#%%
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import cv2 as cv
import numpy as np
from imutils import contours
#%%
# 读取一个模板图像
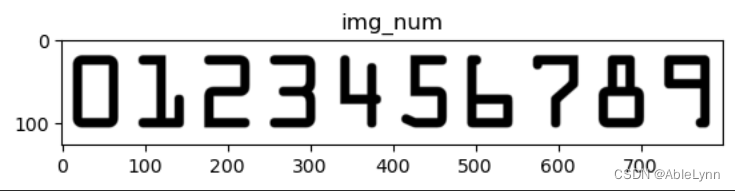
img_num = cv.imread("...") # 数字模板图像地址
plt.imshow(img_num)
plt.title("img_num")
#%%
# 灰度图
img_num_gray = cv.cvtColor(img_num, cv.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
plt.imshow(img_num_gray, cmap="gray")
plt.title("img_num_gray")
#%%
# 二值图像
img_num_thresh = cv.threshold(img_num_gray, 10, 255, cv.THRESH_BINARY_INV)[1]
plt.imshow(img_num_thresh, cmap="gray")
plt.title("img_num_thresh")
#%%
# 计算轮廓
# cv2.findContours()函数接受的参数为二值图,即黑白的(不是灰度图),cv2.RETR_EXTERNAL只检测外轮廓,cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE只保留终点坐标
# 返回的list中每个元素都是图像中的一个轮廓
img_num_conts, hierarchy= cv.findContours(img_num_thresh.copy(), cv.RETR_EXTERNAL, cv.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)
img_num_copy = cv.drawContours(img_num.copy(), img_num_conts, -1, (0,0,255), 2)
plt.imshow(img_num_copy[:,:,::-1])
plt.title("")
img_num_conts = contours.sort_contours(img_num_conts, method="left-to-right")[0] #排序,从左到右,从上到下
#%%
digits = {}
# 遍历每一个轮廓
for(i,c) in enumerate(img_num_conts):
(x,y,w,h) = cv.boundingRect(c)
roi = img_num_thresh[y:y + h, x:x + w]
roi = cv.resize(roi, (57, 88)) # 对每一个数字图像进行缩放 注意 要与后面识别时的缩放大小相同
# 每一个数字对应每一个模板
digits[i] = roi
print(digits)
#%%
# 初始化卷积核
rectKernel = np.ones((3,9), np.uint8)
sqKernel = np.ones((5,5), np.uint8)
#%%
# 读取输入图像
img_card = cv.imread("...") # 识别图像地址
plt.imshow(img_card[:,:,::-1])
plt.title("img_card")
#%%
# 缩放
(h, w) = img_card.shape[:2]
img_card = cv.resize(img_card, (300, int(h * 300 / float(w))), interpolation=cv.INTER_AREA)
plt.imshow(img_card[:,:,::-1])
print(img_card.shape)
plt.title("img_card")
#%%
# 灰度化
img_card_gray = cv.cvtColor(img_card, cv.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
plt.imshow(img_card_gray, cmap="gray")
plt.title("img_card_gray")
#%%
# 礼帽操作,突出高亮部分
img_card_tophat = cv.morphologyEx(img_card_gray, cv.MORPH_TOPHAT, rectKernel)
plt.imshow(img_card_tophat, cmap="gray")
plt.title("img_card_tophat")
#%%
# 梯度运算
gradX = cv.Sobel(img_card_tophat, cv.CV_32F, 1, 0, -1)
gradX = cv.convertScaleAbs(gradX)
gradY = cv.Sobel(img_card_tophat, cv.CV_32F, 0, 1, -1)
gradY = cv.convertScaleAbs(gradY)
grad = cv.addWeighted(gradX, 0.5, gradY, 0.5, 0)
plt.imshow(grad, cmap="gray")
plt.title("gray")
#%%
# 通过闭操作,是数字连接到一起
img_card_close = cv.morphologyEx(grad, cv.MORPH_CLOSE, rectKernel)
plt.imshow(img_card_close, cmap="gray")
plt.title("img_card_close")
#%%
# 阈值操作(二值化)
img_card_thresh = cv.threshold(img_card_close, 0, 255, cv.THRESH_BINARY|cv.THRESH_OTSU)[1]
plt.imshow(img_card_thresh, cmap="gray")
plt.title("img_card_thresh")
#%%
# 通过闭操作,是数字连接到一起
img_card_close1 = cv.morphologyEx(img_card_thresh, cv.MORPH_CLOSE, rectKernel)
plt.imshow(img_card_close1, cmap="gray")
plt.title("img_card_close1")
#%%
# 轮廓运算
img_card_conts, hierarchy = cv.findContours(img_card_close1.copy(), cv.RETR_EXTERNAL, cv.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)
img_card_copy_conts = cv.drawContours(img_card.copy(), img_card_conts, -1, (0,0,255), 3)
plt.imshow(img_card_copy_conts[:,:,::-1])
plt.title("img_card_copy_conts")
#%%
locs = []
# 遍历轮廓
for (i, c) in enumerate(img_card_conts):
# 计算矩形
(x, y, w, h) = cv.boundingRect(c)
ar = w / float(h)
# 选择合适的区域,根据实际任务来,这里的基本都是四个数字一组
if ar > 2.5 and ar < 4.0:
if (w > 40 and w < 55) and (h > 10 and h < 20):
#符合的留下来
locs.append((x, y, w, h))
#%%
for locs_old in locs:
print(locs_old)
#%%
# 将符合的轮廓从左到右排序
locs = sorted(locs, key=lambda x: x[0])
for locs_new in locs:
print(locs_new)
#%%
fig, axes = plt.subplots(nrows=4, ncols=5, figsize=(30,10), dpi=100)
# 遍历每一个轮廓中的数字
for (i, (gX, gY, gW, gH)) in enumerate(locs):
groupOutput = []
# 根据坐标提取每一个组
group = img_card_gray[gY - 5:gY + gH + 5, gX - 5:gX + gW + 5]
axes[i][0].imshow(group, cmap="gray")
axes[i][0].set_title(f"group{i}")
# 预处理 二值化
group = cv.threshold(group, 0, 255, cv.THRESH_BINARY | cv.THRESH_OTSU)[1]
# 计算每一组的轮廓
digit_conts, hierarchy = cv.findContours(group.copy(), cv.RETR_EXTERNAL, cv.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)
digit_conts = contours.sort_contours(digit_conts, method="left-to-right")[0]
# 计算每一组中的每一个数值
for (digit_index, c) in enumerate(digit_conts,1):
# 找到当前数值的轮廓,resize成合适的的大小
(x, y, w, h) = cv.boundingRect(c)
roi = group[y:y + h, x:x + w]
roi = cv.resize(roi, (57, 88)) # 每个数字图像缩放,注意要和前面模板数字图像缩放大小相同
axes[i][digit_index].imshow(roi, cmap="gray")
axes[i][digit_index].set_title("roi")
# 计算匹配得分
scores = []
# 在模板中计算每一个得分
for (digit, digitROI) in digits.items():
# 模板匹配
result = cv.matchTemplate(roi, digitROI, cv.TM_CCOEFF)
(_, score, _, _) = cv.minMaxLoc(result)
scores.append(score)
# 得到最合适的数字
groupOutput.append(str(np.argmax(scores)))
# 画出来
cv.rectangle(img_card, (gX - 5, gY - 5),
(gX + gW + 5, gY + gH + 5), (0, 0, 255), 1)
cv.putText(img_card, "".join(groupOutput), (gX, gY - 15),
cv.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.65, (0, 0, 255), 2)
#%%
plt.imshow(img_card[:,:,::-1])
数字模板图像:
输入识别图像:

最终识别结果:























 2678
2678











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








