C++语言允许程序员重新定义已有的运算符,使其能够按用户的要求完成一些特定的操作,这就是运算符重载。经重载后的运算符重载。经重载后的运算符能够直接对用户自定义的数据进行操作运算。本章介绍有运算符重载方面的内容。
C++语言为实现运算符重载提供了一种方法,即将运算符看作一种特殊类型的函数,运算符重载是通过对运算符的重载实现的。运算符函数名由关键字operator和重载的运算符组成。
重载运算符的函数一般格式如下:
函数类型 operator 运算符(形参列表)
{运算符重载处理}
重载运算符要遵循的规则:
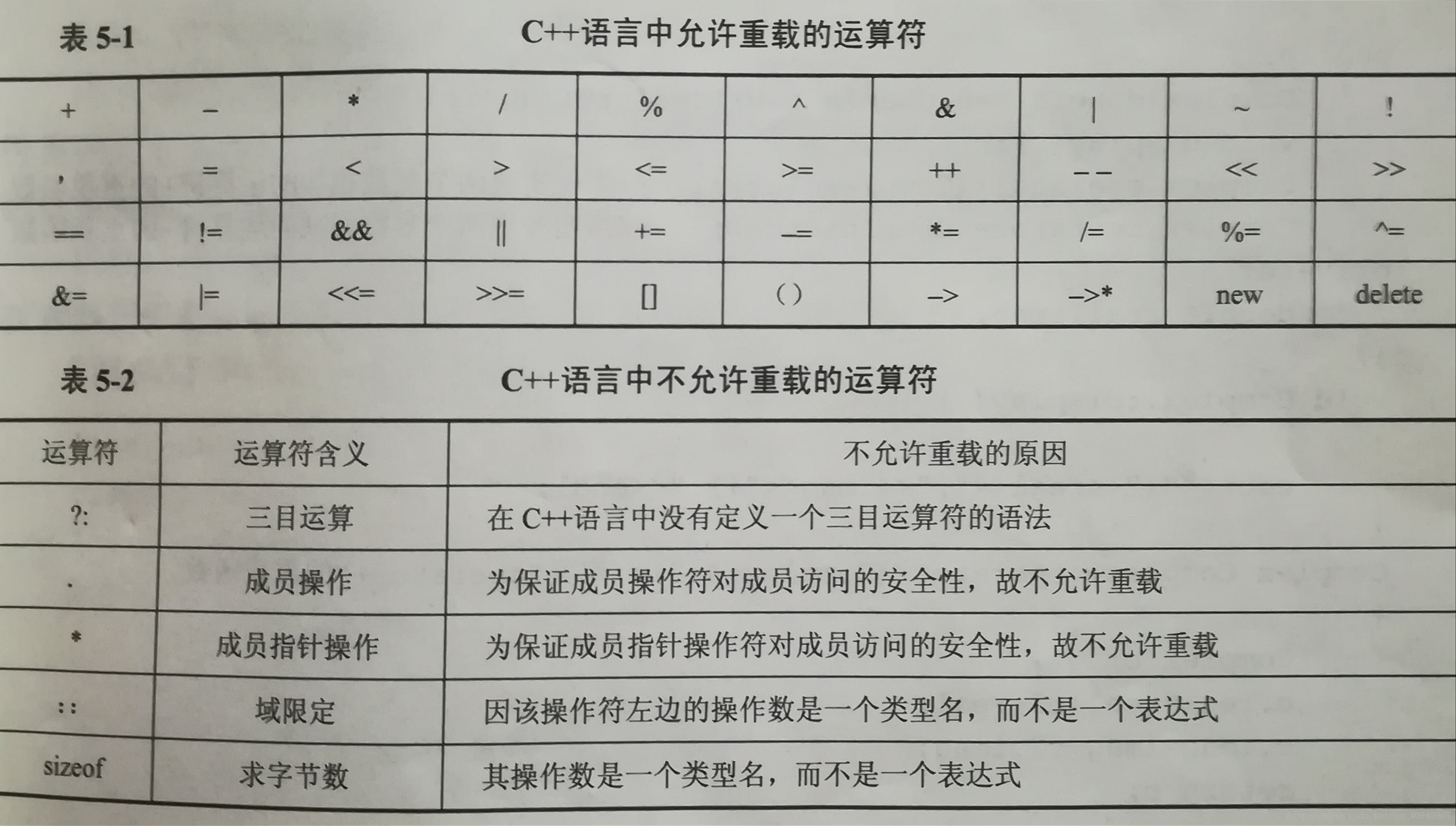
1、C++语言允许重载的运算符表见表5-1,不允许重载的运算符见表5-2。
2、运算符重载是针对新类型数据的实际需要,对原有运算符的运算进行适当的改造。一般来说,重载的功能应与原有功能类似。
3、重载之后,运算符的优先级和结核性都不改变。
4、重载运算符的函数不能有默认的参数。
5、重载时,运算符的操作数个数保持不变,即双目运算符任然是双目运算符,单目运算符任然是单目运算符。
6、重载的运算符至少有一个操作数是自定义类的对象。对于双目运算符,左操作数要求一定是自定义的对象,右操作数可以实对象,也可以是整数、实数等基本数据。
7、运算符重载函数可以使类的成员函数,也可以是类的友元函数,还可以是普通函数。
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Complex
{
public:
friend Complex operator-(Complex &c1, Complex &c2);//通过友元函数实现-法
friend Complex operator--(Complex &c);//通过友元函数实现前置--
friend ostream &operator<<(ostream &out, Complex &c);//只能通过友元函数实现流插入运算符,且必须返回引用
Complex(double r = 0, double i = 0)
{
real = r;
imag = i;
}
Complex operator+(Complex &c2);//通过成员函数实现+法
Complex operator++(int);//通过成员函数实现后置++
bool operator==(Complex &c2);//通过成员函数实现关系运算符==
Complex operator=(int i);//通过成员函数实现赋值运算符=
Complex operator[](int i);//通过成员函数实现下标运算符[]
void display();
private:
double real;
double imag;
};
Complex Complex::operator+(Complex &c2)
{
Complex c;
c.real = real + c2.real;
c.imag = imag + c2.imag;
return c;
}
void Complex::display()
{
cout << real << " + " << imag << "i" << endl;
}
Complex operator-(Complex &c1, Complex &c2)
{
Complex c;
c.real = c1.real - c2.real;
c.imag = c1.imag - c2.imag;
return c;
}
Complex Complex::operator++(int)//后置++
{
Complex tmp(this->real, this->imag);
this->real++;
this->imag++;
return tmp;
}
Complex operator--(Complex &c)//前置--
{
--c.real;
--c.imag;
return c;
}
ostream &operator<<(ostream &out, Complex &c)//流插入运算符
{
out << c.real << " + " << c.imag << "i";
return out;
}
bool Complex::operator==(Complex &c2)
{
return (this->real == c2.real && this->imag == c2.imag);
}
Complex Complex::operator=(int i)
{
this->real = i;
this->imag = i;
return *this;
}
Complex Complex::operator[](int i)
{
this->real = i;
this->imag = i;
return *this;
}
int main()
{
Complex a(1, 2), b(3, 4), c, d;
Complex A[5];
c = a + b;
d = a - b;
cout << "c = ";
c.display();
cout << "d = ";
d.display();
d++;
cout << "d = ";
d.display();
--d;
cout << "d = ";
d.display();
cout << d << endl;
if (c == d)
{
printf("c == d\n");
}
else
{
printf("c != d\n");
}
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++)//期望让A数组中的实部与虚部值都为i
{
A[i] = i;
cout << A[i] << endl;
}
return 0;
}






















 3109
3109

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










