httpClient 学习笔记二
HttpClient 简介
http协议可以说是现在Internet上面最重要,使用最多的协议之一了,越来越多的java应用需要使用http协议来访问网络资源,特别是现在rest api的流行,HttpClient 是 Apache Jakarta Common 下的子项目,用来提供高效的、最新的、功能丰富的支持 HTTP 协议的客户端编程工具包,并且它支持 HTTP 协议最新的版本和建议。HttpClient 已经应用在很多的项目中,比如 Apache Jakarta 上很著名的另外两个开源项目 Cactus 和 HTMLUnit 都使用了 HttpClient,很多的java的爬虫也是通过HttpClient实现的,研究HttpClient对我们来说是非常重要的。
HttpClient 特性
-
基于标准、纯净的java语言。实现了Http1.0和Http1.1
-
以可扩展的面向对象的结构实现了Http全部的方法(GET, POST, PUT, DELETE, HEAD, OPTIONS, and TRACE)。
-
支持HTTPS协议。
-
通过Http代理建立透明的连接。
-
利用CONNECT方法通过Http代理建立隧道的https连接。
-
Basic, Digest, NTLMv1, NTLMv2, NTLM2 Session, SNPNEGO/Kerberos认证方案。
-
插件式的自定义认证方案。
-
便携可靠的套接字工厂使它更容易的使用第三方解决方案。
-
连接管理器支持多线程应用。支持设置最大连接数,同时支持设置每个主机的最大连接数,发现并关闭过期的连接。
-
自动处理Set-Cookie中的Cookie。
-
插件式的自定义Cookie策略。
-
Request的输出流可以避免流中内容直接缓冲到socket服务器。
-
Response的输入流可以有效的从socket服务器直接读取相应内容。
-
在http1.0和http1.1中利用KeepAlive保持持久连接。
-
直接获取服务器发送的response code和 headers。
-
设置连接超时的能力。
-
实验性的支持http1.1 response caching。
-
源代码基于Apache License 可免费获取。
HttpClient 使用方法
使用HttpClient发送请求、接收响应很简单,一般需要如下几步即可。
-
创建HttpClient对象。
-
创建请求方法的实例,并指定请求URL。如果需要发送GET请求,创建HttpGet对象;如果需要发送POST请求,创建HttpPost对象。
-
如果需要发送请求参数,可调用HttpGet、HttpPost共同的setParams(HetpParams params)方法来添加请求参数;对于HttpPost对象而言,也可调用setEntity(HttpEntity entity)方法来设置请求参数。
-
调用HttpClient对象的execute(HttpUriRequest request)发送请求,该方法返回一个HttpResponse。
-
调用HttpResponse的getAllHeaders()、getHeaders(String name)等方法可获取服务器的响应头;调用HttpResponse的getEntity()方法可获取HttpEntity对象,该对象包装了服务器的响应内容。程序可通过该对象获取服务器的响应内容。
-
释放连接。无论执行方法是否成功,都必须释放连接
HttpClient 实例使用
httpClient的使用是比较简单的,主要看一下官方推荐的client(版本:4.5.x)配置项(纯copy…)
详细的见官方导读:https://hc.apache.org/httpcomponents-client-4.5.x/tutorial/html/index.html
/**
* This example demonstrates how to customize and configure the most common aspects
* of HTTP request execution and connection management.
*/
public class ClientConfiguration {
public final static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// Use custom message parser / writer to customize the way HTTP
// messages are parsed from and written out to the data stream.
HttpMessageParserFactory<HttpResponse> responseParserFactory = new DefaultHttpResponseParserFactory() {
@Override
public HttpMessageParser<HttpResponse> create(
SessionInputBuffer buffer, MessageConstraints constraints) {
LineParser lineParser = new BasicLineParser() {
@Override
public Header parseHeader(final CharArrayBuffer buffer) {
try {
return super.parseHeader(buffer);
} catch (ParseException ex) {
return new BasicHeader(buffer.toString(), null);
}
}
};
return new DefaultHttpResponseParser(
buffer, lineParser, DefaultHttpResponseFactory.INSTANCE, constraints) {
@Override
protected boolean reject(final CharArrayBuffer line, int count) {
// try to ignore all garbage preceding a status line infinitely
return false;
}
};
}
};
HttpMessageWriterFactory<HttpRequest> requestWriterFactory = new DefaultHttpRequestWriterFactory();
// Use a custom connection factory to customize the process of
// initialization of outgoing HTTP connections. Beside standard connection
// configuration parameters HTTP connection factory can define message
// parser / writer routines to be employed by individual connections.
HttpConnectionFactory<HttpRoute, ManagedHttpClientConnection> connFactory = new ManagedHttpClientConnectionFactory(
requestWriterFactory, responseParserFactory);
// Client HTTP connection objects when fully initialized can be bound to
// an arbitrary network socket. The process of network socket initialization,
// its connection to a remote address and binding to a local one is controlled
// by a connection socket factory.
// SSL context for secure connections can be created either based on
// system or application specific properties.
SSLContext sslcontext = SSLContexts.createSystemDefault();
// Create a registry of custom connection socket factories for supported
// protocol schemes.
Registry<ConnectionSocketFactory> socketFactoryRegistry = RegistryBuilder.<ConnectionSocketFactory>create()
.register("http", PlainConnectionSocketFactory.INSTANCE)
.register("https", new SSLConnectionSocketFactory(sslcontext))
.build();
// Use custom DNS resolver to override the system DNS resolution.
DnsResolver dnsResolver = new SystemDefaultDnsResolver() {
@Override
public InetAddress[] resolve(final String host) throws UnknownHostException {
if (host.equalsIgnoreCase("myhost")) {
return new InetAddress[] { InetAddress.getByAddress(new byte[] {127, 0, 0, 1}) };
} else {
return super.resolve(host);
}
}
};
// Create a connection manager with custom configuration.
PoolingHttpClientConnectionManager connManager = new PoolingHttpClientConnectionManager(
socketFactoryRegistry, connFactory, dnsResolver);
// Create socket configuration
SocketConfig socketConfig = SocketConfig.custom()
.setTcpNoDelay(true)
.build();
// Configure the connection manager to use socket configuration either
// by default or for a specific host.
connManager.setDefaultSocketConfig(socketConfig);
connManager.setSocketConfig(new HttpHost("somehost", 80), socketConfig);
// Validate connections after 1 sec of inactivity
connManager.setValidateAfterInactivity(1000);
// Create message constraints
MessageConstraints messageConstraints = MessageConstraints.custom()
.setMaxHeaderCount(200)
.setMaxLineLength(2000)
.build();
// Create connection configuration
ConnectionConfig connectionConfig = ConnectionConfig.custom()
.setMalformedInputAction(CodingErrorAction.IGNORE)
.setUnmappableInputAction(CodingErrorAction.IGNORE)
.setCharset(Consts.UTF_8)
.setMessageConstraints(messageConstraints)
.build();
// Configure the connection manager to use connection configuration either
// by default or for a specific host.
connManager.setDefaultConnectionConfig(connectionConfig);
connManager.setConnectionConfig(new HttpHost("somehost", 80), ConnectionConfig.DEFAULT);
// Configure total max or per route limits for persistent connections
// that can be kept in the pool or leased by the connection manager.
connManager.setMaxTotal(100);
connManager.setDefaultMaxPerRoute(10);
connManager.setMaxPerRoute(new HttpRoute(new HttpHost("somehost", 80)), 20);
// Use custom cookie store if necessary.
CookieStore cookieStore = new BasicCookieStore();
// Use custom credentials provider if necessary.
CredentialsProvider credentialsProvider = new BasicCredentialsProvider();
// Create global request configuration
RequestConfig defaultRequestConfig = RequestConfig.custom()
.setCookieSpec(CookieSpecs.DEFAULT)
.setExpectContinueEnabled(true)
.setTargetPreferredAuthSchemes(Arrays.asList(AuthSchemes.NTLM, AuthSchemes.DIGEST))
.setProxyPreferredAuthSchemes(Arrays.asList(AuthSchemes.BASIC))
.build();
// Create an HttpClient with the given custom dependencies and configuration.
CloseableHttpClient httpclient = HttpClients.custom()
.setConnectionManager(connManager)
.setDefaultCookieStore(cookieStore)
.setDefaultCredentialsProvider(credentialsProvider)
.setProxy(new HttpHost("myproxy", 8080))
.setDefaultRequestConfig(defaultRequestConfig)
.build();
try {
HttpGet httpget = new HttpGet("http://httpbin.org/get");
// Request configuration can be overridden at the request level.
// They will take precedence over the one set at the client level.
RequestConfig requestConfig = RequestConfig.copy(defaultRequestConfig)
.setSocketTimeout(5000)
.setConnectTimeout(5000)
.setConnectionRequestTimeout(5000)
.setProxy(new HttpHost("myotherproxy", 8080))
.build();
httpget.setConfig(requestConfig);
// Execution context can be customized locally.
HttpClientContext context = HttpClientContext.create();
// Contextual attributes set the local context level will take
// precedence over those set at the client level.
context.setCookieStore(cookieStore);
context.setCredentialsProvider(credentialsProvider);
System.out.println("executing request " + httpget.getURI());
CloseableHttpResponse response = httpclient.execute(httpget, context);
try {
System.out.println("----------------------------------------");
System.out.println(response.getStatusLine());
System.out.println(EntityUtils.toString(response.getEntity()));
System.out.println("----------------------------------------");
// Once the request has been executed the local context can
// be used to examine updated state and various objects affected
// by the request execution.
// Last executed request
context.getRequest();
// Execution route
context.getHttpRoute();
// Target auth state
context.getTargetAuthState();
// Proxy auth state
context.getTargetAuthState();
// Cookie origin
context.getCookieOrigin();
// Cookie spec used
context.getCookieSpec();
// User security token
context.getUserToken();
} finally {
response.close();
}
} finally {
httpclient.close();
}
}
}
HttpClient 架构设计
(转自:https://blog.csdn.net/szwandcj/article/details/51291967 )
整体架构
对于简单应用,HttpURLConnection完全可以满足。但是对于1)系统复杂度高,2)性能要求高,3)可靠性要求也高的应用,则需要一个更强大的组件。
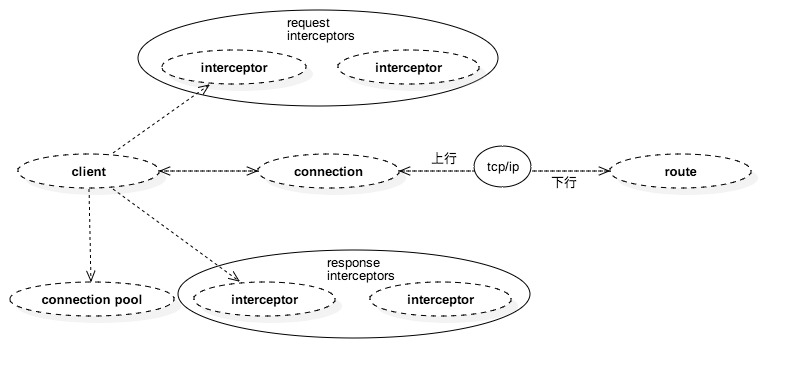
Httpclient里接受者称为为route,并为每个route池化若干连接。Client通过socket发送请求以及接受应答,在发送请求前和接收应答后都会经由interceptor进行链式处理,在httpclient里这些interceptor被称为HttpProcessor,负责处理诸如设置报文头,报文体,编码格式等以及解析报文头,报文体,解码格式等http规范文本格式范畴内的事情。
静态结构
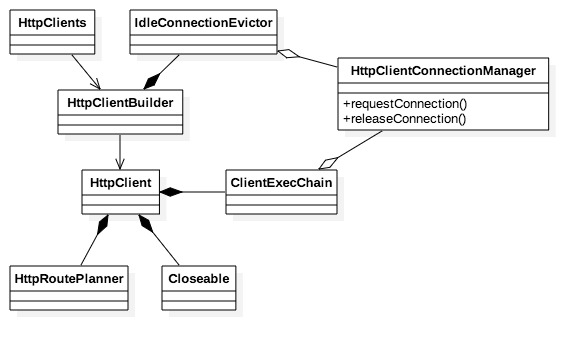
- HttpClient通过建造者构建出来,用户可以通过建造者暴露出来的参数属性方法来组织最终生成的产品属性。HttpClients是个工厂类,用于生产HttpClient,同时也提供custom方法返回builder,由使用者组织client属性。
- HttpClient主要由5个组件组成,分别是:
-
Closeable: 代表需要关闭的组件,client服务关闭时会回调注册的所有Closeable组件依次关闭。用户可以通过HttpClientBuilder#addCloseable添加自定义关闭组件。HttpClient内部利用Closeable关闭IdleConnectionEvictor以及HttpClientConnectionManager
-
IdleConnectionEvictor: 用来关闭闲置连接,它会启动一个守护线程进行清理工作。用户可以通过builder#evictIdleConnections开启该组件,并通过builder#setmaxIdleTime设置最大空闲时间。
-
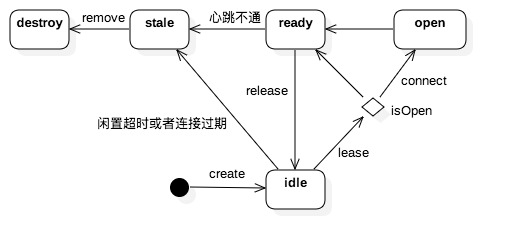
HttpClientConnectionManager,连接池组件,管理连接的整个生命周期。连接在连接池中创建、复用以及移除。 connection被创建出来后处于闲置状态,由连接池管理,被lease后会校验是否是open状态,不是的话会进行connect,connect的过程就是将http请求(连接)绑定到socket的过程。同时连接也会因为心跳或者过期等原因被close变成stale状态,直至被下一次get到时或者连接满时被清理出去。同时连接池还能对连接进行限流–全局和单route连接数。Connection manager封装了对连接池的具体操作,比如向连接池租用和归还连接;还提供了基于不同schema(主要是http和https)创建不同的socket连接(ssl和plain)并且将http请求(连接)绑定到socket的能力,等等。
-
HttpRoutePlanner用来创建HttpRoute。后者代表客户端request的对端服务器,主要包含route的host以及proxy信息。
-
ClientExecChain代表一次完整的调用执行过程,它是一个包装类,类似于java io类,每个包装类完成一个特定的功能,多层嵌套完成一个系统性的功能,比如处理协议范畴的例如cookie、报文解析等,又比如处理自动重试的,等等。
-
连接池
-
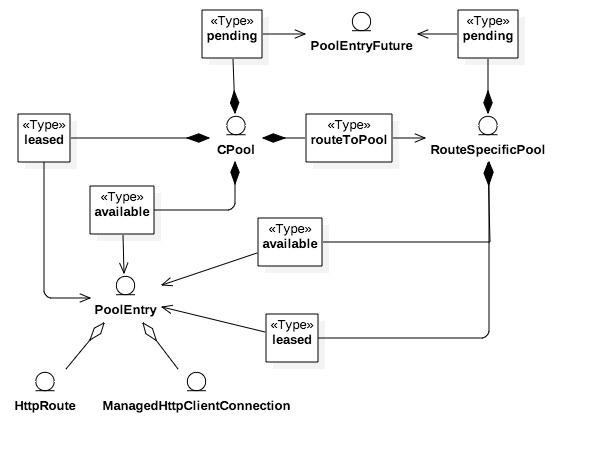
CPool里的连接分为三种–available, leased和pending,分别对应空闲,占用和堵塞三种状态,连接池为这三种状态建立三个列表(List/Set)。对连接数的管理则有两个维度,分别是全局最大数和单route最大数。全局连接和单route连接都对应三种状态列表,CPool内部维护了route和RouteSpecificPool的映射,通过后者对单route连接进行管理,并且严格保证一个route只会对应一个route pool。操作(租用,释放,阻塞或者移除等等)连接时CPool首先会依据route信息取出route pool,对其上维护的连接进行操作,之后再对CPool上的相应连接操作。RouteSpecificPool是个friend的abstract类,也就是说它是CPool隐藏起来的实现细节,对外只暴露CPool的行为甚至用户都可以不理会CPool只关心connection mananger。
-
连接池对外透出的是PoolEntryFuture,后者的get方法能够获取一个闲置连接,或者进入堵塞等待。
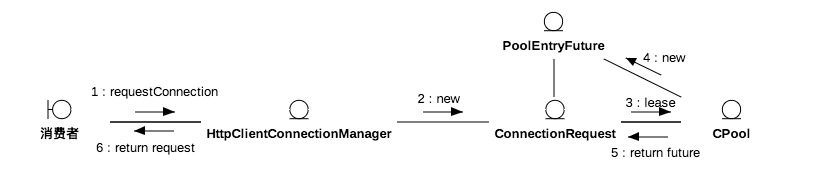
连接池的连接连同route信息一起被包含在PoolEntry里返回给消费者,除此之外,PoolEntry还包含了连接的失效时间等等,超过失效时间会在下一次被get到时close。 -
CPool还有流控功能,get请求在没有空闲连接但连接数没达到阈值时通过连接池创建连接并池化放入available或者leased。leased连接数达到阈值时对请求进行堵塞–PoolEntryFuture#await,并且将PoolEntryFuture放入pending。其他请求释放连接时会唤醒堵塞请求,被唤醒的请求获取到连接后会被从pending列表中移除。
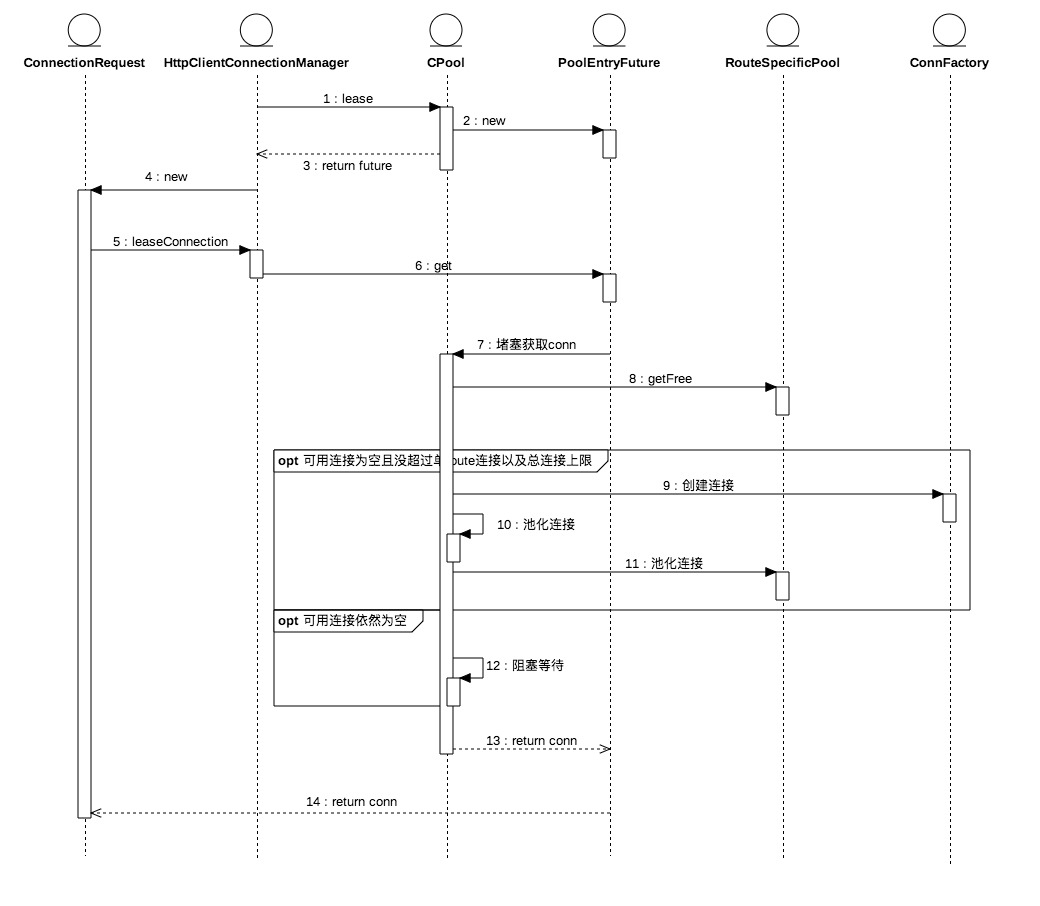
超过任何一个最大数阈值后CPool首先都会进行收缩,超过单route最大数,则收缩单route连接,超过全局最大数,则收缩全局连接。收缩的过程只会关闭空闲连接,直至连接数等于阈值-1。
执行链
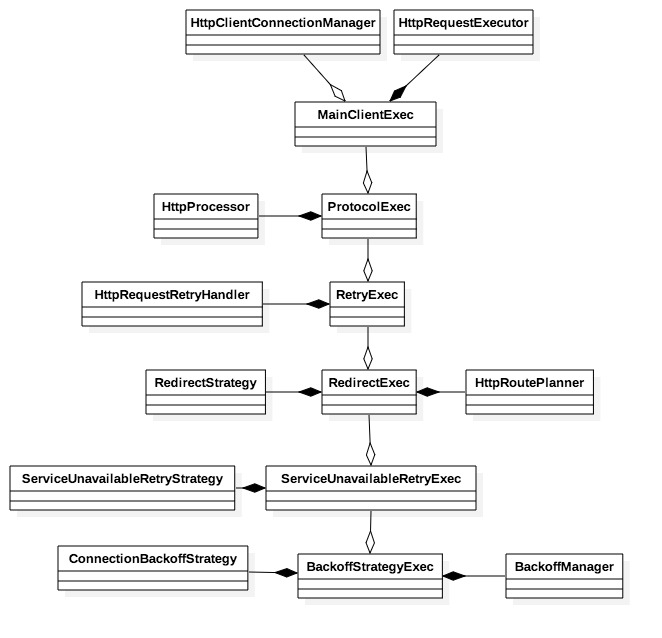
-
MainClientExec是真正执行客户端请求的,它位于包装类的最里层,它通过连接管理器向CPool requestConnection,绑定http请求到socket,通过request executor发送请求,并且还能基于keep-alive策略处理连接的复用等等。
-
ProtocolExec通过一系列的HttpProcessor处理链对Http消息按格式编码以及解码。每一个processor处理一个范畴的事情,比如处理header,content以及cookie等等。
-
RetryExec,对特定的io异常进行重连,保证可用性。特定是指除了一下四中情况的io异常以外:
InterruptedIOException UnknownHostException ConnectException SSLException -
RedirectExec,处理301,302,303和307的情况,即move和redirect。
-
ServiceUnavailableRetryExec, 返回码为503时进行重试。
-
BackoffStrategyExec对出现连接或者响应超时异常的route进行降级,缩小该route上连接数,能使得服务质量更好的route能得到更多的连接。降级的速度可以通过因子设置,默认是每次降级减少一半的连接数,即降级因子是0.5。
最后注意一点,以上的这些exec只有MainClientExec和ProtocolExec是默认开启的,其他的都需要通过HttpClientBuilder设置参数开启,具体可以参考文档或者源码。
调优方向
了解了架构原理后,就可以着手在3个方向进行调优:
- 连接数,通过设立全局最大连接数和单route连接数,增加吞吐能力。用户可通过HttpClientBuilder#maxConnTotal和#maxConnPerRoute分别设置。
- 获取连接的超时时间,调小超时时间能够有效提高响应速度并且降低积压请求量,但相应的也会增加请求失败的几率。用户可以通过RequestConfig的connectionRequestTimeout进行设置。
- 建立连接和route响应的超时时间,调小能够有效的降低bad request对连接的占用,留给质量更好的请求,有效提高系统提高吞吐能力及响应速度。否则有可能在峰值期被慢请求占满连接池,导致系统瘫痪。两者分别可通过RequestConfig#connectionTimeout和socketTimeout进行设置。
- 开启BackoffStrategyExec,对状况差的route进行降级处理,将连接让给其他route。






















 827
827











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








