struts2框架中使用的表达式并不是EL表达式,不是不能用,而是struts2有自己的一套御用的表达式,名字就叫OGNL表达式,本章节就此表达式进行深入的学习,主要是针对OGNL表达式基础语法的Demo联系~
OGNL表达式基础语法Demo
1、OGNL表达式基础语法Demo
在做Demo演示时需要有一个对象,创建一个名为User的对象,其代码如下:
User.Java代码:
package com.java.bean;
// User
public class User {
private String name;
private Integer age;
public User() {
super();
}
public User(String name, Integer age) {
super();
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Integer getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(Integer age) {
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "User [name=" + name + ", age=" + age + "]";
}
}
1.1、Demo1:读取Root中的数据
其代码如下,大部分都是之前提到的代码准备工作,只有最后的getValue才是表达式的语法设置重点;
Demo1.class代码:
@Test
// 取root中的值 --- 既是:root_user中的值
public void Demo1() throws OgnlException {
// 准备ONGL的上下文
// 1、准备Root --- 将一个User对象放入到Root栈中
User root_user = new User("张三", 18);
// 2、准备context --- 将User对象以键值对的形式存入Context栈中
Map<String, User> context = new HashMap<String, User>();
context.put("User1", new User("jeck", 18));
context.put("User2", new User("rose", 22));
OgnlContext og = new OgnlContext();
og.setRoot(root_user);
og.setValues(context);
// 书写ONGL表达式,此表达式目的---取出root_user中的name、age的值
String name = (String) Ognl.getValue("name", og, og.getRoot());
Integer age = (Integer) Ognl.getValue("age", og, og.getRoot());
System.out.println(name + "," + age);
}
其代码junit后运行结果在控制台上显示如下:

注意:Demo1.class代码中的9、10行是没有用的,只是往context栈中存放一些数据,Demo1中并不使用context栈中的数据,只进行调用Root栈中 的数据,不要被迷惑了~
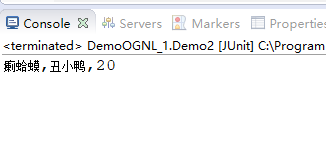
Demo2:读取Context中的数据
Demo2.class代码:
@Test
// 取context中的值
public void Demo2() throws OgnlException {
// 准备ONGL的上下文
// 1、准备Root
User root_user = new User("张三", 18);
// 2、准备context
Map<String, User> context = new HashMap<String, User>();
context.put("user1", new User("瘌蛤蟆", 24));
context.put("user2", new User("丑小鸭", 20));
OgnlContext og = new OgnlContext();
og.setRoot(root_user);
og.setValues(context);
// 书写ONGL:取出context中键为user1、user2的name、age
/*
* 释:
* 1、"#"代表的是从context中取值;
* 2、user1、user2是代表从context中的哪个对象来获取数据;
* 3、.name、.age代表的是取出哪个属性值;
*/
String name1 = (String) Ognl.getValue("#user1.name", og, og.getRoot());
String name2 = (String) Ognl.getValue("#user2.name", og, og.getRoot());
Integer age2 = (Integer) Ognl.getValue("#user2.age", og, og.getRoot());
System.out.println(name1 + "," + name2 + "," + age2);
}
其代码junit后运行结果在控制台上显示如下:
Demo3:给Root、Context中的对象中的属性赋值
Demo3.class代码:
// 为Root、context对象中的属性赋值
@Test
public void Demo3() throws OgnlException {
// 准备ONGL的上下文
// 准备Root
User root_user = new User("张三", 18);
// 准备context
Map<String, User> context = new HashMap<String, User>();
context.put("user1", new User("癞蛤蟆", 24));
context.put("user2", new User("丑小鸭", 20));
OgnlContext og = new OgnlContext();
og.setRoot(root_user);
og.setValues(context);
// 给root_user中的name属性赋值
Ognl.getValue("name='李四'", context, og.getRoot());
String name = (String) Ognl.getValue("name", context, og.getRoot());
System.out.println(name);
// 给context中的user对象的属性赋值;
// 此中用到了语法的串联,是用逗号隔开,但是要注意,多个输出语法串联后只会输出最后一个语法的值,复制、修改等操作无所谓;
// 这段语法意思是赋值给user1的name属性值为”青蛙王子“,并将user1的name值输出;
String name2 = (String) Ognl.getValue("#user1.name='青蛙王子',#user1.name", context, og.getRoot());
System.out.println(name2);
}
其代码junit后运行结果在控制台上显示如下:

Demo4:使用对象中的方法给Root、Context对象中的属性赋值
Demo4.class代码:
// 调用静态方法
@Test
public void Demo4() throws OgnlException {
// 准备ONGL的上下文
// 准备Root
User root_user = new User("张三", 18);
// 准备context
Map<String, User> context = new HashMap<String, User>();
context.put("user1", new User("癞蛤蟆", 24));
context.put("user2", new User("丑小鸭", 20));
OgnlContext og = new OgnlContext();
og.setRoot(root_user);
og.setValues(context);
// 使用方法,给root_user的name属性赋值并获取name属性值
/*
* 释:
* 1、”@“代表、声明使用哪个路径、方法名、属性等;
* 2、 一般在第一个”@“后边写调用的静态方法的全路径,在第二个”@“后边写调用的方法名或者属性
* 3、 如果第一个”@“后没有写全路径,直接在第二个”@“后写属性,则ognl会直接从math方法中开始寻找第二个”@“的属性
*/
String name = (String) Ognl.getValue("@com.java.action.Echo@echo('白雪公主')", context, og.getRoot());
//pi1和pi2的输出是一样的,由于PI这个属性是在Math方法中的,而ognl在第一个”@“后不跟全路径默认从Math方法中查找的,因此PI属性的全路径可以省略
Double pi1 = (Double) Ognl.getValue("@java.lang.Math@PI", context, og.getRoot());
Double pi2 = (Double) Ognl.getValue("@@PI", context, og.getRoot());
System.out.println(name+","+pi1+","+pi2);
}
注意:
1、输出白雪公主的那行代码中,第一个@后跟的是静态方法Echo的全路径
2、@java.lang.Math@PI代码是调用struts2中的lang文件夹下的已经封装好的Math.class类的PI方法,这个方法其实就是一个类似的常数π,不必为此纠结~
`
- 被调用的静态方法:
Echo.class 代码:
//静态方法Echo:
public class Echo {
//这是一个回声函数,即是传递过来什么值就会返回去什么值~
public static Object echo(Object ob){
return ob;
}
}
其代码junit后运行结果在控制台上显示如下:

Demo5:使用OGNL创建List、Map集合对象
Demo5.class代码:
Demo代码:
// OGNL创建对象 --- 创建 list/map 集合对象
@Test
public void Demo6() throws OgnlException {
// 准备ONGL的上下文
// 准备Root
User root_user = new User("张三", 18);
// 准备context
Map<String, User> context = new HashMap<String, User>();
context.put("user1", new User("癞蛤蟆", 24));
context.put("user2", new User("丑小鸭", 20));
OgnlContext og = new OgnlContext();
og.setRoot(root_user);
og.setValues(context);
// OGNL创建List/Map集合对象
// 创建List集合对象 --- 在getValue()中第一个参数使用“{}”代表要创建一个List集合对象 ;
Integer list_size = (Integer) Ognl.getValue("{'AA','BB','CC','DD','EE'}.size()", og, og.getRoot());
String list_value1 = (String) Ognl.getValue("{'AA','BB','CC','DD','EE'}[0]", og, og.getRoot());
String list_value2 = (String) Ognl.getValue("{'AA','BB','CC','DD','EE'}.get(1)", og, og.getRoot());
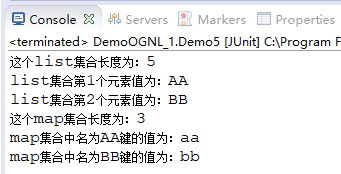
System.out.println("这个list集合长度为:"+list_size);
System.out.println("list集合第1个元素值为:"+list_value1);
System.out.println("list集合第2个元素值为:"+list_value2);
// 创建Map集合对象 --- 在getValue()中第一个参数使用“#{}”代表要创建一个Map集合对象 ;
Integer map_size = (Integer) Ognl.getValue("#{'AA':'aa','BB':'bb','CC':'cc'}.size()", og, og.getRoot());
String map_value1 = (String) Ognl.getValue("#{'AA':'aa','BB':'bb','CC':'cc'}['AA']", og, og.getRoot());
String map_value2 = (String) Ognl.getValue("#{'AA':'aa','BB':'bb','CC':'cc'}.get('BB')", og, og.getRoot());
System.out.println("这个map集合长度为:"+map_size);
System.out.println("map集合中名为AA键的值为:"+map_value1);
System.out.println("map集合中名为BB键的值为:"+map_value2);
}
其代码junit后运行结果在控制台上显示如下:
pass:代码中注释已经很清晰明了了,因此就不没在文中多加解释代码的含义等~
pass:pass:OGNL表达式的初步介绍链接如下:
什么是OGNL表达式: https://blog.csdn.net/qq_40762011/article/details/84987926








 本文通过一系列的Demo展示了OGNL(Object-Graph Navigation Language)表达式在Struts2框架中的应用,包括读取Root和Context中的数据、对象属性赋值、调用方法以及创建List和Map集合对象。每个Demo都附带了运行结果,帮助读者理解OGNL的基本语法和用法。
本文通过一系列的Demo展示了OGNL(Object-Graph Navigation Language)表达式在Struts2框架中的应用,包括读取Root和Context中的数据、对象属性赋值、调用方法以及创建List和Map集合对象。每个Demo都附带了运行结果,帮助读者理解OGNL的基本语法和用法。


















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










