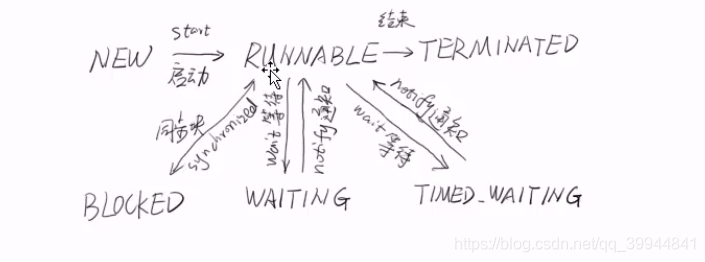
1.什么是线程
线程是进程内的执行单元
2.线程的基本操作
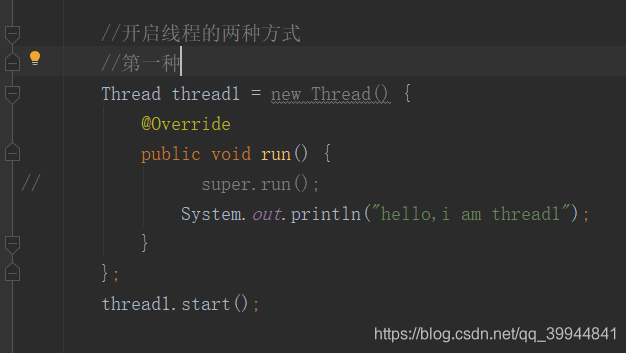
2.1. 开启线程

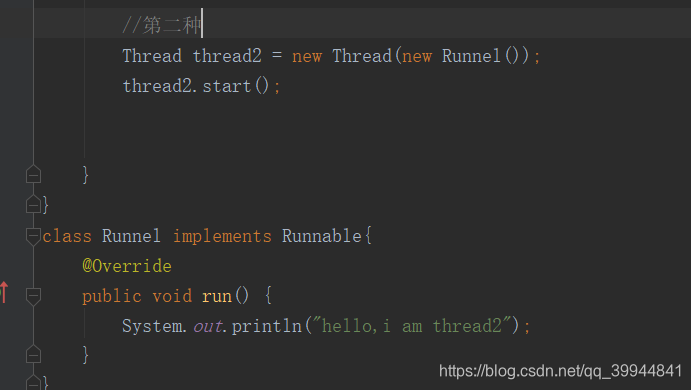
2.2. 结束线程
`thread1.stop();` 不推荐使用,它会释放所有的monitor 太暴力,一致性很难得到保证。
`thread1.interrupt();` //void 中断线程
`thread1.isInterrupted();` //boolean 判断是否被中断
`thread1.interrupted();` //static boolean 判断是否被中断,并清除当前中断状态
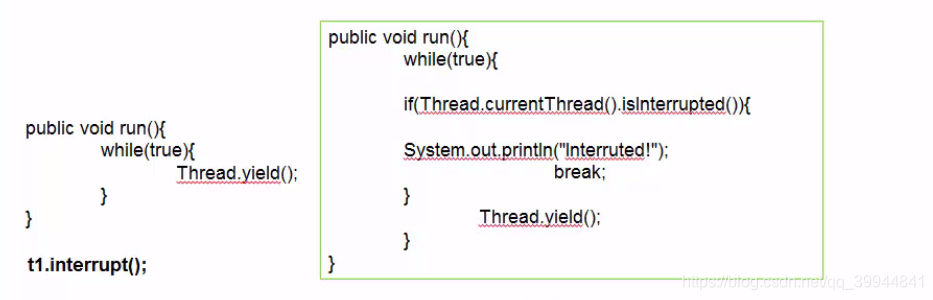
try {
thread.sleep(2000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
//抛出异常后,,中断标志被清空
e.printStackTrace();
}
2.3. 挂起(suspend)和继续执行(resume)线程
不推荐使用
- suspend() 不会释放锁
- 如果加锁发生在resume() 之前,则死锁发生 。(先执行resume() 在执行suspend() 就会一直加锁,不会释放资源,导致其他等待加锁资源的线程,一直无法进行下去。)
public class test {
public static Object u = new Object();
static ChangeObjectThread t1 = new ChangeObjectThread("t1");
static ChangeObjectThread t2 = new ChangeObjectThread("t2");
public static class ChangeObjectThread extends Thread{
public ChangeObjectThread(String name){
super.setName(name);
}
@Override
public void run() {
// super.run();
synchronized(u){
System.out.println("in "+getName());
Thread.currentThread().suspend();
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
t1.start();
Thread.sleep(100);
t2.start();
t1.resume();
t2.resume();
t1.join();
t2.join();
}
}win+R 打开cmd
输入jsp 查看test进程
jstack 119092 查看 线程状态
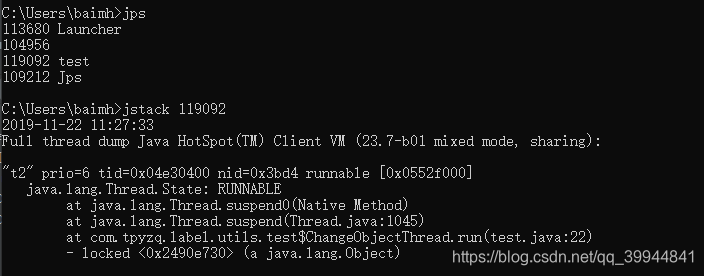
可以看到,t2的进程还在RUNNABLE状态。
jstack Unable to attach to 64-bit process 可查看链接:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_39944841/article/details/103197819
2.4等待线程结束(join)和谦让(yeild)
- 谦让(yeild):是一个静态方法,可能当前线程的优先级不是很高,或者希望给与其他线程有机会争夺cpu。会把当前占用的cpu释放掉,然后与其他线程共同一起去争夺cpu
- 结束(join): 等待线程结束之后执行事情
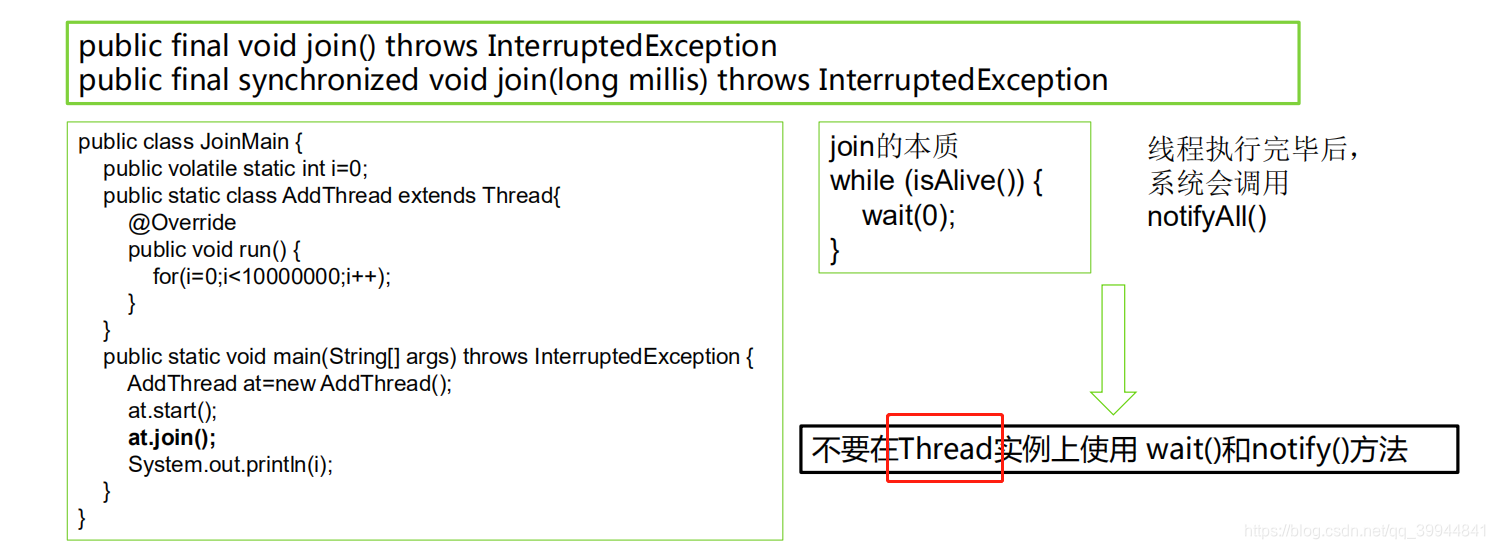
3.守护线程
- 在后台默默的完成一些系统性的服务,比如垃圾回收线程,JIT线程就可以理解为守护线程
- 当一个java应用内,只有守护线程时,java虚拟机就会自然退出
- 在start方法之前告诉系统这是个守护线程方可生效。
/**
* @Author: Baimh
* @Date: 2019/9/25 17:39
*/
public class test {
public static class Daemon extends Thread {
@Override
public void run() {
// super.run();
while (true) {
System.out.println("I am alive");
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread t = new Daemon();
t.setDaemon(true); //设置为守护线程
t.start();
}
}4.线程优先级
高优先级的线程更容易在竞争中获胜 高优先级有更高的概率抢占到资源
- public final static int MIN_PRIORITY = 1;
- public final static int NORM_PRIORITY = 5;
- public final static int MAX_PRIORITY = 10;
public class test {
public static class HighPriority extends Thread{
static int count = 0;
@Override
public void run() {
// super.run();
while (true){
synchronized (test.class){
count++;
if (count>10000000){
System.out.println("HighPriority is complete");
break;
}
}
}
}
}
public static class LowPriority extends Thread{
static int count = 0;
@Override
public void run() {
// super.run();
while (true){
synchronized (test.class){
count++;
if (count>10000000){
System.out.println("LowPriority is complete");
break;
}
}
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread high = new HighPriority();
Thread low = new LowPriority();
low.setPriority(Thread.MAX_PRIORITY); //设置高的优先级MAX_PRIORITY = 10
high.setPriority(Thread.MIN_PRIORITY); //设置低的优先级MIN_PRIORITY = 1
low.start();
high.start();
}
}5.基本的线程同步操作
5.1 synchronized
- 指定加锁对象:对给定对象加锁,进入同步代码前要获得给定对象的锁。
- 直接作用于实例方法:相当于对当前实例加锁,进入同步代码前要获得当前实例的锁。
- 直接作用于静态方法:相当于对当前类加锁,进入同步代码前要获得当前类的锁。
/**
* @Author: Baimh
* 指定加锁对象:对给定对象加锁,进入同步代码前要获得给定对象的锁。
*/
public class test implements Runnable {
static test test1 = new test();
static int i = 0;
@Override
public void run() {
for (int j = 0; j <10000000 ; j++) {
synchronized (test1){
i++;
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Thread t1 = new Thread(test1);
Thread t2 = new Thread(test1);
t1.start();t2.start();
t1.join();t2.join();
System.out.println(i);
}
}/**
* @Author: Baimh
* 直接作用于实例方法:相当于对当前实例加锁,进入同步代码前要获得当前实例的锁。
*/
public class test implements Runnable {
static test test1 = new test();
static int i = 0;
public synchronized void test2(){
i++;
}
@Override
public void run() {
for (int j = 0; j <10000000 ; j++) {
test2();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Thread t1 = new Thread(test1);
Thread t2 = new Thread(test1);
t1.start();t2.start();
t1.join();t2.join();
System.out.println(i);
}
}/**
* @Author: Baimh
* 直接作用于实例方法
* 错误的加锁方式,必须加在同一个实例上边,加锁才会有效
*/
public class test implements Runnable {
// static test test1 = new test();
static int i = 0;
public synchronized void test2(){
i++;
}
@Override
public void run() {
for (int j = 0; j <10000000 ; j++) {
test2();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Thread t1 = new Thread(new test()); //必须加在同一个实例上边,锁才会有效
Thread t2 = new Thread(new test());
t1.start();t2.start();
t1.join();t2.join();
System.out.println(i);
}
}/**
* @Author: Baimh
* 直接作用于静态方法:相当于对当前类加锁,进入同步代码前要获得当前类的锁。
*/
public class test implements Runnable {
// static test test1 = new test();
static int i = 0;
public static synchronized void test2(){
i++;
}
@Override
public void run() {
for (int j = 0; j <10000000 ; j++) {
test2();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Thread t1 = new Thread(new test());
Thread t2 = new Thread(new test());
t1.start();t2.start();
t1.join();t2.join();
System.out.println(i);
}
}5.2.Object.wait() Obejct.notify()
wait() 方法必须是在synchronized拿到锁之后,才可以执行wait方法
wait() 方法会使得当前线程释放监视器
notify() 方法会随机唤醒一个正在等在资源的线程(在notify所在线程执行完之后,继续执行wait接下来的方法)
notifyAll() 方法 会唤醒所有等待在资源上的线程
public class test {
final static Object object = new Object();
public static class T1 extends Thread{
@Override
public void run() {
// super.run();
synchronized (object){
System.out.println(System.currentTimeMillis()+" : T1 start!");
System.out.println(System.currentTimeMillis()+" : t1 wait for object");
try {
object.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(System.currentTimeMillis()+": t1 end!");
}
}
}
public static class T2 extends Thread{
@Override
public void run() {
// super.run();
synchronized (object){
System.out.println(System.currentTimeMillis()+" : T2 start! notify one thread");
object.notify();
System.out.println(System.currentTimeMillis()+": t2 end!");
try {
Thread.sleep(2000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread t1 = new T1();
Thread t2 = new T2();
t1.start();
t2.start();
}
}//执行结果
1574403575818 : T1 start!
1574403575818 : t1 wait for object
1574403575818 : T2 start! notify one thread
1574403575819: t2 end!
1574403577820: t1 end!




















 6801
6801











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








