前言
在开发过程中,我们可能常常需要对一个引用进行非空的判断,以防止空指针异常,比如这样,
if(x != null){
if(xx != null){
if(xxx != null){
...
}
}
}
或者这样
xxobj.setX(x !=null? x :"");
xxobj.setY(y !=null? y :"");
这看起来很麻烦但又无可奈何,对于空指针异常我们是日日防,夜夜防,防不胜防。。
终于Java8中引入了Optional类,通过它我们在处理判空等问题的时候,堪称优雅!我们可以把它看作是一个容器,它既可以含有对象也可以为空,而且提供了很多方法,这样我们就不用显示的进行空值检测,好了,一起看源码把!
Optional提供的方法
一共是这么老些
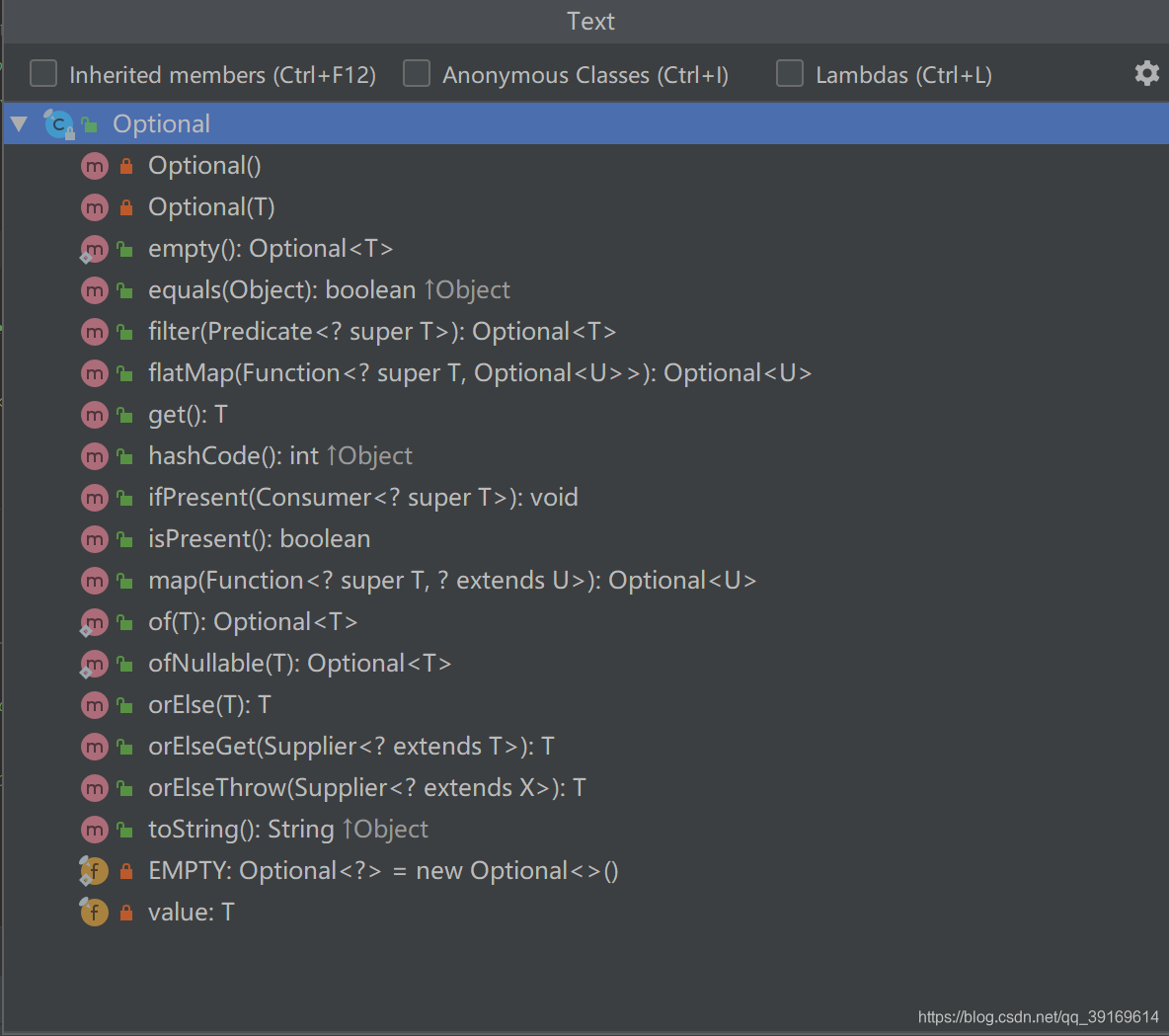
Optional的源码解读
从图上我们可以看到,Optional类有两个私有的构造方法,一个私有静态对象EMPTY以及一个私有的value属性,我们来看看源码是怎么介绍的,
/**
* Common instance for {@code empty()}.
*/
private static final Optional<?> EMPTY = new Optional<>();
/**
* If non-null, the value; if null, indicates no value is present
*/
private final T value;
/**
* Constructs an empty instance.
*
* @implNote Generally only one empty instance, {@link Optional#EMPTY},
* should exist per VM.
*/
private Optional() {
this.value = null;
}
/**
* Constructs an instance with the value present.
*
* @param value the non-null value to be present
* @throws NullPointerException if value is null
*/
private Optional(T value) {
this.value = Objects.requireNonNull(value);
}
不得不说,人家的底层注释写的是真的好,唯一不足的是我的英语水平哈!
Empty对象
首先它有一个公共的实例对象EMPTY,{@code empty()} 告诉我们通过empty()方法可以获得这个对象(因为人家的构造方法都是私有的啦)。
value属性
从上面的源码可以看到,两个构造方法都是在为value进行赋值,无参构造方法value直接为null;带参构造方法在赋值的时候则多了一层判断,Objects.requireNonNull() 方法对传入的对象进行判断,如果为空则抛空指针异常,不为空则返回该对象。
Optional的初始化
由于Optional的构造方法都是私有的,所以对外提供了三个静态方法来构建Optional对象:
方式一、empty()
通过empty()方法可以获得一个空的对象,即上面提到的EMPTY,
public static<T> Optional<T> empty() {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Optional<T> t = (Optional<T>) EMPTY;
return t;
}
但是在通过empty获得实例之后,如果使用get()会抛出异常 “java.util.NoSuchElementException”,所以我并不知道获取到这个空的EMPTY有什么用。。。
方式二、of(T value)
通过of()方法获得的 Optional 对象包含了传入的 value 这个值,但是传入的参数不能为null,否则会抛空指针异常,因为什么,看源码,
/**
* Returns an {@code Optional} with the specified present non-null value.
*
* @param <T> the class of the value
* @param value the value to be present, which must be non-null
* @return an {@code Optional} with the value present
* @throws NullPointerException if value is null
*/
public static <T> Optional<T> of(T value) {
return new Optional<>(value);
}
原因就是因为它底层调用带参构造方法进行构建对象,所以在使用of(T value)时参数一定不能为空!
方式三、ofNullable(T value)
该方法与of(T value)的区别就在于ofNullable()方法中接收的参数可以为null,为什么呢?,看下面,
/**
* Returns an {@code Optional} describing the specified value, if non-null,
* otherwise returns an empty {@code Optional}.
*
* @param <T> the class of the value
* @param value the possibly-null value to describe
* @return an {@code Optional} with a present value if the specified value
* is non-null, otherwise an empty {@code Optional}
*/
public static <T> Optional<T> ofNullable(T value) {
return value == null ? empty() : of(value);
}
原来该方式的精髓就在于拿来主义!如果参数为null用方式一,不为空用方式二,好吧,你厉害。。。
明白了二者的区别之后就知道该如何选择了,也就是说当你明确对象不为null的时候用of(),不明确的时候用ofNullable()。看到这你可能会有疑问了,我用Optional就是进行非空判断的,都明确对象不为null了,那我还拐个弯用Optional干啥?很显然,使用Optional的意义远不止于此,咱们接着往下瞧!
Optional中较简单的方法
get()
获取Optional中的对象,如果为null就抛出异常,
/**
* If a value is present in this {@code Optional}, returns the value,
* otherwise throws {@code NoSuchElementException}.
*
* @return the non-null value held by this {@code Optional}
* @throws NoSuchElementException if there is no value present
*
* @see Optional#isPresent()
*/
public T get() {
if (value == null) {
throw new NoSuchElementException("No value present");
}
return value;
}
isPresent()
判断Optional中的对象是否为null,如果为null返回false,否则返回true,
/**
* Return {@code true} if there is a value present, otherwise {@code false}.
*
* @return {@code true} if there is a value present, otherwise {@code false}
*/
public boolean isPresent() {
return value != null;
}
orElse(T other)
如果Optional中的对象不为null,则返回容器中的对象;如果为null,则返回传入的参数other,
/**
* Return the value if present, otherwise return {@code other}.
*
* @param other the value to be returned if there is no value present, may
* be null
* @return the value, if present, otherwise {@code other}
*/
public T orElse(T other) {
return value != null ? value : other;
}
以上就是Optional中比较常用的方法,也是最简单的,因为参数不是函数式接口,所以还达不到优雅的程度,那么接下来就看看优雅的Optional操作把!
Optional的进阶用法
ifPresent(Consumer<? super T> consumer)
ifPresent()方法在判断对象是否为空的同时还接收一个consumer,如果Optional中的对象不为空时,则执行传入的Lambda表达式,否则什么也不做。
需要注意的是传入的consumer不能为null,否则会抛出空指针异常。
/**
* If a value is present, invoke the specified consumer with the value,
* otherwise do nothing.
*
* @param consumer block to be executed if a value is present
* @throws NullPointerException if value is present and {@code consumer} is
* null
*/
public void ifPresent(Consumer<? super T> consumer) {
if (value != null)
consumer.accept(value);
}
代码示例
Optional <String>opt = Optional.ofNullable("有值");
opt.ifPresent(u-> System.out.println(opt.get()) );//会打印
Optional optEmpty=Optional.empty();
optEmpty.ifPresent(u-> System.out.println(optEmpty.get()) );//什么也不做
上面的代码当Optional中有值的时候,会执行打印部分;而空的时候,则什么也不做。
filter(Predicate<? super T> predicate)
filter()方法根据传入的参数进行过滤(参数不能为null,否则抛出异常),如果Optional中的对象是空,则直接返回该空对象;如果Optional中的值不为空且与传入的参数匹配,则返回该对象;如果不匹配,则调用empty()方法返回一个空的Optional对象,源码如下,
/**
* If a value is present, and the value matches the given predicate,
* return an {@code Optional} describing the value, otherwise return an
* empty {@code Optional}.
*
* @param predicate a predicate to apply to the value, if present
* @return an {@code Optional} describing the value of this {@code Optional}
* if a value is present and the value matches the given predicate,
* otherwise an empty {@code Optional}
* @throws NullPointerException if the predicate is null
*/
public Optional<T> filter(Predicate<? super T> predicate) {
Objects.requireNonNull(predicate);
if (!isPresent())
return this;
else
return predicate.test(value) ? this : empty();
}
代码示例,
Optional<Integer> opt=Optional.of(123);
System.out.println(opt.filter(u->u==123).get());
System.out.println(opt.filter(u->u==1111).get());
第一行打印的时候,匹配成功,可以正常get()并打印123;
第二行打印的时候,由于匹配失败,此时返回一个空的Optional对象,所以调用get()方法时会发生NoSuchElementException 异常。





















 6161
6161











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








