- 类级别注解
- @SpringBootApplication
@Configuration //表明这是一个配置类
@EnableAutoConfiguration //开启自动配置
@ComponentScan() //开启组件扫描
1、@Configuration:
当一个类被 @Configuration 注解时,它就被标识为一个配置类。这意味着该类可以包含一个或多个使用 @Bean 注解的方法,这些方法会返回对象实例,并且这些对象会被注册为 Spring 应用上下文中的 bean。
2、@EnableAutoConfiguration:
允许 Spring Boot 自动配置注解,开启这个注解之后,Spring Boot 就能根据当前类路径下的包或者类来配置 Spring Bean。
@EnableAutoConfiguration实现的关键在于引入了AutoConfigurationImportSelector,其核心逻辑为selectImports方法:
👉 从配置文件META-INF/spring.factories加载所有可能用到的自动配置类
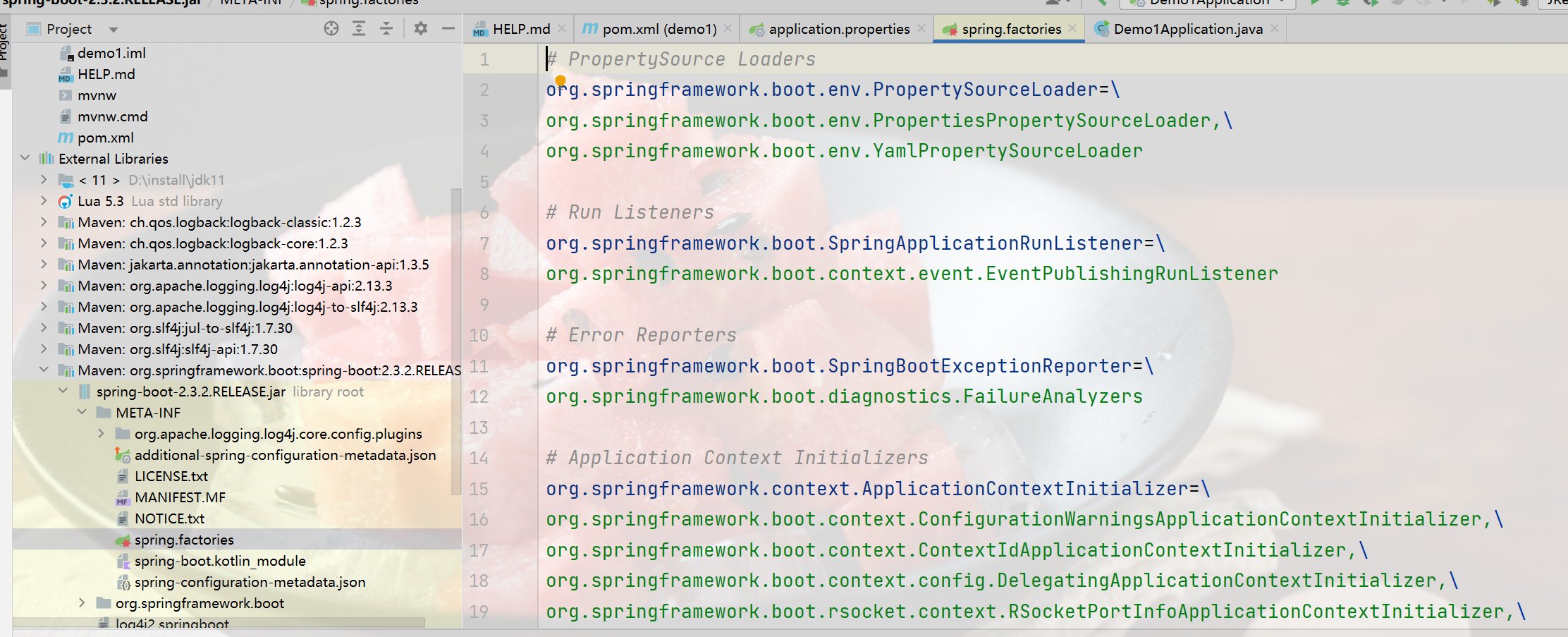
👉 去重,并将exclude和excludeName属性携带的类排除;
在这个例子中,DataSourceAutoConfiguration.class 被明确地从自动配置过程中排除了。这意味着即使你的项目中有数据库相关的依赖(例如 HikariCP, JDBC, 或者某个 ORM 框架),Spring Boot 不会自动配置数据源相关的组件。这通常是在你想要自定义数据源配置或完全不使用数据源时有用。
@SpringBootApplication(exclude = {DataSourceAutoConfiguration.class})
public class MyApplication {
// ...
}
@SpringBootApplication(excludeName = "org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jdbc.DataSourceAutoConfiguration")
public class MyApplication {
// ...
}
👉 过滤,将满足条件(@Conditional)的自动配置类返回;
在这个例子中,只有当应用程序的配置文件中设置了 feature.enabled=true 时,才会创建 MyFeature Bean。
@Configuration
public class FeatureConfig {
@Bean
@ConditionalOnProperty(name = "feature.enabled", havingValue = "true")
public MyFeature myFeature() {
return new MyFeature();
}
}
3、@ComponentScan()
通过 @ComponentScan,开发者不再需要手动在 XML 或 Java 配置类中定义每个组件作为 bean。只要一个类被适当注解了(例如 @Component),并且位于扫描路径下,Spring 就会自动将其注册为容器中的 bean。
@Configuration
@ComponentScan(
basePackages = "com.example",
includeFilters = @ComponentScan.Filter(type = FilterType.ASSIGNABLE_TYPE, classes = MyInterface.class),
useDefaultFilters = false
)
public class AppConfig {
// ...
}
- 依赖注入注解
1、@Autowired
使用 @Autowired 注解,Spring 容器能够自动发现并注入所需的依赖项。这意味着你不需要显式地创建依赖对象的实例,而是让 Spring 来负责管理和提供这些依赖。
@Repository
public class MyRepositoryImpl implements MyRepository {
// Implementation...
}
@Service
public class MyService {
private final MyRepository myRepository;
// 即使没有 @Autowired 注解,Spring 也会自动注入 MyRepository 实现
public MyService(MyRepository myRepository) {
this.myRepository = myRepository;
}
// Methods...
}
如果一个类有多个构造函数,那么你需要至少在一个构造函数上使用 @Autowired 注解,以便告诉 Spring 哪个构造函数应该用于依赖注入。否则,Spring 不知道应该选择哪个构造函数来进行注入。
@Service
public class MyService {
private final MyRepository myRepository;
private final AnotherDependency anotherDependency;
// 主构造函数,使用 @Autowired 标记
@Autowired
public MyService(MyRepository myRepository, AnotherDependency anotherDependency) {
this.myRepository = myRepository;
this.anotherDependency = anotherDependency;
}
// 辅助构造函数,不会被 Spring 用来进行依赖注入
public MyService() {
this(null, null); // 或者其他逻辑
}
// Methods...
}
2、@Qualifier
用于在存在多个相同类型的 bean 时,明确指定要注入哪一个特定的 bean。它可以帮助解决当有多个候选 bean 时,Spring 容器无法确定应该选择哪个 bean 进行依赖注入的问题。
@Component("serviceImpl1")
public class MyServiceImpl1 implements MyService {
// Implementation...
}
@Component("serviceImpl2")
public class MyServiceImpl2 implements MyService {
// Implementation...
}
@Service
public class MyConsumer {
private final MyService myService;
@Autowired
public MyConsumer(@CustomQualifier("serviceImpl1") MyService myService) {
this.myService = myService;
}
// Methods...
}
3、@Resource
主要用于查找和注入资源,如 EJB、数据源等,并且默认情况下是基于名称匹配的。如果找不到指定名称的 bean,则会尝试根据类型进行匹配。
- 请求处理注解
1、@RestController
主要用于构建 RESTful Web 服务。它结合了 @Controller 和 @ResponseBody 注解的功能,使得标记了该注解的类可以自动将返回的对象序列化为 JSON 或 XML 格式,并直接写入 HTTP 响应体中。
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api")
public class MyRestController {
@Autowired
private MyService myService;
// GET 请求,获取资源列表
@GetMapping("/items")
public List<Item> getAllItems() {
return myService.getAllItems();
}
// POST 请求,创建新资源
@PostMapping("/items")
public Item createItem(@RequestBody Item newItem) {
return myService.createItem(newItem);
}
// PUT 请求,更新现有资源
@PutMapping("/items/{id}")
public Item updateItem(@PathVariable Long id, @RequestBody Item updatedItem) {
return myService.updateItem(id, updatedItem);
}
// DELETE 请求,删除资源
@DeleteMapping("/items/{id}")
public void deleteItem(@PathVariable Long id) {
myService.deleteItem(id);
}
}
2、@RequestParam
用于将 HTTP 请求中的查询参数(即 URL 中 ? 后面的部分)绑定到控制器方法的参数上。它使得从 HTTP 请求中提取和处理参数变得更加简单和直观。
@GetMapping("/greet")
public String greetUser(@RequestParam("name") String name) {
return "Hello, " + name + "!";
}
@GetMapping("/greet")
public String greetUser(@RequestParam(name = "name", required = false, defaultValue = "Guest") String name) {
return "Hello, " + name + "!";
}
@GetMapping("/search")
public List<Item> searchItems(@RequestParam("tags") String[] tags) {
// 处理 tags 数组...
return itemService.findByTags(tags);
}
@GetMapping("/query")
public String handleQueryParams(@RequestParam Map<String, String> allParams) {
// 处理 allParams map...
return "Received parameters: " + allParams;
}
@GetMapping("/search")
public List<Item> searchItems(@Valid @RequestParam SearchCriteria criteria, BindingResult result) {
if (result.hasErrors()) {
// Handle validation errors...
}
// Process valid criteria...
return itemService.search(criteria);
}
- 数据校验注解
1、@Valid
用于触发对方法参数或返回值的验证。
public class UserDTO {
@NotNull(message = "Name is required")
private String name;
@Email(message = "Email should be valid")
private String email;
@Min(value = 18, message = "Age must be at least 18")
private int age;
// getters and setters...
}
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/users")
public class UserController {
@PostMapping
public ResponseEntity<String> createUser(@Valid @RequestBody UserDTO user, BindingResult bindingResult) {
if (bindingResult.hasErrors()) {
return new ResponseEntity<>(bindingResult.getAllErrors().stream()
.map(DefaultMessageSourceResolvable::getDefaultMessage)
.collect(Collectors.joining(", ")), HttpStatus.BAD_REQUEST);
}
// 处理有效的用户数据...
return new ResponseEntity<>("User created successfully", HttpStatus.CREATED);
}
}
public interface CreateValidation {}
public interface UpdateValidation {}
public class UserDTO {
@NotNull(groups = CreateValidation.class, message = "Name is required for creation")
@Size(min = 1, max = 50, groups = {CreateValidation.class, UpdateValidation.class}, message = "Name size must be between 1 and 50")
private String name;
// 其他字段...
// getters and setters...
}
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/users")
public class UserController {
@PostMapping
public ResponseEntity<String> createUser(@Validated(CreateValidation.class) @RequestBody UserDTO user, BindingResult bindingResult) {
// 处理创建用户的逻辑...
}
@PutMapping("/{id}")
public ResponseEntity<String> updateUser(@PathVariable Long id, @Validated(UpdateValidation.class) @RequestBody UserDTO user, BindingResult bindingResult) {
// 处理更新用户的逻辑...
}
}
- 事务管理注解
1、@Transactional
用于管理声明式事务。它允许开发者以一种非侵入性的方式定义哪些方法应该参与事务管理,而不需要在代码中显式地编写事务处理逻辑(如开启事务、提交或回滚)。
@Service
public class UserService {
@Autowired
private UserRepository userRepository;
// 方法默认使用 REQUIRED 传播行为和默认隔离级别
@Transactional
public void createUser(User user) {
userRepository.save(user);
// 其他业务逻辑...
}
}
@Service
public class UserService {
@Autowired
private UserRepository userRepository;
@Transactional(
propagation = Propagation.REQUIRES_NEW, // 创建新的事务
isolation = Isolation.SERIALIZABLE, // 设置最高的隔离级别
readOnly = false, // 非只读事务
rollbackFor = {IllegalArgumentException.class} // 指定哪些异常会导致回滚
)
public void updateUser(User user) throws Exception {
if (user.getId() == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("User ID cannot be null");
}
userRepository.update(user);
// 其他业务逻辑...
}
}
- 条件注解
1、@ConditionalOnProperty
用于根据配置文件中的属性值决定是否应该创建某个 bean 或执行某些配置。它使得应用程序能够更加灵活地响应不同的环境或配置需求,例如在开发、测试和生产环境中启用或禁用特定的功能模块。
//只有当应用程序配置文件中存在名为 myfeature.enabled 的属性,并且其值为 "true" 时,MyFeatureConfiguration 类才会生效,进而创建并注册 MyFeatureService bean。如果 myfeature.enabled 不存在或其值不是 "true",那么 MyFeatureConfiguration 类及其内部定义的 bean 将不会被创建。
//atchIfMissing = false:如果配置文件中没有定义 myfeature.enabled 属性,则不匹配(即不会创建 bean)。如果设置为 true,则即使属性不存在也会创建 bean。
@Configuration
@ConditionalOnProperty(name = "myfeature.enabled", havingValue = "true", matchIfMissing = false)
public class MyFeatureConfiguration {
@Bean
public MyFeatureService myFeatureService() {
return new MyFeatureServiceImpl();
}
}
@Configuration
@ConditionalOnProperty({
@ConditionalOnProperty.Property(name = "service.a.enabled", havingValue = "true"),
@ConditionalOnProperty.Property(name = "service.b.enabled", havingValue = "false")
})
public class ConditionalConfiguration {
@Bean
public ComplexService complexService() {
return new ComplexServiceImpl();
}
}
@Configuration
@ConditionalOnProperty(name = "environment.type", regex = "^(dev|test)$")
public class DevelopmentOrTestConfig {
@Bean
public SpecialService specialService() {
return new SpecialServiceImpl();
}
}
- 异常处理注解
1、@ControllerAdvice 标记了一个类作为全局异常处理器。
2、@ExceptionHandler 注解用于定义具体的异常处理逻辑。
@ControllerAdvice
public class GlobalExceptionHandler {
// 处理所有未捕获的运行时异常
@ExceptionHandler(RuntimeException.class)
public ResponseEntity<ErrorResponse> handleRuntimeException(RuntimeException ex) {
ErrorResponse error = new ErrorResponse("INTERNAL_ERROR", "An internal error occurred: " + ex.getMessage());
return new ResponseEntity<>(error, HttpStatus.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR);
}
// 处理自定义异常
@ExceptionHandler(MyCustomException.class)
public ResponseEntity<ErrorResponse> handleMyCustomException(MyCustomException ex) {
ErrorResponse error = new ErrorResponse("CUSTOM_ERROR", ex.getMessage());
return new ResponseEntity<>(error, HttpStatus.BAD_REQUEST);
}
}
可以通过 basePackages 或 assignableTypes 属性来限制其作用范围:
@ControllerAdvice(basePackages = "com.example.web")
public class WebLayerGlobalExceptionHandler {
// 异常处理逻辑...
}



























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








