前言
启动服务-基本使用
通过将 Intent 传递给 startService() 或 startForegroundService(),从 Activity 或其他应用组件启动服务。Android 系统会调用服务的 onStartCommand() 方法,并向其传递 Intent,从而指定要启动的服务。
Intent intent = new Intent(this, MyService.class);
startService(intent);
MyService.java
public class MyService extends Service {
private static final String TAG = MyService.class.getSimpleName();
@Override
public void onCreate() {
super.onCreate();
Log.e(TAG, "onCreate: ");
}
@Override
public int onStartCommand(Intent intent, int flags, int startId) {
Log.e(TAG, "onStartCommand: ");
return super.onStartCommand(intent, flags, startId);
}
@Override
public boolean stopService(Intent name) {
Log.e(TAG, "stopService: ");
return super.stopService(name);
}
@Override
public void onDestroy() {
Log.e(TAG, "onDestroy: ");
super.onDestroy();
}
}
startService() 方法会立即返回,并且 Android 系统会调用目的服务的 onStartCommand() 方法。如果服务尚未运行,则系统首先会调用 onCreate(),然后调用 onStartCommand()。
如果服务亦未提供绑定,则应用组件与服务间的唯一通信模式便是使用 startService() 传递的 Intent。但是,如果您希望服务返回结果,则启动服务的客户端可以为广播(通过 getBroadcast() 获得)创建一个 PendingIntent,并将其传递给启动服务的 Intent 中的服务。然后,服务便可使用广播传递结果。 todo lgy
多个服务启动请求会导致多次对服务的 onStartCommand() 进行相应的调用。但是,如要停止服务,只需一个服务停止请求(service使用 stopSelf() 或 客户端stopService())即可。
停止服务-基本使用
启动服务必须管理自己的生命周期。换言之,系统不会停止或销毁服务,并且服务在 onStartCommand() 返回后仍会继续运行。服务必须通过调用 stopSelf() 自行停止运行,或由另一个组件通过调用 stopService() 来停止它。
注意:为避免浪费系统资源和消耗电池电量,请确保应用在工作完成之后停止其服务。如有必要,其他组件可通过调用 stopService() 来停止服务。
附上生命周期图:
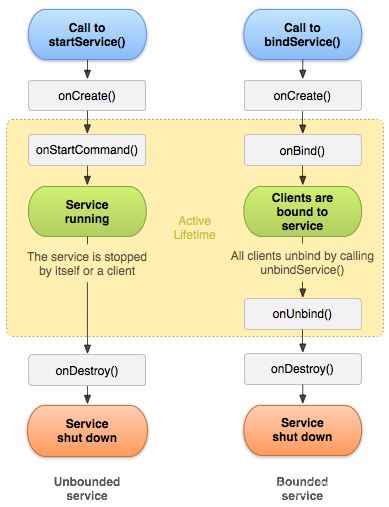
service的启动原理
下面就开始从framework源码焦点探究StartService启动服务的调度流程
\frameworks\base\core\java\android\app.ContextImpl.java
@Override
public ComponentName startService(Intent service) {
warnIfCallingFromSystemProcess();
return startServiceCommon(service, false, mUser);
}
\frameworks\base\core\java\android\app.ContextImpl.java
private ComponentName startServiceCommon(Intent service, boolean requireForeground,
UserHandle user) {
try {
validateServiceIntent(service);
service.prepareToLeaveProcess(this);
//调度AMS 开启服务
ComponentName cn = ActivityManager.getService().startService(
mMainThread.getApplicationThread(), service, service.resolveTypeIfNeeded(
getContentResolver()), requireForeground,
getOpPackageName(), user.getIdentifier());
...
}
framework\frameworks\base\services\core\java\com\android\server\am\ActivityManagerService.java
public ComponentName startService(IApplicationThread caller, Intent service,
String resolvedType, boolean requireForeground, String callingPackage, int userId)
throws TransactionTooLargeException {
...
try {
//mServices 是ActiveServices实例,
//ActiveServices专门用于管理service的生命周期和处理客户端与服务端之间的调度
res = mServices.startServiceLocked(caller, service,
resolvedType, callingPid, callingUid,
requireForeground, callingPackage, userId);
} finally {
Binder.restoreCallingIdentity(origId);
}
...
}
frameworks\base\services\core\java\com\android\server\am\ActiveServices.java
ComponentName startServiceLocked(IApplicationThread caller, Intent service, String resolvedType,
int callingPid, int callingUid, boolean fgRequired, String callingPackage, final int userId)
throws TransactionTooLargeException {
...
//根据请求的Intent去查找ServiceLookupResult,
//每个进程的每个Service都在ams中保存着ServiceRecord对象
ServiceLookupResult res =
retrieveServiceLocked(service, resolvedType, callingPackage,
callingPid, callingUid, userId, true, callerFg, false, false);
if (res == null) {
return null;
}
if (res.record == null) {
return new ComponentName("!", res.permission != null
? res.permission : "private to package");
}
//取出对应的ServiceRecord对象
ServiceRecord r = res.record;
...
//把该服务的启动事件加入到排序队列
r.pendingStarts.add(new ServiceRecord.StartItem(r, false, r.makeNextStartId(),
service, neededGrants, callingUid));
...
//startServiceInnerLocked()进行启动服务
ComponentName cmp = startServiceInnerLocked(smap, service, r, callerFg, addToStarting);
return cmp;
}
frameworks\base\services\core\java\com\android\server\am\ActiveServices.java
ComponentName startServiceInnerLocked(ServiceMap smap, Intent service, ServiceRecord r,
boolean callerFg, boolean addToStarting) throws TransactionTooLargeException {
...
//在bringUpServiceLocked进行下一步工作
String error = bringUpServiceLocked(r, service.getFlags(), callerFg, false, false);
...
}
frameworks\base\services\core\java\com\android\server\am\ActiveServices.java
private ServiceLookupResult retrieveServiceLocked(Intent service,
String resolvedType, String callingPackage, int callingPid, int callingUid, int userId,
boolean createIfNeeded, boolean callingFromFg, boolean isBindExternal,
boolean allowInstant) {
ServiceRecord r = null;
...
/*
获取已安装应用所有的、已记录的service
ServiceMap 是ActiveServices的内部类,专门用于记录进程的service,
内有维护两个ArrayMap:
ArrayMap<ComponentName, ServiceRecord> mServicesByName、
ArrayMap<Intent.FilterComparison, ServiceRecord>mServicesByIntent
*/
ServiceMap smap = getServiceMapLocked(userId);
//获取目的service的Component
final ComponentName comp = service.getComponent();
if (comp != null) {
//根据Component获取service对象
r = smap.mServicesByName.get(comp);
if (DEBUG_SERVICE && r != null) Slog.v(TAG_SERVICE, "Retrieved by component: " + r);
}
if (r == null && !isBindExternal) {
Intent.FilterComparison filter = new Intent.FilterComparison(service);
//根据intent获取service对象
r = smap.mServicesByIntent.get(filter);
if (DEBUG_SERVICE && r != null) Slog.v(TAG_SERVICE, "Retrieved by intent: " + r);
}
...
if (r == null) {//如果没获取到
...
//去pms中获取目的service所属应用的信息
ResolveInfo rInfo = mAm.getPackageManagerInternalLocked().resolveService(service,
resolvedType, flags, userId, callingUid);
ServiceInfo sInfo = rInfo != null ? rInfo.serviceInfo : null;
...
//新建service应用对应的ComponentName实例
ComponentName name = new ComponentName(
sInfo.applicationInfo.packageName, sInfo.name);
...
//新建ServiceRecord对象,加入到mServicesByName队列
r = new ServiceRecord(mAm, ss, name, filter, sInfo, callingFromFg, res);
res.setService(r);
smap.mServicesByName.put(name, r);
smap.mServicesByIntent.put(filter, r);
...
if (r != null) {
......
return new ServiceLookupResult(r, null);
}
return null;
}
...
}
frameworks\base\services\core\java\com\android\server\am\ActiveServices.java
private String bringUpServiceLocked(ServiceRecord r, int intentFlags, boolean execInFg,
boolean whileRestarting, boolean permissionsReviewRequired)
throws TransactionTooLargeException {
//r.app是在调度执行service.onCreate()之前赋值的,对于还没初始化的service对应的ServiceRecord对象(r)的app实例(r.app)是未赋值。
//目的service的应用存在且整在系统中运行
if (r.app != null && r.app.thread != null) {
//调度目的service的onStartCommand()方法,并退出当前方法
sendServiceArgsLocked(r, execInFg, false);
return null;
}
...
ProcessRecord app;
if (!isolated) {
//根据目的service的包名,向ams获取目的service进程的ProcessRecord实例
app = mAm.getProcessRecordLocked(procName, r.appInfo.uid, false);
if (DEBUG_MU) Slog.v(TAG_MU, "bringUpServiceLocked: appInfo.uid=" + r.appInfo.uid
+ " app=" + app);
if (app != null && app.thread != null) {
try {
app.addPackage(r.appInfo.packageName, r.appInfo.longVersionCode, mAm.mProcessStats);
//在realStartServiceLocked()里赋值r(ServiceRecord)的app对象和调用sendServiceArgsLocked()方法,并退出当前方法
//>>>备注1:该方法的探究在下面的app启动后讲解
realStartServiceLocked(r, app, execInFg);
return null;
}
...
}
...
}
//如果在ams中获取到目的service的程序信息对象app为空,则说明目的service的进程未启动
if ((app == null || (app != null && app.pid == 0)) && !permissionsReviewRequired) {
...
//启动目的进程
if ((app = mAm.startProcessLocked(procName, r.appInfo, true, intentFlags,
hostingType, r.name, false, isolated, false)) == null)
...
}
...
//排队启动service的列表中未包含该service记录,则加入排队队列,这里加入排队是为了ams启动新进程后,根据mPendingServices
if (!mPendingServices.contains(r)) {
mPendingServices.add(r);
}
...
return null;
}
对于目的启动的service的所属进程未启动的情况,按照上面源码可知:执行ams请求打开app,并在ActiveServices.mPendingServices数组中加入该服务的作为待启动的标识,待应用启动后,读取mPendingServices中的标识,进行对目的服务启动。
回顾下app启动的基本流程
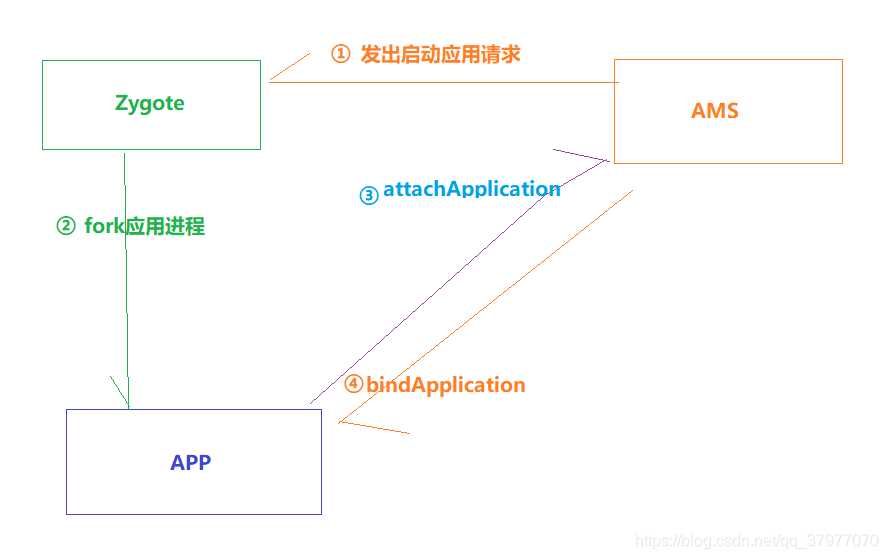
下面就开始跟进下应用启动后怎么读取标识。进而启动服务。
framework\frameworks\base\services\core\java\com\android\server\am\ActivityManagerService.java
@Override
public final void attachApplication(IApplicationThread thread, long startSeq) {
synchronized (this) {
int callingPid = Binder.getCallingPid();
final int callingUid = Binder.getCallingUid();
final long origId = Binder.clearCallingIdentity();
//核心执行记录app信息的方法
attachApplicationLocked(thread, callingPid, callingUid, startSeq);
Binder.restoreCallingIdentity(origId);
}
}
接下来看看attachApplicationLocked()
@GuardedBy("this")
private final boolean attachApplicationLocked(IApplicationThread thread,
int pid, int callingUid, long startSeq) {
...
// Find any services that should be running in this process...
if (!badApp) {
try {
//mServices是ActivwServices的实例,attachApplicationLocked执行j记录进程的service信息
didSomething |= mServices.attachApplicationLocked(app, processName);
checkTime(startTime, "attachApplicationLocked: after mServices.attachApplicationLocked");
} catch (Exception e) {
Slog.wtf(TAG, "Exception thrown starting services in " + app, e);
badApp = true;
}
}
...
}
frameworks\base\services\core\java\com\android\server\am\ActiveServices.java
boolean attachApplicationLocked(ProcessRecord proc, String processName)
throws RemoteException {
boolean didSomething = false;
// Collect any services that are waiting for this process to come up.
//查看是否有service在排队队列待初始化
if (mPendingServices.size() > 0) {
ServiceRecord sr = null;
try {
for (int i=0; i<mPendingServices.size(); i++) {
sr = mPendingServices.get(i);
if (proc != sr.isolatedProc && (proc.uid != sr.appInfo.uid
|| !processName.equals(sr.processName))) {
continue;
}
mPendingServices.remove(i);
i--;
proc.addPackage(sr.appInfo.packageName, sr.appInfo.longVersionCode,
mAm.mProcessStats);
//调用realStartServiceLocked中将ServiceRecord实例sr的app对象赋值且执行service的onCreate()
realStartServiceLocked(sr, proc, sr.createdFromFg);
...
}
frameworks\base\services\core\java\com\android\server\am\ActiveServices.java
private final void realStartServiceLocked(ServiceRecord r,
ProcessRecord app, boolean execInFg) throws RemoteException {
...
//赋值r.app
r.app = app;
...
//通过app.thread得到目的进程(ActivityTHread),调度service的onCreate()方法
app.thread.scheduleCreateService(r, r.serviceInfo,
mAm.compatibilityInfoForPackageLocked(r.serviceInfo.applicationInfo),
app.repProcState);
...
//执行sendServiceArgsLocked()调度onStartCommand()
sendServiceArgsLocked(r, execInFg, true);
...
}
跟进下,看看怎么调度到新进程的Service.onCreate()
frameworks\base\core\java\android\app\ActivityThread.java
private void handleCreateService(CreateServiceData data) {
...
Service service = null;
try {
java.lang.ClassLoader cl = packageInfo.getClassLoader();
//根据CreateServiceData参数活得要启动的service的类名,进而通过类加载器实例化Service对象
service = packageInfo.getAppFactory()
.instantiateService(cl, data.info.name, data.intent);
}
...
Application app = packageInfo.makeApplication(false, mInstrumentation);
//将Service对象和application进行关联
service.attach(context, this, data.info.name, data.token, app,
ActivityManager.getService());
//执行service.onCreate()
service.onCreate();
//mServices存储当前进行里所有生命周期活跃的Service对象
mServices.put(data.token, service);
...
}
service执行完oncreate()方法后,紧接着目的是执行service.onStartCommand()。
private final void sendServiceArgsLocked(ServiceRecord r, boolean execInFg,
boolean oomAdjusted) throws TransactionTooLargeException {
//查看待start的服务数量,如果没有则return
final int N = r.pendingStarts.size();
if (N == 0) {
return;
}
...
//调度服务端进程的onStartCommand(),slice记录了时间,分发服务次数等参数
r.app.thread.scheduleServiceArgs(r, slice);
...
}
frameworks\base\core\java\android\app\ActivityThread.java
public final void scheduleServiceArgs(IBinder token, ParceledListSlice args) {
List<ServiceStartArgs> list = args.getList();
for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) {
ServiceStartArgs ssa = list.get(i);
ServiceArgsData s = new ServiceArgsData();
s.token = token;
s.taskRemoved = ssa.taskRemoved;
s.startId = ssa.startId;
s.flags = ssa.flags;
s.args = ssa.args;
//SERVICE_ARGS消息处理
sendMessage(H.SERVICE_ARGS, s);
}
}
frameworks\base\core\java\android\app\ActivityThread.java
private void handleServiceArgs(ServiceArgsData data) {
//获取目的Service对象
Service s = mServices.get(data.token);
if (s != null) {
try {
if (data.args != null) {
data.args.setExtrasClassLoader(s.getClassLoader());
data.args.prepareToEnterProcess();
}
int res;
if (!data.taskRemoved) {
//执行onStartCommand
res = s.onStartCommand(data.args, data.flags, data.startId);
}
...
}
小结
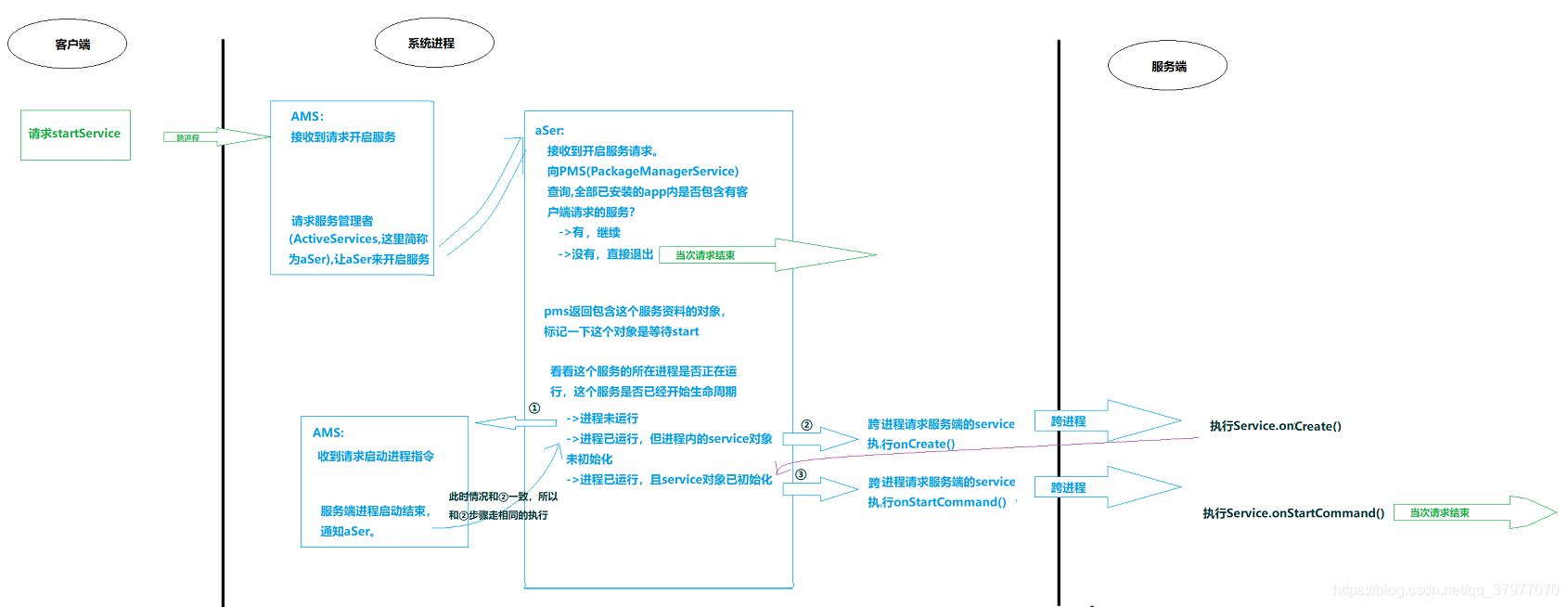
关于startService的调度不算复杂,在上图中,再次把主要的调度流程列出。在开启服务过程中涉及3个进程,分别问请求服务端进程、系统进程、服务端进程。假如zygote进程一开始未启动,则还涉及zygote进程,zygote进程fork启动服务端进程。假如在源码探究过程中还理不清楚代码逻辑,可上图与源码结合学习分析。
























 321
321











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








