前言:什么是全排列?
引用百度百科的词条:
从n个不同元素中任取m(m≤n)个元素,按照一定的顺序排列起来,叫做从n个不同元素中取出m个元素的一个排列。当 m = n m=n m=n 时所有的排列情况叫全排列。
公式:全排列数 f(n) = n! (定义0!=1)
即实现所有可能的排列结果,例如实现{1,2,3}的全排列为:
1 2 3
1 3 2
2 1 3
2 3 1
3 1 2
3 2 1
一、递归实现
首先我们介绍一种递归的全排列方法:
其基本思想是:我们首先固定一个元素,将之后的元素在进行全排列,这样我们就可以递归调用函数,在固定第二个元素,后面元素在进行全排列,直到固定住最后一个元素,即为终止条件。
综上所述,递归调用的全排列就是从第一个数字起每个数分别与它后面的数字交换。

对于上图的第三步,如果我们不还原原来的位置,就会出现如下的问题:
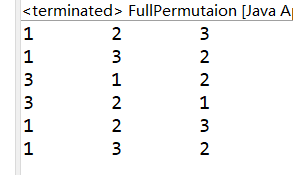
显而易见,原因就在于我们由于在交换过程中改变了数字的顺序,而固定元素位置的指向,只是指示位置而非元素,所以就导致了有些元素被重复固定,这就需要我们每次交换完位置后,需要恢复原来的排列顺序,以便下一次排列交换。
代码示例:
JAVA 实现
package Permutation;
/**
* @Description Full Permutation Algorithm
* @author zhuwei
* @Email zhu_wei2019@163.com
* @version v1.0
*/
public class FullPermutaion {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] nums = {1,2,3};
FullPermutaion obj = new FullPermutaion();
obj.fullpermutaion(nums, 0, 2);
}
/*
* full permutation
* p : the start of the number which is need to permutation;
* q : the end of the number which is need to permutation;
*/
public void fullpermutaion(int[] nums, int p, int q) {
if(p == q) { // means all the number is permuted;
printChar(nums);
}
else {
//we fix a number of char ,then the rest number in the char need to permutation;
for(int i = p; i<=q; i++) {
swap(nums, p, i);
fullpermutaion(nums, p+1, q);
swap(nums, p, i); // to keep the order of nums unchanged
}
}
}
//swap two numbers
public void swap(int[] nums, int j ,int k) {
int temp = nums[j];
nums[j] = nums[k];
nums[k] = temp;
}
// print the number in the char
public void printChar(int[] nums) {
for(int i = 0; i<nums.length; i++) {
System.out.print(nums[i] + "\t");
}
System.out.println();
}
}

C++ 实现:
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
void swap(vector<int> &nums, int j, int k) {
int temp = nums[j];
nums[j] = nums[k];
nums[k] = temp;
}
void printNums(vector<int> nums) {
for (int i : nums) {
cout << i << "\t";
}
cout << endl;
}
void permutation(vector<int> & nums, int p, int q) {
if (p == q) {
printNums(nums);
}
else {
for (int i = p; i < q+1; i++) {
swap(nums, p, i);
permutation(nums, p + 1, q);
swap(nums, p, i);
}
}
}
void main() {
vector<int> nums;
nums.push_back(1);
nums.push_back(2);
nums.push_back(3);
permutation(nums, 0, 2);
system("pause");
}
以上的递归有个问题就是如果出现重的元素时,排列的结果会有重复的现象。
例如 ,nums[3]= {1,3,3} 的排列结果如下:
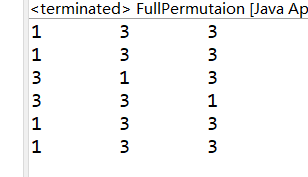
解决以上的问题,我们可以依次循环比较开始交换的位置到交换的前一个位置,是否有元素和当前交换位置重复的数,如果有则不进行交换。
即就是从第一个数字起每个数分别与它后面非重复出现的数字交换。
增加以下的判断方法:
//isSwap
private boolean isSwap(int[] nums, int p, int i) {
for(; p<i; p++) {
if(nums[p] == nums[i]) return false;
}
return true;
}
完整的JAVA代码为:
package Permutation;
/**
* @Description Full Permutation Algorithm
* @author zhuwei
* @Email zhu_wei2019@163.com
* @version v1.0
*/
public class FullPermutaion {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] nums = {1,2,2};
FullPermutaion obj = new FullPermutaion();
obj.fullpermutaion(nums, 0, 2);
}
/*
* full permutation
* p : the start of the number which is need to permutation;
* q : the end of the number which is need to permutation;
*/
public void fullpermutaion(int[] nums, int p, int q) {
if(p == q) { // means all the number is permuted;
printChar(nums);
}
else {
//we fix a number of char ,then the rest number in the char need to permutation;
for(int i = p; i<=q; i++) {
if(isSwap(nums, p, i)) {
swap(nums, p, i);
fullpermutaion(nums, p+1, q);
swap(nums, p, i); // to keep the order of nums unchanged
}
}
}
}
//swap two numbers
public void swap(int[] nums, int j ,int k) {
int temp = nums[j];
nums[j] = nums[k];
nums[k] = temp;
}
// print the number in the char
public void printChar(int[] nums) {
for(int i = 0; i<nums.length; i++) {
System.out.print(nums[i] + "\t");
}
System.out.println();
}
//isSwap
private boolean isSwap(int[] nums, int p, int i) {
for(; p<i; p++) {
if(nums[p] == nums[i]) return false;
}
return true;
}
}
结果:

二、非递归实现
我们知道递归是靠栈实现,这就可能导致栈溢出以及运算时间的问题,为了解决以上问题,我们提出一种非递归的全排列方法,且这种方法可以自动排出掉重复的排列方式。
这种方法的前提要求我们需要对数组进行排序,我们可以使用JAVA Array.sort() 方法或者 C++ STL 中的 sort() 算法解决。
非递归实现的思想就在于,我们先从最小的排序开始,依次寻找比当前排序大的最小排序,实现该方法的关键就在于寻找交换点和交换数。
我们将这种方法分为四步解决,如下,我们以nuns为例,nums[3] = {1,2,3}:

实现代码:
JAVA :
package Permutation;
public class Nonrecursion {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] nums = {3,2,1};
new Nonrecursion().nextPermutaion(nums);
}
public void nextPermutaion(int nums[]) {
int index = 0; //交换点下标
int swapNums = 0;
while(true) {
for(int i = 0; i<nums.length; i++) System.out.print(nums[i]+"\t");
System.out.println();
// Firstly, we need to find the swap point (index)
// 从右向左,循环比较相邻的两个数,找到第一个非递增的数,即为交换点(index)
for(int i = nums.length-2 ; i>=0; i--) {
if(nums[i] < nums[i+1]) {
index = i;
break;
}
if(i == 0) return; //没有找到需要交换的点,即交换全部完成,退出循环
}
// Secondly, we need to find swap number
// 从右向左找第一个比交换点所在的数大的数, 该数即为需要和交换点交换的数
for(int j = nums.length-1; j >= 0; j--) {
if(nums[index] < nums[j]) {
swapNums = j;
break;
}
}
// Thirdly, swap the two numbers
swap(nums, index, swapNums);
//Fourthly, put the numbers after index in positive order
//目的在于保证当前排序是比上一个排序大的最小的一个排序
reverse(nums, index+1);
}
}
//交换两个元素
public void swap(int[] nums, int index, int j) {
int temp = nums[index];
nums[index] = nums[j];
nums[j] = temp;
}
//将 index 后的数正序排序,这样就使得这种排序是当前情况下最小的
private void reverse(int[] nums, int i) {
int j = nums.length - 1;
while(i<j) {
swap(nums, i, j);
i++;
j--;
// swap(nums, i++, j--);
}
}
}
C++:
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
//交换两个元素
void swap(vector <int> & nums, int index, int j) {
int temp = nums[index];
nums[index] = nums[j];
nums[j] = temp;
}
//将 index 后的数正序排序,这样就使得这种排序是当前情况下最小的
void reverse(vector <int> & nums, int i) {
int j = nums.size() - 1;
while (i<j) {
swap(nums, i, j);
i++;
j--;
// swap(nums, i++, j--);
}
}
void nextPermutaion(vector <int> nums) {
int index = 0; //交换点下标
int swapNums = 0;
while (true) {
for (int i : nums) cout << i << "\t";
cout << endl;
for (int i = nums.size() - 2; i >= 0; i--) {
if (nums[i] < nums[i + 1]) {
index = i;
break;
}
if (i == 0) return; //没有找到需要交换的点,即交换全部完成,退出循环
}
for (int j = nums.size() - 1; j >= 0; j--) {
if (nums[index] < nums[j]) {
swapNums = j;
break;
}
}
swap(nums, index, swapNums);
reverse(nums, index + 1);
}
}
void main() {
vector <int> nums;
nums.push_back(1);
nums.push_back(2);
nums.push_back(3);
nums.push_back(4);
nextPermutaion(nums);
system("pause");
}
至此我们已经运用了递归与非递归的方法解决了全排列问题,总结一下就是:
1.全排列就是从第一个数字起每个数分别与它后面的数字交换。
2.去重的全排列就是从第一个数字起每个数分别与它后面非重复出现的数字交换。
3.全排列的非递归就是由后向前找替换数和替换点,然后由后向前找第一个比替换数大的数与替换数交换,最后颠倒替换点后的所有数据。






















 748
748











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








