以下spring流程分析针对spring 4.x
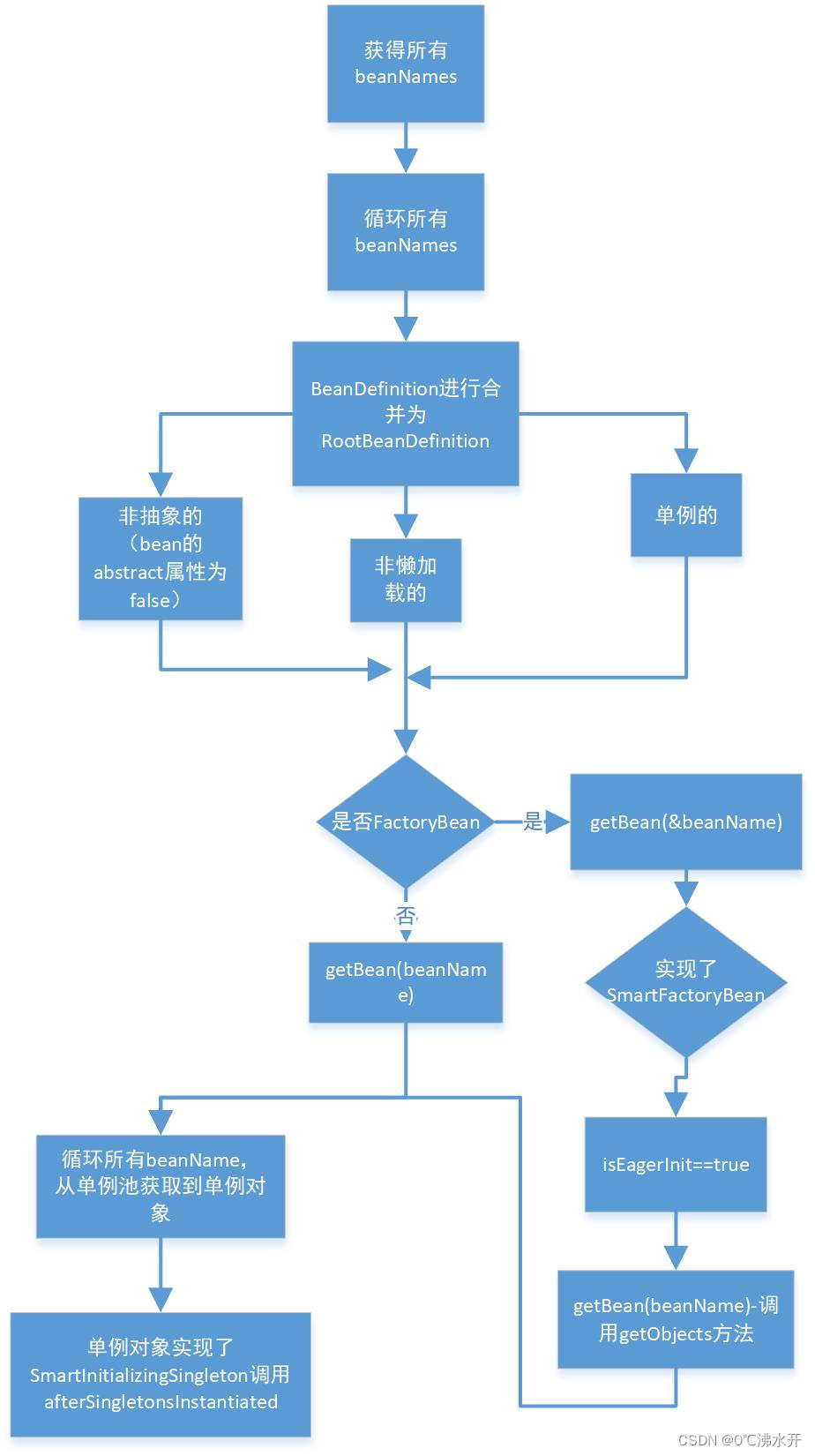
1. spring通过 scan扫描后会对bean定义进行注册,放入到单例池中。那么这一系列的流程是如何进行的呢?接下来我们跟踪一下spring创建bean的流程。源码在DefaultListableBeanFactory.java中,现展示如下:
public void preInstantiateSingletons() throws BeansException {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Pre-instantiating singletons in " + this);
}
List<String> beanNames = new ArrayList<>(this.beanDefinitionNames);
for (String beanName : beanNames) {
//合并bean定义,如在xml中有bean有对应的parent属性需要继承父类的属性
RootBeanDefinition bd = getMergedLocalBeanDefinition(beanName);
/**
* 根据bean定义判断是不是抽象的(在xml文件可配置bean的abstract属性为true)
* && 不是单例的 &&不是懒加载的
*/
if (!bd.isAbstract() && bd.isSingleton() && !bd.isLazyInit()) {
if (isFactoryBean(beanName)) {
Object bean = getBean(FACTORY_BEAN_PREFIX + beanName);
if (bean instanceof FactoryBean) {
final FactoryBean<?> factory = (FactoryBean<?>) bean;
boolean isEagerInit;
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null && factory instanceof SmartFactoryBean) {
isEagerInit = AccessController.doPrivileged((PrivilegedAction<Boolean>)
((SmartFactoryBean<?>) factory)::isEagerInit,
getAccessControlContext());
}
else {
//SmartFactoryBean 的isEagerInit默认为false,但是可进行手动修改
isEagerInit = (factory instanceof SmartFactoryBean &&
((SmartFactoryBean<?>) factory).isEagerInit());
}
//调用真正的getBean的流程 调用getObject对象的方法
if (isEagerInit) {
getBean(beanName);
}
/**
* 实现了FactoryBean对象的bean,在spring启动的时候不会主动去创建getObject里面的对象,
* 创建对象是在主动调用getBean的时候,但是如果实现了SmartFactoryBean接口且isEagerInit=isEagerInit
* 则会在spring启动的时候创建
*/
}
}
else {
getBean(beanName);
}
}
}
for (String beanName : beanNames) {
Object singletonInstance = getSingleton(beanName);
//判断当前的bean是否实现了SmartInitializingSingleton接口
if (singletonInstance instanceof SmartInitializingSingleton) {
final SmartInitializingSingleton smartSingleton = (SmartInitializingSingleton) singletonInstance;
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null) {
AccessController.doPrivileged((PrivilegedAction<Object>) () -> {
smartSingleton.afterSingletonsInstantiated();
return null;
}, getAccessControlContext());
}
else {
smartSingleton.afterSingletonsInstantiated();
}
}
}
}在此处画一个图对上面段代码片段的逻辑说明:
<








 最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
最低0.47元/天 解锁文章















 94
94











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








