目录
前言
SpringBoot开启gzip压缩的配置如下
// 是否开启压缩,默认false
server.compression.enabled:
// 允许压缩的响应缓冲区最小字节数,默认2048
server.compression.min-response-size:
// 允许压缩的mimeType数组(逗号分隔,响应头Content-Type以其中一个数组项开头就能匹配)
server.compression.mime-types:
// 不允许压缩的请求头User-Agent数组(逗号分隔,完全匹配)
server.compression.excluded-user-agents:该配置具体默认值如下
org.springframework.boot.web.server.Compression
private boolean enabled = false;
private String[] mimeTypes = new String[] { "text/html", "text/xml", "text/plain", "text/css", "text/javascript",
"application/javascript", "application/json", "application/xml" };
private String[] excludedUserAgents = null;
private DataSize minResponseSize = DataSize.ofKilobytes(2);正文
这边用个Demo测试下
@RestController
@RequestMapping(value = "/api/gzip")
public class GzipTestController {
@RequestMapping(value = "/gzipTest", method = RequestMethod.GET)
public List<PersonVO> testGzip() {
List<PersonVO> vos = Lists.newArrayList();
for (int i = 1; i <= 20000; i++) {
PersonVO vo = new PersonVO();
vo.setId(i);
vo.setName("test" + i);
vo.setAge(i);
vo.setSex("男");
vos.add(vo);
}
return vos;
}
}在不开启gzip的情况下:

在开启gzip的情况下:

可以看出,两者返回的响应体大小和相应时间还是有差距的。
但是,在开启gzip压缩后,无论如何调整min-response-size,返回的响应体都是压缩过的。
在进行源码追踪后,定位到最终的问题的源码如下
org.apache.coyote.CompressionConfig#useCompression
// If force mode, the length and MIME type checks are skipped
if (compressionLevel != 2) {
// Check if the response is of sufficient length to trigger the compression
long contentLength = response.getContentLengthLong();
if (contentLength != -1 && contentLength < compressionMinSize) {
return false;
}
// Check for compatible MIME-TYPE
String[] compressibleMimeTypes = getCompressibleMimeTypes();
if (compressibleMimeTypes != null &&
!startsWithStringArray(compressibleMimeTypes, response.getContentType())) {
return false;
}
}从上图中可以看出,只有在contentLength不为-1且contentLength小于配置的min-response-size的值时才不会开启压缩。由于contengLength永远为-1,所以无论怎么修改min-response-size的值,响应体都是经过压缩的。
那究竟为什么contentLength为-1呢?这里从DispatcherServlet的doDispatch方法进行追踪,最终将问题定位在org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.AbstractMessageConverterMethodProcessor#writeWithMessageConverters(T, org.springframework.core.MethodParameter, org.springframework.http.server.ServletServerHttpRequest, org.springframework.http.server.ServletServerHttpResponse)这个方法中。
这个方法的具体逻辑就是将响应结果写出,写出的时候需要先选择符合的MediaType后再通过HttpMessageConverter消息转换器(这里符合测试接口的MidiaType为application/json;q=0.8,消息转换器为MappingJackson2HttpMessageConverter)写出时,执行了write方法org.springframework.http.converter.AbstractGenericHttpMessageConverter#write
public final void write(T t, @Nullable Type type, @Nullable MediaType contentType, HttpOutputMessage outputMessage) throws IOException, HttpMessageNotWritableException {
HttpHeaders headers = outputMessage.getHeaders();
this.addDefaultHeaders(headers, t, contentType);
if (outputMessage instanceof StreamingHttpOutputMessage) {
StreamingHttpOutputMessage streamingOutputMessage = (StreamingHttpOutputMessage)outputMessage;
streamingOutputMessage.setBody((outputStream) -> {
this.writeInternal(t, type, new HttpOutputMessage() {
public OutputStream getBody() {
return outputStream;
}
public HttpHeaders getHeaders() {
return headers;
}
});
});
} else {
this.writeInternal(t, type, outputMessage);
outputMessage.getBody().flush();
}
}这里有个this.addDefaultHeaders方法里面有设置contentLength的值
org.springframework.http.converter.AbstractHttpMessageConverter#addDefaultHeaders
...
if (headers.getContentLength() < 0L && !headers.containsKey("Transfer-Encoding")) {
Long contentLength = this.getContentLength(t, headers.getContentType());
if (contentLength != null) {
headers.setContentLength(contentLength);
}
}org.springframework.http.converter.json.AbstractJackson2HttpMessageConverter#getContentLength
protected Long getContentLength(Object object, @Nullable MediaType contentType) throws IOException {
if (object instanceof MappingJacksonValue) {
object = ((MappingJacksonValue)object).getValue();
}
return super.getContentLength(object, contentType);
}由于我返回的object不是MappingJacksonValue的类实例,因此走的super.getContentLength方法
org.springframework.http.converter.AbstractHttpMessageConverter#getContentLength
protected Long getContentLength(T t, @Nullable MediaType contentType) throws IOException {
return null;
}这里直接返回null,那么将不会设置Content-Length。
再回到org.apache.coyote.CompressionConfig#useCompression方法中,再调用response.getContentLengthLong方法时,里面直接取的Response对象的contentLength值,默认为-1
/**
* HTTP specific fields.
*/
String contentType = null;
String contentLanguage = null;
Charset charset = null;
// Retain the original name used to set the charset so exactly that name is
// used in the ContentType header. Some (arguably non-specification
// compliant) user agents are very particular
String characterEncoding = null;
long contentLength = -1;
private Locale locale = DEFAULT_LOCALE;因此,在判断是否需要进行gzip压缩时,min-response-size永远不生效。
扩展
首先看下源码中是如何判断是否需要开启压缩
org.apache.coyote.CompressionConfig#useCompression
...
Enumeration<String> headerValues = request.getMimeHeaders().values("accept-encoding");
boolean foundGzip = false;
while (!foundGzip && headerValues.hasMoreElements()) {
List<AcceptEncoding> acceptEncodings = null;
try {
acceptEncodings = AcceptEncoding.parse(new StringReader(headerValues.nextElement()));
} catch (IOException ioe) {
// If there is a problem reading the header, disable compression
return false;
}
for (AcceptEncoding acceptEncoding : acceptEncodings) {
if ("gzip".equalsIgnoreCase(acceptEncoding.getEncoding())) {
foundGzip = true;
break;
}
}
}从上图中可以看出,判断是否需要开启压缩是根据Request Headers请求头中的Accept-Encoding中是否含有gzip的值。
那么既然contentLength的值没法控制,可以换个思路只针对部分接口开启压缩。那么如何针对部分接口开启gzip压缩呢?我的想法是在配置中心加上需要开启gzip压缩的路径,利用过滤器将不匹配的请求移除Accept-Encoding,下面是具体的Demo。
public class CompressionFilter extends OncePerRequestFilter {
private final String[] gzipUrls = "/api/gzip/*".split(",");
private final AntPathMatcher antPathMatcher = new AntPathMatcher();
@Override
protected void doFilterInternal(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response,
FilterChain filterChain) throws ServletException, IOException {
String requestUri = request.getRequestURI();
boolean match = Arrays.stream(gzipUrls).anyMatch(url -> antPathMatcher.match(url,
requestUri));
if (!match) {
try {
Field requestField = ReflectionUtils
.findField(RequestFacade.class, "request", Request.class);
requestField.setAccessible(true);
Request request1 = (Request) requestField.get(request);
Field coyoteRequestField = ReflectionUtils
.findField(Request.class, "coyoteRequest", org.apache.coyote.Request.class);
coyoteRequestField.setAccessible(true);
org.apache.coyote.Request coyoteRequest =
(org.apache.coyote.Request) coyoteRequestField.get(request1);
Field headersField = ReflectionUtils
.findField(org.apache.coyote.Request.class, "headers", MimeHeaders.class);
headersField.setAccessible(true);
MimeHeaders mimeHeaders = (MimeHeaders) headersField.get(coyoteRequest);
mimeHeaders.removeHeader("Accept-Encoding");
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
filterChain.doFilter(request, response);
}@Configuration
public class FilterConfig {
@Bean
public FilterRegistrationBean compressionFilter() {
FilterRegistrationBean filterRegistrationBean = new FilterRegistrationBean();
filterRegistrationBean.setFilter(new CompressionFilter());
filterRegistrationBean.setOrder(Ordered.HIGHEST_PRECEDENCE);
filterRegistrationBean.addUrlPatterns("/*");
filterRegistrationBean.setName("compressionFilter");
return filterRegistrationBean;
}这里我写了个过滤器,通过路径AntPathMatcher进行路径匹配,不符合的请求通过反射将Accept-Encoding移除。
这里看下执行结果
能成功匹配的:
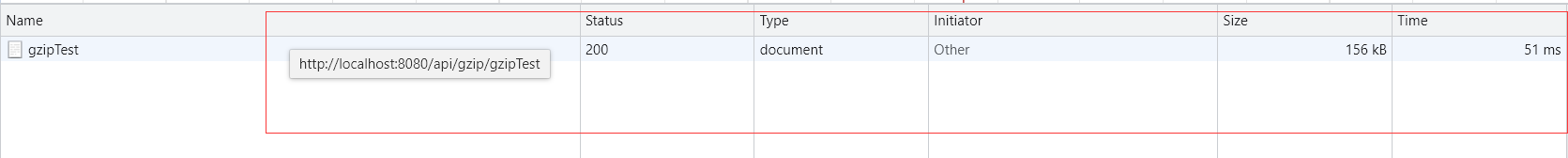
无法匹配的:

由于是Demo方便测试,这里配置的路径我直接写死的。在实际的应用中,都是以分布式的一个配置中心进行配置,以热更新的形式获取到最新配置的值。
总结
gzip压缩好处是可以节约带宽、流量,代价是额外的CPU、内存等系统资源的额外开销。如今性能过剩,带宽明显比cpu等要更重要。在实际应用中,开启gzip压缩通常都是配置在nginx或者网关中。






















 780
780











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








