官网
Vue3适用的版本是 Vue Router 4
Vue 2使用的版本是 Vue Router 3.x.x ,目前适用于Vue2最新的vue-router版本是3.6.5
- https://v3.router.vuejs.org/zh/
- https://github.com/vuejs/vue-router
介绍
Vue Router 是 Vue.js (opens new window)官方的路由管理器。它和 Vue.js 的核心深度集成,让构建单页面应用变得易如反掌。包含的功能有:
- 嵌套的路由/视图表
- 模块化的、基于组件的路由配置
- 路由参数、查询、通配符
- 基于 Vue.js 过渡系统的视图过渡效果
- 细粒度的导航控制
- 带有自动激活的 CSS class 的链接
- HTML5 历史模式或 hash 模式,在 IE9 中自动降级
- 自定义的滚动条行为
源码结构
src
├─ components
│ ├─ link.js # <router-link> 组件的实现
│ └─ view.js # <router-view> 组件的实现
├─ composables
│ ├─ globals.js # 全局变量和函数
│ ├─ guards.js # 路由守卫相关功能
│ ├─ index.js # 导出所有的可组合函数
│ ├─ useLink.js # useLink 组合函数
│ └─ utils.js # 工具函数
├─ entries
│ ├─ cjs.js # CommonJS 入口
│ └─ esm.js # ECMAScript Module 入口
├─ history
│ ├─ abstract.js # 抽象历史模式,用于服务端渲染
│ ├─ base.js # 历史模式的基类
│ ├─ hash.js # Hash 模式的实现
│ └─ html5.js # HTML5 模式的实现
├─ util
│ ├─ async.js # 异步工具函数
│ ├─ dom.js # DOM 操作工具函数
│ ├─ errors.js # 错误处理工具函数
│ ├─ location.js # 处理 URL 位置的工具函数
│ ├─ misc.js # 杂项工具函数
│ ├─ params.js # 参数处理工具函数
│ ├─ path.js # 路径处理工具函数
│ ├─ push-state.js # pushState 操作的工具函数
│ ├─ query.js # 查询字符串处理工具函数
│ ├─ resolve-components.js # 解析路由组件的工具函数
│ ├─ route.js # 路由对象相关工具函数
│ ├─ scroll.js # 滚动行为工具函数
│ ├─ state-key.js # 状态键处理工具函数
│ └─ warn.js # 警告日志工具函数
├─ create-matcher.js # 创建路由匹配器的实现
├─ create-route-map.js # 创建路由映射表的实现
├─ index.js # Vue Router 入口文件
├─ install.js # 安装 Vue Router 插件
└─ router.js # Vue Router 类的实现
工作原理
- url改变
- 触发监听事件 (原理见路由模式)
- 改变vue-router里面的current变量
- vue监听current的监听者
- 获取到新的组件
- render新组件
工作流程
初始化
-
在页面初始化的时候,会使用
Vue.use(VueRouter)进行路由的安装,在这里你只需要记住安装的时候会在Vue中混入了一个生命周期钩子函数(beforeCreate)到所有的Vue对象实例中,它的作用之一是路由根组件(即配置了router选项的组件)的_route进行响应式化(在更改路由的时候会用到)。 -
接下来就是路由的初始化,通过将配置项进行解析,执行以下流程
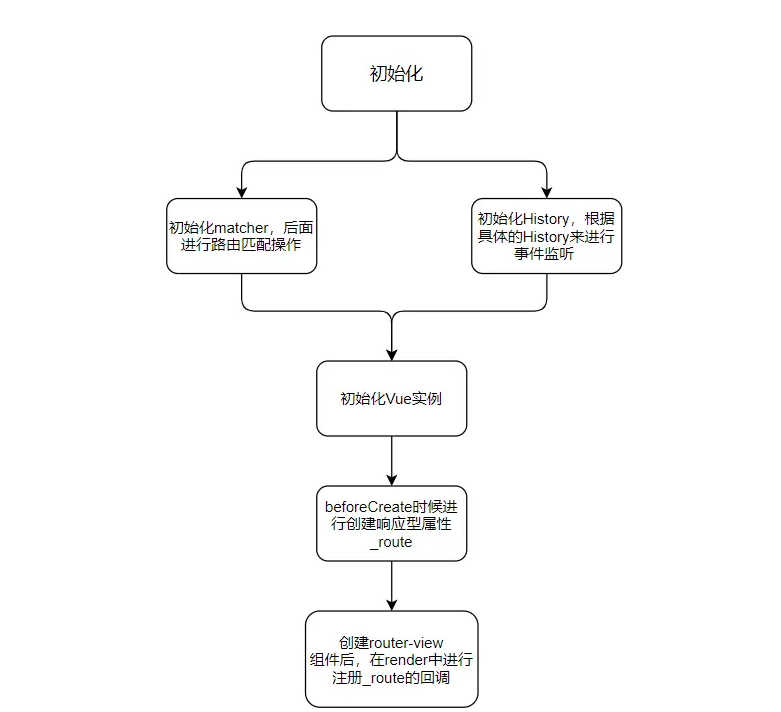
初始化细节
-
Matcher进行初始化的时候,会将路由表制作成路由映射,后面调用
router的切换路由的方法的时候,会从这里拿到相应的路由配置 -
History进行初始化的时候,会进行根据不同的类型路由来进行不同的事件的注册,如果是hash或者h5类型的话,会去监听浏览器原生切换页面的方法,从而进行路由的更换。如果是
abstract类型的路由,则不会使用环境特定的api,而是内部模拟页面切换操作 -
在混入的
beforeCreate的生命周期钩子中,对于路由的根组件(具有router配置,即使用new Vue时候传进来router实例)定义响应型数据_route,这个属性是当前路由信息;非路由根组件实例(根组件的孩子)代理根目录的_route属性 -
router-view是一个functional组件(函数式)。 -
在父组件的
render执行的时候,会创建一个router-view的VNode占位符,进而创建router-view组件。但是由于functional组件里面是没有任何的响应型数据、生命周期钩子和观察者,这样就会使得targetStack(依赖栈,开头有介绍)的栈顶仍然是是父组件实例的渲染函数观察者,那么在子组件对任何响应型数据进行使用的时候,都会进行绑定到父容器的渲染函数观察者中!render (_, { props, children, parent, data }) { // code... const route = parent.$route // code... } -
在根组件中,会将
_route属性代理到$route,并且所有的子组件实例都会进行代理,所有组件访问$route就是在访问_route,如果此时有观察者的时候,会顺便去互相绑定。 -
这样进行更改
_route的时候,会重新执行router-view父容器的渲染函数(router-view是函数式组件),重新进行渲染router-view,router-view读取$route配置进行渲染操作
更新路由
路由分类、更新起点
| 路由类型 | 更新起点 |
|---|---|
| Hash | popState、pushState、hashChange、replaceState、go、push、replace |
| H5 | popState、pushState、replaceState、go、push、replace |
| Abstract | go、push、replace |
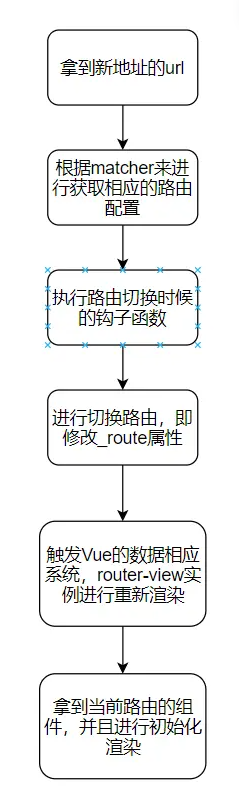
相关概念
-
路由器实例(Router 实例):Vue Router 提供了一个 VueRouter 类,用于创建路由器实例。路由器实例通常通过 new VueRouter() 创建,并通过 Vue 实例的 router 选项进行注册。
-
路由器插件(Router 插件):Vue Router 提供了一个 install 方法,使其可以作为 Vue.js 插件使用。通过在 Vue 实例上调用 Vue.use(VueRouter),可以在应用程序中全局注册路由器。
-
路由表(Route Table):路由表定义了 URL 和组件之间的映射关系。它是一个包含路由配置的 JavaScript 对象或数组,每个路由配置项都定义了一个 URL 匹配规则和对应的组件。
-
路由模式(Router Mode):Vue Router 支持多种路由模式,包括 hash 模式、history 模式和 abstract 模式。这些模式决定了 URL 如何与路由器进行交互。
-
路由导航(Route Navigation):Vue Router 提供了一组导航方法,用于在不同的 URL 之间进行导航。它包括 router.push()、router.replace()、router.go() 等方法,以及 组件用于声明式的导航。
-
导航守卫(Navigation Guards):Vue Router 提供了一组导航守卫,用于在路由导航过程中执行特定的逻辑。导航守卫包括全局前置守卫、路由独享守卫、组件内的守卫等。
-
动态路由和嵌套路由(Dynamic Routing and Nested Routing):Vue Router 支持动态路由和嵌套路由,允许在 URL 中包含动态参数,并且可以在组件中进行嵌套路由的声明。
-
路由状态管理(Router State Management):Vue Router 允许在路由器实例中定义和管理全局的路由状态,并通过 $route 对象和 $router 实例提供了访问和修改路由状态的方法
Router所包含的数据结构
存储访问记录的数据结构
- 无论是
window.history还是抽象路由中,都是使用栈来进行处理的,因为栈具有后进先出的特性,所以能够根据访问的历史进行倒序访问。
路由映射表
pathList
router将VueRouter实例所传进来的options的routes进行处理,routes具有树状结构,其树状访问路径代表着路由匹配url的路径。而pathList是将这棵树进行扁平化操作,制作成一个数组
nameMap
- 是一个
Map结构,Key是String,是路由配置项的name属性,Value是route配置项,可以直接通过name来寻找route,这就要求路由配置中的name具有唯一性
pathMap
- 是一个
Map结构,Key是String,是路由配置项的path属性,Value是route配置项,不过与nameMap不一样的一点是它是使用正则表达式来进行匹配的,因为路由设计中url是允许传参数的
Vue.use介绍
Vue.use方法是用于安装Vue插件的全局方法。它需要在调用new Vue()之前被调用,并且可以安装自定义的Vue插件或第三方库。
Vue.use的详解、参数解释、注意点以及代码示例如下:
详解和参数解释:
Vue.use(plugin, options?):Vue.use接受两个参数,plugin和可选的options。plugin:要安装的插件,可以是一个对象或函数。options:可选的选项对象,用于传递给插件的配置。
注意点:
Vue.use方法只能全局调用一次。重复调用相同的插件将被忽略。- 插件在内部通过向Vue的原型添加方法或者全局组件等来扩展Vue的功能。
- 插件可以是一个对象或函数,如果是对象,必须提供
install()方法,用来安装插件;如果是一个函数,则该函数将被当成install()方法
因为 vue-router 上的一些属性、方法需要挂载到 Vue 实例中,调用 Vue.use 后,install 方法会接受一个参数 Vue,这样就能够在 Vue 实例上挂载任何东西了,Vue.use 就有点像是 vue 和 vue-router 之间的桥梁
两种路由模式
hash
- #号后面的内容
- 可以通过location.hash拿到
- 通过onhashchange监听改变
- 只会把路由给到服务器,并不会发生跳转
history
- 通过location.pathname来获取路径
- 通过onpopstate监听history的改变
源码解析
src/install.js(入口)
在
install.js文件中,对路由、路由组件、路由混入事件、路由响应式对象创建的操作等进行了执行
import View from './components/view'
import Link from './components/link'
// 声明一个私有的_Vue用来接收外部的Vue类
export let _Vue
export function install (Vue) {
if (install.installed && _Vue === Vue) return
install.installed = true
_Vue = Vue // 这种方式只需要在install的时候使用全局的Vue类,并不需要将Vue打包进入Vue-router的源码内
const isDef = v => v !== undefined
// 进行注册router实例
const registerInstance = (vm, callVal) => {
let i = vm.$options._parentVnode
// 在data之后进行初始化
if (isDef(i) && isDef(i = i.data) && isDef(i = i.registerRouteInstance)) {
i(vm, callVal)
}
}
Vue.mixin({
beforeCreate () {
// 在beforeCreate执行环境的时候,this指向的是新创建出来的vm实例
if (isDef(this.$options.router)) {
// 如果配置项有router选项的时候,那么这个vm实例就是router的根组件
this._routerRoot = this
this._router = this.$options.router
this._router.init(this)
// 定义响应数据。在router-view组件(前面说过)中的渲染函数中会访问到这个属性,同时会添加上依赖。
// 当修改到本数据的时候,会触发数据响应系统,重新渲染对应的router-view。更改视图层
Vue.util.defineReactive(this, '_route', this._router.history.current)
} else {
// 如果不是路由根目录组件的时候,那么就会将_routerRoot属性赋值为根目录组件
this._routerRoot = (this.$parent && this.$parent._routerRoot) || this
}
// 进行注册路由操作
registerInstance(this, this)
},
// // 进行移除操作
destroyed () {
registerInstance(this)
}
})
// 代理操作
Object.defineProperty(Vue.prototype, '$router', {
get () { return this._routerRoot._router }
})
Object.defineProperty(Vue.prototype, '$route', {
get () { return this._routerRoot._route }
})
Vue.component('RouterView', View)
Vue.component('RouterLink', Link)
const strats = Vue.config.optionMergeStrategies
// use the same hook merging strategy for route hooks
strats.beforeRouteEnter = strats.beforeRouteLeave = strats.beforeRouteUpdate = strats.created
}
在安装文件干了三件事:
- 混入钩子函数,进行路由注册,并且进行定义响应式数据,方便后面路由改变的时候通知视图层进行更新
- 进行代理操作,实例访问
$router或者$route属性的时候会代理到跟组件的_route属性中(所以其实在对$route进行观察的时候,实际上是对路由根组件的_route属性进行观察,而这个属性已经变成了响应型数据,所以路由改变的时候能够实现回调观察的作用)一张图来说明引用的整个流程: - 注册全局组件。
src/router.js
/* @flow */
import { install } from './install'
import { START } from './util/route'
import { assert, warn } from './util/warn'
import { inBrowser } from './util/dom'
import { cleanPath } from './util/path'
import { createMatcher } from './create-matcher'
import { normalizeLocation } from './util/location'
import { supportsPushState } from './util/push-state'
import { handleScroll } from './util/scroll'
import { isNavigationFailure, NavigationFailureType } from './util/errors'
import { HashHistory } from './history/hash'
import { HTML5History } from './history/html5'
import { AbstractHistory } from './history/abstract'
import type { Matcher } from './create-matcher'
export default class VueRouter {
static install: () => void
static version: string
static isNavigationFailure: Function
static NavigationFailureType: any
static START_LOCATION: Route
app: any
apps: Array<any>
ready: boolean
readyCbs: Array<Function>
options: RouterOptions
mode: string
history: HashHistory | HTML5History | AbstractHistory
matcher: Matcher
fallback: boolean
beforeHooks: Array<?NavigationGuard>
resolveHooks: Array<?NavigationGuard>
afterHooks: Array<?AfterNavigationHook>
constructor (options: RouterOptions = {}) {
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production') {
warn(this instanceof VueRouter, `Router must be called with the new operator.`)
}
this.app = null
this.apps = []
this.options = options
this.beforeHooks = []
this.resolveHooks = []
this.afterHooks = []
this.matcher = createMatcher(options.routes || [], this)
let mode = options.mode || 'hash'
this.fallback =
mode === 'history' && !supportsPushState && options.fallback !== false
if (this.fallback) {
mode = 'hash'
}
if (!inBrowser) {
mode = 'abstract'
}
this.mode = mode
switch (mode) {
case 'history':
this.history = new HTML5History(this, options.base)
break
case 'hash':
this.history = new HashHistory(this, options.base, this.fallback)
break
case 'abstract':
this.history = new AbstractHistory(this, options.base)
break
default:
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production') {
assert(false, `invalid mode: ${mode}`)
}
}
}
match (raw: RawLocation, current?: Route, redirectedFrom?: Location): Route {
return this.matcher.match(raw, current, redirectedFrom)
}
get currentRoute (): ?Route {
return this.history && this.history.current
}
init (app: any /* Vue component instance */) {
process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' &&
assert(
install.installed,
`not installed. Make sure to call \`Vue.use(VueRouter)\` ` +
`before creating root instance.`
)
this.apps.push(app)
// set up app destroyed handler
// https://github.com/vuejs/vue-router/issues/2639
app.$once('hook:destroyed', () => {
// clean out app from this.apps array once destroyed
const index = this.apps.indexOf(app)
if (index > -1) this.apps.splice(index, 1)
// ensure we still have a main app or null if no apps
// we do not release the router so it can be reused
if (this.app === app) this.app = this.apps[0] || null
if (!this.app) this.history.teardown()
})
// main app previously initialized
// return as we don't need to set up new history listener
if (this.app) {
return
}
this.app = app
const history = this.history
if (history instanceof HTML5History || history instanceof HashHistory) {
const handleInitialScroll = routeOrError => {
const from = history.current
const expectScroll = this.options.scrollBehavior
const supportsScroll = supportsPushState && expectScroll
if (supportsScroll && 'fullPath' in routeOrError) {
handleScroll(this, routeOrError, from, false)
}
}
const setupListeners = routeOrError => {
history.setupListeners()
handleInitialScroll(routeOrError)
}
history.transitionTo(
history.getCurrentLocation(),
setupListeners,
setupListeners
)
}
history.listen(route => {
this.apps.forEach(app => {
app._route = route
})
})
}
beforeEach (fn: Function): Function {
return registerHook(this.beforeHooks, fn)
}
beforeResolve (fn: Function): Function {
return registerHook(this.resolveHooks, fn)
}
afterEach (fn: Function): Function {
return registerHook(this.afterHooks, fn)
}
onReady (cb: Function, errorCb?: Function) {
this.history.onReady(cb, errorCb)
}
onError (errorCb: Function) {
this.history.onError(errorCb)
}
push (location: RawLocation, onComplete?: Function, onAbort?: Function) {
// $flow-disable-line
if (!onComplete && !onAbort && typeof Promise !== 'undefined') {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
this.history.push(location, resolve, reject)
})
} else {
this.history.push(location, onComplete, onAbort)
}
}
replace (location: RawLocation, onComplete?: Function, onAbort?: Function) {
// $flow-disable-line
if (!onComplete && !onAbort && typeof Promise !== 'undefined') {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
this.history.replace(location, resolve, reject)
})
} else {
this.history.replace(location, onComplete, onAbort)
}
}
go (n: number) {
this.history.go(n)
}
back () {
this.go(-1)
}
forward () {
this.go(1)
}
getMatchedComponents (to?: RawLocation | Route): Array<any> {
const route: any = to
? to.matched
? to
: this.resolve(to).route
: this.currentRoute
if (!route) {
return []
}
return [].concat.apply(
[],
route.matched.map(m => {
return Object.keys(m.components).map(key => {
return m.components[key]
})
})
)
}
resolve (
to: RawLocation,
current?: Route,
append?: boolean
): {
location: Location,
route: Route,
href: string,
// for backwards compat
normalizedTo: Location,
resolved: Route
} {
current = current || this.history.current
const location = normalizeLocation(to, current, append, this)
const route = this.match(location, current)
const fullPath = route.redirectedFrom || route.fullPath
const base = this.history.base
const href = createHref(base, fullPath, this.mode)
return {
location,
route,
href,
// for backwards compat
normalizedTo: location,
resolved: route
}
}
getRoutes () {
return this.matcher.getRoutes()
}
addRoute (parentOrRoute: string | RouteConfig, route?: RouteConfig) {
this.matcher.addRoute(parentOrRoute, route)
if (this.history.current !== START) {
this.history.transitionTo(this.history.getCurrentLocation())
}
}
addRoutes (routes: Array<RouteConfig>) {
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production') {
warn(false, 'router.addRoutes() is deprecated and has been removed in Vue Router 4. Use router.addRoute() instead.')
}
this.matcher.addRoutes(routes)
if (this.history.current !== START) {
this.history.transitionTo(this.history.getCurrentLocation())
}
}
}
function registerHook (list: Array<any>, fn: Function): Function {
list.push(fn)
return () => {
const i = list.indexOf(fn)
if (i > -1) list.splice(i, 1)
}
}
function createHref (base: string, fullPath: string, mode) {
var path = mode === 'hash' ? '#' + fullPath : fullPath
return base ? cleanPath(base + '/' + path) : path
}
// We cannot remove this as it would be a breaking change
VueRouter.install = install
VueRouter.version = '__VERSION__'
VueRouter.isNavigationFailure = isNavigationFailure
VueRouter.NavigationFailureType = NavigationFailureType
VueRouter.START_LOCATION = START
if (inBrowser && window.Vue) {
window.Vue.use(VueRouter)
}
constructor
- 在 VueRouter 类的构造函数中,定义相关的私有属性。
- 三个路由守卫的钩子函数待执行存储器:this.beforeHooks、resolveHooks、afterHooks;
- 通过 createMatcher 函数生成一个路由匹配器,该函数返回了match、addRoutes、addRoute、getRoutes四个子功能函数;
- 随后通过 options.mode 进行了路由模式匹配:hash、history、abstract, 返回了对应路由监听实例
init
- 根节点的beforeCreate生命周期钩子中,使用了init方法
- init 中主要的操作是:
根据当前路径,显示对应的组件
handleScroll处理滚动
export function handleScroll (
router: Router,
to: Route,
from: Route,
isPop: boolean// 是否popstate,只有浏览器的 前进/后退 按钮才会触发,也只有popstate时,才会保存滚动位置
) {
if (!router.app) {
return
}
const behavior = router.options.scrollBehavior
if (!behavior) {
return
}
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production') {
assert(typeof behavior === 'function', `scrollBehavior must be a function`)
}
// wait until re-render finishes before scrolling
// 重新渲染结束,再处理滚动
router.app.$nextTick(() => {
const position = getScrollPosition() // 获取之前保存的滚动位置
// https://router.vuejs.org/zh/guide/advanced/scroll-behavior.html#%E6%BB%9A%E5%8A%A8%E8%A1%8C%E4%B8%BA
const shouldScroll = behavior.call(
router,
to,
from,
isPop ? position : null // 第三个参数 savedPosition 当且仅当 popstate 导航 (通过浏览器的 前进/后退 按钮触发) 时才可用。,所以是popstate时,才有savedPosition
)
// 返回一个falsy值时,代表不需要滚动
if (!shouldScroll) {
return
}
// v.2.8.0支持异步滚动
// https://router.vuejs.org/zh/guide/advanced/scroll-behavior.html#%E5%BC%82%E6%AD%A5%E6%BB%9A%E5%8A%A8
if (typeof shouldScroll.then === 'function') {
shouldScroll
.then(shouldScroll => {
scrollToPosition((shouldScroll: any), position)
})
.catch(err => {
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production') {
assert(false, err.toString())
}
})
} else {
scrollToPosition(shouldScroll, position)
}
})
}
在$nextTick中调用getScrollPosition获取之前保存好的位置
再调用我们传入的scrollBehavior查看其返回值来确定是否需要进行滚动
还判断了一波是否是异步滚动
若是,则等待其resolved再调用scrollToPosition
否则直接调用scrollToPosition
-
获取滚动位置,是利用
_key从positionStore上读取之前保存的位置信息 -
scrollToPosition的逻辑很清晰,其处理了滚动到指定dom和直接滚动到特定位置的场景 -
vue-router处理滚动主要利用了History API可以保存状态的特性实现 -
在路由进入前保存滚动位置,并在下次路由变化时,尝试取回之前位置,在
$nextTick中真正的处理滚动 -
其支持滚动到指定位置、指定 DOM、异步滚动等场景
history.transitionTo
transitionTo 函数会匹配 url 值处理后续的组件渲染逻辑
history.listen
History 类中直接更换current对象值,响应式是丢失的,需要我们手动更新 _route 值的。history.listen 就恰好帮我们处理了这件事
src/create-matcher.js
/* @flow */
import type VueRouter from './index'
import { resolvePath } from './util/path'
import { assert, warn } from './util/warn'
import { createRoute } from './util/route'
import { fillParams } from './util/params'
import { createRouteMap } from './create-route-map'
import { normalizeLocation } from './util/location'
import { decode } from './util/query'
export type Matcher = {
match: (raw: RawLocation, current?: Route, redirectedFrom?: Location) => Route;
addRoutes: (routes: Array<RouteConfig>) => void;
addRoute: (parentNameOrRoute: string | RouteConfig, route?: RouteConfig) => void;
getRoutes: () => Array<RouteRecord>;
};
export function createMatcher (
routes: Array<RouteConfig>,
router: VueRouter
): Matcher {
// 1.扁平化用户传入的数据,创建路由映射表
const { pathList, pathMap, nameMap } = createRouteMap(routes)
// 动态添加路由
function addRoutes (routes) {
createRouteMap(routes, pathList, pathMap, nameMap)
}
function addRoute (parentOrRoute, route) {
const parent = (typeof parentOrRoute !== 'object') ? nameMap[parentOrRoute] : undefined
// $flow-disable-line
createRouteMap([route || parentOrRoute], pathList, pathMap, nameMap, parent)
// add aliases of parent
if (parent && parent.alias.length) {
createRouteMap(
// $flow-disable-line route is defined if parent is
parent.alias.map(alias => ({ path: alias, children: [route] })),
pathList,
pathMap,
nameMap,
parent
)
}
}
function getRoutes () {
return pathList.map(path => pathMap[path])
}
// 3.用来匹配的方法
function match (
raw: RawLocation,
currentRoute?: Route,
redirectedFrom?: Location
): Route {
const location = normalizeLocation(raw, currentRoute, false, router)
const { name } = location
if (name) {
const record = nameMap[name]
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production') {
warn(record, `Route with name '${name}' does not exist`)
}
if (!record) return _createRoute(null, location)
const paramNames = record.regex.keys
.filter(key => !key.optional)
.map(key => key.name)
if (typeof location.params !== 'object') {
location.params = {}
}
if (currentRoute && typeof currentRoute.params === 'object') {
for (const key in currentRoute.params) {
if (!(key in location.params) && paramNames.indexOf(key) > -1) {
location.params[key] = currentRoute.params[key]
}
}
}
location.path = fillParams(record.path, location.params, `named route "${name}"`)
return _createRoute(record, location, redirectedFrom)
} else if (location.path) {
location.params = {}
for (let i = 0; i < pathList.length; i++) {
const path = pathList[i]
const record = pathMap[path]
if (matchRoute(record.regex, location.path, location.params)) {
return _createRoute(record, location, redirectedFrom)
}
}
}
// no match
return _createRoute(null, location)
}
function redirect (
record: RouteRecord,
location: Location
): Route {
const originalRedirect = record.redirect
let redirect = typeof originalRedirect === 'function'
? originalRedirect(createRoute(record, location, null, router))
: originalRedirect
if (typeof redirect === 'string') {
redirect = { path: redirect }
}
if (!redirect || typeof redirect !== 'object') {
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production') {
warn(
false, `invalid redirect option: ${JSON.stringify(redirect)}`
)
}
return _createRoute(null, location)
}
const re: Object = redirect
const { name, path } = re
let { query, hash, params } = location
query = re.hasOwnProperty('query') ? re.query : query
hash = re.hasOwnProperty('hash') ? re.hash : hash
params = re.hasOwnProperty('params') ? re.params : params
if (name) {
// resolved named direct
const targetRecord = nameMap[name]
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production') {
assert(targetRecord, `redirect failed: named route "${name}" not found.`)
}
return match({
_normalized: true,
name,
query,
hash,
params
}, undefined, location)
} else if (path) {
// 1. resolve relative redirect
const rawPath = resolveRecordPath(path, record)
// 2. resolve params
const resolvedPath = fillParams(rawPath, params, `redirect route with path "${rawPath}"`)
// 3. rematch with existing query and hash
return match({
_normalized: true,
path: resolvedPath,
query,
hash
}, undefined, location)
} else {
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production') {
warn(false, `invalid redirect option: ${JSON.stringify(redirect)}`)
}
return _createRoute(null, location)
}
}
function alias (
record: RouteRecord,
location: Location,
matchAs: string
): Route {
const aliasedPath = fillParams(matchAs, location.params, `aliased route with path "${matchAs}"`)
const aliasedMatch = match({
_normalized: true,
path: aliasedPath
})
if (aliasedMatch) {
const matched = aliasedMatch.matched
const aliasedRecord = matched[matched.length - 1]
location.params = aliasedMatch.params
return _createRoute(aliasedRecord, location)
}
return _createRoute(null, location)
}
function _createRoute (
record: ?RouteRecord,
location: Location,
redirectedFrom?: Location
): Route {
if (record && record.redirect) {
return redirect(record, redirectedFrom || location)
}
if (record && record.matchAs) {
return alias(record, location, record.matchAs)
}
return createRoute(record, location, redirectedFrom, router)
}
return {
match,
addRoute,
getRoutes,
addRoutes
}
}
function matchRoute (
regex: RouteRegExp,
path: string,
params: Object
): boolean {
const m = path.match(regex)
if (!m) {
return false
} else if (!params) {
return true
}
for (let i = 1, len = m.length; i < len; ++i) {
const key = regex.keys[i - 1]
if (key) {
// Fix #1994: using * with props: true generates a param named 0
params[key.name || 'pathMatch'] = typeof m[i] === 'string' ? decode(m[i]) : m[i]
}
}
return true
}
function resolveRecordPath (path: string, record: RouteRecord): string {
return resolvePath(path, record.parent ? record.parent.path : '/', true)
}
-
在这个方法中,有3个步骤
-
扁平化用户传入的数据,创建路由映射表。调用createRouteMap方法,将 new VueRouter 时的配置项 routes 传入
-
递归遍历 routes,如果有父亲,路径前面需要拼接上,处理完成后得到 pathList、pathMap
-
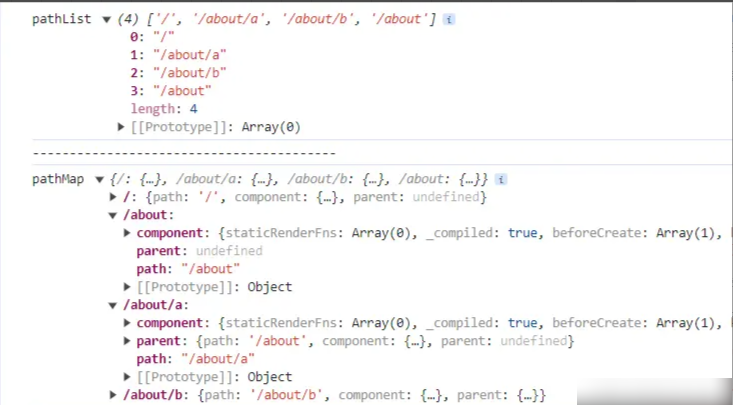
-
其中 pathList 存储的是所有路径,pathMap 存储的是每个路径对应的记录
-
-
提供了一个方法
addRoutes,它内部调用的还是createRouteMap,只不过现在要多传入两个参数,用于处理动态路由 -
用来匹配的math方法:根据传入的路径,找到对应的记录,并且要根据记录产生一个匹配数据
-
src/create-route-map.js
/* @flow */
import Regexp from 'path-to-regexp'
import { cleanPath } from './util/path'
import { assert, warn } from './util/warn'
export function createRouteMap (
routes: Array<RouteConfig>,
oldPathList?: Array<string>,
oldPathMap?: Dictionary<RouteRecord>,
oldNameMap?: Dictionary<RouteRecord>,
parentRoute?: RouteRecord
): {
pathList: Array<string>,
pathMap: Dictionary<RouteRecord>,
nameMap: Dictionary<RouteRecord>
} {
// the path list is used to control path matching priority
// 路由路径列表
const pathList: Array<string> = oldPathList || []
// $flow-disable-line
// 路由路径映射一份 RouteRecord
const pathMap: Dictionary<RouteRecord> = oldPathMap || Object.create(null)
// $flow-disable-line
// 组件模块name映射一份 RouteRecord
const nameMap: Dictionary<RouteRecord> = oldNameMap || Object.create(null)
routes.forEach(route => {
// RouteRecord 路由记录生成器
addRouteRecord(pathList, pathMap, nameMap, route, parentRoute)
})
// ensure wildcard routes are always at the end
for (let i = 0, l = pathList.length; i < l; i++) {
if (pathList[i] === '*') {
pathList.push(pathList.splice(i, 1)[0])
l--
i--
}
}
if (process.env.NODE_ENV === 'development') {
// warn if routes do not include leading slashes
const found = pathList
// check for missing leading slash
.filter(path => path && path.charAt(0) !== '*' && path.charAt(0) !== '/')
if (found.length > 0) {
const pathNames = found.map(path => `- ${path}`).join('\n')
warn(false, `Non-nested routes must include a leading slash character. Fix the following routes: \n${pathNames}`)
}
}
return {
pathList,
pathMap,
nameMap
}
}
function addRouteRecord (
pathList: Array<string>,
pathMap: Dictionary<RouteRecord>,
nameMap: Dictionary<RouteRecord>,
route: RouteConfig,
parent?: RouteRecord,
matchAs?: string
) {
const { path, name } = route
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production') {
assert(path != null, `"path" is required in a route configuration.`)
assert(
typeof route.component !== 'string',
`route config "component" for path: ${String(
path || name
)} cannot be a ` + `string id. Use an actual component instead.`
)
warn(
// eslint-disable-next-line no-control-regex
!/[^\u0000-\u007F]+/.test(path),
`Route with path "${path}" contains unencoded characters, make sure ` +
`your path is correctly encoded before passing it to the router. Use ` +
`encodeURI to encode static segments of your path.`
)
}
const pathToRegexpOptions: PathToRegexpOptions =
route.pathToRegexpOptions || {}
const normalizedPath = normalizePath(path, parent, pathToRegexpOptions.strict)
if (typeof route.caseSensitive === 'boolean') {
pathToRegexpOptions.sensitive = route.caseSensitive
}
const record: RouteRecord = {
path: normalizedPath,
regex: compileRouteRegex(normalizedPath, pathToRegexpOptions),
components: route.components || { default: route.component },
alias: route.alias
? typeof route.alias === 'string'
? [route.alias]
: route.alias
: [],
instances: {},
enteredCbs: {},
name,
parent,
matchAs,
redirect: route.redirect,
beforeEnter: route.beforeEnter,
meta: route.meta || {},
props:
route.props == null
? {}
: route.components
? route.props
: { default: route.props }
}
if (route.children) {
// Warn if route is named, does not redirect and has a default child route.
// If users navigate to this route by name, the default child will
// not be rendered (GH Issue #629)
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production') {
if (
route.name &&
!route.redirect &&
route.children.some(child => /^\/?$/.test(child.path))
) {
warn(
false,
`Named Route '${route.name}' has a default child route. ` +
`When navigating to this named route (:to="{name: '${
route.name
}'}"), ` +
`the default child route will not be rendered. Remove the name from ` +
`this route and use the name of the default child route for named ` +
`links instead.`
)
}
}
route.children.forEach(child => {
const childMatchAs = matchAs
? cleanPath(`${matchAs}/${child.path}`)
: undefined
addRouteRecord(pathList, pathMap, nameMap, child, record, childMatchAs)
})
}
if (!pathMap[record.path]) {
pathList.push(record.path)
pathMap[record.path] = record
}
if (route.alias !== undefined) {
const aliases = Array.isArray(route.alias) ? route.alias : [route.alias]
for (let i = 0; i < aliases.length; ++i) {
const alias = aliases[i]
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' && alias === path) {
warn(
false,
`Found an alias with the same value as the path: "${path}". You have to remove that alias. It will be ignored in development.`
)
// skip in dev to make it work
continue
}
const aliasRoute = {
path: alias,
children: route.children
}
addRouteRecord(
pathList,
pathMap,
nameMap,
aliasRoute,
parent,
record.path || '/' // matchAs
)
}
}
if (name) {
if (!nameMap[name]) {
nameMap[name] = record
} else if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' && !matchAs) {
warn(
false,
`Duplicate named routes definition: ` +
`{ name: "${name}", path: "${record.path}" }`
)
}
}
}
function compileRouteRegex (
path: string,
pathToRegexpOptions: PathToRegexpOptions
): RouteRegExp {
const regex = Regexp(path, [], pathToRegexpOptions)
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production') {
const keys: any = Object.create(null)
regex.keys.forEach(key => {
warn(
!keys[key.name],
`Duplicate param keys in route with path: "${path}"`
)
keys[key.name] = true
})
}
return regex
}
function normalizePath (
path: string,
parent?: RouteRecord,
strict?: boolean
): string {
if (!strict) path = path.replace(/\/$/, '')
if (path[0] === '/') return path
if (parent == null) return path
return cleanPath(`${parent.path}/${path}`)
}
这个函数主要是根据我们给入的 routes 会对
routes配置进行深度优先遍历,创建了 pathMap、nameMap 映射表,通过 addRouteRecord 给对应的 path\name 映射路由记录,完善了单个路由模块的一些信息
src/history/base.js
路由模式的公共功能
/* @flow */
import { _Vue } from '../install'
import type Router from '../index'
import { inBrowser } from '../util/dom'
import { runQueue } from '../util/async'
import { warn } from '../util/warn'
import { START, isSameRoute, handleRouteEntered } from '../util/route'
import {
flatten,
flatMapComponents,
resolveAsyncComponents
} from '../util/resolve-components'
import {
createNavigationDuplicatedError,
createNavigationCancelledError,
createNavigationRedirectedError,
createNavigationAbortedError,
isError,
isNavigationFailure,
NavigationFailureType
} from '../util/errors'
import { handleScroll } from '../util/scroll'
export class History {
router: Router
base: string
current: Route
pending: ?Route
cb: (r: Route) => void
ready: boolean
readyCbs: Array<Function>
readyErrorCbs: Array<Function>
errorCbs: Array<Function>
listeners: Array<Function>
cleanupListeners: Function
// implemented by sub-classes
+go: (n: number) => void
+push: (loc: RawLocation, onComplete?: Function, onAbort?: Function) => void
+replace: (
loc: RawLocation,
onComplete?: Function,
onAbort?: Function
) => void
+ensureURL: (push?: boolean) => void
+getCurrentLocation: () => string
+ setupListeners: Function
constructor(router: Router, base: ?string) {
this.router = router
this.base = normalizeBase(base)
// start with a route object that stands for "nowhere"
this.current = START
this.pending = null
this.ready = false
this.readyCbs = []
this.readyErrorCbs = []
this.errorCbs = []
this.listeners = []
}
listen(cb: Function) {
this.cb = cb
}
onReady(cb: Function, errorCb: ?Function) {
if (this.ready) {
cb()
} else {
this.readyCbs.push(cb)
if (errorCb) {
this.readyErrorCbs.push(errorCb)
}
}
}
onError(errorCb: Function) {
this.errorCbs.push(errorCb)
}
transitionTo(
location: RawLocation,
onComplete ?: Function,
onAbort ?: Function
) {
let route
// catch redirect option https://github.com/vuejs/vue-router/issues/3201
try {
// route就是当前路径需要匹配哪些路由
// 例如:访问路径 /about/a => {path: '/about/a', matched: [{paht: '/about/a', component: xxx, parent: '/about'}, {paht: '/about', component: xxx, parent: undefined}]}
route = this.router.match(location, this.current)
} catch (e) {
this.errorCbs.forEach(cb => {
cb(e)
})
// Exception should still be thrown
throw e
}
const prev = this.current
this.confirmTransition(
route,
() => {
this.updateRoute(route)
onComplete && onComplete(route)
this.ensureURL()
this.router.afterHooks.forEach(hook => {
hook && hook(route, prev)
})
// fire ready cbs once
if (!this.ready) {
this.ready = true
this.readyCbs.forEach(cb => {
cb(route)
})
}
},
err => {
if (onAbort) {
onAbort(err)
}
if (err && !this.ready) {
// Initial redirection should not mark the history as ready yet
// because it's triggered by the redirection instead
// https://github.com/vuejs/vue-router/issues/3225
// https://github.com/vuejs/vue-router/issues/3331
if (!isNavigationFailure(err, NavigationFailureType.redirected) || prev !== START) {
this.ready = true
this.readyErrorCbs.forEach(cb => {
cb(err)
})
}
}
}
)
}
confirmTransition(route: Route, onComplete: Function, onAbort ?: Function) {
const current = this.current
this.pending = route
const abort = err => {
// changed after adding errors with
// https://github.com/vuejs/vue-router/pull/3047 before that change,
// redirect and aborted navigation would produce an err == null
if (!isNavigationFailure(err) && isError(err)) {
if (this.errorCbs.length) {
this.errorCbs.forEach(cb => {
cb(err)
})
} else {
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production') {
warn(false, 'uncaught error during route navigation:')
}
console.error(err)
}
}
onAbort && onAbort(err)
}
const lastRouteIndex = route.matched.length - 1
const lastCurrentIndex = current.matched.length - 1
if (
isSameRoute(route, current) &&
// in the case the route map has been dynamically appended to
lastRouteIndex === lastCurrentIndex &&
route.matched[lastRouteIndex] === current.matched[lastCurrentIndex]
) {
this.ensureURL()
if (route.hash) {
handleScroll(this.router, current, route, false)
}
return abort(createNavigationDuplicatedError(current, route))
}
const { updated, deactivated, activated } = resolveQueue(
this.current.matched,
route.matched
)
const queue: Array<?NavigationGuard> = [].concat(
// in-component leave guards
extractLeaveGuards(deactivated),
// global before hooks
this.router.beforeHooks,
// in-component update hooks
extractUpdateHooks(updated),
// in-config enter guards
activated.map(m => m.beforeEnter),
// async components
resolveAsyncComponents(activated)
)
const iterator = (hook: NavigationGuard, next) => {
if (this.pending !== route) {
return abort(createNavigationCancelledError(current, route))
}
try {
hook(route, current, (to: any) => {
if (to === false) {
// next(false) -> abort navigation, ensure current URL
this.ensureURL(true)
abort(createNavigationAbortedError(current, route))
} else if (isError(to)) {
this.ensureURL(true)
abort(to)
} else if (
typeof to === 'string' ||
(typeof to === 'object' &&
(typeof to.path === 'string' || typeof to.name === 'string'))
) {
// next('/') or next({ path: '/' }) -> redirect
abort(createNavigationRedirectedError(current, route))
if (typeof to === 'object' && to.replace) {
this.replace(to)
} else {
this.push(to)
}
} else {
// confirm transition and pass on the value
next(to)
}
})
} catch (e) {
abort(e)
}
}
runQueue(queue, iterator, () => {
// wait until async components are resolved before
// extracting in-component enter guards
const enterGuards = extractEnterGuards(activated)
const queue = enterGuards.concat(this.router.resolveHooks)
runQueue(queue, iterator, () => {
if (this.pending !== route) {
return abort(createNavigationCancelledError(current, route))
}
this.pending = null
onComplete(route)
if (this.router.app) {
this.router.app.$nextTick(() => {
handleRouteEntered(route)
})
}
})
})
}
updateRoute(route: Route) {
// 更新路由
this.current = route
// 监听路径的变化
this.cb && this.cb(route)
}
setupListeners() {
// Default implementation is empty
}
teardown() {
// clean up event listeners
// https://github.com/vuejs/vue-router/issues/2341
this.listeners.forEach(cleanupListener => {
cleanupListener()
})
this.listeners = []
// reset current history route
// https://github.com/vuejs/vue-router/issues/3294
this.current = START
this.pending = null
}
}
function normalizeBase(base: ?string): string {
if (!base) {
if (inBrowser) {
// respect <base> tag
const baseEl = document.querySelector('base')
base = (baseEl && baseEl.getAttribute('href')) || '/'
// strip full URL origin
base = base.replace(/^https?:\/\/[^\/]+/, '')
} else {
base = '/'
}
}
// make sure there's the starting slash
if (base.charAt(0) !== '/') {
base = '/' + base
}
// remove trailing slash
return base.replace(/\/$/, '')
}
function resolveQueue(
current: Array<RouteRecord>,
next: Array<RouteRecord>
): {
updated: Array<RouteRecord>,
activated: Array<RouteRecord>,
deactivated: Array<RouteRecord>
} {
let i
const max = Math.max(current.length, next.length)
for (i = 0; i < max; i++) {
if (current[i] !== next[i]) {
break
}
}
return {
updated: next.slice(0, i),
activated: next.slice(i),
deactivated: current.slice(i)
}
}
function extractGuards(
records: Array<RouteRecord>,
name: string,
bind: Function,
reverse?: boolean
): Array<?Function> {
const guards = flatMapComponents(records, (def, instance, match, key) => {
const guard = extractGuard(def, name)
if (guard) {
return Array.isArray(guard)
? guard.map(guard => bind(guard, instance, match, key))
: bind(guard, instance, match, key)
}
})
return flatten(reverse ? guards.reverse() : guards)
}
function extractGuard(
def: Object | Function,
key: string
): NavigationGuard | Array<NavigationGuard> {
if (typeof def !== 'function') {
// extend now so that global mixins are applied.
def = _Vue.extend(def)
}
return def.options[key]
}
function extractLeaveGuards(deactivated: Array<RouteRecord>): Array<?Function> {
return extractGuards(deactivated, 'beforeRouteLeave', bindGuard, true)
}
function extractUpdateHooks(updated: Array<RouteRecord>): Array<?Function> {
return extractGuards(updated, 'beforeRouteUpdate', bindGuard)
}
function bindGuard(guard: NavigationGuard, instance: ?_Vue): ?NavigationGuard {
if (instance) {
return function boundRouteGuard() {
return guard.apply(instance, arguments)
}
}
}
function extractEnterGuards(
activated: Array<RouteRecord>
): Array<?Function> {
return extractGuards(
activated,
'beforeRouteEnter',
(guard, _, match, key) => {
return bindEnterGuard(guard, match, key)
}
)
}
function bindEnterGuard(
guard: NavigationGuard,
match: RouteRecord,
key: string
): NavigationGuard {
return function routeEnterGuard(to, from, next) {
return guard(to, from, cb => {
if (typeof cb === 'function') {
if (!match.enteredCbs[key]) {
match.enteredCbs[key] = []
}
match.enteredCbs[key].push(cb)
}
next(cb)
})
}
}
- createRoute:对于嵌套路由,比如
/about/a,在我们要渲染 a 页面的时候,肯定也要把他的父组件也给渲染出来,这里就是 about 页面,因此这个方法会返回一个字段matched,记录当前路径需要渲染的全部页面。上面说到的生成 matcher,也是用到这个方法。 - transitionTo:这是跳转的核心逻辑,通过当前跳转的路径拿到需要匹配的路由,例如:访问路径
/about/a => {path: '/about/a', matched: [{paht: '/about/a', component: xxx, parent: '/about'}, {paht: '/about', component: xxx, parent: undefined}]},然后更新当前路由,如果有传入跳转之后的回调 onComplete ,那么就去执行。 - updateRoute:更新路由的方法,History 类中有个字段 current 记录了当前的路由信息,此时要更新该字段,如果有 cb,再执行一下。
- listen:监听的方法,接收一个 cb,当更新路由的时候调用 cb,从而更新 vue 根实例上的 _route 属性
src/history/hash.js
定义一个 HashHistory 类,继承自 History 类。hash 模式,优先使用 history.pushState/repaceState API 来完成 URL 跳转和
onpopstate事件监听路由变化,不支持再降级为 location.hash API 和onhashchange事件
- 获取当前路径的 hash 值,监听 hashchange 事件,当路径发生变化的时候,执行跳转方法
ensureSlash
- 我们实例化一个 history 对象时,会默认在 constructor 构造函数中执行 ensureSlash 方法,如果没有hash 值的话就给一个默认的 hash 路径
/,确保存在 hash 锚点 - 其作用就是将
http://localhost:8080/自动修改为http://localhost:8080/#/
setupListener
添加路由监听器,当 hash 值变化时调用 transitionTo 方法统一处理跳转逻辑。事件注册采用了降级处理,优先使用 onpopstate 事件,若不支持,则降级使用 onhashchange 事件
当用户点击浏览器的后退、前进按钮,在 js 中调用 HTML5 history API,如
history.back()、history.go()、history.forward(),或者通过location.hash = 'xxx'都会触发 popstate 事件 和 hashchange 事件 需要注意的是调用history.pushState()或者history.replaceState()不会触发 popstate 事件 和 hashchange 事件
触发时机: 在 vueRouter 类的 init 方法中调用
class VueRouter {
// router初始化方法(只会在 根vue实例中的 beforeCreate钩子中调用一次)
init (app) {
const history = this.history
// 手动根据当前路径去匹配对应的组件,渲染,之后监听路由变化
history.transitionTo(history.getCurrentLocation(), () => {
history.setupListener()
})
...
}
}
注意:history.pushState 不会触发 onpopstate 事件
push
- 跳转页面,手动调用 transitionTo 方法去处理跳转逻辑,并在回调中通过
history.pushState或location.hash向路由栈添加一条路由记录,更新地址栏 URL
src/history/html5.js
history 模式,使用 history.pushState/repaceState API 来完成 URL 跳转,使用
onpopstate事件监听路由变化
/* @flow */
import type Router from '../index'
import { History } from './base'
import { cleanPath } from '../util/path'
import { START } from '../util/route'
import { setupScroll, handleScroll } from '../util/scroll'
import { pushState, replaceState, supportsPushState } from '../util/push-state'
export class HTML5History extends History {
_startLocation: string
constructor (router: Router, base: ?string) {
super(router, base)
this._startLocation = getLocation(this.base)
}
setupListeners () {
if (this.listeners.length > 0) {
return
}
const router = this.router
const expectScroll = router.options.scrollBehavior
const supportsScroll = supportsPushState && expectScroll
if (supportsScroll) {
this.listeners.push(setupScroll())
}
const handleRoutingEvent = () => {
const current = this.current
// Avoiding first `popstate` event dispatched in some browsers but first
// history route not updated since async guard at the same time.
const location = getLocation(this.base)
if (this.current === START && location === this._startLocation) {
return
}
this.transitionTo(location, route => {
if (supportsScroll) {
handleScroll(router, route, current, true)
}
})
}
window.addEventListener('popstate', handleRoutingEvent)
this.listeners.push(() => {
window.removeEventListener('popstate', handleRoutingEvent)
})
}
go (n: number) {
window.history.go(n)
}
push (location: RawLocation, onComplete?: Function, onAbort?: Function) {
const { current: fromRoute } = this
this.transitionTo(location, route => {
pushState(cleanPath(this.base + route.fullPath))
handleScroll(this.router, route, fromRoute, false)
onComplete && onComplete(route)
}, onAbort)
}
replace (location: RawLocation, onComplete?: Function, onAbort?: Function) {
const { current: fromRoute } = this
this.transitionTo(location, route => {
replaceState(cleanPath(this.base + route.fullPath))
handleScroll(this.router, route, fromRoute, false)
onComplete && onComplete(route)
}, onAbort)
}
ensureURL (push?: boolean) {
if (getLocation(this.base) !== this.current.fullPath) {
const current = cleanPath(this.base + this.current.fullPath)
push ? pushState(current) : replaceState(current)
}
}
getCurrentLocation (): string {
return getLocation(this.base)
}
}
export function getLocation (base: string): string {
let path = window.location.pathname
const pathLowerCase = path.toLowerCase()
const baseLowerCase = base.toLowerCase()
// base="/a" shouldn't turn path="/app" into "/a/pp"
// https://github.com/vuejs/vue-router/issues/3555
// so we ensure the trailing slash in the base
if (base && ((pathLowerCase === baseLowerCase) ||
(pathLowerCase.indexOf(cleanPath(baseLowerCase + '/')) === 0))) {
path = path.slice(base.length)
}
return (path || '/') + window.location.search + window.location.hash
}
src/components/view.js
router-view是一个函数式组件,有时需要借助父节点的能力,例如使用父节点的渲染函数来解析命名插槽
通过routerView来标识view组件,方便vue-devtools识别出view组件和确定view组件深度
通过向上查找,确定当前view的深度depth,通过depth取到对应的路由记录
再取出通过registerInstance绑定的路由组件实例
如果有动态路由参数,则先填充props然后再渲染
如果view被keep-alive包裹并且处于inactive状态,则从缓存中取出路由组件实例并渲染
负责在匹配到路由记录后将对应路由组件渲染出来
// src/components/view.js
export default {
name: 'RouterView',
functional: true, // 函数式组件,没有this;https://cn.vuejs.org/v2/guide/render-function.html#函数式组件
props: {
name: {
type: String,
default: 'default',
},
}, // _为h即createElement,但router-view没有使用自身的h,而是使用了父节点的h
render(/* h*/ _, /* context*/ { props, children, parent, data }) {
// used by devtools to display a router-view badge
data.routerView = true // 标识当前组件为router-view // directly use parent context's createElement() function // so that components rendered by router-view can resolve named slots
const h = parent.$createElement // 使用父节点的渲染函数
const name = props.name // 命名视图
const route = parent.$route // 依赖父节点的$route,而在install.js中我们知道,所有组件访问到的$route其实都是_routerRoot._route,即Vue根实例上的_route;当路由被确认后,调用updateRoute时,会更新_routerRoot._route,进而导致router-view组件重新渲染 // 缓存
const cache = parent._routerViewCache || (parent._routerViewCache = {}) // determine current view depth, also check to see if the tree // has been toggled inactive but kept-alive.
let depth = 0 // 当前router-view嵌套深度
let inactive = false // 是否被keep-alive包裹并处于非激活状态 // 向上查找,计算depth、inactive // 当parent指向Vue根实例结束循环
while (parent && parent._routerRoot !== parent) {
const vnodeData = parent.$vnode ? parent.$vnode.data : {}
if (vnodeData.routerView) {
depth++
} // 处理keep-alive // keep-alive组件会添加keepAlive=true标识 // https://github.com/vuejs/vue/blob/52719ccab8fccffbdf497b96d3731dc86f04c1ce/src/core/components/keep-alive.js#L120
if (vnodeData.keepAlive && parent._directInactive && parent._inactive) {
inactive = true
}
parent = parent.$parent
}
data.routerViewDepth = depth // render previous view if the tree is inactive and kept-alive // 如果当前组件树被keep-alive包裹,且处于非激活状态,则渲染之前保存的视图
if (inactive) {
const cachedData = cache[name]
const cachedComponent = cachedData && cachedData.component // 找到缓存的组件
if (cachedComponent) {
// #2301
// pass props
// 传递缓存的props
if (cachedData.configProps) {
fillPropsinData(
cachedComponent,
data,
cachedData.route,
cachedData.configProps
)
}
return h(cachedComponent, data, children)
} else {
// 未找到缓存的组件
// render previous empty view
return h()
}
} // 通过depth获取匹配的route record // 由于formatMatch是通过unshift添加父route record的 // 所以route.matched[depth]正好能取到匹配的route record
const matched = route.matched[depth]
const component = matched && matched.components[name] // 取出路由组件 // render empty node if no matched route or no config component // 找不到,渲染空组件
if (!matched || !component) {
cache[name] = null
return h()
} // cache component // 缓存组件
cache[name] = { component } // attach instance registration hook // this will be called in the instance's injected lifecycle hooks // 为路由记录绑定路由组件,在所有组件的beforeCreate、destoryed hook中调用,见install.js中的registerInstance方法 // 此方法只在router-view上定义了 // vm,val都为路由组件实例 // 如下 // matched.instances:{ // default:VueComp, // hd:VueComp2, // bd:VueComp3 // }
data.registerRouteInstance = (vm, val) => {
// val could be undefined for unregistration
const current = matched.instances[name]
if (
(val && current !== vm) || // 绑定
(!val && current === vm)
) {
// 若val不存在,则可视为解绑
matched.instances[name] = val
}
} // also register instance in prepatch hook // in case the same component instance is reused across different routes // 当相同组件在不同路由间复用时,也需要为router-view绑定路由组件
;(data.hook || (data.hook = {})).prepatch = (_, vnode) => {
matched.instances[name] = vnode.componentInstance
} // register instance in init hook // in case kept-alive component be actived when routes changed // keep-alive组件被激活时,需要为router-view注册路由组件
data.hook.init = (vnode) => {
if (
vnode.data.keepAlive &&
vnode.componentInstance &&
vnode.componentInstance !== matched.instances[name]
) {
matched.instances[name] = vnode.componentInstance
}
} // route record设置了路由传参;动态路由传参;https://router.vuejs.org/zh/guide/essentials/passing-props.
const configProps = matched.props && matched.props[name] // save route and configProps in cachce // 如果设置了路由传参,则缓存起来,并将填充props
if (configProps) {
extend(cache[name], {
route,
configProps,
})
fillPropsinData(component, data, route, configProps)
}
return h(component, data, children)
},
}
其被定义成一个函数式组件,这代表它没有状态和实例(this 上下文),只接收了name来做命名视图
我们重点看下render方法
由于其是一个函数式组件,所以很多操作是借助父节点来完成的
- 为了支持解析命名插槽,其没有使用自己的
createElement方法,而是使用父节点的createElement方法 - 由于没有 this 上下文,无法通过
this.$route获得当前路由对象,干脆就直接使用父节点的$route
可以看到添加了一个标志量routerView,主要用来在vue-devtools中标识view组件和在查找深度时用
然后声明了一个缓存对象_routerViewCache并赋值给cache变量,用来在keep-alive激活时快速取出被缓存的路由组件
开始从当前节点往上查找Vue根实例,在查找的过程中计算出view组件的深度以及是否被kepp-alive包裹并处于inative状态
depth主要用来获取当前view对应的路由记录
-
前面说过,
vue-router是支持嵌套路由的,对应的view也是可以嵌套的 -
而且在匹配路由记录时,有下面的逻辑,
当一个路由记录匹配了,如果其还有父路由记录,则父路由记录肯定也是匹配的,其会一直向上查找,找到一个父记录,就通过
unshift塞入
route.matched数组中的,所以父记录肯定在前,子记录在后,当前精准匹配的记录在最后
- 见
src/util/route.js formatMatch方法
- 见
-
depth的计算在遇到父view组件时,自增 1,通过不断向上查找,不断自增depth,直到找到Vue根实例才停止 -
停止时
route.matched[depth]值就是当前view对应的路由记录 -
有了路由记录,我们就可以从上取出对应的路由组件实例,然后渲染即可
我们先看非inactive状态是如何渲染路由组件实例的
- 通过
route.matched[depth]取出当前view匹配的路由记录 - 然后再取出对应的路由组件实例
- 如果路由记录和路由组件实例有一个不存在,则渲染空结点,并重置
cache[name]值 - 如果都能找到,则先把组件实例缓存下来
- 如果有配置动态路由参数,则把路由参数缓存到路由组件实例上,并调用
fillPropsinData填充props
- 如果有配置动态路由参数,则把路由参数缓存到路由组件实例上,并调用
- 调用
h渲染对应的路由组件实例即可
当组件处于inactive状态时,我们就可以从cache中取出之前缓存的路由组件实例和路由参数,然后渲染就可以了
主流程如上,但还有一个重要的点没提
- 路由记录和路由组件实例是如何绑定的?
- 相信你已经注意到
data.registerRouteInstance方法,没错,他就是用来为路由记录绑定路由组件实例的
registerInstance
- 我们先看下调用的地方
- 主要在
src/install.js的全局混入中
typescript 代码解读复制代码export function install(Vue){
...
// 注册全局混入
Vue.mixin({
beforeCreate () {
...
// 为router-view组件关联路由组件
registerInstance(this, this)
},
destroyed () {
// destroyed hook触发时,取消router-view和路由组件的关联
registerInstance(this)
}
})
}
- 可以看到其在全局混入的
beforeCreate、destroyed钩子中都有被调用 - 前者传入了两个 vm 实例,后者只传入了一个 vm 实例
- 我们看下实现,代码也位于
src/install.js中
typescript 代码解读复制代码// 为路由记录、router-view关联路由组件
const registerInstance = (vm, callVal) => {
let i = vm.$options._parentVnode // 调用vm.$options._parentVnode.data.registerRouteInstance方法 // 而这个方法只在router-view组件中存在,router-view组件定义在(../components/view.js @71行) // 所以,如果vm的父节点为router-view,则为router-view关联当前vm,即将当前vm做为router-view的路由组件
if (isDef(i) && isDef((i = i.data)) && isDef((i = i.registerRouteInstance))) {
i(vm, callVal)
}
}
-
可以看到其接收一个
vm实例和callVal做为入参 -
然后取了
vm的父节点做为 i 的初值 -
接着一步一步给
i赋值,同时判断i是否定义 -
到最后,
i的值为vm.$options._parentVnode.data.registerRouteInstance -
然后将两个入参传入
i中调用 -
注意,这时的 i 是 vm 父节点上的方法,并不是 vm 上的方法
-
我们全局检索下
registerRouteInstance关键字,发现其只被定义在了
view.js中,也就是
router-view组件中
- 结合上面一条,i 即
registerRouteInstance是vm父节点上的方法,而只有router-view组件定义了registerRouteInstance - 所以,只有当
vm是router-view的子节点时,registerRouteInstance方法才会被调用 i(vm, callVal)可以表达为vm._parentVnode.registerRouteInstance(vm,vm)
- 结合上面一条,i 即
-
看下
registerRouteInstance的实现
typescript 代码解读复制代码// src/components/view.js
...
// 为路由记录绑定路由组件,在所有组件的beforeCreate、destoryed hook中调用,见install.js中的registerInstance方法
// 此方法只在router-view上定义了
// vm,val都为路由组件实例
// 如下
// matched.instances:{
// default:VueComp,
// hd:VueComp2,
// bd:VueComp3
// }
data.registerRouteInstance = (vm, val) => {
// val could be undefined for unregistration
const current = matched.instances[name]
if (
(val && current !== vm) || // 绑定
(!val && current === vm) // 若val不存在,则可视为解绑
) {
matched.instances[name] = val
}
}
-
matched保存的是当前匹配到的路由记录,name是命名视图名 -
如果
val存在,并且当前路由组件和传入的不同,重新赋值 -
如果
val不存在,且当前路由组件和传入的相同,也重新赋值,但是此时 val 为undefined,相当于解绑 -
可以看到参数数量不同,一个函数实现了绑定和解绑的双重操作
-
通过这个方法就完成了路由记录和路由组件实例的绑定与解绑操作
-
这样就可以在
view组件render时,通过route.matched[depth].components[name]取到路由组件进行渲染 -
还有些场景也需要进行绑定
- 当相同组件在不同路由间复用时,需要为路由记录绑定路由组件
keep-alive组件被激活时,需要为路由记录绑定路由组件
-
导航解析成功后会调用
updateRoute方法,重新为全局的_routerRoot._route即$route赋值
typescript 代码解读复制代码// src/history/base.js
// 更新路由,触发afterEach钩子
updateRoute (route: Route) {
const prev = this.current
this.current = route// 更新current
this.cb && this.cb(route) // 调用updateRoute回调,回调中会重新为_routerRoot._route赋值,进而触发router-view的重新渲染
...
}
- 在
view组件中,会使用$parent.$route即全局的_routerRoot._route
typescript 代码解读复制代码 // src/components/view.js
...
render (/* h*/_, /* context*/{ props, children, parent, data }) {
...
const route = parent.$route // 依赖父节点的$route,而在install.js中我们知道,所有组件访问到的$route其实都是_routerRoot._route,即Vue根实例上的_route;当路由被确认后,调用updateRoute时,会更新_routerRoot._route,进而导致router-view组件重新渲染
...
}
- 而在
install.js的全局混入中,将_route定义为响应式的,依赖了_route的地方,在_route发生变化时,都会重新渲染
typescript 代码解读复制代码// src/install.js
// 注册全局混入
Vue.mixin({
beforeCreate () {
...
// 响应式定义_route属性,保证_route发生变化时,组件(router-view)会重新渲染
Vue.util.defineReactive(this, '_route', this._router.history.current)
}
})
- 这样就完成了渲染的闭环,
view依赖$route,导航解析成功更新$route,触发view渲染
src/components/link.js
/* @flow */
import { createRoute, isSameRoute, isIncludedRoute } from '../util/route'
import { extend } from '../util/misc'
import { normalizeLocation } from '../util/location'
import { warn } from '../util/warn'
// work around weird flow bug
const toTypes: Array<Function> = [String, Object]
const eventTypes: Array<Function> = [String, Array]
const noop = () => {}
export default {
name: 'RouterLink',
props: {
to: {
type: toTypes, // string | Location
required: true,
},
tag: {
type: String,
default: 'a', // 默认a标签
},
exact: Boolean, // 是否精确匹配
append: Boolean, // 是否追加
replace: Boolean, // 为true,调用router.replace否则调用router.push
activeClass: String, // 激活的类名
exactActiveClass: String, // 精确匹配的类名
ariaCurrentValue: {
// 无障碍化
type: String,
default: 'page',
},
event: {
type: eventTypes, // 触发导航的事件
default: 'click',
},
},
render(h: Function) {
const router = this.$router
const current = this.$route
const { location, route, href } = router.resolve(
this.to,
current,
this.append
) // 解析目标位置
const classes = {}
const globalActiveClass = router.options.linkActiveClass
const globalExactActiveClass = router.options.linkExactActiveClass // Support global empty active class
const activeClassFallback =
globalActiveClass == null ? 'router-link-active' : globalActiveClass
const exactActiveClassFallback =
globalExactActiveClass == null
? 'router-link-exact-active'
: globalExactActiveClass
const activeClass =
this.activeClass == null ? activeClassFallback : this.activeClass
const exactActiveClass =
this.exactActiveClass == null
? exactActiveClassFallback
: this.exactActiveClass // 目标route,用来比较是否和当前route是相同route
const compareTarget = route.redirectedFrom
? createRoute(null, normalizeLocation(route.redirectedFrom), null, router)
: route
classes[exactActiveClass] = isSameRoute(current, compareTarget)
classes[activeClass] = this.exact
? classes[exactActiveClass]
: isIncludedRoute(current, compareTarget) // 非精准匹配时,判断目标route path是否包含当前route path
const ariaCurrentValue = classes[exactActiveClass]
? this.ariaCurrentValue
: null // 事件处理
const handler = (e) => {
if (guardEvent(e)) {
if (this.replace) {
router.replace(location, noop)
} else {
router.push(location, noop)
}
}
}
const on = { click: guardEvent }
if (Array.isArray(this.event)) {
this.event.forEach((e) => {
on[e] = handler
})
} else {
on[this.event] = handler
}
const data: any = { class: classes } // 读取作用域插槽
const scopedSlot =
!this.$scopedSlots.$hasNormal &&
this.$scopedSlots.default &&
this.$scopedSlots.default({
href,
route,
navigate: handler,
isActive: classes[activeClass],
isExactActive: classes[exactActiveClass],
})
if (scopedSlot) {
// 作用域插槽仅有一个子元素
if (scopedSlot.length === 1) {
return scopedSlot[0]
} else if (scopedSlot.length > 1 || !scopedSlot.length) {
// 作用域插槽提供多个后代或未提供后,给予提示
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production') {
warn(
false,
`RouterLink with to="${this.to}" is trying to use a scoped slot but it didn't provide exactly one child. Wrapping the content with a span element.`
)
} // 有多个后代时,在外层用一个span包裹
return scopedSlot.length === 0 ? h() : h('span', {}, scopedSlot)
}
} // tag为a
if (this.tag === 'a') {
data.on = on
data.attrs = { href, 'aria-current': ariaCurrentValue }
} else {
// tag不为a,则找后代首个a绑定事件
// find the first <a> child and apply listener and href
const a = findAnchor(this.$slots.default)
if (a) {
// in case the <a> is a static node
a.isStatic = false
const aData = (a.data = extend({}, a.data))
aData.on = aData.on || {} // transform existing events in both objects into arrays so we can push later // a上可能还绑定有其他事件,需要兼容
for (const event in aData.on) {
const handler = aData.on[event]
if (event in on) {
aData.on[event] = Array.isArray(handler) ? handler : [handler]
}
} // append new listeners for router-link // 绑定其他事件处理器
for (const event in on) {
if (event in aData.on) {
// on[event] is always a function
aData.on[event].push(on[event])
} else {
aData.on[event] = handler
}
}
const aAttrs = (a.data.attrs = extend({}, a.data.attrs))
aAttrs.href = href
aAttrs['aria-current'] = ariaCurrentValue
} else {
// doesn't have <a> child, apply listener to self
// 没找到,则给当前元素绑定事件
data.on = on
}
}
return h(this.tag, data, this.$slots.default)
},
}
// 特殊场景,点击不做跳转响应
function guardEvent(e) {
// don't redirect with control keys
if (e.metaKey || e.altKey || e.ctrlKey || e.shiftKey) return // don't redirect when preventDefault called
if (e.defaultPrevented) return // don't redirect on right click
if (e.button !== undefined && e.button !== 0) return // don't redirect if `target="_blank"`
if (e.currentTarget && e.currentTarget.getAttribute) {
const target = e.currentTarget.getAttribute('target')
if (/\b_blank\b/i.test(target)) return
} // this may be a Weex event which doesn't have this method
if (e.preventDefault) {
e.preventDefault()
}
return true
}
// 递归查找后代a标签
function findAnchor(children) {
if (children) {
let child
for (let i = 0; i < children.length; i++) {
child = children[i]
if (child.tag === 'a') {
return child
}
if (child.children && (child = findAnchor(child.children))) {
return child
}
}
}
}
- 实现了点击时跳转到
to对应的路由功能 - 由于支持点击时需要标识样式类、精准匹配
exact场景,所以通过sameRoute、isIncludedRoute来实现样式类的标识和精准匹配标识 - 在点击时,屏蔽了部分特殊场景,如点击时同时按下
ctrl、alt、shift等control keys时,不做跳转
相关实例属性
-
router.app- 配置了 router 的 Vue 根实例
-
router.mode- 路由使用的模式
-
router.currentRoute- 当前路由对象,等同于
this.$route
- 当前路由对象,等同于
相关实例方法
用注册全局导航守卫
router.beforeEachrouter.beforeResolverouter.afterEach
编程式导航相关
router.pushrouter.replacerouter.gorouter.backrouter.forward
服务端渲染相关
-
router.getMatchedComponents- 返回目标位置或是当前路由匹配的组件数组 (是数组的定义/构造类,不是实例)
-
router.onReady- 该方法把一个回调排队,在路由完成初始导航时调用,这意味着它可以解析所有的异步进入钩子和路由初始化相关联的异步组件
-
router.onError- 注册一个回调,该回调会在路由导航过程中出错时被调用
动态路由
-
router.addRoutes- 动态添加路由规则
解析
router.resolve- 传入一个对象,尝试解析并返回一个目标位置






















 8080
8080











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








