文章目录
- MyBatis源码解析
- 一、mybatis怎么处理参数以及执行方法?
- 二、Mybatis工作原理
- 三、代理对象如何执行增删改查
- 1. MapperProxy的invoke
- 2. MapperMethod的execute方法
- 3. DefaultSqlSession的selectOne方法
- 4. Executor的query系列(不是重要方法)
- 5. Executor执行方法,默认是SIMPLE
- 6. BaseExecutor的queryFromDatabase
- 7. SimpleExecutor的doQuery方法
- 8. Configuration的newStatementHandler
- 9. PreparedStatementHandler的query
- 10. handleResultSets处理参数
- 11. Resulthandler的getPropertyMappingValue
- 总结
- 其他
MyBatis源码解析
一、mybatis怎么处理参数以及执行方法?
ParamNameResolver解析参数封装map的;
MapperProxy代理对象调用invoke方法:
-
MapperProxy的invoke方法public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable { if (Object.class.equals(method.getDeclaringClass())) { try { return method.invoke(this, args); } catch (Throwable var5) { throw ExceptionUtil.unwrapThrowable(var5); } } else { MapperMethod mapperMethod = this.cachedMapperMethod(method); return mapperMethod.execute(this.sqlSession, args); } }调用
mapperMethod.execute() -
MapperMethod的mapperMethod.execute()判断是什么类型(Select、Update…),解析参数之后,还是调用的SqlSession的原生方法(sqlSession.insert、sqlSession.update)。
所以,如何处理参数,就在this.method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);,这个方法又调用了paramNameResolver.getNamedParams(args)public Object execute(SqlSession sqlSession, Object[] args) { Object param; Object result; switch(this.command.getType()) { case INSERT: param = this.method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args); result = this.rowCountResult(sqlSession.insert(this.command.getName(), param)); break; case UPDATE: param = this.method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args); result = this.rowCountResult(sqlSession.update(this.command.getName(), param)); break; case DELETE: param = this.method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args); result = this.rowCountResult(sqlSession.delete(this.command.getName(), param)); break; case SELECT: if (this.method.returnsVoid() && this.method.hasResultHandler()) { this.executeWithResultHandler(sqlSession, args); result = null; } else if (this.method.returnsMany()) { result = this.executeForMany(sqlSession, args); } else if (this.method.returnsMap()) { result = this.executeForMap(sqlSession, args); } else if (this.method.returnsCursor()) { result = this.executeForCursor(sqlSession, args); } else { param = this.method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args); result = sqlSession.selectOne(this.command.getName(), param); } break; -
ParamNameResolver的convertArgsToSqlCommandParampublic Object convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(Object[] args) { return this.paramNameResolver.getNamedParams(args); } -
ParamNameResolver的getNamedParams(args)确定流程:
-
获取每个标了param注解的参数的@Param的值:id,lastName; 赋值给name;
-
每次解析一个参数给map中保存信息:(key:参数索引,value:name的值)
name的值:
标注了param注解:注解的值
没有标注:-
全局配置:
useActualParamName(jdk1.8):name=参数名 -
name=map.size();相当于当前元素的索引
-
{0=id, 1=lastName,2=2}
-
-
public Object getNamedParams(Object[] args) { int paramCount = this.names.size(); if (args != null && paramCount != 0) { //1、如果只有一个元素,并且没有Param注解;args[0]:单个参数直接返回 if (!this.hasParamAnnotation && paramCount == 1) { return args[(Integer)this.names.firstKey()]; //2、多个元素或者有Param标注 } else { Map<String, Object> param = new ParamMap(); int i = 0; //3、遍历names集合;{0=id, 1=lastName,2=2} for(Iterator i$ = this.names.entrySet().iterator(); i$.hasNext(); ++i) { Entry<Integer, String> entry = (Entry)i$.next(); //names集合的value作为key; names集合的key又作为取值的参考args[0]:args【1,"Tom"】: //eg:{id=args[0]:1,lastName=args[1]:Tom,2=args[2]} param.put(entry.getValue(), args[(Integer)entry.getKey()]); //额外的将每一个参数也保存到map中,使用新的key:param1...paramN //效果:有Param注解可以#{指定的key},或者#{param1} String genericParamName = "param" + String.valueOf(i + 1); if (!this.names.containsValue(genericParamName)) { param.put(genericParamName, args[(Integer)entry.getKey()]); } } return param; } // 参数为null直接返回 } else { return null; } } -
总结:参数多时会封装map,为了不混乱,我们可以使用@Param来指定封装时使用的key;
{key}就可以取出map中的值;
二、Mybatis工作原理
Mybatis四大对象:
• Executor (update, query, flushStatements, commit, rollback, getTransaction, close, isClosed)
• ParameterHandler (getParameterObject, setParameters)
• ResultSetHandler (handleResultSets, handleOutputParameters)
• StatementHandler (prepare, parameterize, batch, update, query)
混个眼熟,后面会遇到。
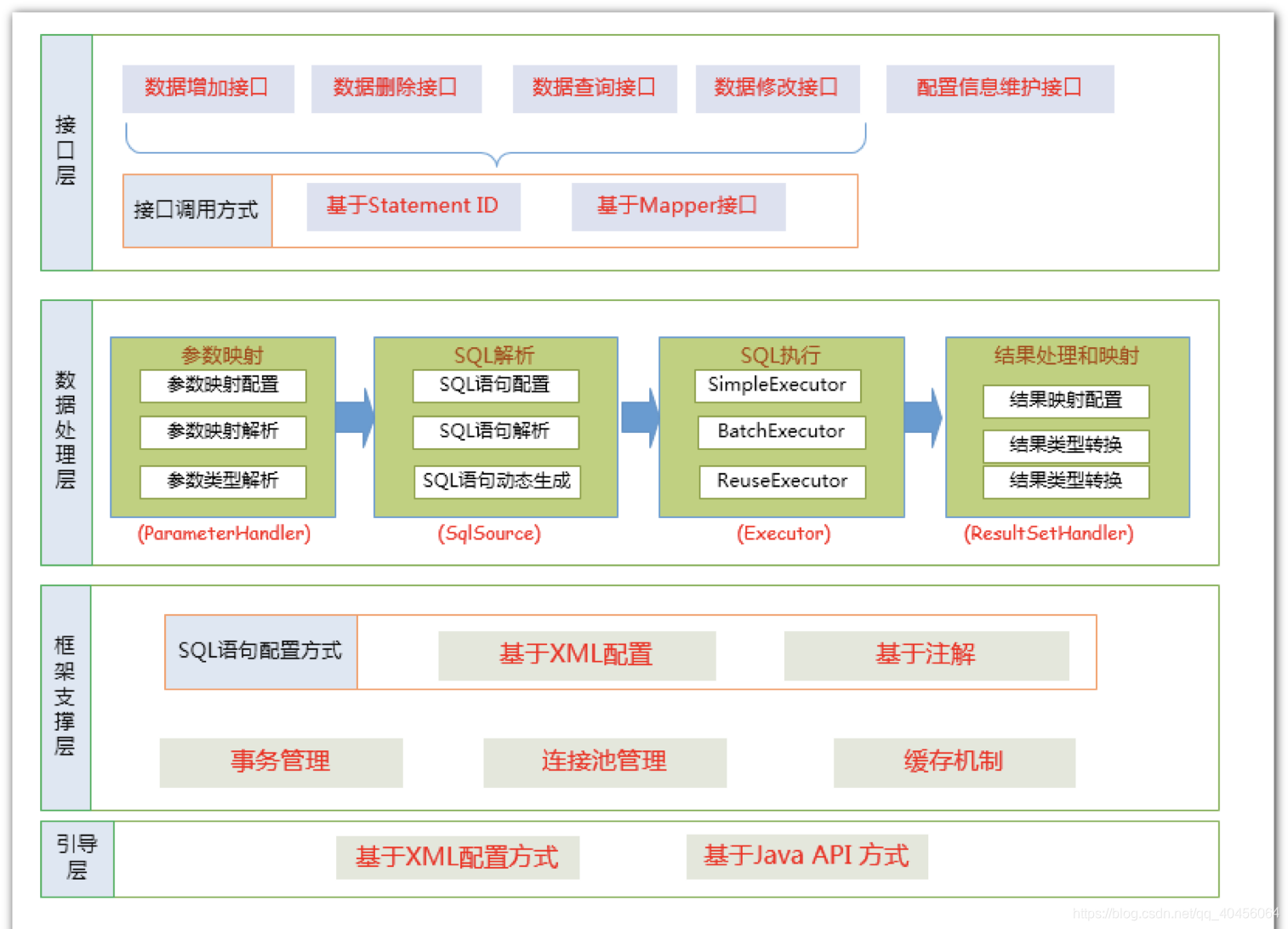
Mybatis框架分层:我们关注:数据处理层,其实就对应上面的四大对象!!!

/**
* 1、获取sqlSessionFactory对象:
* 解析文件的每一个信息保存在Configuration中,返回包含Configuration的DefaultSqlSession;
* 注意:【MappedStatement】:代表一个增删改查的详细信息
*
* 2、获取sqlSession对象
* 返回一个DefaultSQlSession对象,包含Executor和Configuration;
* 这一步会创建Executor对象;
*
* 3、获取接口的代理对象(MapperProxy)
* getMapper,使用MapperProxyFactory创建一个MapperProxy的代理对象
* 代理对象里面包含了,DefaultSqlSession(Executor)
* 4、执行增删改查方法
*
* 总结:
* 1、根据配置文件(全局,sql映射)初始化出Configuration对象
* 2、创建一个DefaultSqlSession对象,
* 他里面包含Configuration以及
* Executor(根据全局配置文件中的defaultExecutorType创建出对应的Executor)
* 3、DefaultSqlSession.getMapper():拿到Mapper接口对应的MapperProxy;
* 4、MapperProxy里面有(DefaultSqlSession);
* 5、执行增删改查方法:
* 1)、调用DefaultSqlSession的增删改查(Executor);
* 2)、会创建一个StatementHandler对象。
* (同时也会创建出ParameterHandler和ResultSetHandler)
* 3)、调用StatementHandler预编译参数以及设置参数值;
* 使用ParameterHandler来给sql设置参数
* 4)、调用StatementHandler的增删改查方法;
* 5)、ResultSetHandler封装结果
* 注意:
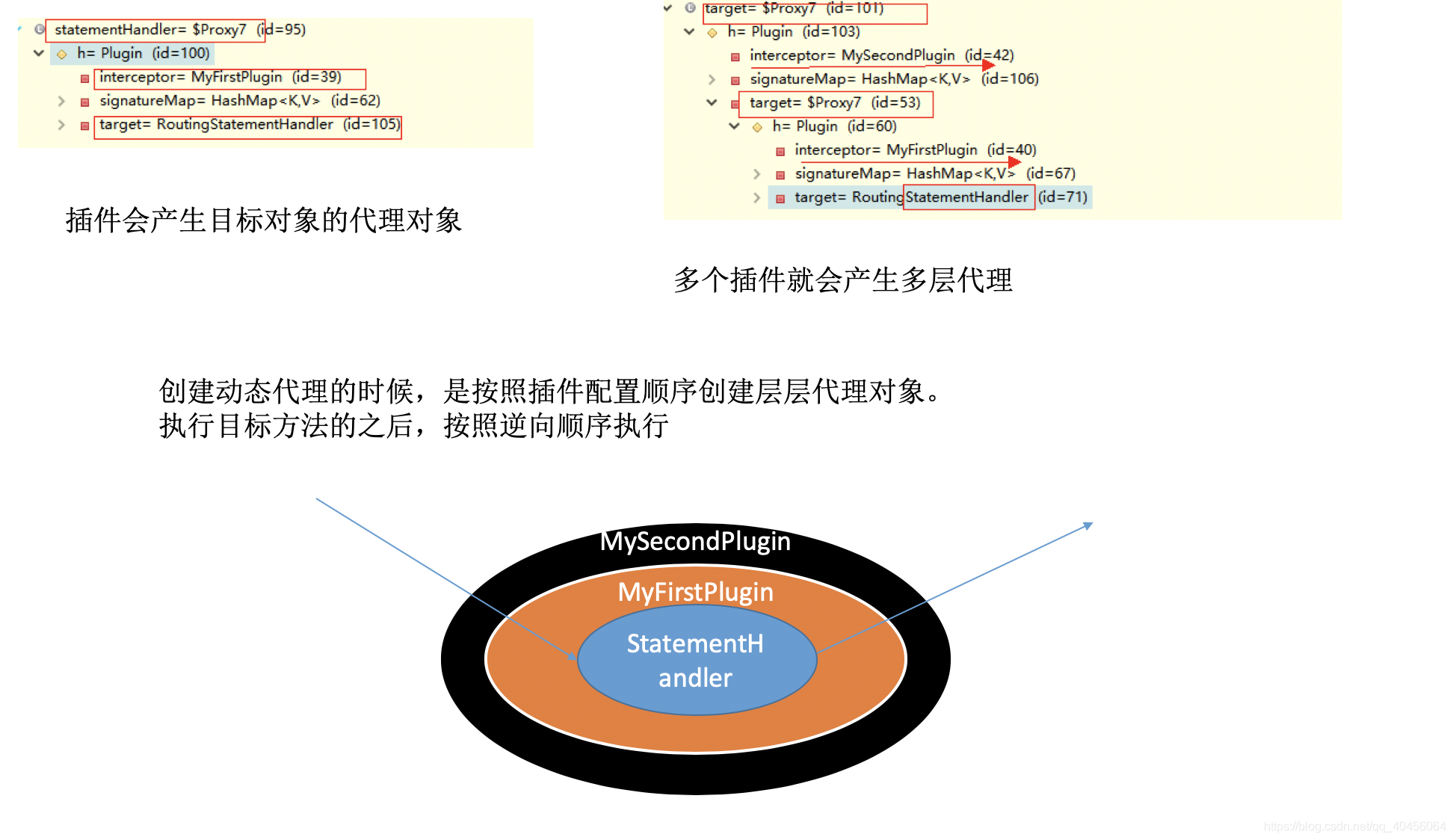
* 四大对象每个创建的时候都有一个interceptorChain.pluginAll(parameterHandler);
*
* @throws IOException
*/
@Test
public void test02() {
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = getSqlSessionFactory();
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
try {
EmployeeMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(EmployeeMapper.class);
Employee employee = mapper.getEmpById(1);
System.out.println(employee);
System.out.println(mapper.getClass());
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
sqlSession.close();
}
}
-
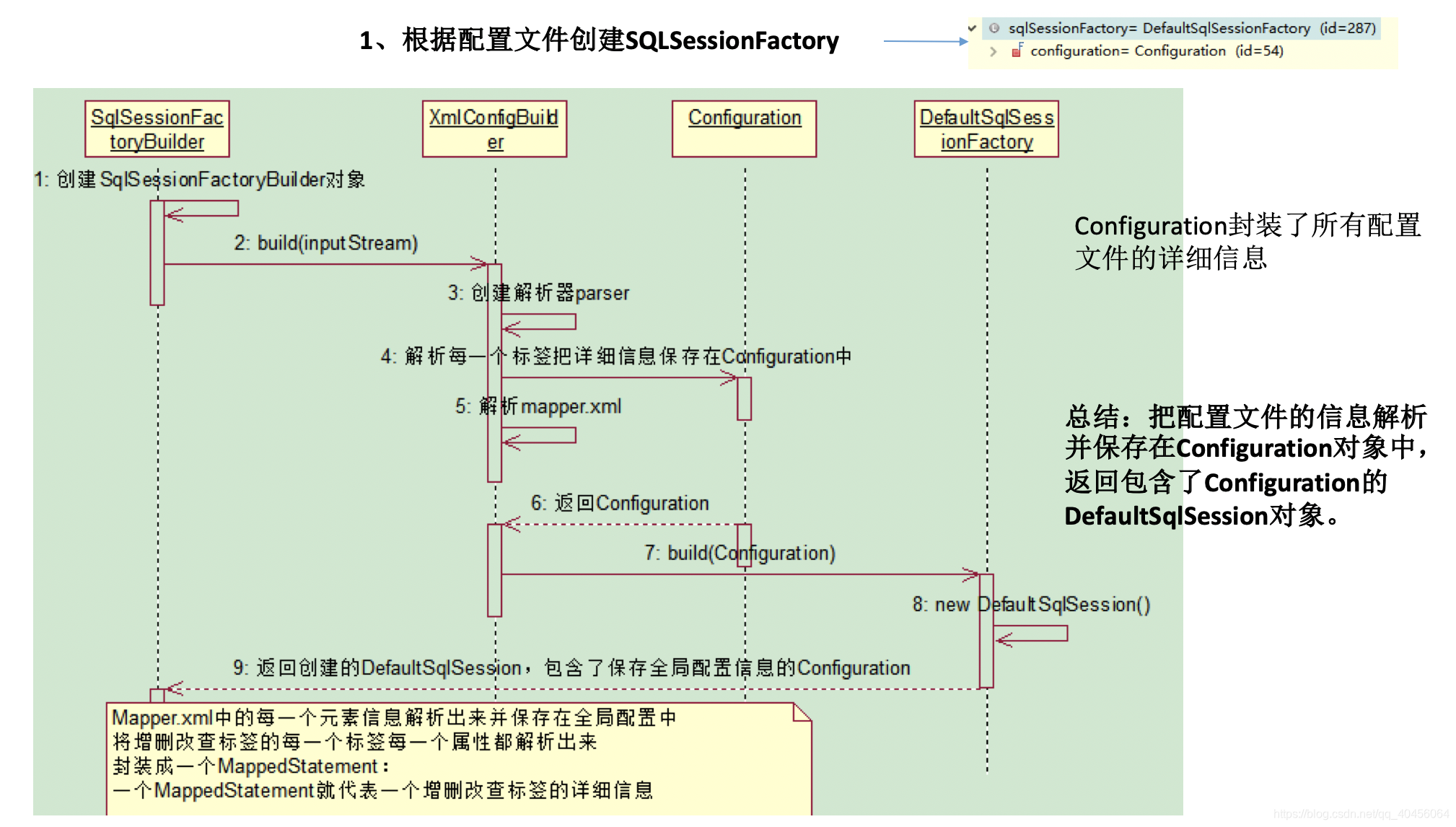
获取
sqlSessionFactory对象:解析文件的每一个信息保存在Configuration中,返回包含Configuration的DefaultSqlSession;
注意:
【MappedStatement】:代表一个增删改查的详细信息
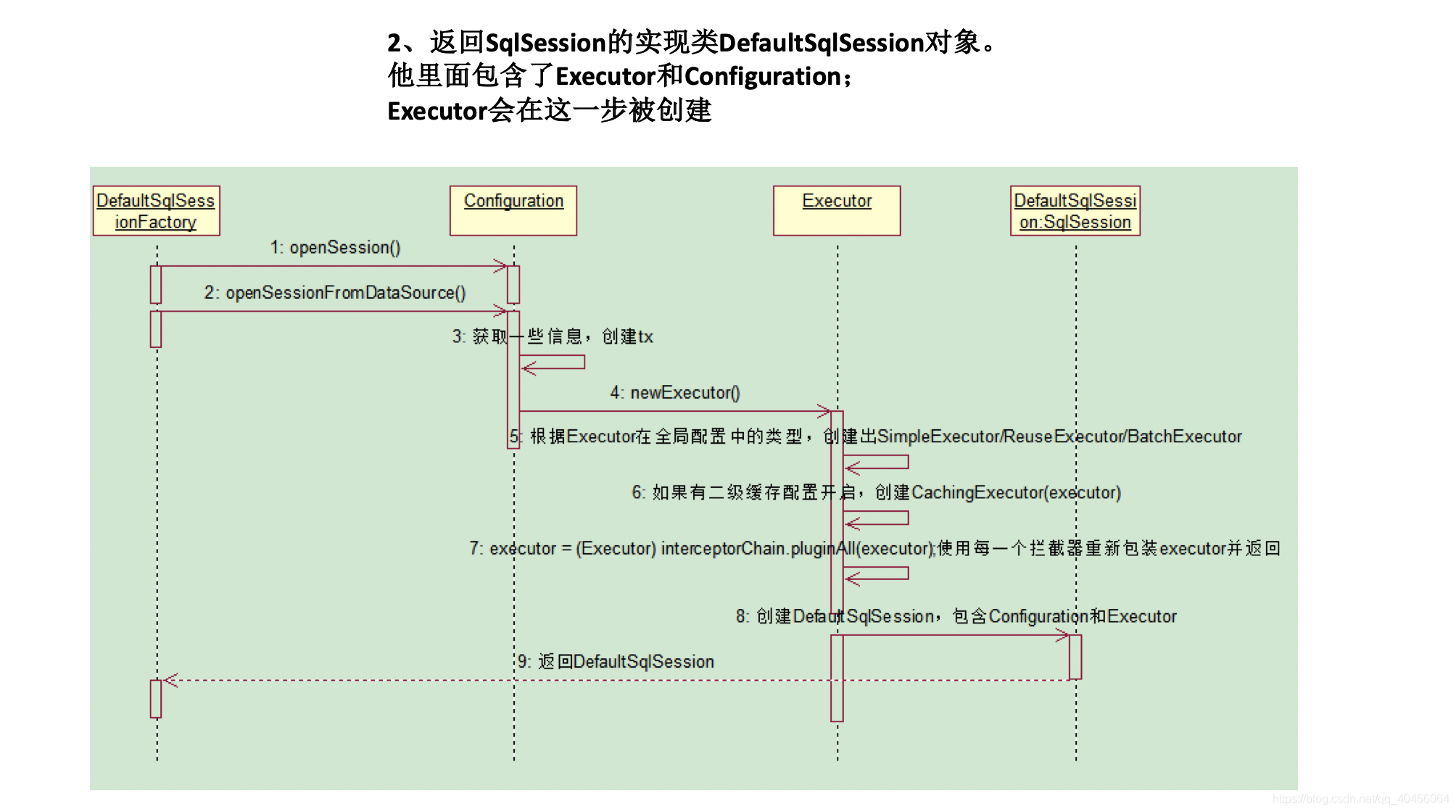
2. 获取sqlSession对象
返回一个DefaultSQlSession对象,包含Executor和Configuration;这一步会创建Executor对象
this.openSessionFromConnection(this.configuration.getDefaultExecutorType(), connection);
this.configuration.getDefaultExecutorType():
配置文件里可以配置Executor的类型(defaultExecutorType):SIMPLE、REUSE、BATCH。默认SIMPLE
private SqlSession openSessionFromDataSource(ExecutorType execType, TransactionIsolationLevel level, boolean autoCommit) {
Transaction tx = null;
DefaultSqlSession var8;
try {
// 获取当前环境
Environment environment = this.configuration.getEnvironment();
// 创建事务
TransactionFactory transactionFactory = this.getTransactionFactoryFromEnvironment(environment);
tx = transactionFactory.newTransaction(environment.getDataSource(), level, autoCommit);
// *************四大对象之一:Executor在这里创建**************
// Executor就是进行增删改查的
Executor executor = this.configuration.newExecutor(tx, execType);
// 最终返回的SqlSession是DefaultSqlSession,包含Configuration、刚刚创建的executor
var8 = new DefaultSqlSession(this.configuration, executor, autoCommit);
} catch (Exception var12) {
this.closeTransaction(tx);
throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error opening session. Cause: " + var12, var12);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
}
return var8;
}
//创建Executor,【Configuration.java】
public Executor newExecutor(Transaction transaction, ExecutorType executorType) {
executorType = executorType == null ? this.defaultExecutorType : executorType;
executorType = executorType == null ? ExecutorType.SIMPLE : executorType;
Object executor;
// 根据全局配置中的配置的类型创建Executor(默认SIMPLE)
if (ExecutorType.BATCH == executorType) {
executor = new BatchExecutor(this, transaction);
} else if (ExecutorType.REUSE == executorType) {
executor = new ReuseExecutor(this, transaction);
} else {
executor = new SimpleExecutor(this, transaction);
}
// 如果配置了二级缓存,利用CachingExecutor进行包装(Executor执行之前,对缓存进行查询)
if (this.cacheEnabled) {
executor = new CachingExecutor((Executor)executor);
}
// 拿到所有的拦截器,执行plugin方法,这一步非常重要,与插件有关
// 使用每一个拦截器重新包装Executor,再返回
Executor executor = (Executor)this.interceptorChain.pluginAll(executor);
return executor;
}
// 最终返回的SqlSession是DefaultSqlSession,包含Configuration、刚刚创建的executor
var8 = new DefaultSqlSession(this.configuration, executor, autoCommit);
最终返回的SqlSession是DefaultSqlSession,包含Configuration、刚刚创建的executor
-
获取接口的代理对象(
MapperProxy)getMapper,使用MapperProxyFactory创建一个MapperProxy的代理对象,代理对象里面包含了,DefaultSqlSession(Executor)
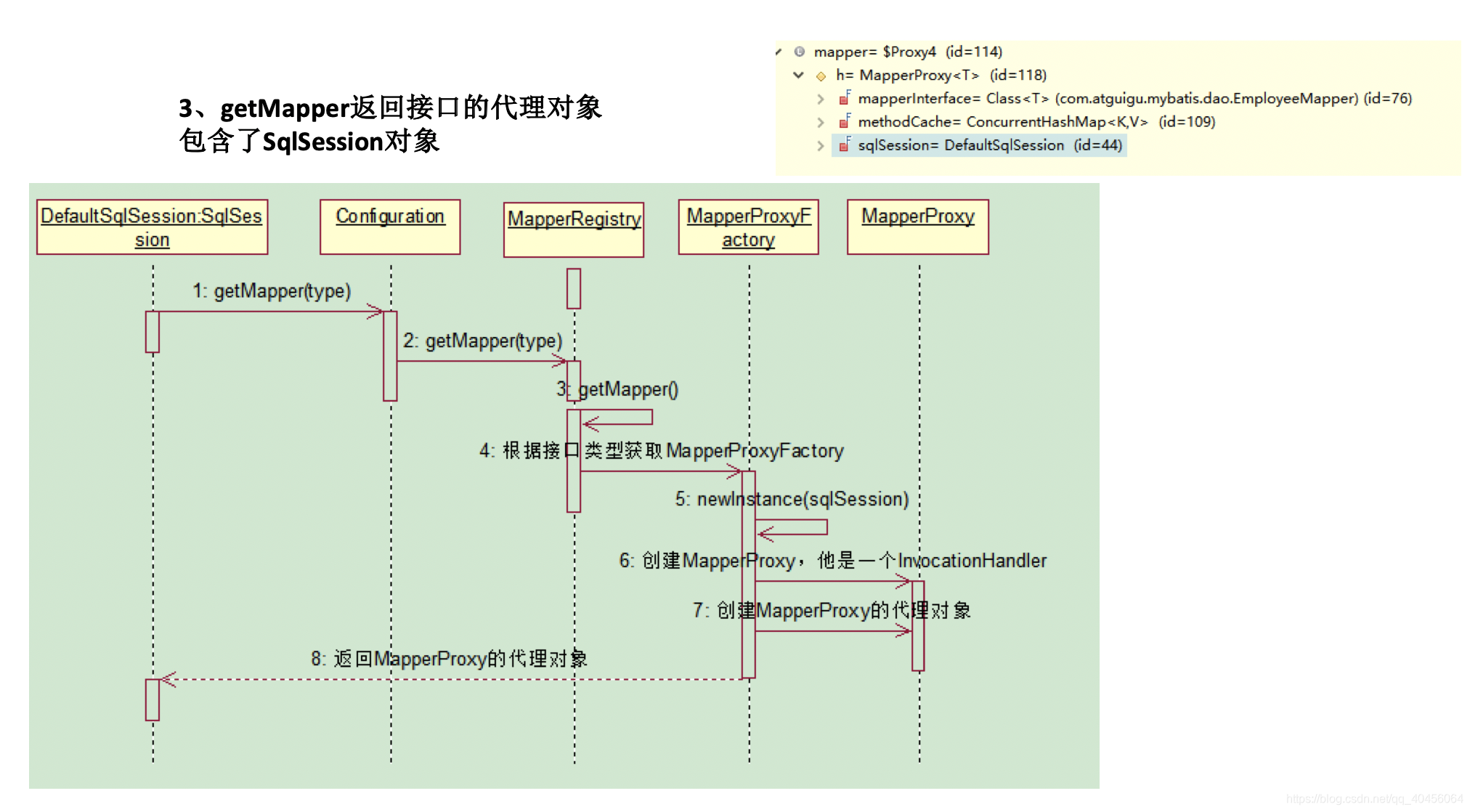
Configuration里有一个很重要的属性:MapperRegistry ,用于获取接口的代理对象MapperProxy:
// MapperRegistry的getMapper方法:
public <T> T getMapper(Class<T> type, SqlSession sqlSession) {
// 根据<接口类型>获取MapperProxyFactory
MapperProxyFactory<T> mapperProxyFactory = (MapperProxyFactory)this.knownMappers.get(type);
if (mapperProxyFactory == null) {
throw new BindingException("Type " + type + " is not known to the MapperRegistry.");
} else {
try {
// 调用MapperProxyFactory的newInstance创建代理对象
return mapperProxyFactory.newInstance(sqlSession);
} catch (Exception var5) {
throw new BindingException("Error getting mapper instance. Cause: " + var5, var5);
}
}
}
// MapperProxyFactory的newInstance方法
public T newInstance(SqlSession sqlSession) {
// SqlSession、接口方法
MapperProxy<T> mapperProxy = new MapperProxy(sqlSession, this.mapperInterface, this.methodCache);
return this.newInstance(mapperProxy);
}
// MapperProxy是一个InvocationHandler类型的对象,可以用来创建动态代理
public class MapperProxy<T> implements InvocationHandler, Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = -6424540398559729838L;
private final SqlSession sqlSession;
private final Class<T> mapperInterface;
// 接口方法映射
private final Map<Method, MapperMethod> methodCache;
}
// 用JDK的API创建代理对象,这个代理对象会一步步的返回,最终拿到的Mapper是一个代理对象
protected T newInstance(MapperProxy<T> mapperProxy) {
return Proxy.newProxyInstance(this.mapperInterface.getClassLoader(), new Class[]{this.mapperInterface}, mapperProxy);
}
最终拿到的mapper:包含sqlSession(MapperProxy有invoke方法,是一个InvocationHandler类型的对象)

4. 代理对象执行增删改查
三、代理对象如何执行增删改查
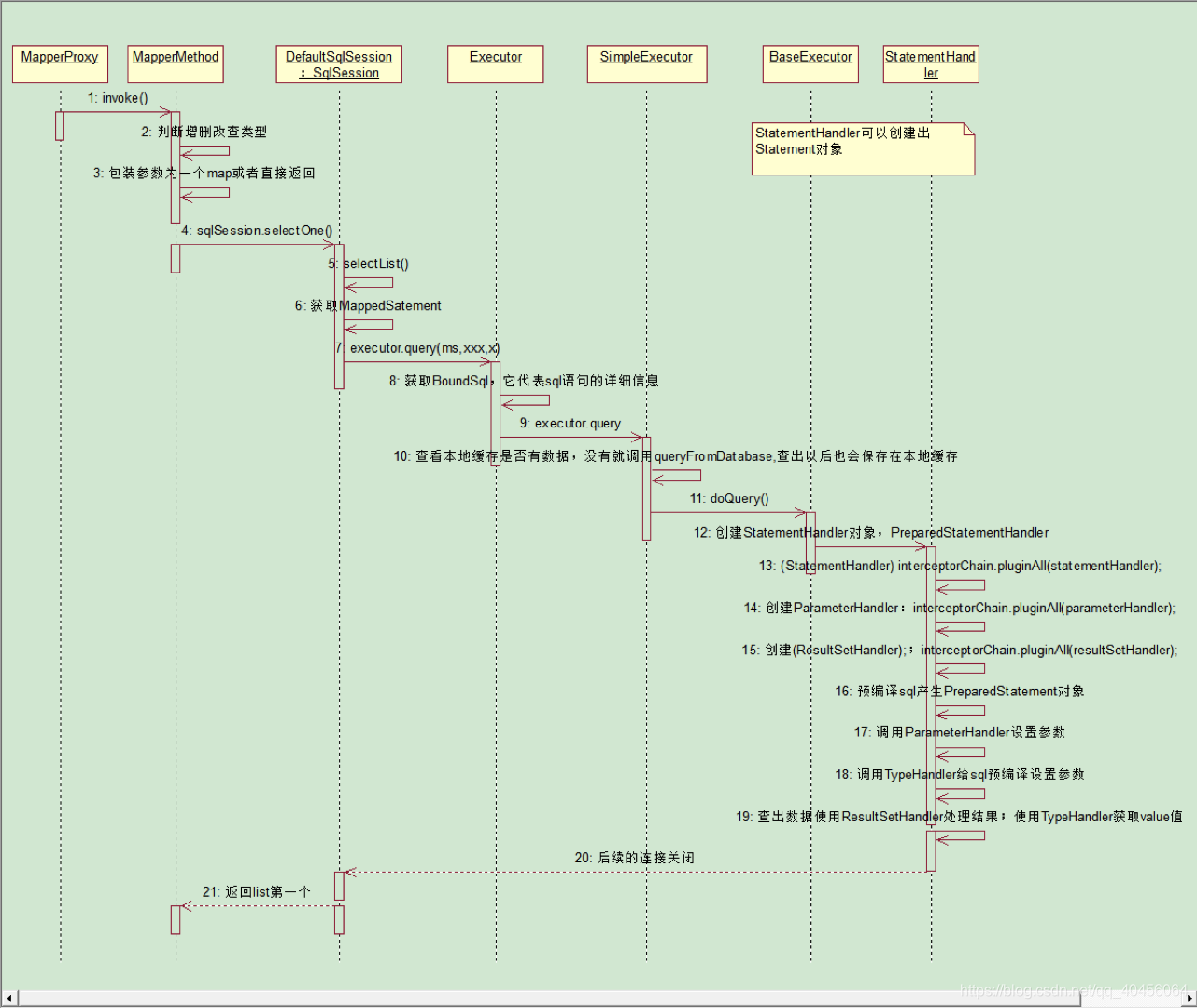
1. MapperProxy的invoke
// MapperProxy的invoke
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
// 有些方法是Object的方法,例如toString、hashCode等等,这些方法直接执行就行了
if (Object.class.equals(method.getDeclaringClass())) {
try {
return method.invoke(this, args);
} catch (Throwable var5) {
throw ExceptionUtil.unwrapThrowable(var5);
}
} else {
MapperMethod mapperMethod = this.cachedMapperMethod(method);
// invoke的时候调用MapperMethod的execute方法
return mapperMethod.execute(this.sqlSession, args);
}
}
2. MapperMethod的execute方法
invoke的时候调用MapperMethod的execute方法,传入SqlSession以及需要的参数args
// MapperMethod的execute方法
public Object execute(SqlSession sqlSession, Object[] args) {
Object param;
Object result;
switch(this.command.getType()) {
// 判断当前执行的方法是哪种类型,执行方法之前都会解析参数(解析方法名)
case INSERT:
param = this.method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = this.rowCountResult(sqlSession.insert(this.command.getName(), param));
break;
case UPDATE:
param = this.method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = this.rowCountResult(sqlSession.update(this.command.getName(), param));
break;
case DELETE:
param = this.method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = this.rowCountResult(sqlSession.delete(this.command.getName(), param));
break;
case SELECT:
// 如果是SELECT,还会判断返回的数量以及返回类型
if (this.method.returnsVoid() && this.method.hasResultHandler()) {
this.executeWithResultHandler(sqlSession, args);
result = null;
} else if (this.method.returnsMany()) {
result = this.executeForMany(sqlSession, args);
} else if (this.method.returnsMap()) {
result = this.executeForMap(sqlSession, args);
} else if (this.method.returnsCursor()) {
result = this.executeForCursor(sqlSession, args);
} else {
// 其他情况,如果只有一个返回值,先解析参数
param = this.method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = sqlSession.selectOne(this.command.getName(), param);
}
break;
case FLUSH:
result = sqlSession.flushStatements();
break;
default:
throw new BindingException("Unknown execution method for: " + this.command.getName());
}
if (result == null && this.method.getReturnType().isPrimitive() && !this.method.returnsVoid()) {
throw new BindingException("Mapper method '" + this.command.getName() + " attempted to return null from a method with a primitive return type (" + this.method.getReturnType() + ").");
} else {
return result;
}
}
3. DefaultSqlSession的selectOne方法
调用sqlSession.selectOne(this.command.getName(), param),SqlSession的原生方法:
// DefaultSqlSession的selectOne方法
public <T> T selectOne(String statement, Object parameter) {
List<T> list = this.selectList(statement, parameter);
if (list.size() == 1) {
return list.get(0);
} else if (list.size() > 1) {
throw new TooManyResultsException("Expected one result (or null) to be returned by selectOne(), but found: " + list.size());
} else {
return null;
}
}
就算是查询单个,最后也是调用selectList,返回第一个元素
// DefaultSqlSession的selectOne方法
public <E> List<E> selectList(String statement, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds) {
List var5;
try {
// 从全局配置中获取statement对应的MappedStatement信息
MappedStatement ms = this.configuration.getMappedStatement(statement);
// 调用Executor的增删改查
var5 = this.executor.query(ms, this.wrapCollection(parameter), rowBounds, Executor.NO_RESULT_HANDLER);
} catch (Exception var9) {
throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error querying database. Cause: " + var9, var9);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
}
return var5;
}
调用Executor的增删改查:this.executor.query(ms, this.wrapCollection(parameter), rowBounds, Executor.NO_RESULT_HANDLER);
//Collection array list 参数名称逻辑,了解即可
private Object wrapCollection(Object object) {
DefaultSqlSession.StrictMap map;
if (object instanceof Collection) {
map = new DefaultSqlSession.StrictMap();
map.put("collection", object);
if (object instanceof List) {
map.put("list", object);
}
return map;
} else if (object != null && object.getClass().isArray()) {
map = new DefaultSqlSession.StrictMap();
map.put("array", object);
return map;
} else {
return object;
}
}
4. Executor的query系列(不是重要方法)
// Executor的query 不是重要方法
public <E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameterObject, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler) throws SQLException {
// BoundSql:Sql语句相关的信息,参数等
BoundSql boundSql = ms.getBoundSql(parameterObject);
// 缓存相关,了解即可
CacheKey key = this.createCacheKey(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, boundSql);
return this.query(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
}
// this.query() 5个参数的重载方法,不是重要方法
public <E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameterObject, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, CacheKey key, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException {
// 缓存相关, 从缓存中拿
// 这里是二级缓存
Cache cache = ms.getCache();
if (cache != null) {
this.flushCacheIfRequired(ms);
if (ms.isUseCache() && resultHandler == null) {
this.ensureNoOutParams(ms, parameterObject, boundSql);
List<E> list = (List)this.tcm.getObject(cache, key);
if (list == null) {
list = this.delegate.query(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
this.tcm.putObject(cache, key, list);
}
return list;
}
}
// 真正的Executor进行执行方法
return this.delegate.query(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
}
5. Executor执行方法,默认是SIMPLE
// Executor执行方法,默认是SIMPLE
public <E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, CacheKey key, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException {
ErrorContext.instance().resource(ms.getResource()).activity("executing a query").object(ms.getId());
if (this.closed) {
throw new ExecutorException("Executor was closed.");
} else {
if (this.queryStack == 0 && ms.isFlushCacheRequired()) {
this.clearLocalCache();
}
List list;
try {
++this.queryStack;
// 缓存相关,一级缓存在这里
list = resultHandler == null ? (List)this.localCache.getObject(key) : null;
if (list != null) {
this.handleLocallyCachedOutputParameters(ms, key, parameter, boundSql);
} else {
//*********************主要方法*********************
list = this.queryFromDatabase(ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
//************************************************
}
} finally {
--this.queryStack;
}
if (this.queryStack == 0) {
Iterator i$ = this.deferredLoads.iterator();
while(i$.hasNext()) {
BaseExecutor.DeferredLoad deferredLoad = (BaseExecutor.DeferredLoad)i$.next();
deferredLoad.load();
}
this.deferredLoads.clear();
if (this.configuration.getLocalCacheScope() == LocalCacheScope.STATEMENT) {
this.clearLocalCache();
}
}
return list;
}
}
6. BaseExecutor的queryFromDatabase
//BaseExecutor的queryFromDatabase
private <E> List<E> queryFromDatabase(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, CacheKey key, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException {
// 缓存中放一个占位符
this.localCache.putObject(key, ExecutionPlaceholder.EXECUTION_PLACEHOLDER);
List list;
try {
list = this.doQuery(ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql);
} finally {
this.localCache.removeObject(key);
}
// 数据保存在缓存中(一级缓存)
this.localCache.putObject(key, list);
if (ms.getStatementType() == StatementType.CALLABLE) {
this.localOutputParameterCache.putObject(key, parameter);
}
return list;
}
7. SimpleExecutor的doQuery方法
//SimpleExecutor的doQuery方法
//传入参数:MappedStatement、parameter参数、rowBounds(数据数量限制,不重要,Mybatis做逻辑分页的)、resultHandler(到这里还是null)、boundSql(Sql语句信息)
public <E> List<E> doQuery(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException {
// 这个Statement就是原生JDBC的Statement
Statement stmt = null;
List var9;
try {
Configuration configuration = ms.getConfiguration();
// 四大对象之一,StatementHandler可以创建出Statement对象
// 创建了一个PreparedStatement对象,Prepared是默认值,也可以是Callable等
StatementHandler handler = configuration.newStatementHandler(this.wrapper, ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql);
stmt = this.prepareStatement(handler, ms.getStatementLog());
var9 = handler.query(stmt, resultHandler);
} finally {
this.closeStatement(stmt);
}
return var9;
}
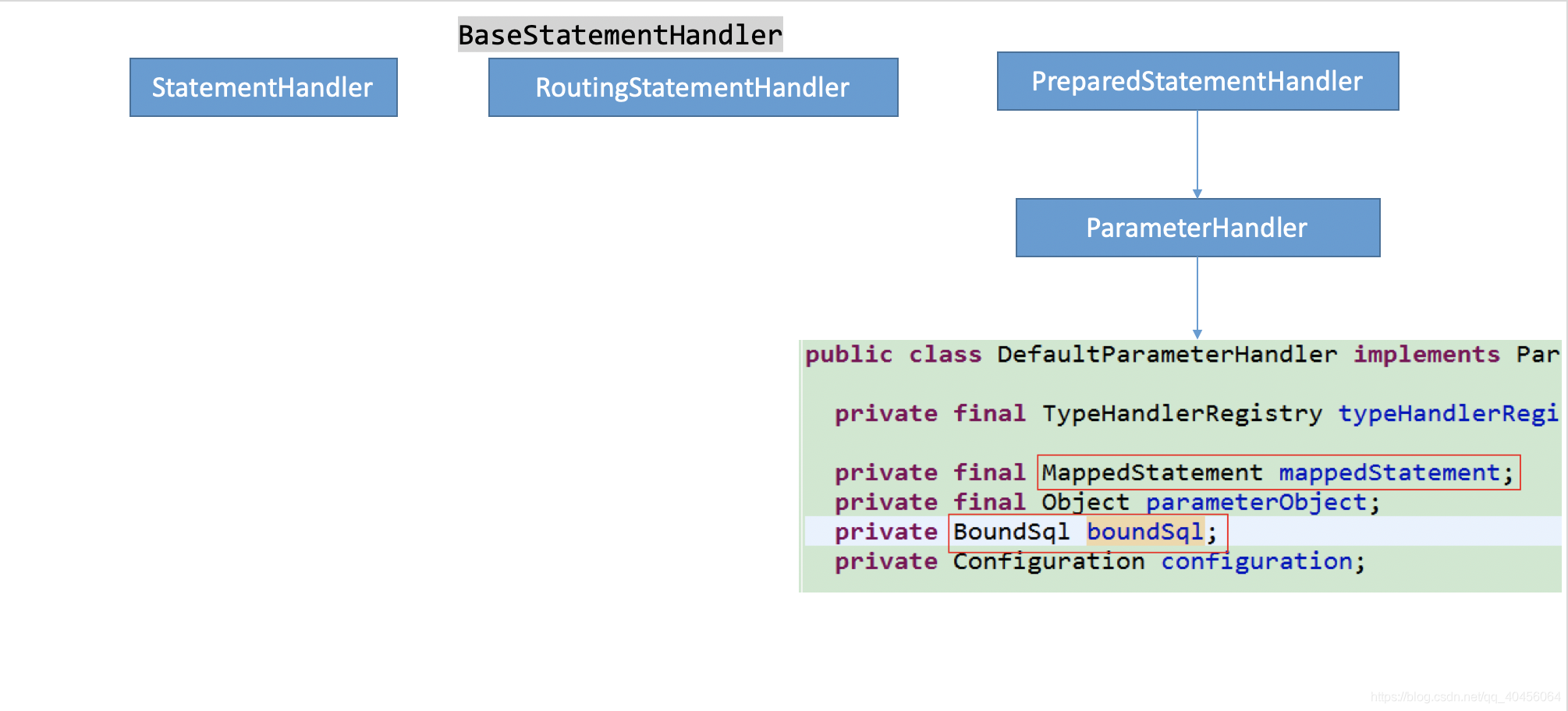
8. Configuration的newStatementHandler
// Configuration的newStatementHandler
public StatementHandler newStatementHandler(Executor executor, MappedStatement mappedStatement, Object parameterObject, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, BoundSql boundSql) {
StatementHandler statementHandler = new RoutingStatementHandler(executor, mappedStatement, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql);
// 这里创建了StatementHandler之后,也会执行所有拦截器的方法
StatementHandler statementHandler = (StatementHandler)this.interceptorChain.pluginAll(statementHandler);
return statementHandler;
}
9. PreparedStatementHandler的query
预编译SQL:PreparedStatement,预编译使用ParamenterHandler设置参数
// PreparedStatementHandler的query
public <E> List<E> query(Statement statement, ResultHandler resultHandler) throws SQLException {
PreparedStatement ps = (PreparedStatement)statement;
ps.execute();
// 数据查出来后,使用resultSetHandler封装数据
return this.resultSetHandler.handleResultSets(ps);
}
10. handleResultSets处理参数
// handleResultSets处理参数
// 还是使用到了原生的JDBC
public List<Object> handleResultSets(Statement stmt) throws SQLException {
ErrorContext.instance().activity("handling results").object(this.mappedStatement.getId());
List<Object> multipleResults = new ArrayList();
int resultSetCount = 0;
ResultSetWrapper rsw = this.getFirstResultSet(stmt);
List<ResultMap> resultMaps = this.mappedStatement.getResultMaps();
int resultMapCount = resultMaps.size();
this.validateResultMapsCount(rsw, resultMapCount);
while(rsw != null && resultMapCount > resultSetCount) {
ResultMap resultMap = (ResultMap)resultMaps.get(resultSetCount);
this.handleResultSet(rsw, resultMap, multipleResults, (ResultMapping)null);
rsw = this.getNextResultSet(stmt);
this.cleanUpAfterHandlingResultSet();
++resultSetCount;
}
String[] resultSets = this.mappedStatement.getResultSets();
if (resultSets != null) {
while(rsw != null && resultSetCount < resultSets.length) {
ResultMapping parentMapping = (ResultMapping)this.nextResultMaps.get(resultSets[resultSetCount]);
if (parentMapping != null) {
String nestedResultMapId = parentMapping.getNestedResultMapId();
ResultMap resultMap = this.configuration.getResultMap(nestedResultMapId);
this.handleResultSet(rsw, resultMap, (List)null, parentMapping);
}
rsw = this.getNextResultSet(stmt);
this.cleanUpAfterHandlingResultSet();
++resultSetCount;
}
}
return this.collapseSingleResultList(multipleResults);
}
11. Resulthandler的getPropertyMappingValue
// Resulthandler的getPropertyMappingValue,
// 将查询的值和属性值映射起来
private Object getPropertyMappingValue(ResultSet rs, MetaObject metaResultObject, ResultMapping propertyMapping, ResultLoaderMap lazyLoader, String columnPrefix) throws SQLException {
if (propertyMapping.getNestedQueryId() != null) {
return this.getNestedQueryMappingValue(rs, metaResultObject, propertyMapping, lazyLoader, columnPrefix);
} else if (propertyMapping.getResultSet() != null) {
this.addPendingChildRelation(rs, metaResultObject, propertyMapping);
return DEFERED;
} else {
TypeHandler<?> typeHandler = propertyMapping.getTypeHandler();
String column = this.prependPrefix(propertyMapping.getColumn(), columnPrefix);
return typeHandler.getResult(rs, column);
}
}
总结
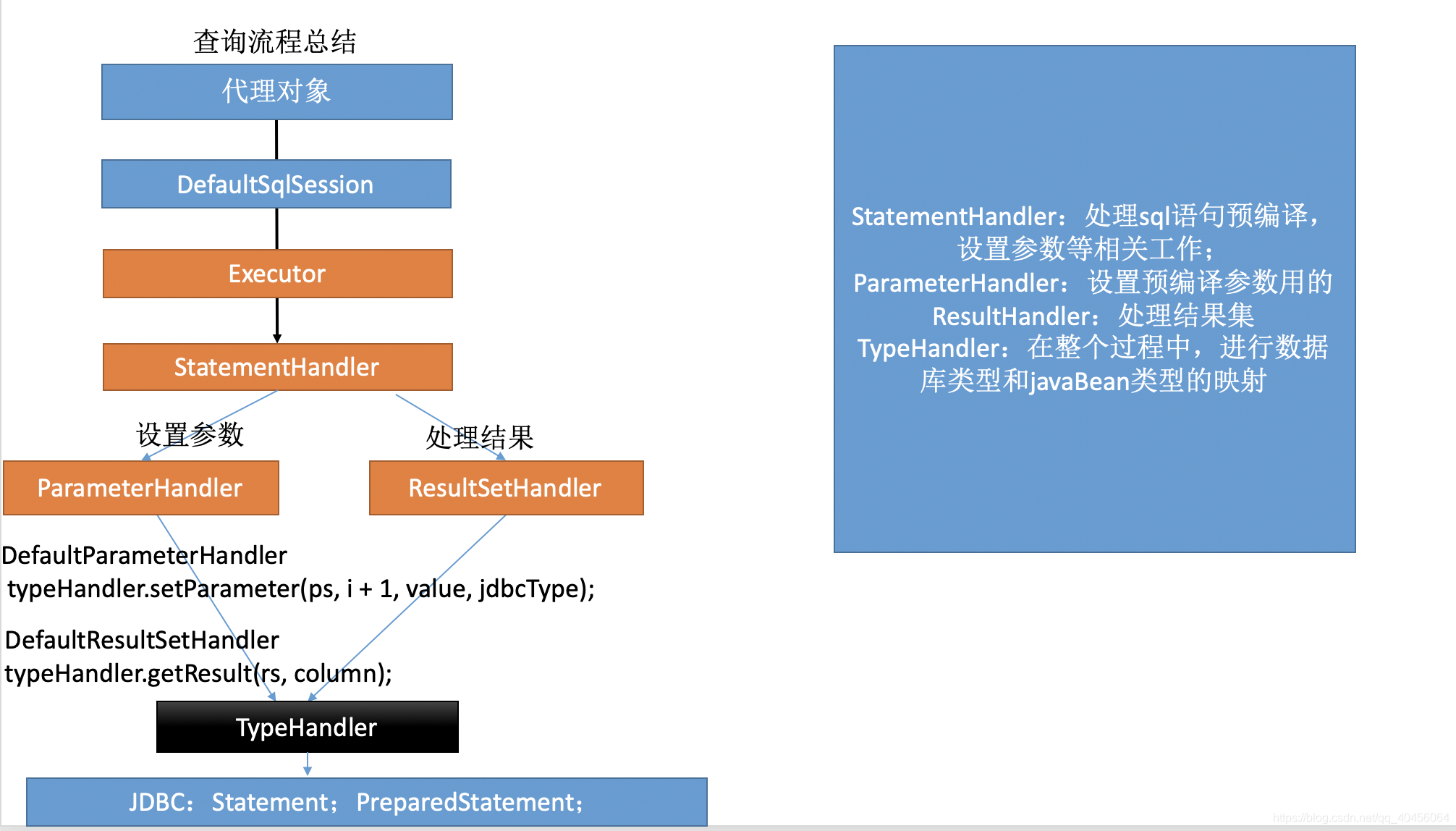
四大对象,代理对象使用里面的SqlSession,SqlSession又使用里面的Executor。使用StatementHandler设置Sql预编译(创建StatementHandler的同时,会创建Parameterhandler和ResultSetHandler),使用Parameterhandler设置参数,使用ResultSetHandler处理结果,这两个都涉及到TypeHandler,
其他
1、参数值的获取(#、$)
#{}:可以获取map中的值或者pojo对象属性的值;
${}:可以获取map中的值或者pojo对象属性的值;
select * from tbl_employee where id=${id} and last_name=#{lastName}
Preparing: select * from tbl_employee where id=2 and last_name=?
区别:
#{}:是以预编译的形式,将参数设置到sql语句中;PreparedStatement;防止sql注入
${}:取出的值直接拼装在sql语句中;会有安全问题;
大多情况下,我们去参数的值都应该去使用#{};
原生jdbc不支持占位符的地方我们就可以使用${}进行取值
比如分表、排序。。。;按照年份分表拆分
select * from ${year}_salary where xxx;
select * from tbl_employee order by ${f_name} ${order}
#{}:更丰富的用法:
规定参数的一些规则:
javaType、 jdbcType、 mode(存储过程)、 numericScale、
resultMap、 typeHandler、 jdbcTypeName、 expression(未来准备支持的功能);
jdbcType通常需要在某种特定的条件下被设置:
在我们数据为null的时候,有些数据库可能不能识别mybatis对null的默认处理。比如Oracle(报错);
JdbcType OTHER:无效的类型;因为mybatis对所有的null都映射的是原生Jdbc的OTHER类型,oracle不能正确处理;
由于全局配置中:jdbcTypeForNull=OTHER;oracle不支持;两种办法
1、#{email,jdbcType=OTHER};
2、jdbcTypeForNull=NULL
<setting name="jdbcTypeForNull" value="NULL"/>
2、 映射文件
-
返回list:resultMap填list元素类型就可以
-
返回一个Map
可能遇到这样的需求:查出来一个对象,但是没有定义这个对象的实体类。单条记录:resultMap=“map”。
多条记录封装Map:resultMap还是填元素类型就可以,但是在接口方法处使用一个注解告诉返回的Map使用哪一个属性作为Key:
@MapKey("id") -
自定义属性封装规则:(
resultType)resultType和resultMap只能用一个<resultMap type="com.atguigu.mybatis.bean.Employee" id="MySimpleEmp"> <!--指定主键列的封装规则 id定义主键会底层有优化; column:指定哪一列 property:指定对应的javaBean属性 --> <id column="id" property="id"/> <!-- 定义普通列封装规则 --> <result column="last_name" property="lastName"/> <!-- 其他不指定的列会自动封装:我们只要写resultMap就把全部的映射规则都写上。 --> <result column="email" property="email"/> <result column="gender" property="gender"/> </resultMap> <!-- resultMap:自定义结果集映射规则; --> <!-- public Employee getEmpById(Integer id); --> <select id="getEmpById" resultMap="MySimpleEmp"> select * from tbl_employee where id=#{id} </select> -
关联查询
级联属性封装
<!-- 联合查询:级联属性封装结果集 --> <resultMap type="com.atguigu.mybatis.bean.Employee" id="MyDifEmp"> <id column="id" property="id"/> <result column="last_name" property="lastName"/> <result column="gender" property="gender"/> <result column="did" property="dept.id"/> <result column="dept_name" property="dept.departmentName"/> </resultMap> SQL: <select id="getEmpAndDept" resultMap="MyDifEmp"> SELECT e.id id,e.last_name last_name,e.gender gender,e.d_id d_id, d.id did,d.dept_name dept_name FROM tbl_employee e,tbl_dept d WHERE e.d_id=d.id AND e.id=#{id} </select>另一种办法
association:<!-- 使用association定义关联的单个对象的封装规则; --> <resultMap type="com.atguigu.mybatis.bean.Employee" id="MyDifEmp2"> <id column="id" property="id"/> <result column="last_name" property="lastName"/> <result column="gender" property="gender"/> <!-- association可以指定联合的javaBean对象 property="dept":指定哪个属性是联合的对象 javaType:指定这个属性对象的类型[不能省略] --> <association property="dept" javaType="com.atguigu.mybatis.bean.Department"> <id column="did" property="id"/> <result column="dept_name" property="departmentName"/> </association> </resultMap>association可以分步查询(需要定义两条SQL)<!-- 使用association进行分步查询: 1、先按照员工id查询员工信息 2、根据查询员工信息中的d_id值去部门表查出部门信息 3、部门设置到员工中; --> <!-- id last_name email gender d_id --> <resultMap type="com.atguigu.mybatis.bean.Employee" id="MyEmpByStep"> <id column="id" property="id"/> <result column="last_name" property="lastName"/> <result column="email" property="email"/> <result column="gender" property="gender"/> <!-- association定义关联对象的封装规则 select:表明当前属性是调用select指定的方法查出的结果 column:指定将哪一列的值传给这个方法 流程:使用select指定的方法(传入column指定的这列参数的值)查出对象,并封装给property指定的属性 --> <association property="dept" select="com.atguigu.mybatis.dao.DepartmentMapper.getDeptById" column="d_id"> </association> </resultMap> <!-- public Employee getEmpByIdStep(Integer id);--> <select id="getEmpByIdStep" resultMap="MyEmpByStep"> select * from tbl_employee where id=#{id} </select>分布查询可以支持延迟加载:
<!-- 可以使用延迟加载(懒加载);(按需加载) Employee==>Dept: 我们每次查询Employee对象的时候,都将一起查询出来。 部门信息在我们使用的时候再去查询; 分段查询的基础之上加上两个配置: --> 加上两个配置: setting中,加:lazyLoading=true、aggressiveLazyLoading=fasle关联集合查询:查询部门的时候,找到所有的部门员工:
<!-- 场景二: 查询部门的时候将部门对应的所有员工信息也查询出来:注释在DepartmentMapper.xml中 --><!-- public class Department { private Integer id; private String departmentName; private List<Employee> emps; did dept_name || eid last_name email gender --> <!--嵌套结果集的方式,使用collection标签定义关联的集合类型的属性封装规则 --> <resultMap type="com.atguigu.mybatis.bean.Department" id="MyDept"> <id column="did" property="id"/> <result column="dept_name" property="departmentName"/> <!-- collection定义关联集合类型的属性的封装规则 ofType:指定集合里面元素的类型 --> <collection property="emps" ofType="com.atguigu.mybatis.bean.Employee"> <!-- 定义这个集合中元素的封装规则 --> <id column="eid" property="id"/> <result column="last_name" property="lastName"/> <result column="email" property="email"/> <result column="gender" property="gender"/> </collection> </resultMap> <!-- public Department getDeptByIdPlus(Integer id); --> <select id="getDeptByIdPlus" resultMap="MyDept"> SELECT d.id did,d.dept_name dept_name, e.id eid,e.last_name last_name,e.email email,e.gender gender FROM tbl_dept d LEFT JOIN tbl_employee e ON d.id=e.d_id WHERE d.id=#{id} </select>























 367
367











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








