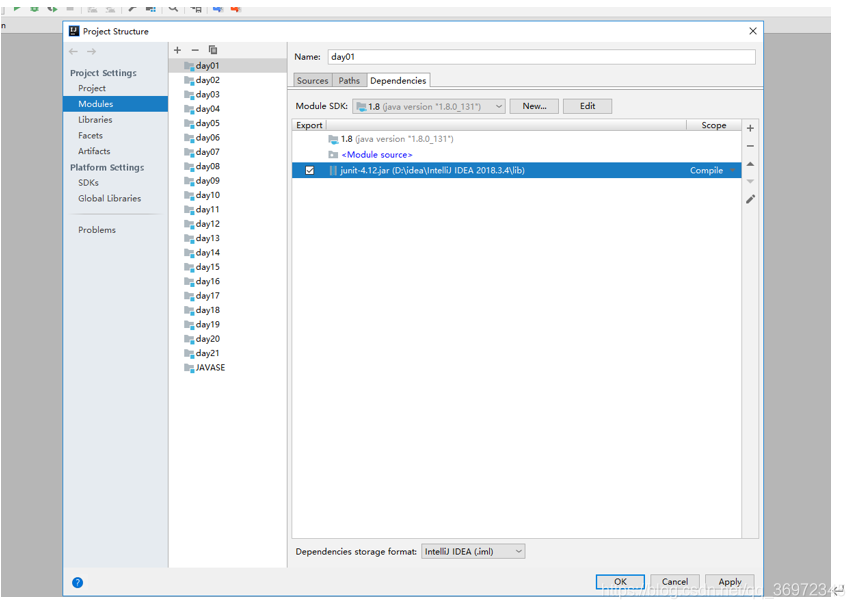
也可以创建一个目录lib然后把jar包移动到目录上右键ADD AS LIBIRARY
3.程序编写
1.加载驱动
作用:告诉JVM使用哪个驱动类。
语法
Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver");
8.0以前版本
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
2.获取连接
作用:获取到连接数据库的对象。
语法
Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mydb1?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8&useSSL=false&serverTimezone=UTC","root","mysql");
8.0以前版本
Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mydb1?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8","root","mysql");
3.获得执行SQL语句的对象
获取Statement对象,用来向数据库发送SQL语句。
通过Connection对象的createStatement()方法来获取。
语法
Statement st = conn.createStatement();
4.执行SQL
通过Statement对象把SQL语句发送给数据库执行。
executeUpdate(SQL语句)用来执行增、删、改语句。
executeQuery(SQL语句)用来执行查询语句。
语法
String sql = "select * from student";
ResultSet rs = st.executeQuery(sql);
5.处理结果集
ResultSet就是一张二维的表格,它内部有一个“行光标”,光标默认的位置在“第一行上方”,我们可以调用rs对象的next()方法把“行光标”向下移动一行,当第一次调用next()方法时,“行光标”就到了第一行记录的位置,这时就可以使用ResultSet提供的getXXX(int col)或getXXX(“列名”)方法来获取指定列的数据了。
next()方法有两层含义:第一,判断行光标是否可以移动。第二,移动行光标。
getXXX()方法有两种写法:getXXX(int col)或getXXX(“列名”)
rs.getInt(1);获取第一列数据
rs.getInt(“id”)获取id列数据
在ResultSet类中提供了一系列的getXXX()方法,比较常用的方法有:
Object getObject(int col或列名)
String getString(int col或列名)
int getInt(int col或列名)
double getDouble(int col或列名)
语法
while(rs.next()){
System.out.println(rs.getInt("id")+"\t"+rs.getString("name")+"\t"+rs.getInt("age")+"\t"+rs.getDate("birthday"));
}
6.释放资源
所谓释放资源是指开启的连接Connection、执行SQL语句的对象Statement、结果集ResultSet在使用完成后,必须关闭。
语法
rs.close();
st.close()
conn.close();
4.完整案例
package com.offcn.test;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.Statement;
public class JdbcTest1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
//加载驱动
Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver");
//获取连接
Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mydb1?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8&useSSL=false&serverTimezone=UTC","root","mysql");
//System.out.println(conn);
//获取执行SQL的对象
Statement st = conn.createStatement();
//执行SQL
String sql = "select * from student";
ResultSet rs = st.executeQuery(sql);
//处理结果集
while(rs.next()){
System.out.println(rs.getInt("id")+"\t"+rs.getString("name")+"\t"+rs.getInt("age")+"\t"+rs.getDate("birthday"));
}
rs.close();
st.close();
conn.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
5.规范代码
在jdbc操作中,资源必须释放,也就是说要保证释放资源的代码能够执行。在前面的程序中无法保证做到这点。如何保证只要资源开启成功就必须能够执行到释放资源的代码?可以使用try catch finally 结构。
Connection conn = null;
Statement st = null;
ResultSet rs = null;
try{
}catch(Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}finally{
if(rs!=null){
try {
rs.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(st!=null){
try {
st.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(conn!=null){
try {
conn.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
三、使用JDBC完成CRUD操作
(一)准备数据
使用第一个案例中的student表即可。
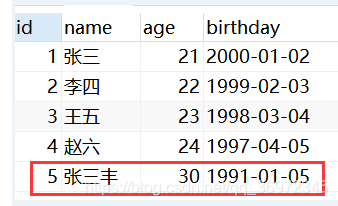
(二)添加数据
1、需求
从键盘录入数据,添加到student表中。
2、步骤
1、从控制台获取数据
2、加载驱动
3、获取连接Connection
4、获取执行SQL的对象Statement
5、拼接SQL语句
6、执行SQL
7、释放资源
3、示例代码
package com.offcn.test;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.sql.Statement;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Demo01 {
// 添加数据
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 1、获取控制台输入的数据
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入姓名");
String name = sc.nextLine();
System.out.println("请输入年龄");
String age = sc.nextLine();
System.out.println("请输入生日");
String birthday = sc.nextLine();
Connection conn = null;
Statement st = null;
try {
//2、加载驱动
Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver");
//3、获取连接
conn = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mydb1?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8&useSSL=false&serverTimezone=UTC","root","mysql");
// 4、获取执行SQL的对象Statement
st = conn.createStatement();
//5、拼接SQL
String sql = "insert into student values(null,'"+name+"',"+age+",'"+birthday+"')";
//6、执行SQL
int result = st.executeUpdate(sql);
// Statement的executeUpdate方法用来执行增、删、改语句。
// 返回值为数据库中受影响的数据的条数
System.out.println(result);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally{
//7、释放资源
if(st!=null){
try {
st.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(conn!=null){
try {
conn.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
(三)更新数据
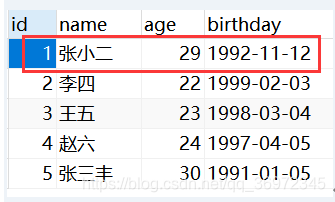
1、需求
根据键盘输入的内容,更新student表中的指定数据
2.步骤
1、从控制台获取数据
2、加载驱动
3、获取连接Connection
4、获取执行SQL的对象Statement
5、拼接SQL语句
6、执行SQL
7、释放资源
3、示例代码
package com.offcn.test;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.sql.Statement;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Demo02 {
//更新数据
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 1、输入数据
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入要更新的学生id");
String id = sc.nextLine();
System.out.println("请输入更新的姓名");
String name = sc.nextLine();
System.out.println("请输入更新的年龄");
String age = sc.nextLine();
System.out.println("请输入更新的生日");
String birthday = sc.nextLine();
Connection conn = null;
Statement st = null;
try {
//2、加载驱动
Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver");
//3、获取连接
conn = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mydb1?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8&useSSL=false&serverTimezone=UTC","root","mysql");
// 4、获取执行SQL的对象Statement
st = conn.createStatement();
//5、拼接SQL
String sql = "update student set name='"+name+"',age="+age+",birthday='"+birthday+"' where id="+id;
//6、执行SQL
int result = st.executeUpdate(sql);
// Statement的executeUpdate方法用来执行增、删、改语句。
// 返回值为数据库中受影响的数据的条数
System.out.println(result);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally{
if(st!=null){
try {
st.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(conn!=null){
try {
conn.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
(四)删除数据
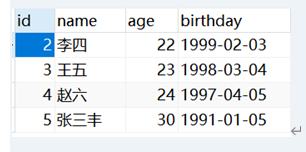
1、需求
根据输入的id删除student表中的指定数据。
2、步骤
1、从控制台获取数据
2、加载驱动
3、获取连接Connection
4、获取执行SQL的对象Statement
5、拼接SQL语句
6、执行SQL
7、释放资源
3.示例代码
package com.offcn.test;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.sql.Statement;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Demo03 {
// 删除指定数据
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 1、输入数据
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入要删除的学生id");
String id = sc.nextLine();
Connection conn = null;
Statement st = null;
try {
//2、加载驱动
Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver");
//3、获取连接
conn = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mydb1?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8&useSSL=false&serverTimezone=UTC","root","mysql");
// 4、获取执行SQL的对象Statement
st = conn.createStatement();
//5、拼接SQL
String sql = "delete from student where id="+id;
//6、执行SQL
int result = st.executeUpdate(sql);
// Statement的executeUpdate方法用来执行增、删、改语句。
// 返回值为数据库中受影响的数据的条数
System.out.println(result);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally{
if(st!=null){
try {
st.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(conn!=null){
try {
conn.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
(五)根据id查询
1、需求
根据键盘输入的id查询指定数据。
2、步骤
1、从控制台获取数据
2、加载驱动
3、获取连接Connection
4、获取执行SQL的对象Statement
5、拼接SQL语句
6、执行SQL
7、处理结果集合
8、释放资源
3、示例代码
package com.offcn.test;
import java.sql.*;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Demo04 {
//根据id查询数据
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 1、输入数据
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入要查询的学生id");
String id = sc.nextLine();
Connection conn = null;
Statement st = null;
ResultSet rs = null;
try {
//2、加载驱动
Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver");
//3、获取连接
conn = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mydb1?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8&useSSL=false&serverTimezone=UTC","root","mysql");
// 4、获取执行SQL的对象Statement
st = conn.createStatement();
//5、拼接SQL
String sql = "select * from student where id="+id;
//6、执行SQL
rs = st.executeQuery(sql);
//7、处理结果集
while(rs.next()){
System.out.println(rs.getInt("id")+"\t"+rs.getString("name")+"\t"+rs.getInt("age")+"\t"+rs.getDate("birthday"));
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally{
// 8、释放资源
if(rs!=null){
try {
st.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(st!=null){
try {
st.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(conn!=null){
try {
conn.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
(六)根据name模糊查询
1、需求
根据键盘输入的name值进行模糊查询。
2、步骤
1、从控制台获取数据
2、加载驱动
3、获取连接Connection
4、获取执行SQL的对象Statement
5、拼接SQL语句
6、执行SQL
7、处理结果集合
8、释放资源
3、示例代码
package com.offcn.test;
import java.sql.*;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Demo05 {
//根据name模糊查询数据
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 1、输入数据
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入要查询的学生姓名");
String name = sc.nextLine();
Connection conn = null;
Statement st = null;
ResultSet rs = null;
try {
//2、加载驱动
Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver");
//3、获取连接
conn = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mydb1?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8&useSSL=false&serverTimezone=UTC","root","mysql");
// 4、获取执行SQL的对象Statement
st = conn.createStatement();
//5、拼接SQL
String sql = "select * from student where name like '%"+name+"%'";
//6、执行SQL
rs = st.executeQuery(sql);
//7、处理结果集
while(rs.next()){
System.out.println(rs.getInt("id")+"\t"+rs.getString("name")+"\t"+rs.getInt("age")+"\t"+rs.getDate("birthday"));
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally{
// 8、释放资源
if(rs!=null){
try {
st.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(st!=null){
try {
st.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(conn!=null){
try {
conn.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
(七)封装JDBC工具类
通过上面的增、删、改、查操作我们发现,加载驱动、获取连接和释放资源都是重复操作。可以封装一个工具类,类中包括获取连接和释放资源的方法。
为了便于日后项目的修改和维护,数据库的连接信息可以存放在一个properties文件中。在工具类中读取信息。
src/db.properties
driverclass=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mydb1?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8&useSSL=false&serverTimezone=UTC
username=root
password=mysql
示例代码
public class JDBCUtils {
static String url = null;
static String username = null;
static String password = null;
static String dirverClass = null;
static {
try {
//获取配置文件中的相关配置
Properties pp = new Properties();
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("day01/db.properties");
pp.load(fis);
url = pp.getProperty("url");
username = pp.getProperty("username");
password = pp.getProperty("password");
dirverClass = pp.getProperty("dirverClass");
Class.forName(dirverClass);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static Connection getConnection(){
Connection con=null;
try {
con = DriverManager.getConnection(url,username,password);
} catch (SQLException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
return con;
}
public static void close(Connection conn, Statement stmt, ResultSet rs) {
if (rs != null) {
try {
rs.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {}
}
if (stmt != null) {
try {
stmt.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {}
}
if (conn != null) {
try {
conn.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {}
}
}
public static void close(Connection conn, Statement stmt) {
close(conn, stmt, null);
}
}





 本文详细介绍了JDBC的基本概念、历史背景,展示了如何使用JDBC进行数据库操作,包括创建连接、执行SQL和释放资源,以及如何封装工具类简化CRUD操作。涵盖了添加、更新、删除和查询数据,以及模糊查询和数据库连接配置。
本文详细介绍了JDBC的基本概念、历史背景,展示了如何使用JDBC进行数据库操作,包括创建连接、执行SQL和释放资源,以及如何封装工具类简化CRUD操作。涵盖了添加、更新、删除和查询数据,以及模糊查询和数据库连接配置。
















 473
473

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








