本题重点在于怎么个复制法(包含random指针)。
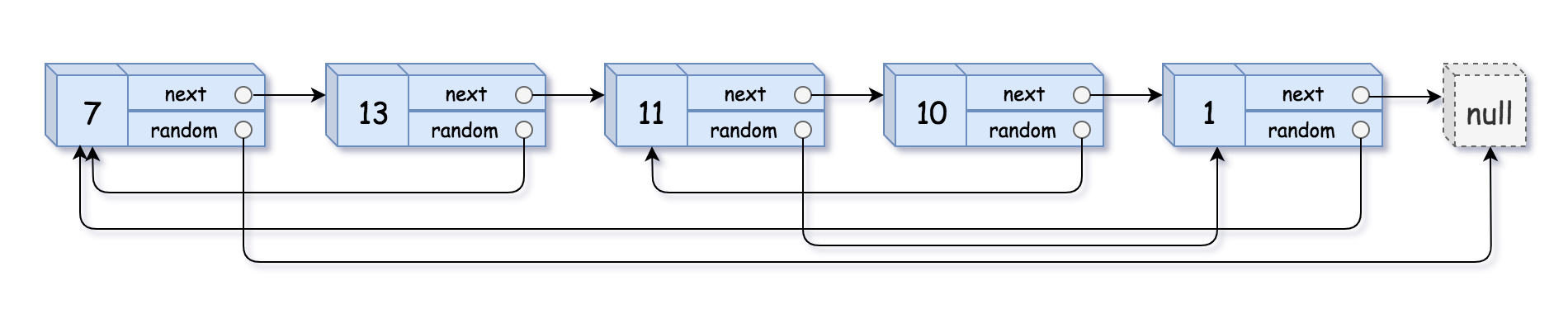
两种方法:1、哈希表
2、拼接与拆分
1、哈希表
特点在于将节点保存,取节点及链接时方便。
class Solution {
public Node copyRandomList(Node head) {
if(head == null) return null;
Node cur = head;
Map<Node, Node> map = new HashMap<>();
// 3. 复制各节点,并建立 “原节点 -> 新节点” 的 Map 映射
while(cur != null) {
map.put(cur, new Node(cur.val));
cur = cur.next;
}
cur = head;
// 4. 构建新链表的 next 和 random 指向
while(cur != null) {
map.get(cur).next = map.get(cur.next);
map.get(cur).random = map.get(cur.random);
cur = cur.next;
}
// 5. 返回新链表的头节点
return map.get(head);
}
}2、 拼接与拆分
在原节点后复制创建新的节点,在通过 cur.next.random = cur.random.next 解决random指针问题。
class Solution {
public Node copyRandomList(Node head) {
if(head == null) return null;
Node cur = head;
// 1. 复制各节点,并构建拼接链表
while(cur != null) {
Node tmp = new Node(cur.val);
tmp.next = cur.next;
cur.next = tmp;
cur = tmp.next;
}
// 2. 构建各新节点的 random 指向
cur = head;
while(cur != null) {
if(cur.random != null)
cur.next.random = cur.random.next;
cur = cur.next.next;
}
// 3. 拆分两链表
cur = head.next;
Node pre = head, res = head.next;
while(cur.next != null) {
pre.next = pre.next.next;
cur.next = cur.next.next;
pre = pre.next;
cur = cur.next;
}
pre.next = null; // 单独处理原链表尾节点
return res; // 返回新链表头节点
}
}






















 765
765











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








