136. 只出现一次的数字
给定一个非空整数数组,除了某个元素只出现一次以外,其余每个元素均出现两次。找出那个只出现了一次的元素。
说明:
你的算法应该具有线性时间复杂度。 你可以不使用额外空间来实现吗?
示例 1:
输入: [2,2,1]
输出: 1
示例 2:
输入: [4,1,2,1,2]
输出: 4
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/single-number
方法 4:位操作
概念
如果我们对 0 和二进制位做 XOR 运算,得到的仍然是这个二进制位
a⊕0 = a
如果我们对相同的二进制位做 XOR 运算,返回的结果是 0
a ⊕a = 0
XOR 满足交换律和结合律
a ⊕b⊕a = (a⊕a) ⊕ b = 0 ⊕b = b
所以我们只需要将所有的数进行 XOR 操作,得到那个唯一的数字。
public int singleNumber(int[] nums) {
int result = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
result ^= nums[i];
}
return result;
}
给定一个链表,判断链表中是否有环。
为了表示给定链表中的环,我们使用整数 pos 来表示链表尾连接到链表中的位置(索引从 0 开始)。 如果 pos 是 -1,则在该链表中没有环。
示例 1:
输入:head = [3,2,0,-4], pos = 1
输出:true
解释:链表中有一个环,其尾部连接到第二个节点。
示例 2:
输入:head = [1,2], pos = 0
输出:true
解释:链表中有一个环,其尾部连接到第一个节点。
示例 3:
输入:head = [1], pos = -1
输出:false
解释:链表中没有环。
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/linked-list-cycle
方法一:双指针
通过使用具有 不同速度 的快、慢两个指针遍历链表,空间复杂度可以被降低至 O(1)。慢指针每次移动一步,而快指针每次移动两步。
如果列表中不存在环,最终快指针将会最先到达尾部,此时我们可以返回 false。
现在考虑一个环形链表,把慢指针和快指针想象成两个在环形赛道上跑步的运动员(分别称之为慢跑者与快跑者)。而快跑者最终一定会追上慢跑者。
public boolean hasCycle(ListNode head) {
ListNode slow = head;
ListNode fast = head;
if(head != null)
fast = slow.next;
while(fast != null){
if(fast == slow){
return true;
}
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next;
if(fast != null)
fast = fast.next;
}
return false;
}
方法二:哈希表
思路
我们可以通过检查一个结点此前是否被访问过来判断链表是否为环形链表。常用的方法是使用哈希表。
算法
我们遍历所有结点并在哈希表中存储每个结点的引用(或内存地址)。如果当前结点为空结点 null(即已检测到链表尾部的下一个结点),那么我们已经遍历完整个链表,并且该链表不是环形链表。如果当前结点的引用已经存在于哈希表中,那么返回 true(即该链表为环形链表)。
public boolean hasCycle(ListNode head) {
Set<ListNode> nodesSeen = new HashSet<>();
while (head != null) {
if (nodesSeen.contains(head)) {
return true;
} else {
nodesSeen.add(head);
}
head = head.next;
}
return false;
}编写一个程序,找到两个单链表相交的起始节点。
如下面的两个链表:
在节点 c1 开始相交。
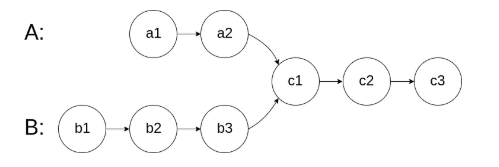
示例 1:
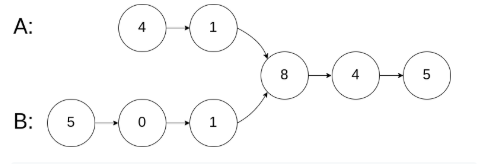
输入:intersectVal = 8, listA = [4,1,8,4,5], listB = [5,0,1,8,4,5], skipA = 2, skipB = 3
输出:Reference of the node with value = 8
输入解释:相交节点的值为 8 (注意,如果两个列表相交则不能为 0)。从各自的表头开始算起,链表 A 为 [4,1,8,4,5],链表 B 为 [5,0,1,8,4,5]。在 A 中,相交节点前有 2 个节点;在 B 中,相交节点前有 3 个节点。
示例 2:

输入:intersectVal = 2, listA = [0,9,1,2,4], listB = [3,2,4], skipA = 3, skipB = 1
输出:Reference of the node with value = 2
输入解释:相交节点的值为 2 (注意,如果两个列表相交则不能为 0)。从各自的表头开始算起,链表 A 为 [0,9,1,2,4],链表 B 为 [3,2,4]。在 A 中,相交节点前有 3 个节点;在 B 中,相交节点前有 1 个节点。
示例 3:

输入:intersectVal = 0, listA = [2,6,4], listB = [1,5], skipA = 3, skipB = 2
输出:null
输入解释:从各自的表头开始算起,链表 A 为 [2,6,4],链表 B 为 [1,5]。由于这两个链表不相交,所以 intersectVal 必须为 0,而 skipA 和 skipB 可以是任意值。
解释:这两个链表不相交,因此返回 null。
注意:
如果两个链表没有交点,返回 null.
在返回结果后,两个链表仍须保持原有的结构。
可假定整个链表结构中没有循环。
程序尽量满足 O(n) 时间复杂度,且仅用 O(1) 内存。
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/intersection-of-two-linked-lists
第一种解法
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) {
* val = x;
* next = null;
* }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
public ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) {
int lengthA = getLength(headA);
int lengthB = getLength(headB);
int c = Math.abs(lengthA-lengthB);
ListNode slow = headA;
ListNode fast = headB;
if(lengthA < lengthB){
slow = headB;
fast = headA;
}
for (int i = 0; i < c ; i++) {
slow = slow.next;
}
while(slow!=null && fast != null){
if(slow == fast){
return slow;
}
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next;
}
return null;
}
public int getLength(ListNode head){
int len = 0 ;
while(head != null){
len ++;
head = head.next;
}
return len;
}
}第二种解法
根据题目意思
如果两个链表相交,那么相交点之后的长度是相同的
我们需要做的事情是,让两个链表从同距离末尾同等距离的位置开始遍历。这个位置只能是较短链表的头结点位置。
为此,我们必须消除两个链表的长度差
指针 pA 指向 A 链表,指针 pB 指向 B 链表,依次往后遍历
如果 pA 到了末尾,则 pA = headB 继续遍历
如果 pB 到了末尾,则 pB = headA 继续遍历
比较长的链表指针指向较短链表head时,长度差就消除了
如此,只需要将最短链表遍历两次即可找到位置
听着可能有点绕,看图最直观,链表的题目最适合看图了
public ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) {
if (headA == null || headB == null) return null;
ListNode pA = headA, pB = headB;
while (pA != pB) {
pA = pA == null ? headB : pA.next;
pB = pB == null ? headA : pB.next;
}
return pA;
}给定一个已按照升序排列 的有序数组,找到两个数使得它们相加之和等于目标数。
函数应该返回这两个下标值 index1 和 index2,其中 index1 必须小于 index2。
说明:
返回的下标值(index1 和 index2)不是从零开始的。
你可以假设每个输入只对应唯一的答案,而且你不可以重复使用相同的元素。
示例:
输入: numbers = [2, 7, 11, 15], target = 9
输出: [1,2]
解释: 2 与 7 之和等于目标数 9 。因此 index1 = 1, index2 = 2 。
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/two-sum-ii-input-array-is-sorted
class Solution {
public int[] twoSum(int[] numbers, int target) {
int start = 0;
int end = numbers.length-1;
while(start < end){
if(numbers[start] + numbers[end] == target){
return new int[]{start+1,end+1};
}else if(numbers[start] + numbers[end] < target){
start++;
}else {
end -- ;
}
}
return null;
}
}给定一个大小为 n 的数组,找到其中的众数。众数是指在数组中出现次数大于 ⌊ n/2 ⌋ 的元素。
你可以假设数组是非空的,并且给定的数组总是存在众数。
示例 1:
输入: [3,2,3]
输出: 3
示例 2:
输入: [2,2,1,1,1,2,2]
输出: 2
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/majority-element
class Solution {
public int majorityElement(int[] nums) {
Arrays.sort(nums);
return nums[nums.length/2];
}
}给定一个正整数,返回它在 Excel 表中相对应的列名称。
例如,
1 -> A
2 -> B
3 -> C
...
26 -> Z
27 -> AA
28 -> AB
...
示例 1:
输入: 1
输出: "A"
示例 2:
输入: 28
输出: "AB"
示例 3:
输入: 701
输出: "ZY"
class Solution {
public String convertToTitle(int n) {
StringBuffer res = new StringBuffer();
while (!(n / 26 == 0 && n % 26 == 0)) {
int pop = n % 26;
char letter;
if (pop == 0) {
letter = 'Z';
n = n / 26 - 1;
} else {
letter = (char) ('A' + pop - 1);
n /= 26;
}
res.insert(0, letter);
}
return res.toString();
}
}
给定一个整数 n,返回 n! 结果尾数中零的数量。
示例 1:
输入: 3
输出: 0
解释: 3! = 6, 尾数中没有零。
示例 2:
输入: 5
输出: 1
解释: 5! = 120, 尾数中有 1 个零.
说明: 你算法的时间复杂度应为 O(log n) 。
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/factorial-trailing-zeroes
class Solution {
public int trailingZeroes(int n) {
int res = 0;
while(n!=0){
res+=n/5;
n/=5;
}
return res;
}
}表1: Person
+-------------+---------+
| 列名 | 类型 |
+-------------+---------+
| PersonId | int |
| FirstName | varchar |
| LastName | varchar |
+-------------+---------+
PersonId 是上表主键
表2: Address
+-------------+---------+
| 列名 | 类型 |
+-------------+---------+
| AddressId | int |
| PersonId | int |
| City | varchar |
| State | varchar |
+-------------+---------+
AddressId 是上表主键
编写一个 SQL 查询,满足条件:无论 person 是否有地址信息,都需要基于上述两表提供 person 的以下信息:
FirstName, LastName, City, State
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/combine-two-tables
select FirstName, LastName, City, State from
Person p left join Address a
on p.PersonId = a.PersonId;
给定一个包含 n 个整数的数组 nums,判断 nums 中是否存在三个元素 a,b,c ,使得 a + b + c = 0 ?找出所有满足条件且不重复的三元组。
注意:答案中不可以包含重复的三元组。
例如, 给定数组 nums = [-1, 0, 1, 2, -1, -4],
满足要求的三元组集合为:
[
[-1, 0, 1],
[-1, -1, 2]
]
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/3sum
class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> threeSum(int[] nums) {
List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList<>();
if (nums.length == 0) {
return result;
}
Arrays.sort(nums);
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
if (nums[i] > 0) {
break;
}
if(i>0&&nums[i]==nums[i-1]){
continue;
}
int m = i + 1, n = nums.length - 1;
while (m < n) {
if (n<nums.length-1&&nums[n]==nums[n+1]||nums[i] + nums[m] + nums[n] > 0) {
n--;
} else if (m>i+1&&nums[m]==nums[m-1]||nums[i] + nums[m] + nums[n] < 0) {
m++;
} else {
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add(nums[i]);
list.add(nums[m++]);
list.add(nums[n--]);
result.add(list);
}
}
}
return result;
}
}171. Excel表列序号
给定一个Excel表格中的列名称,返回其相应的列序号。
例如,
A -> 1
B -> 2
C -> 3
...
Z -> 26
AA -> 27
AB -> 28
...
示例 1:
输入: "A"
输出: 1
示例 2:
输入: "AB"
输出: 28
示例 3:
输入: "ZY"
输出: 701
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/excel-sheet-column-number
class Solution {
public int titleToNumber(String s) {
int result = 0;
char[] charArray = s.toCharArray();
int k = 0;
for (int i = charArray.length -1; i >= 0; i--) {
result += (s.charAt(i) - 'A' +1 ) *(int) Math.pow(26, k++);
}
return result;
}
}





















 264
264











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








