MVC 是 Model、View 和 Controller 的缩写,分别代表 Web 应用程序中的 3 种职责。
- 模型:用于存储数据以及处理用户请求的业务逻辑。
- 视图:向控制器提交数据,显示模型中的数据。
- 控制器:根据视图提出的请求判断将请求和数据交给哪个模型处理,将处理后的有关结果交给哪个视图更新显示。
基于 Servlet 的 MVC 模式的具体实现如下。
- 模型:一个或多个 JavaBean 对象,用于存储数据(实体模型,由 JavaBean 类创建)和处理业务逻辑(业务模型,由一般的 Java 类创建)。
- 视图:一个或多个 JSP 页面,向控制器提交数据和为模型提供数据显示,JSP 页面主要使用 HTML 标记和 JavaBean 标记来显示数据。
- 控制器:一个或多个 Servlet 对象,根据视图提交的请求进行控制,即将请求转发给处理业务逻辑的 JavaBean,并将处理结果存放到实体模型 JavaBean 中,输出给视图显示。
基于 Servlet 的 MVC 模式的流程如图 1 所示。

基本环境配置
1、需要有基本的Dao层
package com.itheima.dao.impl;
import com.itheima.dao.UserDao;
/**
* @version V1.0
* @author: wusier
* @date: 2020/9/10 11:04
* @Description: Spring
* @modifiedBy:
*/
public class UserDaoImpl implements UserDao {
public void save() {
System.out.println("save running....");
}
}
package com.itheima.dao;
/**
* @version V1.0
* @author: wusier
* @date: 2020/9/10 11:10
* @Description: TODO
* @modifiedBy:
*/
public interface UserDao {
public void save();
}
2、需要有持久层service
package com.itheima.service;
/**
* @version V1.0
* @author: wusier
* @date: 2020/9/10 11:15
* @Description: Spring
* @modifiedBy:
*/
public interface UserService {
public void save();
}
package com.itheima.service.impl;
import com.itheima.dao.UserDao;
import com.itheima.service.UserService;
/**
* @version V1.0
* @author: wusier
* @date: 2020/9/10 11:14
* @Description: Spring
* @modifiedBy:
*/
public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService {
private UserDao userDao;
public void setUserDao(UserDao userDao) {
this.userDao = userDao;
}
public void save() {
userDao.save();
}
}
3、建立web表现层
package com.itheima.web;
import com.itheima.service.UserService;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.web.context.support.WebApplicationContextUtils;
import javax.servlet.ServletContext;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import java.io.IOException;
/**
* @version V1.0
* @author: wusier
* @date: 2020/9/10 13:42
* @Description: Spring
* @modifiedBy:
*/
public class UserServlet extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
ApplicationContext app = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
UserService userService = app.getBean(UserService.class);
userService.save();
}
}4、配置applicationContext.xml
注意增加了context的命名空间
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<!--加载外部的properties文件-->
<context:property-placeholder location="classpath:jdbc.properties"/>
<!--配置数据源-->
<bean id="dataSource" class="com.mchange.v2.c3p0.ComboPooledDataSource">
<property name="driverClass" value="${jdbc.driver}"></property>
<property name="jdbcUrl" value="${jdbc.url}"></property>
<property name="user" value="${jdbc.username}"></property>
<property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}"></property>
</bean>
<!--配置Dao-->
<bean id="userDao" class="com.itheima.dao.impl.UserDaoImpl"></bean>
<!--配置service-->
<bean id="userService" class="com.itheima.service.impl.UserServiceImpl">
<property name="userDao" ref="userDao"/>
</bean>
</beans>5、同样需要tomcat的web层配置,导入war包

<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<web-app version="3.0" xmlns="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_3_0.xsd">
<servlet>
<servlet-name>UserServlet</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>com.itheima.web.UserServlet</servlet-class>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>UserServlet</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/userServlet</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
</web-app>
1. Spring与Web环境集成
1.1 ApplicationContext应用上下文获取方式
应用上下文对象是通过new ClasspathXmlApplicationContext(spring配置文件) 方式获取的,但是每次从容器中获得Bean时都要编写new ClasspathXmlApplicationContext(spring配置文件) ,这样的弊端是配置文件加载多次,应用上下文对象创建多次。
在Web项目中,可以使用ServletContextListener监听Web应用的启动,我们可以在Web应用启动时,就加载Spring的配置文件,创建应用上下文对象ApplicationContext,在将其存储到最大的域servletContext域中,这样就可以在任意位置从域中获得应用上下文ApplicationContext对象了
1、建立监听器实现类listen
package com.itheima.listener;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
import javax.servlet.ServletContext;
import javax.servlet.ServletContextEvent;
import javax.servlet.ServletContextListener;
public class ContextLoaderListener implements ServletContextListener {
public void contextInitialized(ServletContextEvent servletContextEvent) {
//读取web.xml中的全局参数
ApplicationContext app = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
//将Spring的应用上下文对象存储到ServletContext域中
ServletContext servletContext = servletContextEvent.getServletContext();
servletContext.setAttribute("app",app);
System.out.println("spring容器创建完毕....");
}
public void contextDestroyed(ServletContextEvent servletContextEvent) {
}
}
2、配置监听器
<!--配置监听器-->
<listener>
<listener-class>com.itheima.listener.ContextLoaderListener</listener-class>
</listener>
3、使用类的代码
public class UserServlet extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
// ApplicationContext app = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
ServletContext servletContext = this.getServletContext();
ApplicationContext app= (ApplicationContext) servletContext.getAttribute("app");
UserService userService = app.getBean(UserService.class);
userService.save();
}
}4、优化代码:解耦合配置文件
<!--全局初始化参数-->
<context-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>classpath:applicationContext.xml</param-value>
</context-param>
public class ContextLoaderListener implements ServletContextListener {
public void contextInitialized(ServletContextEvent servletContextEvent) {
ServletContext servletContext = servletContextEvent.getServletContext();
String contextConfigLocation = servletContext.getInitParameter("contextConfigLocation");
ApplicationContext app = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(contextConfigLocation);
servletContext.setAttribute("app",app);
System.out.println("spring容器创建完毕....");
}
public void contextDestroyed(ServletContextEvent servletContextEvent) {
}
}
5、优化代码:提取字符串名
public class WebApplicationContextUtils {
public static ApplicationContext getWebApplicationContext(ServletContext servletContext){
return (ApplicationContext) servletContext.getAttribute("app");
}
}
public class UserServlet extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
// ApplicationContext app = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
ServletContext servletContext = this.getServletContext();
//ApplicationContext app= (ApplicationContext) servletContext.getAttribute("app");
ApplicationContext app = WebApplicationContextUtils.getWebApplicationContext(servletContext);
UserService userService = app.getBean(UserService.class);
userService.save();
}
}
1.2 Spring提供获取应用上下文的工具
上面的分析不用手动实现,Spring提供了一个监听器ContextLoaderListener就是对上述功能的封装,该监听器内部加载Spring配置文件,创建应用上下文对象,并存储到ServletContext域中,提供了一个客户端工具WebApplicationContextUtils供使用者获得应用上下文对象。
所以我们需要做的只有两件事:
①在web.xml中配置ContextLoaderListener监听器(导入spring-web坐标)
②使用WebApplicationContextUtils获得应用上下文对象ApplicationContext
1.3 导入Spring集成web的坐标
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-web</artifactId>
<version>5.0.5.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>1.4 配置ContextLoaderListener监听器
<!--全局参数-->
<context-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>classpath:applicationContext.xml</param-value>
</context-param>
<!--Spring的监听器-->
<listener>
<listener-class>
org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener
</listener-class>
</listener>1.5 通过工具获得应用上下文对象
public class UserServlet extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
//ApplicationContext app = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
ServletContext servletContext = this.getServletContext();
//ApplicationContext app = (ApplicationContext) servletContext.getAttribute("app");
//ApplicationContext app = WebApplicationContextUtils.getWebApplicationContext(servletContext);
ApplicationContext app = WebApplicationContextUtils.getWebApplicationContext(servletContext);
UserService userService = app.getBean(UserService.class);
userService.save();
}
}
知识要点
①配置ContextLoaderListener监听器
②使用WebApplicationContextUtils获得应用上下文
2. SpringMVC的简介
2.1 SpringMVC概述
C(控制器)将V(视图、用户客户端)与M(javaBean:封装数据)分开构成了MVC
SpringMVC 是一种基于 Java 的实现 MVC 设计模型的请求驱动类型的轻量级 Web 框架,属于SpringFrameWork 的后续产品,已经融合在 Spring Web Flow 中。
SpringMVC 已经成为目前最主流的MVC框架之一,并且随着Spring3.0 的发布,全面超越 Struts2,成为最优秀的 MVC 框架。它通过一套注解,让一个简单的 Java 类成为处理请求的控制器,而无须实现任何接口。同时它还支持 RESTful 编程风格的请求。


2.3 SpringMVC快速入门
需求:客户端发起请求,服务器端接收请求,执行逻辑并进行视图跳转。
开发步骤
①导入SpringMVC相关坐标
②配置SpringMVC核心控制器DispathcerServlet
③创建Controller类和视图页面
④使用注解配置Controller类中业务方法的映射地址
⑤配置SpringMVC核心文件 spring-mvc.xml
⑥客户端发起请求测试
代码实现
①导入Spring和SpringMVC的坐标、导入Servlet和Jsp的坐标
<!--Spring坐标-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context</artifactId>
<version>5.0.5.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<!--SpringMVC坐标-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-webmvc</artifactId>
<version>5.0.5.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<!--Servlet坐标-->
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.servlet</groupId>
<artifactId>servlet-api</artifactId>
<version>2.5</version>
</dependency>
<!--Jsp坐标-->
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.servlet.jsp</groupId>
<artifactId>jsp-api</artifactId>
<version>2.0</version>
</dependency>②在web.xml配置SpringMVC的前端控制器
<servlet>
<servlet-name>DispatcherServlet</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class>
<init-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>classpath:spring-mvc.xml</param-value>
</init-param>
<load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>DispatcherServlet</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>③创建Controller和业务方法
public class QuickController {
public String quickMethod(){
System.out.println("quickMethod running.....");
return "index";
}
}③创建视图页面index.jsp
<html>
<body>
<h2>Hello SpringMVC!</h2>
</body>
</html>④配置注解
@Controller
public class QuickController {
@RequestMapping("/quick")
public String quickMethod(){
System.out.println("quickMethod running.....");
return "index";
}
}⑤创建spring-mvc.xml
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:mvc="http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc
http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc/spring-mvc.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<!--配置注解扫描\Controller的组件扫描-->
<context:component-scan base-package="com.itheima.controller"/>
</beans>⑥访问测试地址
http://localhost:8080/itheima_springmvc1/quick 控制台打印
![]()
页面显示
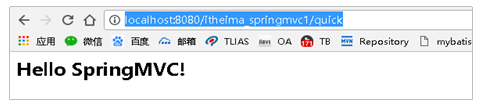
2.3 SpringMVC流程图示



2.4 知识要点
SpringMVC的开发步骤
①导入SpringMVC相关坐标
②配置SpringMVC核心控制器DispathcerServlet
③创建Controller类和视图页面
④使用注解配置Controller类中业务方法的映射地址
⑤配置SpringMVC核心文件 spring-mvc.xml
⑥客户端发起请求测试
3. SpringMVC的组件解析
3.1 SpringMVC的执行流程

①用户发送请求至前端控制器DispatcherServlet。
②DispatcherServlet收到请求调用HandlerMapping处理器映射器。
③处理器映射器找到具体的处理器(可以根据xml配置、注解进行查找),生成处理器对象及处理器拦截器(如果有则生成)一并返回给DispatcherServlet。
④DispatcherServlet调用HandlerAdapter处理器适配器。
⑤HandlerAdapter经过适配调用具体的处理器(Controller,也叫后端控制器)。
⑥Controller执行完成返回ModelAndView。
⑦HandlerAdapter将controller执行结果ModelAndView返回给DispatcherServlet。
⑧DispatcherServlet将ModelAndView传给ViewReslover视图解析器。
⑨ViewReslover解析后返回具体View。
⑩DispatcherServlet根据View进行渲染视图(即将模型数据填充至视图中)。DispatcherServlet响应用户。
3.2 SpringMVC组件解析
1、前端控制器:DispatcherServlet
用户请求到达前端控制器,它就相当于 MVC 模式中的 C,DispatcherServlet 是整个流程控制的中心,由
它调用其它组件处理用户的请求,DispatcherServlet 的存在降低了组件之间的耦合性。
2、处理器映射器:HandlerMapping
HandlerMapping 负责根据用户请求找到 Handler 即处理器,SpringMVC 提供了不同的映射器实现不同的
映射方式,例如:配置文件方式,实现接口方式,注解方式等。
3、处理器适配器:HandlerAdapter
通过 HandlerAdapter 对处理器进行执行,这是适配器模式的应用,通过扩展适配器可以对更多类型的处理
器进行执行。
4、处理器:Handler
它就是我们开发中要编写的具体业务控制器。由 DispatcherServlet 把用户请求转发到 Handler。由
Handler 对具体的用户请求进行处理。
5、视图解析器:View Resolver
View Resolver 负责将处理结果生成 View 视图,View Resolver 首先根据逻辑视图名解析成物理视图名,即具体的页面地址,再生成 View 视图对象,最后对 View 进行渲染将处理结果通过页面展示给用户。
6、视图:View
SpringMVC 框架提供了很多的 View 视图类型的支持,包括:jstlView、freemarkerView、pdfView等。最常用的视图就是 jsp。一般情况下需要通过页面标签或页面模版技术将模型数据通过页面展示给用户,需要由程序员根据业务需求开发具体的页面
3.3 SpringMVC注解解析
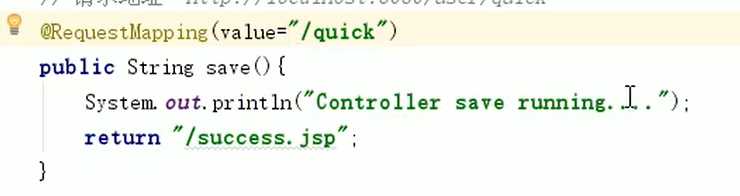
@RequestMapping
作用:用于建立请求 URL 和处理请求方法之间的对应关系
位置:
-
类上,请求URL 的第一级访问目录。此处不写的话,就相当于应用的根目录
-
方法上,请求 URL 的第二级访问目录,与类上的使用@ReqquestMapping标注的一级目录一起组成访问虚拟路径

加 / 代表在当前web应用下找 jsp
![]()
![]()
属性:
- value:用于指定请求的URL。它和path属性的作用是一样的
- method:用于指定请求的方式
- params:用于指定限制请求参数的条件。它支持简单的表达式。要求请求参数的key和value必须和配置的一模一样
例如:
params = {"accountName"},表示请求参数必须有accountName
params = {"moeny!100"},表示请求参数中money不能是100
![]()

1.mvc命名空间引入
命名空间:xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:mvc="http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc"
约束地址:http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc
http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc/spring-mvc.xsd2. 组件扫描
SpringMVC基于Spring容器,所以在进行SpringMVC操作时,需要将Controller存储到Spring容器中,如果使用@Controller注解标注的话,就需要使用<context:component-scan base-package=“com.itheima.controller"/>进行组件扫描。
<!--Controller的组件扫描-->
<context:component-scan base-package="com.itheima">
<context:include-filter type="annotation" expression="org.springframework.stereotype.Controller"/>
</context:component-scan><context:component-scan base-package=“com.itheima.controller"/>3.4 SpringMVC的XML配置解析
SpringMVC有默认组件配置,默认组件都是DispatcherServlet.properties配置文件中配置的,该配置文件地址org/springframework/web/servlet/DispatcherServlet.properties,该文件中配置了默认的视图解析器,如下:
org.springframework.web.servlet.ViewResolver=org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceViewResolver

翻看该解析器源码,可以看到该解析器的默认设置,如下:
REDIRECT_URL_PREFIX = "redirect:" --重定向前缀
FORWARD_URL_PREFIX = "forward:" --转发前缀(默认值)
prefix = ""; --视图名称前缀
suffix = ""; --视图名称后缀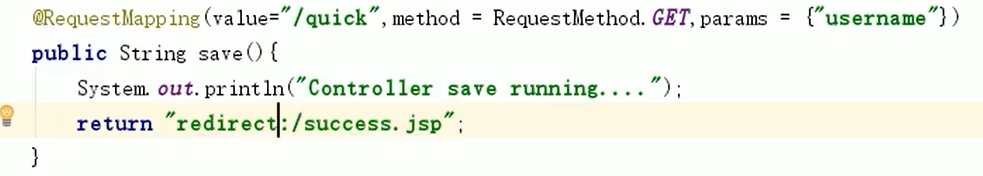
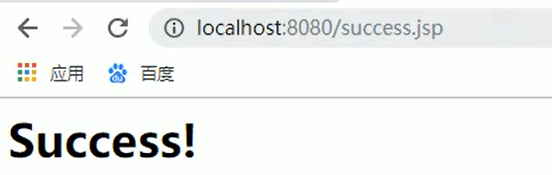
1、视图解析器
我们可以通过属性注入的方式修改视图的的前后缀
<!--配置内部资源视图解析器-->
<bean id="viewResolver" class="org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceViewResolver">
<!-- /jsp/success.jsp -->
<property name="prefix" value="/jsp/"></property>
<property name="suffix" value=".jsp"></property>
</bean>还有很多东西可以配置
3.5 知识要点
SpringMVC的相关组件
- 前端控制器:DispatcherServlet
- 处理器映射器:HandlerMapping
- 处理器适配器:HandlerAdapter
- 处理器:Handler
- 视图解析器:View Resolver
- 视图:View
SpringMVC的注解和配置
- 请求映射注解:@RequestMapping
- 视图解析器配置:
REDIRECT_URL_PREFIX = "redirect:"
FORWARD_URL_PREFIX = "forward:"
prefix = "";
suffix = "";






















 371
371











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








