链表
实际内存中的布局图

单链表

应用实例

第一种添加:

按顺序添加:

删除:

修改思路:
1.先找到该节点,通过辅助变量
2.修改
package lianbiao;
/**
* @author : sky
* @version : 1.0
*/
public class SingleLinkedListDemo{
public static void main(String[] args) {
//先创建节点
HeroNode node1=new HeroNode(1,"宋江","及时雨");
HeroNode node2=new HeroNode(2,"卢俊义","玉麒麟");
HeroNode node3=new HeroNode(3,"吴用","智多星");
HeroNode node4=new HeroNode(4,"林冲","豹子头");
//再创建链表
SingleLinkedList sll=new SingleLinkedList();
//加入
/*sll.add1(node1);
sll.add1(node2);
sll.add1(node3);
sll.add1(node4);*/
sll.addByOrder(node1);
sll.addByOrder(node4);
sll.addByOrder(node2);
sll.addByOrder(node3);
//显示
System.out.println("原来链表:");
sll.list();
System.out.println("--------------------------------------------");
System.out.println("反转链表:");
SingleLinkedList.reverseList(sll.getHead());
sll.list();
System.out.println("--------------------------------------------");
System.out.println("逆序打印单链表~");
SingleLinkedList.reversePrint(sll.getHead());
System.out.println("--------------------------------------------");
//修改节点
HeroNode newNode=new HeroNode(2,"小卢","玉麒麟~~");
sll.update(newNode);
sll.delete(4);
System.out.println(SingleLinkedList.getLength(sll.getHead()));
sll.list();
System.out.println("--------------------------------------------");
HeroNode res=SingleLinkedList.findLastIndexNode(sll.getHead(),3);
System.out.println(res);
}
}
//定义管理英雄
class SingleLinkedList {
//先初始化一个头节点,头节点不要动,不存放具体数据
private HeroNode head=new HeroNode(0,"","");
public HeroNode getHead() {
return head;
}
//添加节点到单向链表,直接添加到链表的最后
//思路:当不考虑编号顺序时;1.找到当前链表的最后节点;2.将最后这个next指向新的节点
public void add(HeroNode heroNode){
//因为head节点不能动,所以需要一个辅助变量
HeroNode temp=head;
//遍历链表,找到最后
while(true){
if(temp.next==null){//找到了链表的最后
break;
}
temp=temp.next;//如果没有找到链表的最后,将temp后移
}
//当退出while循环时,temp就指向了链表的最后
//将最后这个节点next指向新的节点
temp.next=heroNode;
heroNode.next=null;
}
//第二种方式添加英雄,根据排名将英雄插入到指定位置
//如果有这个排名则给出提示添加失败
public void addByOrder(HeroNode heroNode){
//一个辅助变量
//因为时单链表,我们找的temp是要位于添加位置的前一个,否则插入不了
HeroNode temp=head;
//标志添加的编号是否存在,默认为false
boolean flag=false;
while(true){
if(temp.next==null){
break;
}
if(temp.next.no>heroNode.no){//位置找到了,在temp后加入
break;
}else if(temp.next.no==heroNode.no){//说明希望添加的节点已存在
flag=true;//说明编号存在
break;
}
temp=temp.next;//后移,遍历当前链表
}
//判断fla的值
if(flag){
System.out.printf("英雄编号 %d 已存在,不能再次加入\n",heroNode.no);
}else{
//插入到链表中,temp的后面
heroNode.next=temp.next;
temp.next=heroNode;
}
}
//修改节点的信息,根据no来修改,即no不能改
//1.根据heronode的no来修改即可
public void update(HeroNode heroNode){
//判断是否为空
if(head.next==null){
System.out.println("链表为空~");
return;
}
//定义辅助变量
HeroNode temp=head.next;
boolean flag=false;//表示是否找到该节点
//找到需要修改的节点
while(true){
if(temp==null){
break;//已经遍历完链表
}
if(temp.no==heroNode.no){
flag=true;//找到了
break;
}
temp=temp.next;
}
//根据flag判断是否找到要修改的节点
if(flag){
temp.name=heroNode.name;
temp.nickname=heroNode.nickname;
}else{
System.out.printf("没有找到编号为%d的节点,不能修改\n",heroNode.no);
}
}
//删除节点
//思路:1.head不能动,通过辅助节点temp找到删除节点的前一个节点
//2.说明我们在比较时,是temp next no与需要删除节点no比较
public void delete(int no){
//首先判断链表是否为空
if(head.next==null){
System.out.println("链表为空,不能删除节点~");
return;
}
HeroNode temp=head;//因为要指向删除节点的前一个,所以直接指向head
boolean flag=false;//标志是否找到待删除节点
while(true){
if(temp.next==null){//已经到了链表的最后
break;
}
if(temp.next.no==no){
//找到的待删除节点的前一个节点temp
flag=true;
break;
}
temp=temp.next;
}
if(flag){
//找到了,可以删除
temp.next=temp.next.next;
}else{
System.out.printf("编号为%d的节点没有找到,不能删除\n",no);
}
}
//显示链表,也就是遍历
public void list(){
//先判断链表是否为空
if(head.next==null){
System.out.println("链表为空");
return;
}
//因为head节点不能动,所以需要一个辅助变量遍历
HeroNode temp=head.next;
while(true){
if(temp==null){//找到了链表的最后
break;
}
//输出节点信息
System.out.println(temp);
//将temp后移
temp=temp.next;
}
}
//方法:获取单链表的节点的个数,如果是带有头节点的链表,不需要统计头节点
/**
* @param head 链表的头节点
* @return 返回的是有效节点的个数
*/
public static int getLength(HeroNode head){
if(head.next==null){//空链表
return 0;
}
int length=0;
HeroNode cur=head.next;
while(cur!=null){
length++;
cur=cur.next;
}
return length;
}
//查找单链表中倒数第k个节点
public static HeroNode findLastIndexNode(HeroNode head,int index){
//判断如果链表为空,返回null
if(head.next==null){
return null;
}
//1.第一次遍历得到链表的长度
int size=getLength(head);
//2.第二次遍历到size-index位置,就是倒数第k个节点
//先做一个数据的校验
if(index<=0||index>size){
return null;
}
//定义一个辅助变量
HeroNode cur=head.next;
for (int i = 0; i <(size-index) ; i++) {
cur=cur.next;
}
return cur;
}
//将单链表反转
public static void reverseList(HeroNode head){
//如果当前链表为空或者只有一个节点,就无需反转,直接返回
if(head.next==null||head.next.next==null){
return;
}
//顶一个辅助指针,帮助我们遍历原来的链表
HeroNode cur=head.next;
HeroNode curNext=null;//指向当前节点的下一个节点
HeroNode reverseHead=new HeroNode(0,"","");
//遍历原来的链表并放在reverseHead中
while(cur!=null){
curNext=cur.next;//现暂时保存当前节点的下一个节点,因为后面需要使用
cur.next=reverseHead.next;//单链表插入操作
reverseHead.next=cur;
cur=curNext;//让cur后移
}
//将head.next指向reverseHead.next,实现单链表反转
head.next=reverseHead.next;
}
//利用栈逆序打印链表
public static void reversePrint(HeroNode head){
if(head.next==null){
return;//空链表,不能打印
}
//创建一个栈,将各个节点压入栈中
Stack<HeroNode> stack=new Stack<>();
HeroNode cur=head.next;
//将链表的所有节点压入栈中
while(cur!=null){
stack.push(cur);
cur=cur.next;
}
//将栈中的节点进行打印
while (stack.size()>0){
System.out.println(stack.pop());
}
}
//合并两个有序链表
public static HeroNode mergeTwo(HeroNode head1,HeroNode head2){
HeroNode cur1=head1.next;
HeroNode cur2=head2.next;
HeroNode mergeHead=new HeroNode(0,"","");
HeroNode mergeCur=mergeHead;
while(cur1!=null&&cur2!=null){
if(cur1.no<=cur2.no){
mergeCur.next=cur1;
cur1=cur1.next;
mergeCur=mergeCur.next;
}else{
mergeCur.next=cur2;
cur2=cur2.next;
mergeCur=mergeCur.next;
}
}
mergeCur.next= cur1==null?cur2:cur1;
return mergeHead;
}
}
//定义HeroNode,每个HeroNode对象就是一个节点
class HeroNode{
public int no;
public String name;
public String nickname;
public HeroNode next;//指向下一个节点
//构造器
public HeroNode(int no, String name, String nickname) {
this.no = no;
this.name = name;
this.nickname = nickname;
}
//为了显示方便,重写toString方法
@Override
public String toString() {
return "HeroNode{" +
"no=" + no +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
", nickname='" + nickname + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
小结:
先定义一个节点类,再定义一个链表类,链表类里有增删改查各种方法
题目

1.求单链表中有效节点的个数
public static int getLength(HeroNode head){
if(head.next==null){//空链表
return 0;
}
int length=0;
HeroNode cur=head.next;
while(cur!=null){
length++;
cur=cur.next;
}
return length;
}
2.查找单链表中倒数第k个节点
思路:
1.编写一个方法,接收head节点,同时接收一个index
2.index表示是倒数第index个节点
3.先把链表从头到尾遍历一下,得到链表的总长度getLength
4.得到size后,我们从链表的第一个开始遍历,遍历(size-index)个,就可以得到
5.如果找到了,则返回该节点,找不到则返回null
//查找单链表中倒数第k个节点
public static HeroNode findLastIndexNode(HeroNode head,int index){
//判断如果链表为空,返回null
if(head.next==null){
return null;
}
//1.第一次遍历得到链表的长度
int size=getLength(head);
//2.第二次遍历到size-index位置,就是倒数第k个节点
//先做一个数据的校验
if(index<=0||index>size){
return null;
}
//定义一个辅助变量
HeroNode cur=head.next;
for (int i = 0; i <(size-index) ; i++) {
cur=cur.next;
}
return cur;
}
3.单链表的反转



//将单链表反转
public static void reverseList(HeroNode head){
//如果当前链表为空或者只有一个节点,就无需反转,直接返回
if(head.next==null||head.next.next==null){
return;
}
//顶一个辅助指针,帮助我们遍历原来的链表
HeroNode cur=head.next;
HeroNode curNext=null;//指向当前节点的下一个节点
HeroNode reverseHead=new HeroNode(0,"","");
//遍历原来的链表并放在reverseHead中
while(cur!=null){
curNext=cur.next;//现暂时保存当前节点的下一个节点,因为后面需要使用
cur.next=reverseHead.next;//单链表插入操作
reverseHead.next=cur;
cur=curNext;//让cur后移
}
//将head.next指向reverseHead.next,实现单链表反转
head.next=reverseHead.next;
}
4.从尾到头打印单链表
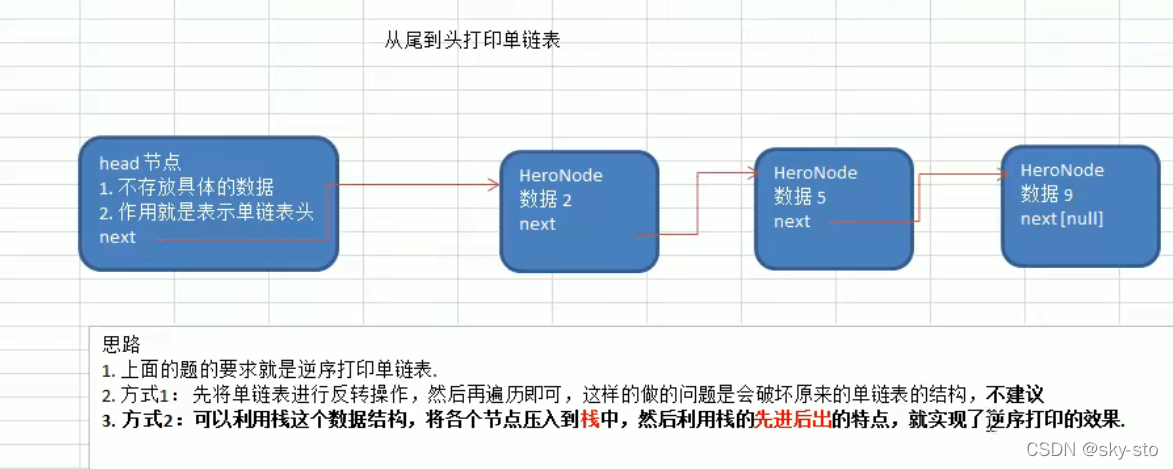
//利用栈逆序打印链表
public static void reversePrint(HeroNode head){
if(head.next==null){
return;//空链表,不能打印
}
//创建一个栈,将各个节点压入栈中
Stack<HeroNode> stack=new Stack<>();
HeroNode cur=head.next;
//将链表的所有节点压入栈中
while(cur!=null){
stack.push(cur);
cur=cur.next;
}
//将栈中的节点进行打印
while (stack.size()>0){
System.out.println(stack.pop());
}
}
5.合并两个有序的单链表,合并之后链表依然有序
合并两个升序链表思路如下:
1、新创建一个头结点,该头结点的数据域不存储数据,指针域存储指向链表中第一个元素,因为新链表中暂时还没有元素,所以头结点指向空。
2、从两个所给链表的第一个结点开始比较结点中数值的大小,将数值小的结点链入第一步创建的新链表的头结点后面。由于创建的新链表的头节点不能随意移动,所以需要一个辅助变量遍历新链表
3、如果两个链表中有一个链表的所有结点都已链接到新链表中而另一个链表还有剩余元素未链接到新链表中,则将这个链表中剩下的元素链入新链表中。
4、返回新链表的头节点
//合并两个有序(升序)链表
public static HeroNode mergeTwo(HeroNode head1,HeroNode head2){
HeroNode cur1=head1.next;
HeroNode cur2=head2.next;
HeroNode mergeHead=new HeroNode(0,"","");
HeroNode mergeCur=mergeHead;
while(cur1!=null&&cur2!=null){
if(cur1.no<=cur2.no){
mergeCur.next=cur1;
cur1=cur1.next;
mergeCur=mergeCur.next;
}else{
mergeCur.next=cur2;
cur2=cur2.next;
mergeCur=mergeCur.next;
}
}
mergeCur.next= cur1==null?cur2:cur1;
return mergeHead;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
//先创建节点
HeroNode node1=new HeroNode(1,"宋江","及时雨");
HeroNode node2=new HeroNode(3,"卢俊义","玉麒麟");
HeroNode node3=new HeroNode(4,"吴用","智多星");
HeroNode node4=new HeroNode(7,"林冲","豹子头");
//再创建链表
SingleLinkedList sll=new SingleLinkedList();
//加入
sll.add(node1);
sll.add(node2);
sll.add(node3);
sll.add(node4);
sll.list();
System.out.println("--------------------------------------------");
HeroNode node5=new HeroNode(2,"宋江","及时雨");
HeroNode node6=new HeroNode(4,"卢俊义","玉麒麟");
HeroNode node7=new HeroNode(6,"吴用","智多星");
HeroNode node8=new HeroNode(8,"林冲","豹子头");
//再创建链表
SingleLinkedList sll2=new SingleLinkedList();
//加入
sll2.add(node5);
sll2.add(node6);
sll2.add(node7);
sll2.add(node8);
sll2.list();
System.out.println("--------------------------------------------");
HeroNode newnode=SingleLinkedList.mergeTwo(sll.getHead(),sll2.getHead());
HeroNode curNew=newnode.next;
while(curNew!=null){
System.out.println(curNew);
curNew=curNew.next;
}
}
双向链表


package lianbiao;
/**
* @author : sky
* @version : 1.0
*/
public class DoubleLinkedListDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("双向链表的测试");
//先创建节点
DoubleNode node1=new DoubleNode(1,"宋江","及时雨");
DoubleNode node2=new DoubleNode(2,"卢俊义","玉麒麟");
DoubleNode node3=new DoubleNode(3,"吴用","智多星");
DoubleNode node4=new DoubleNode(4,"林冲","豹子头");
//在创建双向链表对象
DoubleLinkedList dll=new DoubleLinkedList();
/*dll.add(node1);
dll.add(node4);
dll.add(node3);
dll.add(node2);*/
dll.addByOrder(node1);
dll.addByOrder(node4);
dll.addByOrder(node3);
dll.addByOrder(node2);
dll.list();
//修改
DoubleNode node5=new DoubleNode(7,"公孙胜","入云龙");
dll.modify(node5);
System.out.println("修改后的链表情况");
dll.list();
//删除
dll.delete(4);
System.out.println("删除后的链表");
dll.list();
}
}
class DoubleLinkedList{
//先初始化一个头节点,头节点不要动,不存放具体数据
DoubleNode head=new DoubleNode(0,"","");
//返回头节点
public DoubleNode getHead(){
return head;
}
//遍历并显示
public void list(){
//首先判断双向链表是否为空
if(head.next==null){
System.out.println("双向链表为空!");
return;
}
DoubleNode temp=head.next;
while(true){
//判断是否已经遍历到链表尾
if(temp==null){
break;
}
System.out.println(temp);
temp=temp.next;
}
}
//添加,默认添加到队尾
public void add(DoubleNode doubleNode){
DoubleNode temp=head;
while(true){
//判断是否到了队尾
if(temp.next==null){
break;
}
temp=temp.next;
}//当退出while循环时,temp就指向了链表的最后
//形成一个双向链表
temp.next=doubleNode;
doubleNode.pre=temp;
}
//添加,按照编号顺序添加
//需要找的temp是位于添加位置的前一个,否则加入不进去
//这里需要判断是在队尾进行添加还是插入
public void addByOrder(DoubleNode doubleNode){
DoubleNode temp=head;
//标志需要添加的东西是否存在
boolean flag=false;
while(true){
if(temp.next==null){
break;
}
if(temp.next.no>doubleNode.no){//位置找到就在temp的后面插入
break;
}else if(temp.next.no==doubleNode.no){
flag=true;
break;
}
temp=temp.next;
}
if(flag){
System.out.printf("编号为%d的节点已经存在,不用添加\n",doubleNode.no);
}else{//插入到链表中temp的后面
if(temp.next==null){
temp.next=doubleNode;
doubleNode.pre=temp;
}else{
doubleNode.next=temp.next;
temp.next.pre=doubleNode;
temp.next=doubleNode;
doubleNode.pre=temp;
}
}
}
//修改节点
public void modify(DoubleNode doubleNode){
//首先判断链表是否为空
if(head.next==null){
System.out.println("链表为空,不能修改~");
return;
}
DoubleNode temp=head.next;
boolean flag=false;
while(true){
//遍历完了没找到
if(temp==null){
break;
}
if(temp.no==doubleNode.no){
flag=true;
break;
}
temp=temp.next;
}
if(flag){
temp.name=doubleNode.name;
temp.nickname=doubleNode.nickname;
}else{
System.out.printf("没有找到编号为%d的节点,不能修改\n",doubleNode.no);
}
}
//从双向链表中删除节点
//对于双向链表,我们可以直接找到要删除的节点,不需要找到要删除节点的前一个节点;找到后自我删除即可
public void delete(int no){
//首先判断链表是否为空
if(head.next==null){
System.out.println("链表为空,不能删除节点~");
return;
}
DoubleNode temp=head.next;//直接找到要删除的节点
boolean flag=false;
while(true){
//判断是否到了队尾没找到
if(temp==null){//实际上指向链表最后一个节点的next域
break;
}
if(temp.no==no){
flag=true;
break;
}
temp=temp.next;
}
if(flag){
temp.pre.next=temp.next;
//这里有问题,如果删除的是最后一个节点,就不需要执行下面这句话,否则会出现空指针异常
if(temp.next!=null){
temp.next.pre=temp.pre;
}
}else {
System.out.printf("没有找到编号为%d的节点,不能删除\n",no);
}
}
}
class DoubleNode{
public int no;
public String name;
public String nickname;
public DoubleNode next;//指向下一个节点,默认为null
public DoubleNode pre;//指向前一个节点,默认为null
//构造器
public DoubleNode(int no, String name, String nickname) {
this.no = no;
this.name = name;
this.nickname = nickname;
}
//为了显示方便,重写toString方法
@Override
public String toString() {
return "DoubleNode{" +
"no=" + no +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
", nickname='" + nickname + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
双向链表按顺序添加
//添加,按照编号顺序添加
//需要找的temp是位于添加位置的前一个,否则加入不进去
//这里需要判断是在队尾进行添加还是插入
public void addByOrder(DoubleNode doubleNode){
DoubleNode temp=head;
//标志需要添加的东西是否存在
boolean flag=false;
while(true){
if(temp.next==null){
break;
}
if(temp.next.no>doubleNode.no){//位置找到就在temp的后面插入
break;
}else if(temp.next.no==doubleNode.no){
flag=true;
break;
}
temp=temp.next;
}
if(flag){
System.out.printf("编号为%d的节点已经存在,不用添加\n",doubleNode.no);
}else{//插入到链表中temp的后面
if(temp.next==null){
temp.next=doubleNode;
doubleNode.pre=temp;
}else{
doubleNode.next=temp.next;
temp.next.pre=doubleNode;
temp.next=doubleNode;
doubleNode.pre=temp;
}
}
}
单向环形链表:约瑟夫问题



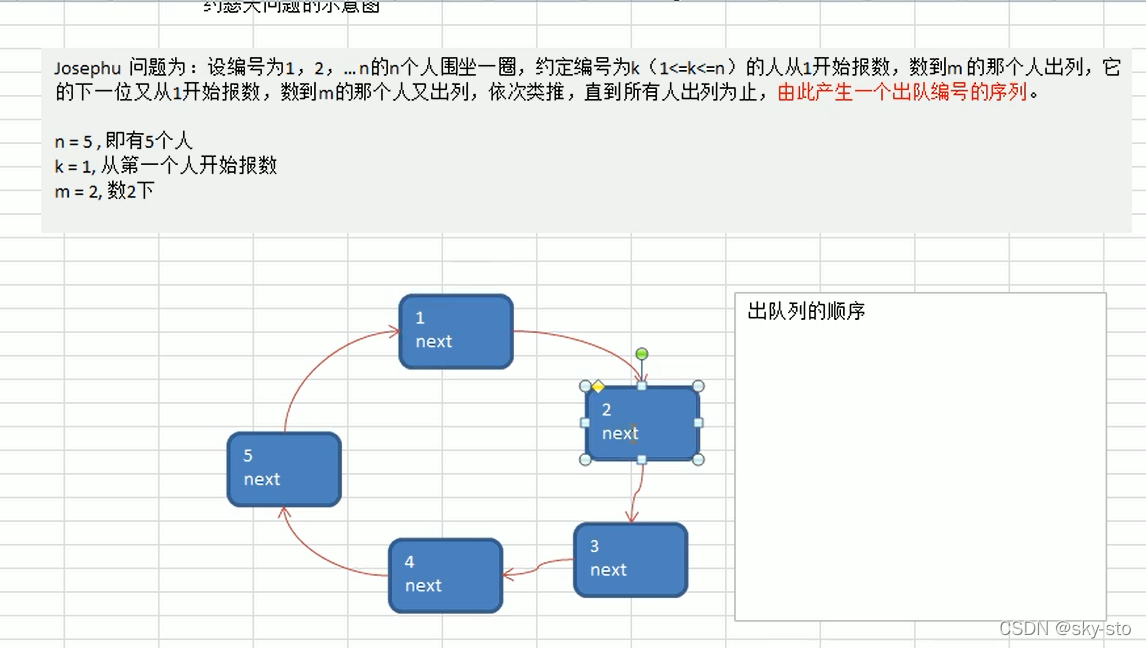


构建单项环形链表和遍历的思路:

//添加节点,构建成一个环形链表
public void add(int nums){
//对nums做一个数据校验
if(nums<1){
System.out.println("nums的值不正确");
return;
}
BoyNode curBoy=null;//辅助指针帮助构建环形链表
//使用for循环来创建环形链表
for (int i =1; i <=nums ; i++) {
//根据编号创建节点
BoyNode boy=new BoyNode(i);
//如果是第一个小孩
if(i==1){
first=boy;
first.setNext(first);//构成一个环,只有一个节点的环
curBoy=first;//让辅助指针指向第一个小孩
}else{
curBoy.setNext(boy);//连接到上一个
boy.setNext(first);//链接到first,构成环
curBoy=boy;//让curboy指向最新的boy
}
}
}
//遍历当前环形链表
public void showBoy(){
//判断链表是否为空
if(first==null){
System.out.println("链表为空,没有任何小孩");
return;
}
//因为first不能动,因此使用一个辅助指针完成遍历
BoyNode curBoy=first;
while(true){
System.out.printf("小孩的编号:%d\n",curBoy.getNo());
if(curBoy.getNext()==first){//说明遍历完毕
System.out.println("遍历结束");
break;
}
curBoy=curBoy.getNext();//curBoy后移
}
}
出圈的思路:
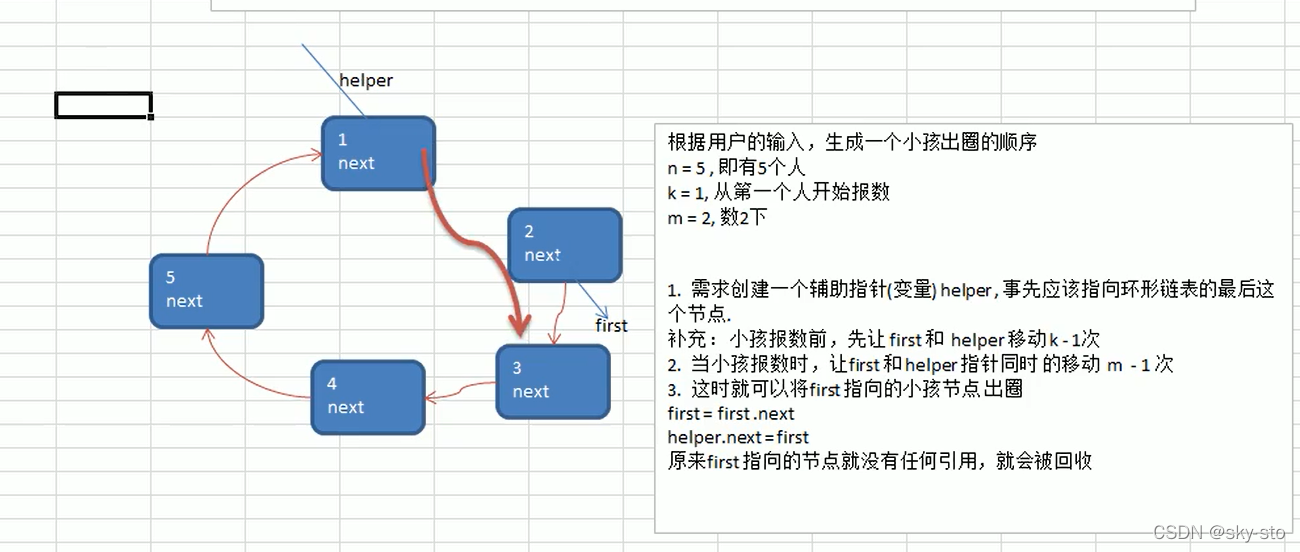
/**
*
* @param startNo 即约瑟夫问题的k,从谁开始数
* @param countNum 即约瑟夫问题的m,数几个数
* @param nums 表示最初有多少个小孩在圈中
*/
//根据用户的输入,生成一个小孩出队的顺序
/*
* 思路:
* 1.辅助指针需要指在待删除节点的前一个节点*/
public void countBoy(int startNo,int countNum,int nums){
//先对数据进行一个校验
if(first==null||startNo<1||startNo>nums){
System.out.println("参数输入有误,请重新输入");
return;
}
//创建要给的辅助指针,帮助完成小孩出圈
BoyNode helper=first;
while(true){
if(helper.getNext()==first){//说明helper指向最后的小孩节点
break;
}
helper=helper.getNext();
}
//小孩报数前,先让first和helper移动k-1次,即first移到编号为k的小孩那个位置
for (int i = 0; i <startNo-1 ; i++) {
first=first.getNext();
helper=helper.getNext();
}
//当小孩报数时,先让first和helper移动m-1次,即first移到要出去的小孩那个位置
while(true){
if(helper==first){//说明圈中只有一人
break;
}else{
for (int i = 0; i <countNum-1 ; i++) {
first=first.getNext();
helper=helper.getNext();
}
//这时,first指向的节点就是要出圈的节点
System.out.printf("小孩%d出圈\n",first.getNo());
//将first指向的小孩节点出圈
first=first.getNext();
helper.setNext(first);//相当于helper.next=first
}
}
//当退出while循环时,圈中就只有一个节点了
System.out.printf("最后留在圈中的小孩编号:%d\n",first.getNo());
}
}
package lianbiao;
import java.security.PublicKey;
/**
* @author : sky
* @version : 1.0
*/
public class Josephu {
public static void main(String[] args) {
CircleSingleLinkedList csll = new CircleSingleLinkedList();
csll.add(5);//加入5个小孩节点
csll.showBoy();
System.out.println("-------------------");
System.out.println(csll.getFirst());
//测试小孩出圈
csll.countBoy(1,2,5);//对应的顺序2->4->1->5->3
}
}
class CircleSingleLinkedList{
//创建一个first节点,当前没有编号
private BoyNode first=null;
public BoyNode getFirst() {
return first;
}
//添加节点,构建成一个环形链表
public void add(int nums){
//对nums做一个数据校验
if(nums<1){
System.out.println("nums的值不正确");
return;
}
BoyNode curBoy=null;//辅助指针帮助构建环形链表
//使用for循环来创建环形链表
for (int i =1; i <=nums ; i++) {
//根据编号创建节点
BoyNode boy=new BoyNode(i);
//如果是第一个小孩
if(i==1){
first=boy;
first.setNext(first);//构成一个环,只有一个节点的环
curBoy=first;//让辅助指针指向第一个小孩
}else{
curBoy.setNext(boy);//连接到上一个
boy.setNext(first);//链接到first,构成环
curBoy=boy;//让curboy指向最新的boy
}
}
}
//遍历当前环形链表
public void showBoy(){
//判断链表是否为空
if(first==null){
System.out.println("链表为空,没有任何小孩");
return;
}
//因为first不能动,因此使用一个辅助指针完成遍历
BoyNode curBoy=first;
while(true){
System.out.printf("小孩的编号:%d\n",curBoy.getNo());
if(curBoy.getNext()==first){//说明遍历完毕
System.out.println("遍历结束");
break;
}
curBoy=curBoy.getNext();//curBoy后移
}
}
/**
*
* @param startNo 即约瑟夫问题的k,从谁开始数
* @param countNum 即约瑟夫问题的m,数几个数
* @param nums 表示最初有多少个小孩在圈中
*/
//根据用户的输入,生成一个小孩出队的顺序
/*
* 思路:
* 1.辅助指针需要指在待删除节点的前一个节点*/
public void countBoy(int startNo,int countNum,int nums){
//先对数据进行一个校验
if(first==null||startNo<1||startNo>nums){
System.out.println("参数输入有误,请重新输入");
return;
}
//创建要给的辅助指针,帮助完成小孩出圈
BoyNode helper=first;
while(true){
if(helper.getNext()==first){//说明helper指向最后的小孩节点
break;
}
helper=helper.getNext();
}
//小孩报数前,先让first和helper移动k-1次,即first移到编号为k的小孩那个位置
for (int i = 0; i <startNo-1 ; i++) {
first=first.getNext();
helper=helper.getNext();
}
//当小孩报数时,先让first和helper移动m-1次,即first移到要出去的小孩那个位置
while(true){
if(helper==first){//说明圈中只有一人
break;
}else{
for (int i = 0; i <countNum-1 ; i++) {
first=first.getNext();
helper=helper.getNext();
}
//这时,first指向的节点就是要出圈的节点
System.out.printf("小孩%d出圈\n",first.getNo());
//将first指向的小孩节点出圈
first=first.getNext();
helper.setNext(first);//相当于helper.next=first
}
}
//当退出while循环时,圈中就只有一个节点了
System.out.printf("最后留在圈中的小孩编号:%d\n",first.getNo());
}
}
//表示节点
class BoyNode{
private int no;//编号
private BoyNode next;//指向下一个节点
public BoyNode(int no) {
this.no = no;
}
public int getNo() {
return no;
}
public void setNo(int no) {
this.no = no;
}
public BoyNode getNext() {
return next;
}
public void setNext(BoyNode next) {
this.next = next;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "BoyNode{" +
"no=" + no +
'}';
}
}








 本文详细介绍了链表的概念,包括单链表的应用实例、常见操作如添加、删除和修改节点。此外,还讨论了单链表的题目解决方案,如查找倒数第k个节点、链表反转等。接着,文章讲解了双向链表的顺序添加以及单向环形链表在约瑟夫问题中的应用。
本文详细介绍了链表的概念,包括单链表的应用实例、常见操作如添加、删除和修改节点。此外,还讨论了单链表的题目解决方案,如查找倒数第k个节点、链表反转等。接着,文章讲解了双向链表的顺序添加以及单向环形链表在约瑟夫问题中的应用。

















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








