1:PSNR
PSNR是最为常用的图像质量评估指标:

其中K为图像对应二进制位数,一般为8。MSE为均方误差,计算公式为:
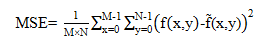
2:SSIM
SSIM[1]主要用来衡量图像结构完整性,是另一种比较常用的客观评估指标。实际应用中,一般用滑动窗口对图像进行分块,这里的滑动窗口一般为高斯窗口,并用高斯加权计算每个窗口的均值、方差和协方差。这样每块的SSIM计算如下:
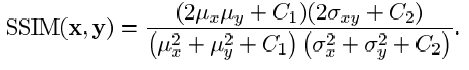
其中:
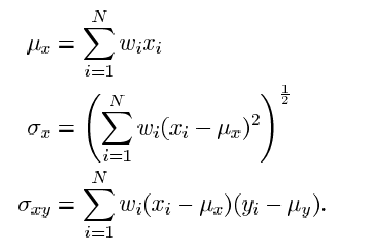
文献[1]给出公式中默认参数:窗口w为11*11的高斯窗口;其中K1=0.01,K2=0.02,L=255,C1=(K1*L)^2,C2=(K2*L)^2
3:代码
问题在于给定了一副彩色图片,彩色图片有RGB三通道,如何计算其PSNR或者SSIM值,方法有以下三种(以PSNR为例):
(1)计算彩色图像RGB三通道每一通道的PSNR值,然后求均值
(2)计算彩色图像RGB三通道每一通道的MSE值,求平均,然后再代入求PSNR
(3)求图像YUV空间中的Y分量,仅仅计算Y分量的PSNR值(YUV空间中Y表示亮度信息,UV分别为浓度偏移分量,在视频编解码中比较常用)
其中方法(2)和(3)比较常用,下面给出方法(2)和(3)的c++代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <opencv2\highgui\highgui.hpp>
#include <opencv2\imgproc\imgproc.hpp>
#include <opencv2\core\core.hpp>
using namespace std;
using namespace cv;
double getPSNR(const Mat& I1, const Mat& I2){
Mat s1;
absdiff(I1, I2, s1);
s1.convertTo(s1, CV_32F);
s1 = s1.mul(s1);
Scalar s = sum(s1);
double sse = s.val[0] + s.val[1] + s.val[2];
if(sse <= 1e-10)
return 0;
else{
double mse = sse/(double)(I1.channels()*I1.total());
double psnr = 10.0*log10(255*255/mse);
return psnr;
}
}
Scalar getMSSIM(const Mat& i1, const Mat& i2){
const double C1=6.5025, C2 = 58.5225;
int d = CV_32F;
Mat I1, I2;
i1.convertTo(I1, d);
i2.convertTo(I2, d);
Mat I2_2 = I2.mul(I2);
Mat I1_2 = I1.mul(I1);
Mat I1_I2 = I1.mul(I2);
Mat mu1, mu2;
GaussianBlur(I1, mu1, Size(11, 11), 1.5);
GaussianBlur(I2, mu2 ,Size(11, 11), 1.5);
Mat mu1_2 = mu1.mul(mu1);
Mat mu2_2 = mu2.mul(mu2);
Mat mu1_mu2 = mu1.mul(mu2);
Mat sigma1_2, sigma2_2, sigma12;
GaussianBlur(I1_2, sigma1_2, Size(11, 11), 1.5);
sigma1_2 -= mu1_2;
GaussianBlur(I2_2, sigma2_2, Size(11,11), 1.5);
sigma2_2 -= mu2_2;
GaussianBlur(I1_I2, sigma12, Size(11,11), 1.5);
sigma12 -= mu1_mu2;
Mat t1, t2, t3;
t1 = 2*mu1_mu2 + C1;
t2 = 2*sigma12 + C2;
t3 = t1.mul(t2);
t1 = mu1_2 + mu2_2 + C1;
t2 = sigma1_2 + sigma2_2 + C2;
t1 = t1.mul(t2);
Mat ssim_map;
divide(t3, t1, ssim_map);
Scalar mssim = mean(ssim_map);
return mssim;
}
int main(){
Mat i1 = imread("E:\\leetcode\\calcEvaluation\\1.jpg");
Mat i2 = imread("E:\\leetcode\\calcEvaluation\\2.jpg");
if(!i1.data || !i2.data){
cout << "图片路径有误!" << endl;
return -1;
}
cout << "PSNR: " << getPSNR(i1, i2) << endl;
Scalar result = getMSSIM(i1, i2);
if(i2.channels() == 3)
cout<< "SSIM: " << (result.val[0]+ result.val[1]+result.val[2])/3 << endl;
else cout << "SSIM: " << result.val[0] << endl;
Mat i11, i22;
cvtColor(i1, i11, COLOR_BGR2YUV);
cvtColor(i2, i22, COLOR_BGR2YUV);
vector<Mat> mv1, mv2;
split(i11, mv1);
split(i22, mv2);
cout << "Y 分量PSNR: " << getPSNR(mv1[0], mv2[0]) << endl;
cout << "Y 分量SSIM: " << getMSSIM(mv1[0], mv2[0]).val[0] << endl;
return 0;
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
最后参考网友[2]给出的一份matlab代码,仅针对方法(3)中的Y分量。
psnr.m:
function [PSNR, MSE] = psnr(X, Y)
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
%
% 计算峰值信噪比PSNR
% 将RGB转成YCbCr格式进行计算
% 如果直接计算会比转后计算值要小2dB左右(当然是个别测试)
%
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
if size(X,3)~=1 %判断图像时不是彩色图,如果是,结果为3,否则为1
org=rgb2ycbcr(X);
test=rgb2ycbcr(Y);
Y1=org(:,:,1);
Y2=test(:,:,1);
Y1=double(Y1); %计算平方时候需要转成double类型,否则uchar类型会丢失数据
Y2=double(Y2);
else %灰度图像,不用转换
Y1=double(X);
Y2=double(Y);
end
if nargin<2
D = Y1;
else
if any(size(Y1)~=size(Y2))
error('The input size is not equal to each other!');
end
D = Y1 - Y2;
end
MSE = sum(D(:).*D(:)) / numel(Y1);
PSNR = 10*log10(255^2 / MSE);
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
ssim.m
function [mssim, ssim_map] = ssim(img1, img2, K, window, L)
if (nargin < 2 | nargin > 5)
ssim_index = -Inf;
ssim_map = -Inf;
return;
end
if (size(img1) ~= size(img2))
ssim_index = -Inf;
ssim_map = -Inf;
return;
end
[M N] = size(img1);
if (nargin == 2)
if ((M < 11) | (N < 11))
ssim_index = -Inf;
ssim_map = -Inf;
return
end
window = fspecial('gaussian', 11, 1.5);
K(1) = 0.01;
K(2) = 0.03;
L = 255;
end
if (nargin == 3)
if ((M < 11) | (N < 11))
ssim_index = -Inf;
ssim_map = -Inf;
return
end
window = fspecial('gaussian', 11, 1.5);
L = 255;
if (length(K) == 2)
if (K(1) < 0 | K(2) < 0)
ssim_index = -Inf;
ssim_map = -Inf;
return;
end
else
ssim_index = -Inf;
ssim_map = -Inf;
return;
end
end
if (nargin == 4)
[H W] = size(window);
if ((H*W) < 4 | (H > M) | (W > N))
ssim_index = -Inf;
ssim_map = -Inf;
return
end
L = 255;
if (length(K) == 2)
if (K(1) < 0 | K(2) < 0)
ssim_index = -Inf;
ssim_map = -Inf;
return;
end
else
ssim_index = -Inf;
ssim_map = -Inf;
return;
end
end
if (nargin == 5)
[H W] = size(window);
if ((H*W) < 4 | (H > M) | (W > N))
ssim_index = -Inf;
ssim_map = -Inf;
return
end
if (length(K) == 2)
if (K(1) < 0 | K(2) < 0)
ssim_index = -Inf;
ssim_map = -Inf;
return;
end
else
ssim_index = -Inf;
ssim_map = -Inf;
return;
end
end
if size(img1,3)~=1
org=rgb2ycbcr(img1);
test=rgb2ycbcr(img2);
y1=org(:,:,1);
y2=test(:,:,1);
y1=double(y1);
y2=double(y2);
else
y1=double(img1);
y2=double(img2);
end
img1 = double(y1);
img2 = double(y2);
C1 = (K(1)*L)^2;
C2 = (K(2)*L)^2;
window = window/sum(sum(window));
mu1 = filter2(window, img1, 'valid');
mu2 = filter2(window, img2, 'valid');
mu1_sq = mu1.*mu1;
mu2_sq = mu2.*mu2;
mu1_mu2 = mu1.*mu2;
sigma1_sq = filter2(window, img1.*img1, 'valid') - mu1_sq;
sigma2_sq = filter2(window, img2.*img2, 'valid') - mu2_sq;
sigma12 = filter2(window, img1.*img2, 'valid') - mu1_mu2;
if (C1 > 0 & C2 > 0)
ssim_map = ((2*mu1_mu2 + C1).*(2*sigma12 + C2))./((mu1_sq + mu2_sq + C1).*(sigma1_sq + sigma2_sq + C2));
else
numerator1 = 2*mu1_mu2 + C1;
numerator2 = 2*sigma12 + C2;
denominator1 = mu1_sq + mu2_sq + C1;
denominator2 = sigma1_sq + sigma2_sq + C2;
ssim_map = ones(size(mu1));
index = (denominator1.*denominator2 > 0);
ssim_map(index) = (numerator1(index).*numerator2(index))./(denominator1(index).*denominator2(index));
index = (denominator1 ~= 0) & (denominator2 == 0);
ssim_map(index) = numerator1(index)./denominator1(index);
end
mssim = mean2(ssim_map);
return
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
- 123
- 124
- 125
- 126
- 127
- 128
- 129
- 130
- 131
- 132
- 133
- 134
- 135
- 136
- 137
- 138
- 139
- 140
- 141
- 142
- 143
- 144
- 145
- 146
- 147
- 148
- 149
- 150
- 151
- 152
- 153
- 154
- 155
- 156
- 157
- 158
- 159
- 160
- 161
- 162
- 163
- 164
- 165
- 166
- 167
- 168
- 169
- 170
- 171
- 172
- 173
- 174
- 175
- 176
- 177
- 178
- 179
- 180
- 181
- 182
- 183
- 184
- 185
- 186
- 187
- 188
- 189
- 190
- 191
- 192
- 193
- 194
- 195
- 196
- 197
- 198
- 199
- 200
- 201
- 202
- 203
- 204
- 205
- 206
- 207
- 208
- 209
- 210
- 211
- 212
- 213
- 214
- 215
- 216
- 217
- 218
- 219
- 220
- 221
- 222
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
- 123
- 124
- 125
- 126
- 127
- 128
- 129
- 130
- 131
- 132
- 133
- 134
- 135
- 136
- 137
- 138
- 139
- 140
- 141
- 142
- 143
- 144
- 145
- 146
- 147
- 148
- 149
- 150
- 151
- 152
- 153
- 154
- 155
- 156
- 157
- 158
- 159
- 160
- 161
- 162
- 163
- 164
- 165
- 166
- 167
- 168
- 169
- 170
- 171
- 172
- 173
- 174
- 175
- 176
- 177
- 178
- 179
- 180
- 181
- 182
- 183
- 184
- 185
- 186
- 187
- 188
- 189
- 190
- 191
- 192
- 193
- 194
- 195
- 196
- 197
- 198
- 199
- 200
- 201
- 202
- 203
- 204
- 205
- 206
- 207
- 208
- 209
- 210
- 211
- 212
- 213
- 214
- 215
- 216
- 217
- 218
- 219
- 220
- 221
- 222
参考文献
[1] Image Quality Assessment: From Error Visibility to Structural Similarity
[2]http://download.csdn.net/download/xiaohaijiejie/9058653
[3]http://blog.csdn.net/xiaxiazls/article/details/47952611
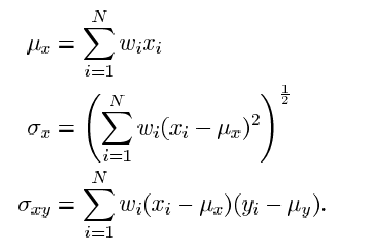









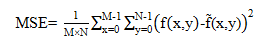
















 3506
3506

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








