链表
链表数据结构可能是继数组结构之后第二种使用广泛的数据结构,它可以取代数组,作为其他存储结构的基础,例如栈、队列,除非需要使用下标随机访问各个数据,否则多处都可以使用链表替代
链接点(Link)
在链表中,每个数据项都被包含在“链结点”(Link)中。一个链结点是某个类的对象,这个类可以叫做 Link。每个Link对象中都包含一个对下一个链结点引用的字段(通常叫做 next)
Link类定义的一部分,它包含了一些数据和下一个链结点的引用。这种类的定义有时叫做“自引用”式,因为它包含了和自己类型相同的字段。
class Link{
public int iData;
public double dData;
public Link next;
}
引用和基本类型
Link对象并没有真正包含另外一个Link对象,尽管看起来好像包含了。类型为 Link 的 next 字段仅仅是对另外一个 Link 对象的“引用”,而不是一个对象。一个引用是一个对某个对象的参照数值,它是一个计算机内存中的对象地址,不需要知道它的具体值。
- 例如 int 和 double 等基本类型的存储和对象存储是完全不同的,含有基本类型是实实在在的数值
double salary = 65000.00;
它在内存中创建了一个空间,并将数值放入其中。
Link aLink = someLink;
它把对 Link 对象的应用,叫做 someLink,放到变量 aLink 中,此处并没有创建对象,而只是对于 someLink的引用,创建对象必须用到 new 关键字。 someLink 字段也没有真正拥有对象,它也是一个引用,真正的对象在内存中的某个地方。
关系,而不是位置
在数组中,每一项占用一个特定的位置,这个位置可以用下标号直接访问;而在链表中,可以寻找一个特定的元素的唯一方法便是延着这个元素的链一直向下寻找;必须通过数据之间的关系来定位。
单链表

LinkList 类只包含一个数据项:即对链表中第一个链结点的引用,叫做 first。它是唯一的链表需要维护的永久信息,用以定位所有其他的链结点,从 first 出发,沿着链表通过每个链结点的next。
public class Link {
public int iData;
public double dData;
public Link next;
public Link(int iData, double dData) {
super();
this.iData = iData;
this.dData = dData;
}
public void displayLink() {
System.out.print("{" + this.iData + ", " + this.dData + "} ");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
LinkList list = new LinkList();
list.insertFirst(1, 1.1);
list.insertFirst(2, 2.2);
list.insertFirst(3, 3.3);
list.insertFirst(4, 4.4);
list.displayList();
list.deleteFirst();
list.displayList();
if (list.find(3) != null) {
list.find(3).displayLink();
System.out.println();
}
list.delete(3);
list.displayList();
}
}
class LinkList {
private Link first;
public LinkList() {
this.first = null;
}
public boolean isEmpty() {
return this.first == null;
}
public void insertFirst(int iData, double dData) {
Link newLink = new Link(iData, dData);
newLink.next = this.first;
this.first = newLink;
}
public Link deleteFirst() {
Link temp = this.first;
this.first = this.first.next;
return temp;
}
public Link find(int key) {
Link current = this.first;
while (current.iData != key) {
if (current.next == null) {
return null;
} else {
current = current.next;
}
}
return current;
}
public Link delete(int key) {
Link current = this.first;
Link previous = this.first;
while (current.iData != key) {
if (current.next == null) {
return null;
} else {
previous = current;
current = current.next;
}
}
if (current == this.first) {
this.first = this.first.next;
} else {
previous.next = current.next;
}
return current;
}
public void displayList() {
System.out.println("List (first-->last):");
Link current = first;
while (current != null) {
current.displayLink();
current = current.next;
}
System.out.println();
}
}
循环链表

public class LoopNode {
int data;
LoopNode next = this;
public LoopNode(int data) {
this.data = data;
}
public void after(LoopNode node) {
LoopNode nextNext = this.next;
this.next = node;
node.next = nextNext;
}
public int getData() {
return this.data;
}
public LoopNode next() {
return this.next;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
LoopNode node1 = new LoopNode(1);
LoopNode node2 = new LoopNode(2);
LoopNode node3 = new LoopNode(3);
LoopNode node4 = new LoopNode(4);
node1.after(node2);
node2.after(node3);
node3.after(node4);
System.out.println(node1.next().getData());
System.out.println(node2.next().getData());
System.out.println(node3.next().getData());
System.out.println(node4.next().getData());
}
}
双向循环链表
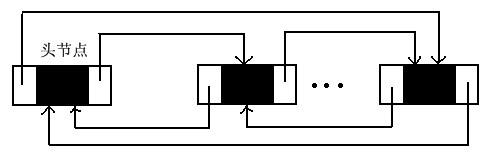
public class DoubleNode {
DoubleNode pre = this;
DoubleNode next = this;
int data;
public DoubleNode(int data) {
this.data = data;
}
// 增加节点
public void after(DoubleNode node) {
DoubleNode nextNext = this.next;
this.next = node;
node.pre = this;
node.next = nextNext;
nextNext.pre = node;
}
public DoubleNode pre() {
return this.pre;
}
public DoubleNode next() {
return this.next;
}
public int getData() {
return this.data;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
DoubleNode node1 = new DoubleNode(1);
DoubleNode node2 = new DoubleNode(2);
DoubleNode node3 = new DoubleNode(3);
DoubleNode node4 = new DoubleNode(4);
node1.after(node2);
node2.after(node3);
node3.after(node4);
System.out.println(node1.pre().getData());
System.out.println(node1.next().next().getData());
System.out.println(node1.next().pre().getData());
}
}
扩展
算法题-反转链表
输入一个链表,反转链表后,输出新链表的表头。
/*
public class ListNode {
int val;
ListNode next = null;
ListNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
}*/
public class Solution {
public ListNode ReverseList(ListNode head) {
if (head == null) {
return null;
}
ListNode pre = null;
ListNode next = null;
// 如 1-2-3-4-5-null
while (head != null) {
// 2-3-4-5-null
next = head.next;
// 1-null
head.next = pre;
// 1-null
pre = head;
// 2-3-4-5-null
head = next;
}
return pre;
}
}
算法题-删除链表中重复的结点
在一个排序的链表中,存在重复的结点,请删除该链表中重复的结点,重复的结点不保留,返回链表头指针。 例如,链表1->2->3->3->4->4->5 处理后为 1->2->5
/*
public class ListNode {
int val;
ListNode next = null;
ListNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
}
*/
public class Solution {
public ListNode deleteDuplication(ListNode pHead)
{
if (pHead == null) {
return null;
}
// 备用头节点,因为头节点可能删除
ListNode firstNode = new ListNode(-1);
firstNode.next = pHead;
ListNode cur = pHead;
// 前节点
ListNode pre = firstNode;
while (cur != null && cur.next != null) {
// 两节点相等
if (cur.val == cur.next.val) {
// 记录val值,循环判断后面是否有相同值的节点
int val = cur.val;
// 循环跳过,删除
while (cur != null && cur.val == val) {
cur = cur.next;
}
// 删除操作,直接指向不同于val值的第一个节点
pre.next = cur;
}else{
pre = cur;
cur = cur.next;
}
}
return firstNode.next;
}
}






















 100
100











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








