Vue初探
语法糖
const { zhi } = Gao;
//等价于
const zhi = Gao.zhi
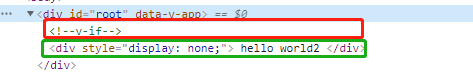
v-if&v-show(控制html标签显示与否)
v-if=true,标签显示,v-if=false,标签隐藏,实现原理是这个标签节点删除了
v-show=true,标签显示,v-show=false,标签隐藏,实现原理是设置了这个标签的style=“display:none;”,标签还在
<body>
<div id="root">
</div>
</body>
<script>
const app = Vue.createApp({
data () {
return {
show:false
}
},
template:`
<div v-if="show">
hello world1
</div>
<div v-show="show">
hello world2
</div>
`
});
app.mount('#root');
</script>
v-if&v-else-if&v-else
<body>
<div id="root">
</div>
</body>
<script>
const app = Vue.createApp({
data () {
return {
conditionOne:false,
conditionTwo:true
}
},
template:`
<div v-if="conditionOne">
if
</div>
<div v-else-if="conditionTwo">
else if
</div>
<div v-else>
else
</div>
`
});
app.mount('#root');
</script>
v-on:click(点击触发事件)
<body>
<div id="root">
<span v-if="show">{{content}}</span>
<button v-on:click="visbleBtnClick">显示/隐藏</button>
</div>
</body>
<script>
Vue.createApp({
data () {
return {
show:true,
content:'hello world'
}
},
methods: {
visbleBtnClick(){
this.show = !this.show;
}
}
}).mount('#root');
</script>
v-for(for循环数据)
循环数组和对象
循环时最好写一个唯一key, v-bind:key=“index”,此处使用下标,因为每次循环下标是唯一的;这样更改数据时,下次vue渲染页面时,不必把原来的dom摧毁重建
<body>
<div id="root">
</div>
</body>
<script>
const app = Vue.createApp({
data () {
return {
listArr:['1','2','3'],
listObj:{
first:1,
two:2,
three:3
}
}
},
methods: {
handleAddItem(){
// 数组变更函数
this.listArr.push(4)
// 从尾部删除内容
this.listArr.pop;
// 从头部删除内容
this.listArr.shift();
// 开头添加内容
this.listArr.unshift(4);
// splite,sort,reverse
}
},
template:`
<div v-for="(item,index) in listArr" v-bind:key="index">
{{item}} --{{index}}
</div>
<button v-on:click="handleAddItem">新增</button>
<div v-for="(value,key,index) in listObj">
{{value}} --{{key}} -- {{index}}
</div>
`
});
app.mount('#root');
</script>
v-model(数据双向绑定)
<body>
<div id="root">
</div>
</body>
<script>
<body>
<div id="root">
</div>
</body>
<script>
Vue.createApp({
data () {
return {
inputValue:'',
list:[]
}
},
methods: {
addItem(){
this.list.push(this.inputValue);
this.inputValue = '';
}
},
template:`
<div>
<input v-model="inputValue"/>
<button v-on:click=addItem>增加</button>
<ul>
<li v-for="(item,index) of list">{{item}}-{{index}}</li>
</ul>
</div>
`
}).mount('#root');
</script>
实现效果:点击增加会把输入框内容增加到下面的列表中,同时清空输入框

v-bind(标签上的属性对应值进行动态数据绑定)
一般的数据绑定发生在标签之间,如 < span>{{content}}</ span>
但是如果想让属性和数据发生绑定,则使用v-bind,且数据无需使用{{}}括起来
<body>
<div id="root">
</div>
</body>
<script>
Vue.createApp({
data () {
return {
inputValue:'',
list:[]
}
},
methods: {
addItem(){
this.list.push(this.inputValue);
this.inputValue = '';
}
},
template:`
<div>
<input v-model="inputValue"/>
<button v-bind:title="inputValue" v-on:click=addItem>增加</button>
<ul>
<li v-for="(item,index) of list">{{item}}-{{index}}</li>
</ul>
</div>
`
}).mount('#root');
</script>
实现效果:

组件初探(双向绑定)
<body>
<div id="root">
</div>
</body>
<script>
// 创建实例
const app = Vue.createApp({
data () {
return {
inputValue:'',
list:[]
}
},
methods: {
addItem(){
this.list.push(this.inputValue);
this.inputValue = '';
}
},
template:`
<div>
<input v-model="inputValue"/>
<button v-bind:title="inputValue" v-on:click=addItem>增加</button>
<ul>
<todo-item v-for="(item,index) of list" v-bind:content="item" />
</ul>
</div>
`
});
// 定义组件
app.component('todo-item',{
props: ['content'],
template: '<li>{{content}}</li>'
});
// 挂载实例到节点下
app.mount('#root');
</script>
实现效果:

Vue基础语法
组件基本概念
mvvm设计模式:
m -> model 数据层(data),v -> view 视图层(template),vm -> viewModel 视图数据连接层
<body>
<div id="root"></div>
</body>
<script>
// MVVM设计模式 m -> model 数据层(data),v -> view 视图层(template),vm -> viewModel 视图数据连接层
// 创建vue应用
const app = Vue.createApp({
data() {
return {
message: "hello world",
};
},
template: `
<div>{{message}}</div>
`,
});
// vue应用挂载到root节点上
// vm代表的就是vue应用的根组件
const vm = app.mount("#root");
// 可通过vm操作数据,再反映到视图展示上,注意data前加$
vm.$data.message = "bbb";
</script>
Vue生命周期函数

常用模板语法
简写(v-on及v-bind简写)
<div v-on:click="handleClike" v-bind:title="message">{{message}}</div>
// 可简写成
<div @click="handleClike" :title="message">{{message}}</div>
动态属性(标签上的属性进行动态数据绑定)
<body>
<div id="root"></div>
</body>
<script>
// 生命周期函数:在某一时刻会自动执行的函数
const app = Vue.createApp({
data() {
return {
message: "hello world",
name:"title",
event:"click"
};
},
methods: {
handleClike() {
alert("aaa");
},
},
template: `
<div v-on:[event]="handleClike" v-bind:[name]="message">
{{message}}
</div>
`,
});
const vm = app.mount("#root");
</script>
v-html(当成html标签进行解析,而不是字符串)
<body>
<div id="root"></div>
</body>
<script>
const app = Vue.createApp({
data() {
return {
message: "<strong>hello world</strong>",
};
},
template: `
<div v-html="message"></div>
`,
});
const vm = app.mount("#root");
</script>
v-once(只渲染一次,再通过外部修改数据则不能修改)
再通过vm.$data.message=“aaa”也不能更改显示值,减少无用渲染
<body>
<div id="root"></div>
</body>
<script>
const app = Vue.createApp({
data() {
return {
message: "hello world",
};
},
template: `
<div v-once>{{message}}</div>
`,
});
const vm = app.mount("#root");
</script>
修饰符语法(提前做一些工作)
阻止默认行为(下面代码不会跳转百度了)
<body>
<div id="root"></div>
</body>
<script>
const app = Vue.createApp({
data() {
return {
message: "hello world",
name:"title",
event:"click"
};
},
methods: {
handleClick(e) {
e.preventDefault();
alert("aa");
},
},
template: `
<form action="http://www.baidu.com" @click="handleClick">
<button type="submit">提交</button>
</form>
`,
});
const vm = app.mount("#root");
</script>
// 可被替换为============================================================
<body>
<div id="root"></div>
</body>
<script>
const app = Vue.createApp({
data() {
return {
message: "hello world",
name:"title",
event:"click"
};
},
methods: {
handleClick() {
alert("aa");
},
},
template: `
<form action="http://www.baidu.com" @click.prevent="handleClick">
<button type="submit">提交</button>
</form>
`,
});
const vm = app.mount("#root");
</script>
{{}}中写表达式
<body>
<div id="root"></div>
</body>
<script>
const app = Vue.createApp({
data() {
return {
message: "hello world",
};
},
methods: {
formatStr(string){
return string.toUpperCase();
}
},
template: `
<div>{{formatStr(message)}}</div>
`,
});
const vm = app.mount("#root");
</script>
计算属性
计算属性和方法的区别:
计算属性依赖的内容发生变更时,才会重新执行计算,当计算属性返回当前日期时,其他数据更改时,是不会重新计算的,所以值不会变。
只要页面重新渲染,才会重新计算,当方法返回当前日期时,其他数据更改时会导致页面重新渲染,会发生重新计算
<body>
<div id="root"></div>
</body>
<script>
const app = Vue.createApp({
data() {
return {
message:"hello world"
};
},
computed: {
total(){
return "计算属性:"+Date.now();
}
},
methods: {
formatStr(string){
return string.toUpperCase();
},
getTotal(){
return "方法:"+ Date.now();
}
},
template: `
<div>{{message}}-{{total}}</div>
<div>{{message}}-{{getTotal()}}</div>
`,
});
const vm = app.mount("#root");
</script>
</script>
实现效果:
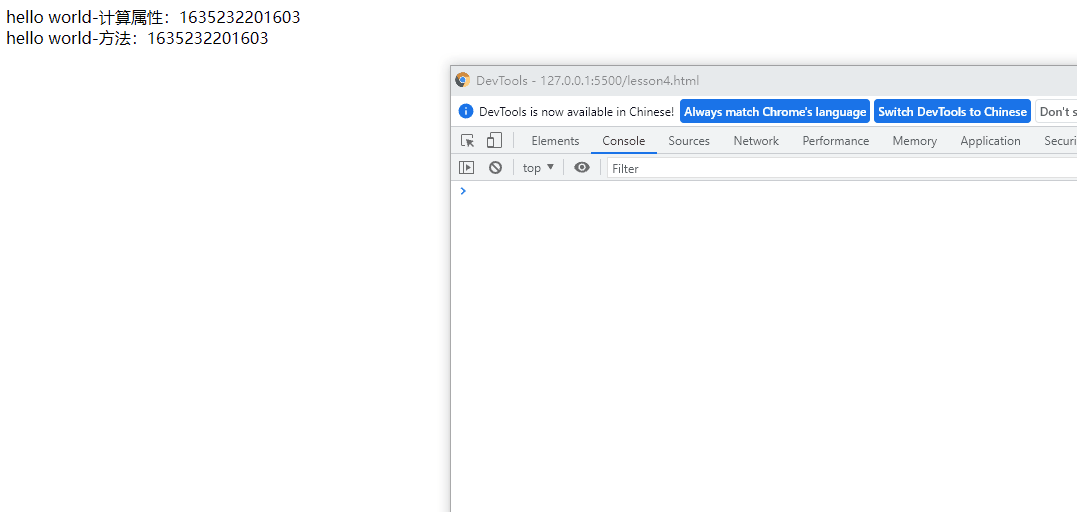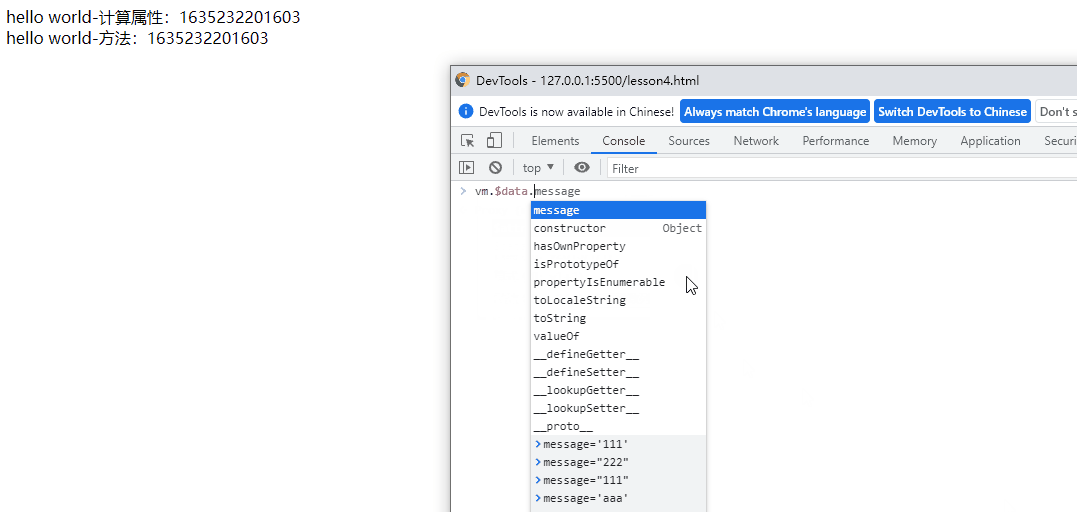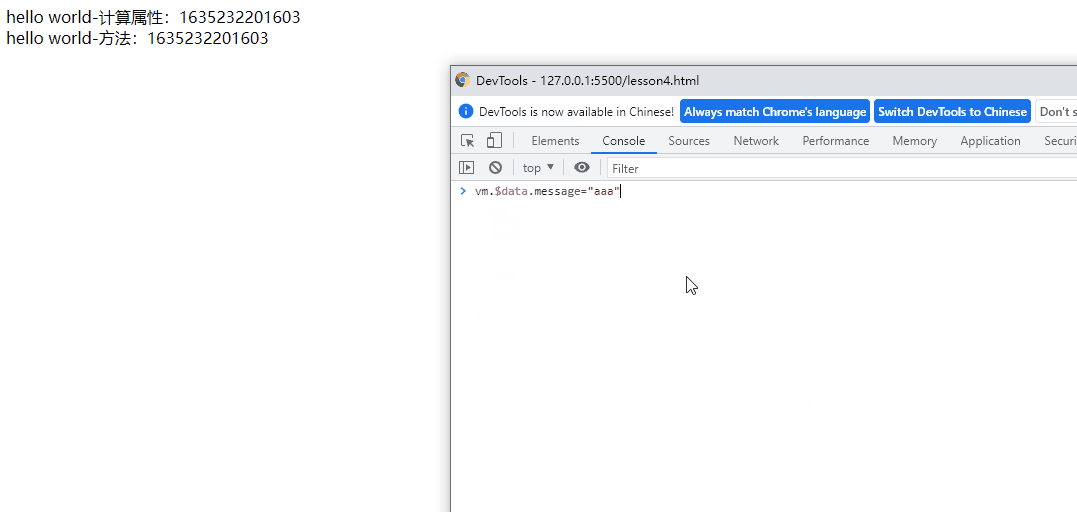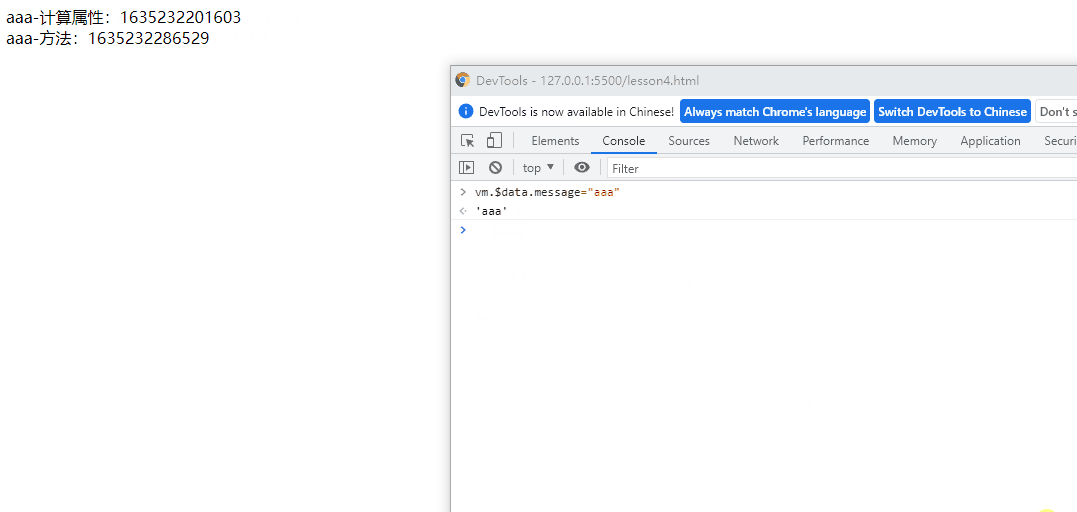
侦听器(watch监听data中数据的改变)
<body>
<div id="root"></div>
</body>
<script>
const app = Vue.createApp({
data() {
return {
count:1,
price:5
};
},
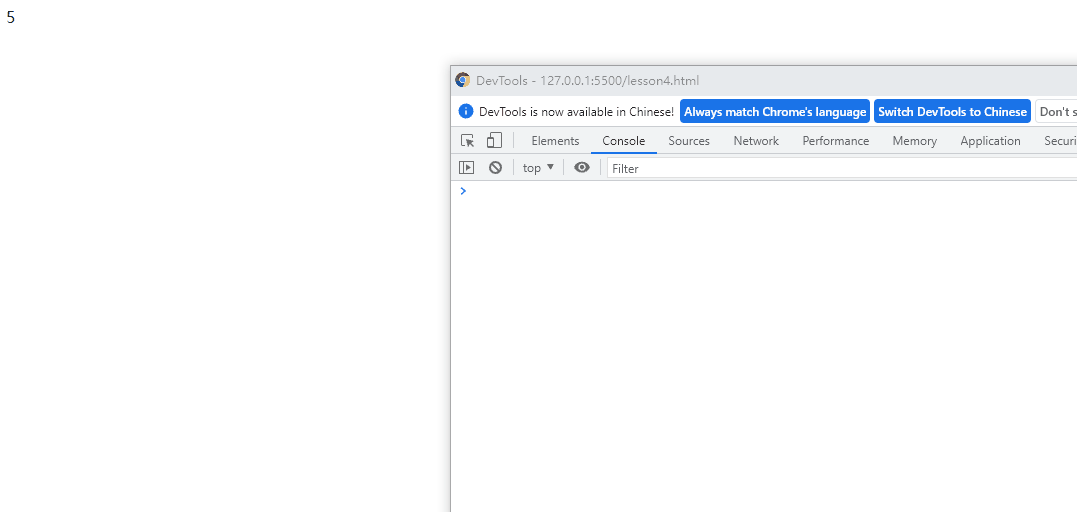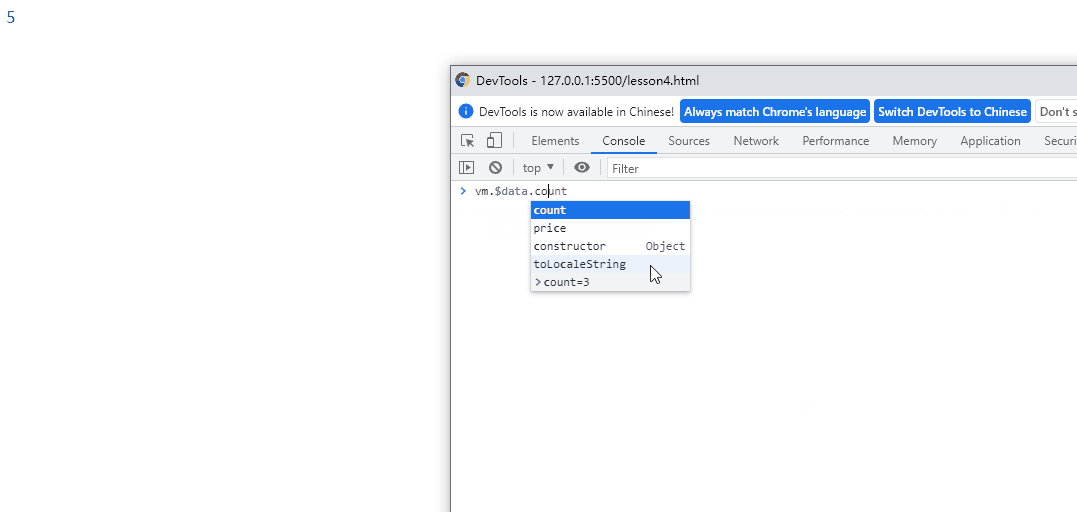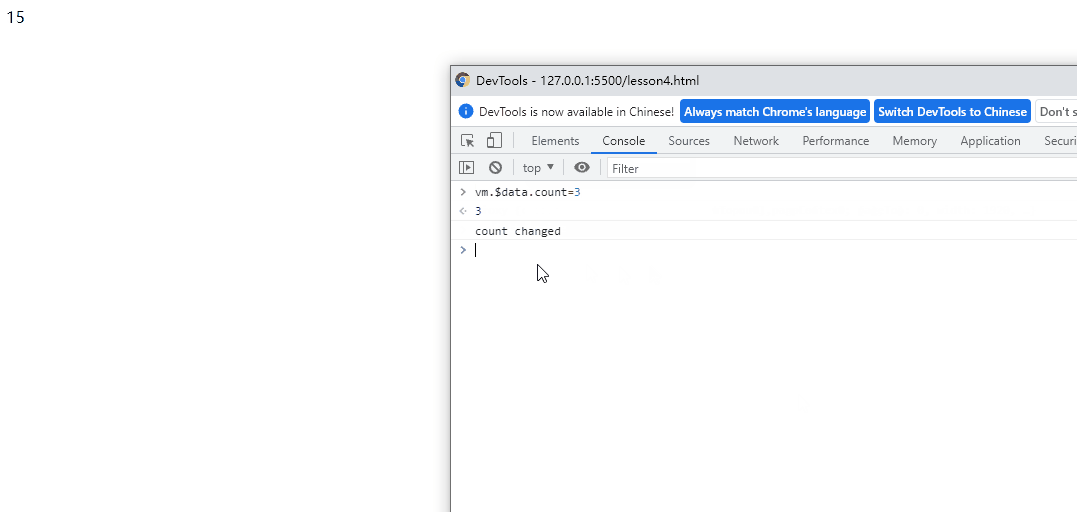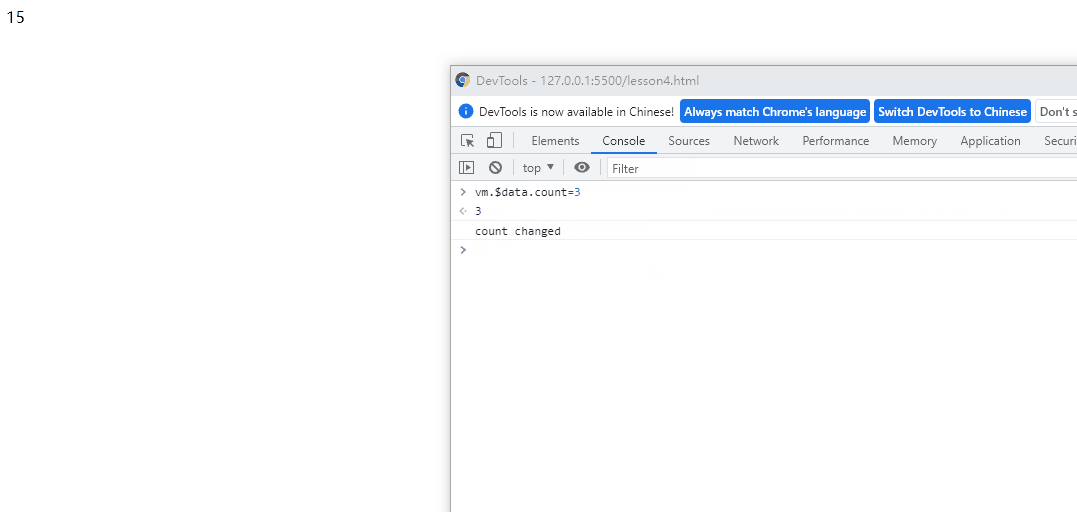
watch: {
// count发生变化时,会执行
count(current,pre){
setInterval(() => {
console.log("count changed");
}, 3000);
}
},
computed: {
total(){
return this.count*this.price;
}
},
template: `
<div>{{total}}</div>
`,
});
const vm = app.mount("#root");
</script>
实现效果:
样式绑定语法(子组件引用父组件属性$attrs)
class绑定三种方式
行内样式绑定两种方式
子组件引用父组件属性
<style>
.red{
color:red;
}
.green{
color: green;
}
</style>
<body>
<div id="root">
</div>
</body>
<script>
const app = Vue.createApp({
data () {
return {
classStr:'red',
classObj:{red:true,green:true},
classArr:['red','green',{brown:true}]
}
},
template:`
<div v-bind:class="classStr">
hello world1
</div>
<div v-bind:class="classObj">
hello world2
</div>
<div v-bind:class="classArr">
hello world3
</div>
<demo class="green"/>
`
});
// attrs.class 子组件上的值是父组件上的值
app.component('demo',{
template:`
<div v-bind:class="$attrs.class">one</div>
<div v-bind:class="$attrs.class">two</div>
`
});
// 挂载实例到节点下
app.mount('#root');
</script>

列表渲染
< template></ template> 占位符的概念,不做任何渲染
<body>
<div id="root">
</div>
</body>
<script>
const app = Vue.createApp({
data () {
return {
listArr:['1','2','3'],
listObj:{
first:1,
two:2,
three:3
}
}
},
methods: {
handleAddItem(){
// 1. 数组变更函数
// 尾部添加元素
this.listArr.push(4)
// 从尾部删除内容
this.listArr.pop;
// 从头部删除内容
this.listArr.shift();
// 开头添加内容
this.listArr.unshift(4);
// 翻转
this.listArr.reverse();
// 2. 直接替换数组
this.listArr = ['7','9'];
// 筛出等于9的元素
this.listArr = ['7'].conncat(['9']).filter(item =>item==='7');
// 3. 直接更新数组
this.listArr[1] = '0';
}
},
template:`
<div v-for="(item,index) in listArr" v-bind:key="index">
{{item}} --{{index}}
</div>
<button v-on:click="handleAddItem">新增</button>
<div v-for="(value,key,index) in listObj">
{{value}} --{{key}} -- {{index}}
</div>
`
});
app.mount('#root');
</script>
事件绑定
基础
同时传递参数和获取原生时间对象,tempalte需要传递$event
同一个标签可以绑定多个事件,逗号隔开,方法名一定要有括号
<body>
<div id="root">
</div>
</body>
<script>
const app = Vue.createApp({
data () {
return {
counter:0
}
},
methods: {
// 同时传递参数和获取原生时间对象,tempalte需要传递$event
// 同一个标签可以绑定多个事件,逗号隔开,方法名一定要有括号
handleItem(num,event){
console.log(event);
this.counter+=num;
},
handleItem2(){
alert(2);
}
},
template:`
<div>
{{counter}}
<button v-on:click="handleItem(2,$event),handleItem2()">button</button>
</div>
`
});
app.mount('#root');
</script>
进阶(事件、按键、鼠标、精确修饰符)
事件修饰符:
事件冒泡和事件捕获
冒泡:事件又内往外传递
捕获:事件由外往内传递
v-on:click.stop:阻止冒泡
v-on:click.capture:阻止捕获
v-on:click.self:只要点击自己的标签才触发
v-on:click.once:事件只执行一次
v-on:scoll.passive:滚动时,通俗点说就是每次滚动事件产生,浏览器都会去查询一下是否有preventDefault阻止该次事件的默认动作。我们加上passive就是为了告诉浏览器,不用查询了,我们没用preventDefault阻止默认动作
按键修饰符:
当按键是对应按键的时候才会执行,例如enter、tab、delete、esc、up、down
<body>
<div id="root">
</div>
</body>
<script>
// 当按键是enter的时候才会执行,例如enter、tab、delete、esc、up、down
const app = Vue.createApp({
methods: {
handleKeyDown(){
console.log("handleKeyDown")
}
},
template:`
<div>
<input @keydown.enter="handleKeyDown"/>
</div>
`
});
app.mount('#root');
</script>
鼠标修饰符
v-on:click.left
v-on:click.right
v-on:click.middle
精确修饰符
exact
按住ctrl键,再按住其他键,再点击就会执行
v-on:click.ctrl
如果想要精确只按住ctrl键再点击才会执行
v-on:click.ctrl.exact
表单双向绑定
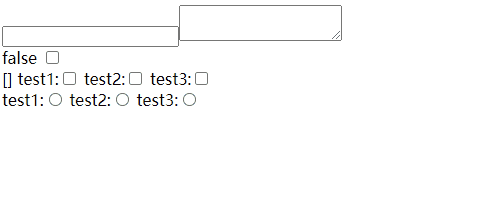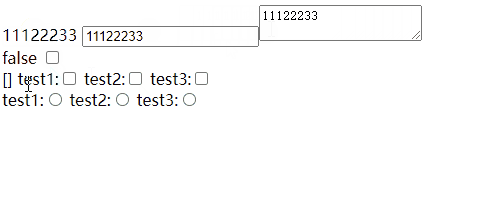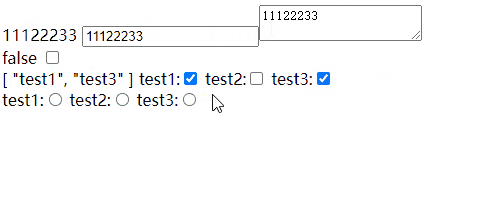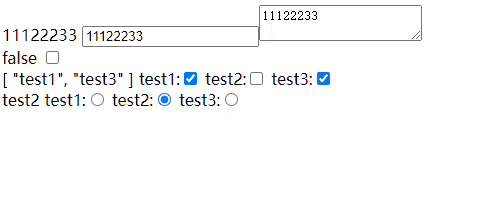
基础(input、testarea、checkbox、radio)
input、testarea、checkbox、radio
如果checkbox 是数组,标签上一定要写value,不然数组不知道显示什么
<body>
<div id="root">
</div>
</body>
<script>
const app = Vue.createApp({
data () {
return {
inputValue:'',
checkBoxFlag:false,
checkBoxArr:[],
radioValue:''
}
},
template:`
<div>
{{inputValue}}
<input v-model="inputValue"/>
<textarea v-model="inputValue"/>
<br/>
{{checkBoxFlag}}
<input type="checkbox" v-model="checkBoxFlag" />
<br/>
{{checkBoxArr}}
test1:<input type="checkbox" v-model="checkBoxArr" value="test1" />
test2:<input type="checkbox" v-model="checkBoxArr" value="test2" />
test3:<input type="checkbox" v-model="checkBoxArr" value="test3" />
<br/>
{{radioValue}}
test1:<input type="radio" v-model="radioValue" value="test1" />
test2:<input type="radio" v-model="radioValue" value="test2" />
test3:<input type="radio" v-model="radioValue" value="test3" />
</div>
`
});
// 挂载实例到节点下
app.mount('#root');
</script>
进阶
<body>
<div id="root">
</div>
</body>
<script>
const app = Vue.createApp({
data () {
return {
selectValue:[],
options:[
{
text:'A',value:'A'
},
{
text:'B',value:'B'
},
{
text:'C',value:'C'
}
]
}
},
template:`
<div>
{{selectValue}}
<select v-model="selectValue" multiple>
<option v-for="(item,index) in options " v-bind:value="item.value">{{item.text}}</option>
</select>
</div>
`
});
// 挂载实例到节点下
app.mount('#root');
</script>

深入(checkbox用自定义表示选中与否,不是用true/false)
<body>
<div id="root">
</div>
</body>
<script>
const app = Vue.createApp({
data () {
return {
checkBoxFlag:'hello'
}
},
template:`
<div>
{{checkBoxFlag}}
<input type="checkbox" v-model="checkBoxFlag" true-value="hello" false-value="world" />
</div>
`
});
// 挂载实例到节点下
app.mount('#root');
</script>

其他(v-model修饰符)
<body>
<div id="root">
</div>
</body>
<script>
// v-model.lazy失去焦点时触发;
// v-model.number写入message值时变成number类型的
// v-model.trim去除前后空格
const app = Vue.createApp({
data () {
return {
message:'111'
}
},
template:`
<div>
{{message}}
<input v-model.lazy="message" />
{{typeof message}}
<input v-model.number="message" type="number" />
</div>
`
});
// 挂载实例到节点下
app.mount('#root');
</script>

其他(v-model自定义修饰符)
modelModifiers 接收父组件v-model后面自定义的修饰符
<body>
<div id="root"></div>
</body>
<script>
const app = Vue.createApp({
data() {
return {
count: 'a',
}
},
template: `
<counter v-model.uppercase="count" />
`
});
app.component('counter', {
props: {
'modelValue': String,
'modelModifiers': {
default: ()=> ({})
}
},
methods: {
handleClick() {
let newValue = this.modelValue + 'b';
if(this.modelModifiers.uppercase) {
newValue = newValue.toUpperCase();
}
this.$emit('update:modelValue', newValue);
},
},
template: `
<div @click="handleClick">{{modelValue}}</div>
`
});
const vm = app.mount('#root');
</script>
组件
全局组件和局部组件
局部组件 首字母最好大写
<body>
<div id="root">
</div>
</body>
<script>
const app = Vue.createApp({
template:`
<counter />
`
});
app.component('counter',{
data () {
return {
count:1
}
},
template:`<div v-on:click = "count+=1">
{{count}}
</div>`
});
// 挂载实例到节点下
app.mount('#root');
</script>
<body>
<div id="root">
</div>
</body>
<script>
const Counter = {
data () {
return {
count:1
}
},
template:`<div v-on:click = "count+=1">
{{count}}
</div>`
};
const app = Vue.createApp({
components: {
counterValueue:Counter
},
template:`
<counterValueue />
`
});
// 挂载实例到节点下
app.mount('#root');
</script>
父子组件传值
基本应用
// type: String ,Boolean,Array Object,Function,Symbol。。。
// required 必传
// default: 默认值
// validator
<body>
<div id="root">
</div>
</body>
<script>
const counter = {
// type: String ,Boolean,Array Object,Function,Symbol。。。
// required 必传
// default: 默认值
// validator
props: {
count:{
type:String,
required:true,
default:function(value){
return 456;
},
validator:function(value){
return value<1000;
}
}
},
template:`<div>
{{typeof count}}
</div>`
};
const app = Vue.createApp({
components: {
counterValueue:counter
},
data () {
return {
num:1
}
},
template:`
<div >
<counterValueue v-bind:count="num" />
</div>
`
});
// 挂载实例到节点下
app.mount('#root');
</script>
进阶应用
注意:
v-bind=“params” 等价于 v-bind:a=“params.a” v-bind:b=“params.b” v-bind:b=“params.c”
属性传值的时候,使用content-abc这种命名,接的时候,使用contentAbc
<body>
<div id="root">
</div>
</body>
<script>
// v-bind="params" 等价于 v-bind:a="params.a" v-bind:b="params.b" v-bind:b="params.c"
const counter = {
props: ['a','b','c'],
template:`<div>
{{a}}--{{b}}--{{c}}
</div>`
};
const app = Vue.createApp({
components: {
counterValueue:counter
},
data () {
return {
params:{
a:1,
b:2,
c:3
}
}
},
template:`
<div >
<counterValueue v-bind="params" />
</div>
`
});
// 挂载实例到节点下
app.mount('#root');
</script>
单项数据流
子组件可以使用父组件的数据,但不能反向修改父组件的数据
如果想要更改,子组件可以复制一份
<body>
<div id="root">
</div>
</body>
<script>
const counter = {
props: ['count'],
data () {
return {
myCount:this.count
}
},
template:`<div v-on:click="myCount+=1">
{{myCount}}
</div>`
};
const app = Vue.createApp({
components: {
counterValueue:counter
},
data () {
return {
num:1
}
},
template:`
<div>
<counterValueue v-bind:count="num" />
</div>
`
});
// 挂载实例到节点下
app.mount('#root');
</script>
父子组件传值(Non-props)
<body>
<div id="root"></div>
</body>
<script>
// Non-prop 属性
const app = Vue.createApp({
template: `
<div>
<counter msg="hello" msg1="hello1" />
</div>
`
});
app.component('counter', {
// inheritAttrs: false,
mounted() {
console.log(this.$attrs.msg);
},
template: `
<div :msg="$attrs.msg">Counter</div>
<div v-bind="$attrs">Counter</div>
<div :msg1="$attrs.msg1">Counter</div>
`
});
const vm = app.mount('#root');
</script>

组件之间通过事件通信
初级
注意:对应关系,必须是-

<body>
<div id="root"></div>
</body>
<script>
const app = Vue.createApp({
data() {
return { count: 1 }
},
methods: {
handleItemClick(param){
this.count+=param;
}
},
template: `
<counter v-bind:count="count" v-on:handle-click="handleItemClick"/>
`
});
app.component('counter', {
props: ['count'],
methods: {
handleClick() {
this.$emit('handleClick', 3);
}
},
template: `
<div @click="handleClick">{{count}}</div>
`
});
const vm = app.mount('#root');
</script>
进阶(父子组件存在双向绑定)
接收v-model的值时,下面的两个参数是固定的
modelValue
update:modelValue
<body>
<div id="root"></div>
</body>
<script>
const app = Vue.createApp({
data() {
return { count: 1 }
},
template: `
<counter v-model="count" />
`
});
app.component('counter', {
props: ['modelValue'],
methods: {
handleClick() {
this.$emit('update:modelValue', this.modelValue + 3);
}
},
template: `
<div @click="handleClick">{{modelValue}}</div>
`
});
const vm = app.mount('#root');
</script>
使用插槽和具名插槽解决组件内容传递问题
插槽
<body>
<div id="root"></div>
</body>
<script>
// slot 插槽
// slot 中使用的数据,作用域的问题
// 父模版里调用的数据属性,使用的都是父模版里的数据
// 子模版里调用的数据属性,使用的都是子模版里的数据
const app = Vue.createApp({
data () {
return {
text:'提交'
}
},
template: `
<myform>
<div>{{text}}</div>
</myform>
<myform>
<button>{{text}}</button>
</myform>
`
});
app.component('myform', {
methods: {
handleClick(){
alert("11");
}
},
template: `
<div>
<input />
<span @click="handleClick">
<slot></slot>
</span>
</div>
`
});
const vm = app.mount('#root');
</script>
具名插槽
<body>
<div id="root"></div>
</body>
<script>
// slot 插槽
// slot 中使用的数据,作用域的问题
// 父模版里调用的数据属性,使用的都是父模版里的数据
// 子模版里调用的数据属性,使用的都是子模版里的数据
// 具名插槽
const app = Vue.createApp({
template: `
<layout>
<template v-slot:header>
<div>header</div>
</template>
<template v-slot:footer>
<div>footer</div>
</template>
</layout>
`
});
app.component('layout', {
template: `
<div>
<slot name="header"></slot>
<div>content</div>
<slot name="footer"></slot>
</div>
`
});
const vm = app.mount('#root');
</script>
作用域插槽
父组件使用子组件的数据
// 作用域插槽
const app = Vue.createApp({
template: `
<list v-slot="{item}">
<div>{{item}}</div>
</list>
`
});
app.component('list', {
data() {return {list: [1, 2, 3]}},
template: `
<div>
<slot v-for="item in list" :item="item" />
</div>
`
});
const vm = app.mount('#root');
</script>
动态组件和异步组件
动态组件
:is 根据数据的切换显示不同组件
keep-alive 缓存,防止每次切换数据没有
<body>
<div id="root"></div>
</body>
<script>
const app = Vue.createApp({
data () {
return {
currentItem:'input-item'
}
},
methods: {
handle(){
this.currentItem = this.currentItem=="input-item" ? "common-item" :"input-item"
}
},
template: `
<keep-alive>
<component :is="currentItem"/>
</keep-alive>
<button @click="handle">切换</button>
`
});
app.component('input-item', {
template: `
<div> <input /></div>
`
});
app.component('common-item', {
template: `
<div>hello world</div>
`
});
const vm = app.mount('#root');
</script>

异步组件
<body>
<div id="root"></div>
</body>
<script>
// 动态组件: 根据数据的变化,结合 compoent 这个标签,来随时动态切换组件的现实
// 异步组件: 是异步执行某些组件的逻辑,这叫做异步组件
const app = Vue.createApp({
template: `
<div>
<common-item />
<async-common-item />
</div>
`
});
app.component('common-item', {
template: `<div>hello world</div>`
});
app.component('async-common-item', Vue.defineAsyncComponent(() => {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
resolve({
template: `<div>this is an async component</div>`
})
}, 4000)
})
}))
const vm = app.mount('#root');
</script>
查漏补缺(ref(对dom进行操作)、 provide / inject)
// ref 实际上是获取 Dom 节点 / 组件引用 的一个语法
// provide / inject 对父组件的data传值,provide: {count:this.count}这样的语法是不可行的
通过 provide / inject 传递的值是一次性的,所以说更改父组件的值,子组件不会改变
<body>
<div id="root"></div>
</body>
<script>
// ref 实际上是获取 Dom 节点 / 组件引用 的一个语法
// provide / inject 对父组件的data传值,provide: {count:this.count}这样的语法是不可行的
const app = Vue.createApp({
data() {
return { count: 1}
},
provide() {
return {
count: this.count,
}
},
mounted () {
console.log(this.$refs.count.innerHTML);
console.log(this.$refs.common);
},
template: `
<div>
<div ref="count">{{count}}</div>
<child ref="common" :count="count" />
<button @click="count += 1">Add</button>
</div>
`
});
app.component('child', {
template: `<child-child />`
});
app.component('child-child', {
inject: ['count'],
template: `<div>{{count}}</div>`
});
const vm = app.mount('#root');
</script>
动画
过渡:一个元素状态的变更
动画:一个元素的运动情况
高级语法
Mixin混入
下面是局部Mixin,如果是全局,下面myMixin 对应的对象放入app.mixix()括号里即可
注意:
// 组件 data, methods 优先级高于 mixin data, methods 优先级
// 生命周期函数,先执行 mixin 里面的,再执行组件里面的
<body>
<div id="root"></div>
</body>
<script>
const myMixin = {
data () {
return {
number:1
}
}
}
const app = Vue.createApp({
mixins: [myMixin],
data () {
return {
number:2
}
},
template: `
<div>
<div>{{number}}</div>
</div>
`
});
const vm = app.mount('#root');
</script>
注意:
// 自定义的属性,组件种的属性优先级高于 mixin 属性的优先级
this.$options 获取自定义属性值
<body>
<div id="root"></div>
</body>
<script>
// mixin 混入
// 组件 data, methods 优先级高于 mixin data, methods 优先级
// 生命周期函数,先执行 mixin 里面的,再执行组件里面的
// 自定义的属性,组件种的属性优先级高于 mixin 属性的优先级
const myMixin = {
number: 1
}
const app = Vue.createApp({
mixins: [myMixin],
number: 2,
template: `
<div>
<div>{{this.$options.number}}</div>
</div>
`
});
// 修改优先级,如果有mixin值,优先返回混入中的,再返回app中的
app.config.optionMergeStrategies.number = (mixinVal, appValue) => {
return mixinVal || appValue;
}
const vm = app.mount('#root');
</script>
Vue自定义指令
局部指令和全局指令
如果使用全局Vue.createApp不用再引入directives属性了,
<body>
<div id="root"></div>
</body>
<script>
// 局部自定义指令
const directives = {
focus:{
mounted (el) {
el.focus();
}
}
}
const app = Vue.createApp({
directives: directives,
template: `
<div>
<div><input v-focus /></div>
</div>
`
});
// 全局自定义指令,使用全局Vue.createApp不用再引入directives属性了,
// app.directive('focus',{
// mounted (el) {
// el.focus();
// }
// })
const vm = app.mount('#root');
</script>
自定义指令传值
<style>
.header { position: absolute}
</style>
<body>
<div id="root"></div>
</body>
<script>
// 自定义指令 directive
const app = Vue.createApp({
data() {
return {
distance: 110
}
},
template: `
<div>
<div v-pos:right="distance" class="header">
<input />
</div>
</div>
`
});
app.directive('pos', (el, binding) => {
el.style[binding.arg] = (binding.value + 'px');
})
const vm = app.mount('#root');
</script>
Teleport传送门
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>lesson 30</title>
<style>
.area {
position: absolute;
left: 50%;
top: 50%;
transform: translate(-50%, -50%);
width: 200px;
height: 300px;
background: green;
}
.mask {
position: absolute;
left: 0;
right: 0;
top: 0;
bottom: 0;
background: #000;
opacity: 0.5;
color: #fff;
font-size: 100px;
}
</style>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/vue@next"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="root"></div>
<div id="hello"></div>
</body>
<script>
// teleport 传送门
const app = Vue.createApp({
data() {
return {
show: false,
message: 'hello'
}
},
methods: {
handleBtnClick() {
this.show = !this.show;
}
},
template: `
<div class="area">
<button @click="handleBtnClick">按钮</button>
<teleport to="#hello">
<div class="mask" v-show="show">{{message}}</div>
</teleport>
</div>
`
});
const vm = app.mount('#root');
</script>
</html>
render函数(虚拟DOM)
<body>
<div id="root"></div>
</body>
<script>
// render function
// template -> render -> h -> 虚拟DOM(JS对象)-> 真实 DOM -> 展示到页面上
const app = Vue.createApp({
template: `
<my-title :level="2">
hello dell
</my-title>
`
});
app.component('my-title', {
props: ['level'],
render() {
const { h } = Vue;
return h('h' + this.level, {}, [
this.$slots.default(),
h('h4', {}, 'dell')
])
}
})
const vm = app.mount('#root');
</script>
插件的定义与使用
定义
<body>
<div id="root"></div>
</body>
<script>
// plugin 插件, 也是把通用性的功能封装起来
const myPlugin = {
install(app, options) {
app.provide('name', 'Dell Lee');
app.directive('focus', {
mounted(el) {
el.focus();
}
})
app.mixin({
mounted(){
console.log('mixin')
}
})
app.config.globalProperties.$sayHello = 'hello world';
}
}
const app = Vue.createApp({
template: `
<my-title />
`
});
app.component('my-title', {
inject: ['name'],
mounted() {
console.log(this.$sayHello);
},
template: `<div>{{name}}<input v-focus /></div>`
})
app.use(myPlugin, { name: 'dell'});
const vm = app.mount('#root');
</script>
使用
<body>
<div id="root"></div>
</body>
<script>
// 对数据做校验的插件
const app = Vue.createApp({
data() {
return { name: 'dell', age: 23}
},
rules: {
age: {
validate: age => age > 25,
message: 'too young, to simple'
},
name: {
validate: name => name.length >= 4,
message: 'name too short'
}
},
template: `
<div>name:{{name}}, age:{{age}}</div>
`
});
const validatorPlugin = (app, options) => {
app.mixin({
created() {
for(let key in this.$options.rules) {
const item = this.$options.rules[key];
this.$watch(key, (value) => {
const result = item.validate(value);
if(!result) console.log(item.message);
})
}
}
})
}
app.use(validatorPlugin);
const vm = app.mount('#root');
</script>
Composition API
Setup函数使用
setup中的return的内容,会直接暴露在外部,可以直接使用,setup中因为是在实例化之前调用的,所以this这样的关键词是不能用的,因为data、template…还没有实例化呢
<body>
<div id="root"></div>
</body>
<script>
const app = Vue.createApp({
template: `
<div @click="handleClick">{{name}}</div>
`,
methods: {
test() {
console.log(this.$options.setup());
}
},
mounted() {
this.test();
},
// created 实例被完全初始化之前
setup(props, context) {
return {
name: 'dell',
handleClick: () => {
alert(123)
}
}
}
});
const vm = app.mount('#root');
</script>
ref、reactive、toRefs(把setup中普通的变量变成响应式变量)
// ref, reactive 响应式的引用
// 原理,通过 proxy 对数据进行封装,当数据变化时,触发模版等内容的更新
// ref 处理基础类型的数据
// reactive 处理非基础类型的数据
// readonly 处理非基础类型的数据,而且此响应式变量不能更改
// toRefs 用于将响应式对象转换为结果对象,其中结果对象的每个属性都是指向原始对象相应属性的ref,常用于es6的解构赋值操作,因为在对一个响应式对象直接解构时解构后的数据将不再有响应式,而使用toRefs可以方便解决这一问题
<body>
<div id="root"></div>
</body>
<script>
const app = Vue.createApp({
template: `
<div>{{name}}</div>
<div>{{nameObj.name}}</div>
<div>{{nameArr[0]}}</div>
<div>{{nameByRefs}}</div>
<div>{{nameOnly.name}}</div>
`,
setup(props, context) {
const { ref,reactive,readonly, toRefs } = Vue;
// proxy ,把这个值 'dell' 变成 proxy({value: 'dell'}) 这样的一个响应式引用,赋值用name.value
let name = ref('第一段代码');
setTimeout(() => {
name.value = '第一段代码change'
}, 2000)
// proxy , { name: 'dell'} 变成 proxy({ name: 'dell'}) 这样的一个响应式引用
const nameObj = reactive({name: '第二段代码', age: 28});
setTimeout(() => {
nameObj.name = '第二段代码change'
}, 2000)
// 数组变成响应式引用
const nameArr = reactive([123]);
setTimeout(() => {
nameArr[0] = 456
}, 2000)
// toRefs proxy({ name: 'dell', age: 28}),变成下面这样的
// {
// name: proxy({ value: 'dell'}),
// age: proxy({value: 28})
// }
const nameRefs = reactive({nameByRefs: '最后一段代码', ageByRefs: 28});
setTimeout(() => {
nameRefs.nameByRefs = '最后一段代码change'
}, 2000)
const { nameByRefs, ageByRefs } = toRefs(nameRefs);
// 不能更改的响应式变量
const nameOnly = readonly({name: 'dell', age: 28});
setTimeout(() => {
nameOnly.name = 'lee'
}, 2000)
return { name,nameObj,nameArr,nameOnly,nameByRefs }
}
});
const vm = app.mount('#root');
</script>
toRef
// 避免toRefs 中取变量取不到,可以使用toRef,toRef(data,''age')的意思就是
如果age有值,则取age作为变量作为响应式变量,如果没有age变量,则创建一个age的响应式变量

setUp(content参数)
attrs 获取父组件上的属性
slots 获取父组件的插槽
emit 调用父组件方法


<body>
<div id="root"></div>
</body>
<script>
const app = Vue.createApp({
methods: {
handleChange() {
alert('change');
}
},
template: `<child @change="handleChange">parent</child>`,
});
app.component('child', {
template: '<div @click="handleClick">123123</div>',
setup(props, context) {
const { h } = Vue;
const { attrs, slots, emit } = context;
function handleClick() { emit('change'); }
return { handleClick }
}
})
const vm = app.mount('#root');
</script>
实现todolist
<body>
<div id="root"></div>
</body>
<script>
// 关于 list 操作的内容进行了封装
const listRelativeEffect = () => {
const { reactive } = Vue;
const list = reactive([]);
const addItemToList = (item) => {
list.push(item);
}
return { list, addItemToList }
}
// 关于 inputValue 操作的内容进行了封装
const inputRelativeEffect = () => {
const { ref } = Vue;
const inputValue = ref('');
const handleInputValueChange = (e) => {
inputValue.value = e.target.value
}
return { inputValue, handleInputValueChange}
}
const app = Vue.createApp({
setup() {
// 流程调度中转
const { list, addItemToList } = listRelativeEffect();
const { inputValue, handleInputValueChange} = inputRelativeEffect();
return {
list, addItemToList,
inputValue, handleInputValueChange
}
},
template: `
<div>
<div>
<input :value="inputValue" @input="handleInputValueChange" />
<button @click="() => addItemToList(inputValue)">提交</button>
</div>
<ul>
<li v-for="(item, index) in list" :key="index">{{item}}</li>
</ul>
</div>
`,
});
const vm = app.mount('#root');
</script>
computed计算属性
<script>
// computed 计算属性
const app = Vue.createApp({
setup() {
const { reactive, computed } = Vue;
const countObj = reactive({ count: 0});
const handleClick = () => {
countObj.count += 1;
}
let countAddFive = computed({
get: () => {
return countObj.count + 5;
},
set: (param) => {
countObj.count = param - 5;
}
})
setTimeout(() => {
countAddFive.value = 100;
}, 3000)
return { countObj, countAddFive, handleClick }
},
template: `
<div>
<span @click="handleClick">{{countObj.count}}</span> -- {{countAddFive}}
</div>
`,
});
const vm = app.mount('#root');
</script>
watch和watchEffect 的使用和差异性(侦听器)
<body>
<div id="root"></div>
</body>
<script>
// watch 侦听器
// watchEffect 侦听器,偏向于 effect
const app = Vue.createApp({
setup() {
const { reactive, watch, watchEffect, toRefs } = Vue;
const nameObj = reactive({
name: 'dell', englishName: 'lee'
})
// 具备一定的惰性 lazy
// 参数可以拿到原始和当前值
// 可以侦听多个数据的变化,用一个侦听器承载
// immediate 惰性
watch([() => nameObj.name, () => nameObj.englishName], ([curName, curEng], [prevName, preEng]) => {
console.log('watch', curName, prevName, '---', curEng, preEng);
}, { immediate: true })
// 立即执行,没有惰性 immediate
// 不需要传递你要侦听的内容,自动会感知代码依赖,不需要传递很多参数,只要传递一个回调函数
// 不能获取之前数据的值
// const stop = watchEffect(() => {
// console.log(nameObj.name);
// console.log(nameObj.englishName);
// setTimeout(() => {
// stop();
// }, 5000)
// })
const { name, englishName } = toRefs(nameObj);
return { name, englishName }
},
template: `
<div>
<div>
Name: <input v-model="name">
</div>
<div>
Name is {{name}}
</div>
<div>
EnglishName: <input v-model="englishName">
</div>
<div>
EnglishName is {{englishName}}
</div>
</div>
`,
});
const vm = app.mount('#root');
</script>
生命周期函数

<body>
<div id="root"></div>
</body>
<script>
const app = Vue.createApp({
setup() {
const {
ref, onBeforeMount, onMounted, onBeforeUpdate, onUpdated,
onRenderTracked, onRenderTriggered
} = Vue;
const name = ref('dell')
onBeforeMount(() => {
console.log('onBeforeMount')
})
onMounted(() => {
console.log('onMounted')
})
onBeforeUpdate(() => {
console.log('onBeforeUpdate')
})
onUpdated(() => {
console.log('onUpdated')
})
// 每次渲染后重新收集响应式依赖
onRenderTracked(() => {
console.log('onRenderTracked')
})
// 每次触发页面重新渲染时自动执行
onRenderTriggered(() => {
console.log('onRenderTriggered')
})
const handleClick = () => {
name.value = 'lee'
}
return { name, handleClick }
},
template: `
<div @click="handleClick">
{{name}}
</div>
`,
});
const vm = app.mount('#root');
</script>
provide、inject
<body>
<div id="root"></div>
</body>
<script>
// provide, inject
// dom ref
// const app = Vue.createApp({
// setup() {
// const { provide, ref, readonly } = Vue;
// const name = ref('dell');
// provide('name', readonly(name));
// provide('changeName', (value) => {
// name.value = value;
// });
// return { }
// },
// template: `
// <div>
// <child />
// </div>
// `,
// });
// app.component('child', {
// setup() {
// const { inject } = Vue;
// const name = inject('name');
// const changeName = inject('changeName');
// const handleClick = () => {
// changeName('lee');
// }
// return { name, handleClick }
// },
// template: '<div @click="handleClick">{{name}}</div>'
// })
// CompositionAPI 的语法下,获取真实的 DOM 元素节点
const app = Vue.createApp({
setup() {
const { ref, onMounted } = Vue;
const hello = ref(null);
onMounted(() => {
console.log(hello.value);
})
return { hello }
},
template: `
<div>
<div ref="hello">hello world</div>
</div>
`,
});
const vm = app.mount('#root');
</script><body>
<div id="root"></div>
</body>
<script>
// provide, inject
const app = Vue.createApp({
setup() {
const { provide, ref} = Vue;
const name = ref('dell');
provide('name', name);
provide('changeName', (value) => {
name.value = value;
});
return { }
},
template: `
<div>
<child />
</div>
`,
});
app.component('child', {
setup() {
const { inject } = Vue;
const name = inject('name');
const changeName = inject('changeName');
const handleClick = () => {
changeName('lee');
}
return { name, handleClick }
},
template: '<div @click="handleClick">{{name}}</div>'
})
const vm = app.mount('#root');
</script>
ref 获取dom节点
固定写法:命名一致
const hello = ref(null);
return { hello }
ref=“hello”
<body>
<div id="root"></div>
</body>
<script>
// CompositionAPI 的语法下,获取真实的 DOM 元素节点
const app = Vue.createApp({
setup() {
const { ref, onMounted } = Vue;
const hello = ref(null);
onMounted(() => {
console.log(hello.value);
})
return { hello }
},
template: `
<div>
<div ref="hello">hello world</div>
</div>
`,
});
const vm = app.mount('#root');
</script>
路由
<template>
<div id="nav">
<!-- router-link 是跳转路由的标签 -->
<router-link to="/">Home</router-link> |
<router-link to="/about">About</router-link> |
<router-link to="/login">Login</router-link>
</div>
<!-- router-view 负责展示当前路由对应的组件内容 -->
<router-view/>
</template>
<style></style>
import { createRouter, createWebHashHistory } from 'vue-router'
import Home from '../views/Home.vue'
import Login from '../views/Login.vue'
const routes = [
{
path: '/',
name: 'Home',
component: Home
},
{
path: '/login',
name: 'Login',
component: Login
},
{
path: '/about',
name: 'About',
// 异步加载路由
component: () => import(/* webpackChunkName: "about" */ '../views/About.vue')
}
]
const router = createRouter({
history: createWebHashHistory(),
routes
})
export default router
VueX
应用
import { createStore } from 'vuex'
// VueX 数据管理框架
// VueX 创建了一个全局唯一的仓库,用来存放全局的数据
export default createStore({
state: { name: 'dell' },
// mutation 里面只允许写同步代码,不允许写异步代码,比如setTimeout就不能写
// commit 和 mutation 做关联
mutations: {
change(state, str) {
state.name = str;
}
},
// dispatch 和 actions 做关联
actions: {
change(store, str) {
setTimeout(() => {
store.commit('change', str)
}, 2000)
}
}
})
<template>
<div class="about">
<h1 @click="handleClick">This is an about page</h1>
<h1>{{myName}}</h1>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: 'Home',
computed: {
myName() {
return this.$store.state.name;
}
},
methods: {
handleClick() {
// 1. dispatch 方法,派发一个 action,名字叫做change
// 2. 感知到 change 这个action,执行store 中 actions 下面的 change 方法
// 3. commit 提交一个叫做 change 的数据改变
// 4. mutation 感知到提交的change改变,执行 change 方法改变数据
this.$store.dispatch('change', 'hello world');
}
}
}
</script>
composition 使用vuex
import { createStore } from 'vuex'
export default createStore({
state: { name: 'dell' },
mutations: {
changeName(state, str) {
state.name = str;
}
},
actions: {
getData(store) {
setTimeout(() => {
store.commit('changeName', 'hello')
}, 2000)
}
}
})
<template>
<div class="about">
<h1 @click="handleClick">This is an about page</h1>
<h1>{{name}}</h1>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import { toRefs } from 'vue';
import { useStore } from 'vuex';
export default {
name: 'Home',
setup() {
const store = useStore();
const { name } = toRefs(store.state);
const handleClick = () => {
store.dispatch('getData')
}
return { name, handleClick }
}
}
</script>·






















 815
815











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








