文章目录
参考:
https://blog.csdn.net/lufeng20/article/details/24314381
https://www.cnblogs.com/coshaho/p/5127135.html
https://www.jianshu.com/p/98b68c97df9b
1. 引言
ThreadLocal是一个本地线程副本变量工具类。主要用于将私有线程和该线程存放的副本对象做一个映射,各个线程保存需要使用的变量副本而不互相干扰。
一句话概括Synchronized与ThreadLocal的区别:Synchronized用于线程间的数据共享,而ThreadLocal则用于线程间的数据隔离。所以ThreadLocal的应用场合,最适合的是按线程多实例(每个线程对应一个实例)的对象的访问,并且这个对象很多地方都要用到。
数据隔离的秘诀其实是这样的,Thread有个TheadLocalMap类型的属性,叫做threadLocals,该属性用来保存该线程本地变量。这样每个线程都有自己的数据,就做到了不同线程间数据的隔离,保证了数据安全。
采用jdk1.8源码进行深挖一下TheadLocal和TheadLocalMap
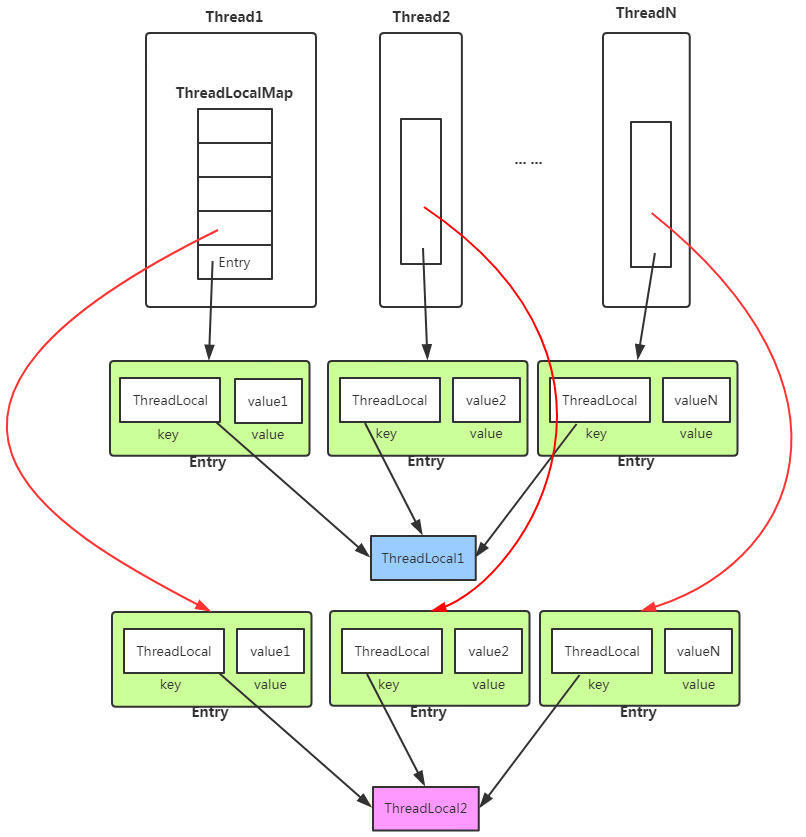
2. ThreadLocal是什么
从上面的结构图,我们已经窥见ThreadLocal的核心机制:
- 每个Thread线程内部都有一个ThreadLocal.ThreadLocalMap类型的threadLocals属性
- Map里面将ThreadLocal对象作为key,线程的变量副本为value
- 但是,Thread内部的Map是由ThreadLocal维护的,由ThreadLocal负责向map获取和设置线程的变量值。
所以对于不同的线程,每次获取副本值时,别的线程并不能获取到当前线程的副本值,形成了副本的隔离,互不干扰。当使用ThreadLocal维护变量时,ThreadLocal为每个使用该变量的线程提供独立的变量副本,所以每一个线程都可以独立地改变自己的副本,而不会影响其它线程所对应的副本。
ThreadLocal有个ThreadLocalMap内部类,存储的数据就放在这儿。
ThreadLocal、ThreadLocal、Thread之间的关系可以概括为:ThreadLocalMap是ThreadLocal内部类,由ThreadLocal创建,Thread有ThreadLocal.ThreadLocalMap类型的threadLocals属性。
3. ThreadLocal类
在讲ThreadLocal之前先说明一下Thread中的ThreadLocal.ThreadLocalMap属性
public
class Thread implements Runnable {
/*...其他属性...*/
/* ThreadLocal values pertaining to this thread. This map is maintained
* by the ThreadLocal class. */
ThreadLocal.ThreadLocalMap threadLocals = null;
/*
* InheritableThreadLocal values pertaining to this thread. This map is
* maintained by the InheritableThreadLocal class.
*/
ThreadLocal.ThreadLocalMap inheritableThreadLocals = null;
...
ThreadLocal类核心方法如下:
//用于保存当前线程的副本变量值
public void set(T value)
//用于获取当前线程的副本变量值
public T get()
//当前线程初始化副本变量值
protected T initialValue()
//移除当前线程的副本变量值
public void remove()
public static <S> ThreadLocal<S> withInitial(Supplier<? extends S> supplier)
private T setInitialValue()
3.1 get方法
/**
* Returns the value in the current thread's copy of this
* thread-local variable. If the variable has no value for the
* current thread, it is first initialized to the value returned
* by an invocation of the {@link #initialValue} method.
* 返回当前线程的变量副本,如果值为空,那么调用initialValue方法初始化
* @return the current thread's value of this thread-local
*/
public T get() {
//返回当前线程
Thread t = Thread.currentThread();
//getMap(t)返回t.threadLocals属性
ThreadLocalMap map = getMap(t);
if (map != null) {
ThreadLocalMap.Entry e = map.getEntry(this);
if (e != null)
return (T)e.value;
}
//如果threadLocals为空则初始化
//最终默认结果为threadLocals=new ThreadLocalMap(this, null)
return setInitialValue();
}
步骤:
- 获取当前线程的ThreadLocalMap对象threadLocals
- 从map中获取线程存储的K-V Entry节点。
- 从Entry节点获取存储的Value副本值返回。
- map为空的话初始化map
3.2 set方法
/**
* Sets the current thread's copy of this thread-local variable
* to the specified value. Most subclasses will have no need to
* override this method, relying solely on the {@link #initialValue}
* method to set the values of thread-locals.
* 向threadLocals存储值
* @param value the value to be stored in the current thread's copy of
* this thread-local.
*/
public void set(T value) {
Thread t = Thread.currentThread();
ThreadLocalMap map = getMap(t);
if (map != null)
map.set(this, value);
else
createMap(t, value);
}
ThreadLocalMap getMap(Thread t) {
return t.threadLocals;
}
void createMap(Thread t, T firstValue) {
t.threadLocals = new ThreadLocalMap(this, firstValue);
}
步骤:
- 获取当前线程的成员变量threadLocals赋值给map
- 若map非空,则重新将ThreadLocal和新的value副本放入到map中。
- 若map空,则对线程的成员变量ThreadLocalMap进行初始化创建,并将ThreadLocal和value副本放入map中。
3.3 remove方法
/**
* Removes the current thread's value for this thread-local
* variable. If this thread-local variable is subsequently
* {@linkplain #get read} by the current thread, its value will be
* reinitialized by invoking its {@link #initialValue} method,
* unless its value is {@linkplain #set set} by the current thread
* in the interim. This may result in multiple invocations of the
* <tt>initialValue</tt> method in the current thread.
* 删除线程的变量副本,如果后面有读取请求的话可能会多次调用initialValue方法
* @since 1.5
*/
public void remove() {
ThreadLocalMap m = getMap(Thread.currentThread());
if (m != null)
m.remove(this);
}
ThreadLocalMap getMap(Thread t) {
return t.threadLocals;
}
4. ThreadLocal.ThreadLocalMap类
ThreadLocalMap是ThreadLocal的内部类,没有实现Map接口,用独立的方式实现了Map的功能,其内部的Entry也独立实现,其结构如下:
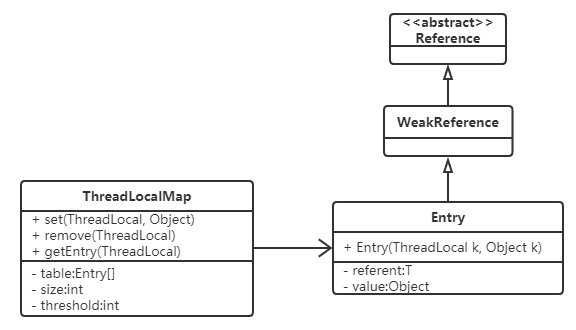
在ThreadLocalMap中,也是用Entry来保存K-V结构数据的。但是Entry中key只能是ThreadLocal对象,这点被Entry的构造方法已经限定死了。
static class Entry extends WeakReference<ThreadLocal> {
/** The value associated with this ThreadLocal. */
Object value;
Entry(ThreadLocal k, Object v) {
super(k);
value = v;
}
}
Entry继承自WeakReference(弱引用,生命周期只能存活到下次GC前),但只有Key是弱引用类型的,Value并非弱引用。
这里需要指出的就是Entry在初始化时调用了super(key),即调用了
public WeakReference(T referent) {
super(referent);
}
而WeakReference在初始话中又调用了super(referent),即调用了
Reference(T referent) {
this(referent, null);
}
这样最终ThreaLocal对象会存储在抽象类Reference的referent属性中。
4.1 ThreadLocalMap属性
static class ThreadLocalMap {
/**
* The initial capacity -- MUST be a power of two.
*/
private static final int INITIAL_CAPACITY = 16;
/**
* The table, resized as necessary.
* table.length MUST always be a power of two.
*/
private Entry[] table;
/**
* The number of entries in the table.
*/
private int size = 0;
/**
* The next size value at which to resize.
table长度阈值
*/
private int threshold; // Default to 0
}
4.2 ThreadLocalMap对Hash冲突的解决
和HashMap的最大的不同在于,ThreadLocalMap结构非常简单,没有next引用,也就是说ThreadLocalMap中解决Hash冲突的方式并非链表的方式,而是采用线性探测的方式(具体介绍线性探测请前往传送门),所谓线性探测,就是根据初始key的hashcode值确定元素在table数组中的位置,如果发现这个位置上已经有其他key值的元素被占用,则利用固定的算法寻找一定步长的下个位置,依次判断,直至找到能够存放的位置。
ThreadLocalMap解决Hash冲突的方式就是简单的步长加1或减1,寻找下一个相邻的位置。
private void set(ThreadLocal<?> key, Object value) {
Entry[] tab = table;
int len = tab.length;
//这一步的操作叫做压缩散列码
//threadLocalHashCode是一个AtomicInteger的数字,从0开始,每次加HASH_INCREMENT = 0x61c88647
//len为table的长度,必须为2的n次方,这样原来通过%取余的操作可以变为 key & (len - 1),按位与的计算速度更快
int i = key.threadLocalHashCode & (len-1);
for (Entry e = tab[i];
e != null;
//若第一次得到的索引有冲突,此后每次返回的i为上次的i值加1
e = tab[i = nextIndex(i, len)]) {
ThreadLocal<?> k = e.get();
if (k == key) {
e.value = value;
return;
}
if (k == null) {
replaceStaleEntry(key, value, i);
return;
}
}
//新存储的条目存储在tab数组当中
tab[i] = new Entry(key, value);
int sz = ++size;
if (!cleanSomeSlots(i, sz) && sz >= threshold)
rehash();
}
显然ThreadLocalMap采用线性探测的方式解决Hash冲突的效率很低,如果有大量不同的ThreadLocal对象放入map中时发送冲突,或者发生二次冲突,则效率很低。
所以这里引出的良好建议是:每个线程的ThreadLocal.ThreadLocalMap threadLocals属性只存一个变量,如果一个线程的threadLocals属性要保存多个变量,就需要创建多个ThreadLocal,多个ThreadLocal放入Map中时会极大的增加Hash冲突的可能。
4.3 避免内存泄漏
当线程没有结束,由于entry是弱引用发生GC时弱引用Key会被回收,而Value不会回收,这样可能会发生内存泄露。为了防止此类情况的出现,我们有两种手段。
1、既然Key是弱引用,那么我们要养成良好的习惯,就是在调用ThreadLocal的get()、set()方法完成后再调用remove方法,将Map对Entry的引用关系移除,这样整个Entry对象在GC Roots分析后就变成不可达了,下次GC的时候就可以被回收。
ThreadLocal<Session> threadLocal = new ThreadLocal<Session>();
try {
threadLocal.set(new Session(key,value));
// 其它业务逻辑
} finally {
threadLocal.remove();
}
2、JDK建议ThreadLocal定义为private static,这样ThreadLocal的弱引用问题则不存在了。
5. 简单使用
/**
* ThreadLocal用法
* @author littlemotor
*
*/
public class MyThreadLocal {
/**
* ThreadLocal实例作为了线程内部属性threadLocals(类型为ThreadLocal.ThreadLocalMap)的key
*/
private static final ThreadLocal<Object> threadLocal0 = new ThreadLocal<Object>();
private static final ThreadLocal<Object> threadLocal1 = new ThreadLocal<Object>();
private static final ThreadLocal<Object> threadLocal2 = new ThreadLocal<Object>();
public static void main(String[] args) {
new Thread(new MyIntegerTask("IntegerTask1")).start();
}
public static class MyIntegerTask implements Runnable {
private String name;
MyIntegerTask(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
if(i == 0){
threadLocal0.set(0);
}
if(i == 1){
threadLocal1.set(1);
}
if(i == 2){
threadLocal2.set(2);
}
}
for(int i = 0; i < 3; i++){
if(i == 0){
System.out.println("线程" + name + i + ": " + threadLocal0.get());
}
if(i == 1){
System.out.println("线程" + name + i + ": " + threadLocal1.get());
}
if(i == 2){
System.out.println("线程" + name + i + ": " + threadLocal2.get());
}
}
}
}
}
6. 总结
- 每个ThreadLocal只能保存一个变量副本,如果想要上线一个线程能够保存多个副本以上,就需要创建多个ThreadLocal。
- ThreadLocal内部的ThreadLocalMap键为弱引用,会有内存泄漏的风险。
- 适用于无状态,副本变量独立后不影响业务逻辑的高并发场景。如果如果业务逻辑强依赖于副本变量,则不适合用ThreadLocal解决,需要另寻解决方案。
























 5255
5255

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








