| 03-19 | 《剑指offer第2版》Java题解总结(上)_科技小猎豹的博客-CSDN博客 |
| 20-39 | |
| 40-68 | 《剑指offer第2版》Java题解总结(下)-CSDN博客 |
20-39
20. 表示数值的字符串
力扣大佬用有限自动机,Java用map存。以下为常规做法。
class Solution {
public boolean isNumber(String s) {
if(s == null || s.length() == 0) return false; // s为空对象或 s长度为0(空字符串)时, 不能表示数值
boolean isNum = false, isDot = false, ise_or_E = false; // 标记是否遇到数位、小数点、‘e’或'E'
char[] str = s.trim().toCharArray(); // 删除字符串头尾的空格,转为字符数组,方便遍历判断每个字符
for(int i=0; i<str.length; i++) {
if(str[i] >= '0' && str[i] <= '9') isNum = true; // 判断当前字符是否为 0~9 的数位
else if(str[i] == '.') { // 遇到小数点
if(isDot || ise_or_E) return false; // 小数点之前可以没有整数,但是不能重复出现小数点、或出现‘e’、'E'
isDot = true; // 标记已经遇到小数点
}
else if(str[i] == 'e' || str[i] == 'E') { // 遇到‘e’或'E'
if(!isNum || ise_or_E) return false; // ‘e’或'E'前面必须有整数,且前面不能重复出现‘e’或'E'
ise_or_E = true; // 标记已经遇到‘e’或'E'
isNum = false; // 重置isNum,因为‘e’或'E'之后也必须接上整数,防止出现 123e或者123e+的非法情况
}
else if(str[i] == '-' ||str[i] == '+') {
if(i!=0 && str[i-1] != 'e' && str[i-1] != 'E') return false; // 正负号只可能出现在第一个位置,或者出现在‘e’或'E'的后面一个位置
}
else return false; // 其它情况均为不合法字符
}
return isNum;
}
}21.调整数组顺序是奇数位于偶数前面
首位指针。(x&1 位运算 等价于 x \% 2x%2 取余运算,即皆可用于判断数字奇偶性。)
块慢指针只是写起来更简洁,实际上交换的次数总是大于等于首尾指针,因为快慢指针把奇数跟奇数也交换了。 快慢指针性能更差。
22. 链表中倒数第 k 个节点
力扣快慢指针不必先遍历链表长度去走n-k。
23.
24.反转链表
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
ListNode cur = head, pre = null;
while(cur != null) {
ListNode tmp = cur.next; // 暂存后继节点 cur.next
cur.next = pre; // 修改 next 引用指向
pre = cur; // pre 暂存 cur
cur = tmp; // cur 访问下一节点
}
return pre;
}
25.合并两个排序的链表
与主站 21 题相同:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/merge-two-sorted-lists/
迭代:O(M+N),O(1).
递归空间复杂度:O(n+m),递归调用 mergeTwoLists 函数时需要消耗栈空间,栈空间的大小取决于递归调用的深度。结束递归调用时 mergeTwoLists 函数最多调用 n+mn+m 次,因此空间复杂度为 O(n+m)。
26.树的子结构(先序遍历
27.二叉树的镜像
与主站 226 题相同:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/invert-binary-tree/
方法一:递归法力扣
根据二叉树镜像的定义,考虑递归遍历(dfs)二叉树,交换每个节点的左 / 右子节点,即可生成二叉树的镜像。
public TreeNode mirrorTree(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null) return null;
TreeNode tmp = root.left;
root.left = mirrorTree(root.right);
root.right = mirrorTree(tmp);
return root;
}
28.对称的二叉树
与主站 101 题相同:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/symmetric-tree/
class Solution {
public boolean isSymmetric(TreeNode root) {
return root == null ? true : recur(root.left, root.right);
}
boolean recur(TreeNode L, TreeNode R) {
if(L == null && R == null) return true;
if(L == null || R == null || L.val != R.val) return false;
return recur(L.left, R.right) && recur(L.right, R.left);
}
}
29.顺时针打印矩阵(螺旋矩阵)
与主站 54 题相同:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/spiral-matrix/
30.包含 min 函数的栈
与主站 155 题相同:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/min-stack/
Java 代码中,由于 Stack 中存储的是 int 的包装类 Integer ,因此需要使用 equals() 代替 == 来比较值是否相等。
此题如果用==将会无法通过 Integer的equals重写过,比较的是内部value的值, ==如果在[-128,127]会被cache缓存,超过这个范围则比较的是对象是否相同
自动拆箱
public void pop() {
int x = stackA.pop();
if (x == stackB.peek()) {
stackB.pop();
}
}
class MinStack {
Stack<Integer> A, B;
public MinStack() {
A = new Stack<>();
B = new Stack<>();
}
public void push(int x) {
A.add(x);
if(B.empty() || B.peek() >= x)
B.add(x);
}
public void pop() {
if(A.pop().equals(B.peek()))
B.pop();
}
public int top() {
return A.peek();
}
public int min() {
return B.peek();
}
}31.栈的压入、弹出序列
与主站 946 题相同:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/validate-stack-sequences/
模拟
public boolean validateStackSequences(int[] pushed, int[] popped) {
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<>();
int i = 0;
for(int num : pushed) {
stack.push(num); // num 入栈
while(!stack.isEmpty() && stack.peek() == popped[i]) { // 循环判断与出栈
stack.pop();
i++;
}
}
return stack.isEmpty();
}
32 - I. 从上到下打印二叉树
层序遍历 BFS
复杂度分析:
时间复杂度 O(N) : N 为二叉树的节点数量,即 BFS 需循环 N 次。
空间复杂度 O(N): 最差情况下,即当树为平衡二叉树时,最多有 N/2个树节点同时在 queue 中,使用 O(N)大小的额外空间。
32 - II. 从上到下打印二叉树 II(层序遍历 BFS
32 - III. 从上到下打印二叉树之字形 III(层序遍历 BFS / 双端队列
利用双端队列的两端皆可添加元素的特性,设打印列表(双端队列) tmp ,并规定:
奇数层 则添加至 tmp 尾部 ,
偶数层 则添加至 tmp 头部 。方法三:层序遍历 + 倒序
此方法的优点是只用列表即可,无需其他数据结构。
偶数层倒序: 若 res 的长度为 奇数 ,说明当前是偶数层,则对 tmp 执行 倒序 操作。
复杂度分析:
时间复杂度 O(N) : NN 为二叉树的节点数量,即 BFS 需循环 NN 次,占用 O(N) 。共完成 少于 N个节点的倒序操作,占用O(N) 。
空间复杂度 O(N) : 最差情况下,即当树为满二叉树时,最多有 N/2个树节点同时在 queue 中,使用 O(N)大小的额外空间。
class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> levelOrder(TreeNode root) {
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();
if(root != null) queue.add(root);
while(!queue.isEmpty()) {
List<Integer> tmp = new ArrayList<>();
for(int i = queue.size(); i > 0; i--) {
TreeNode node = queue.poll();
tmp.add(node.val);
if(node.left != null) queue.add(node.left);
if(node.right != null) queue.add(node.right);
}
if(res.size() % 2 == 1) Collections.reverse(tmp);
res.add(tmp);
}
return res;
}
}33. 二叉搜索树的后序遍历序列
大佬分享单调栈巧妙解法力扣
34. 二叉树中和为某一值的路径
与主站 113 题相同:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/path-sum-ii/
本问题是典型的二叉树方案搜索问题,使用回溯法解决,其包含 先序遍历 + 路径记录 两部分。力扣
35. 复杂链表的复制中等
与主站 138 题相同:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/copy-list-with-random-pointer/
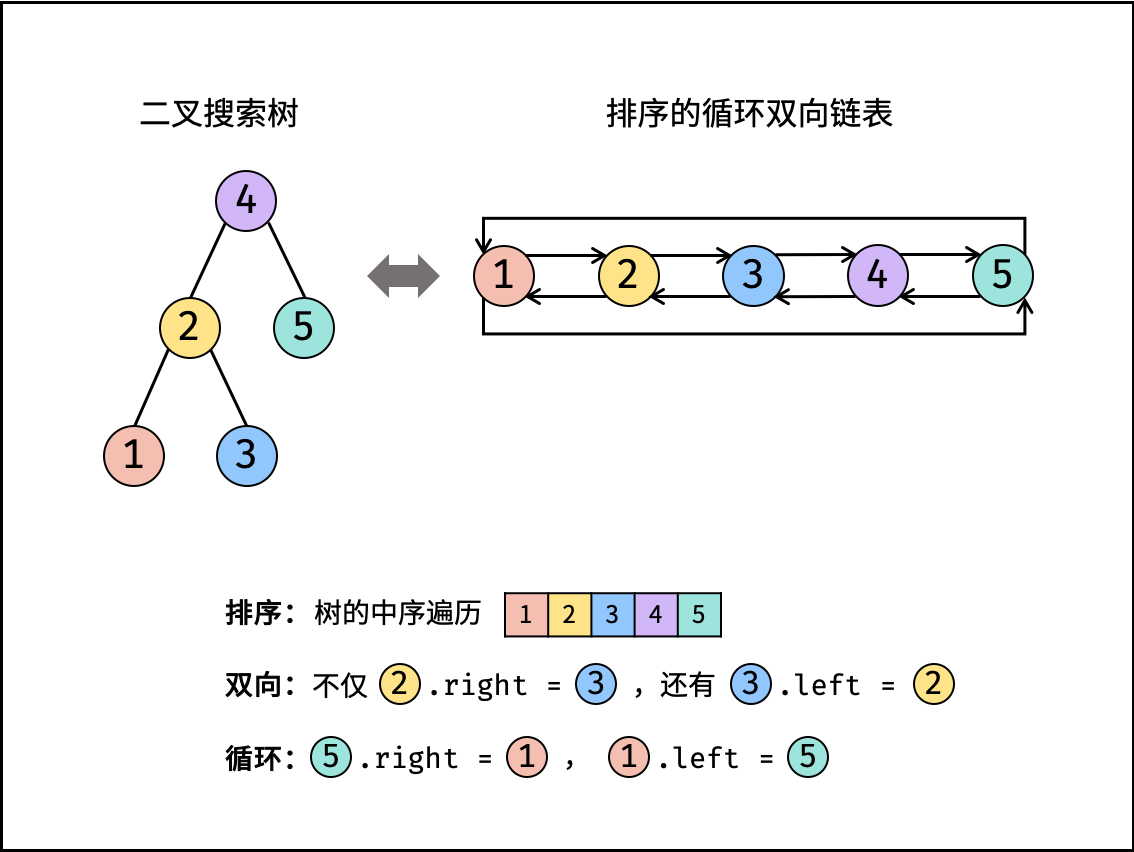
36. 二叉搜索树与双向链表
与主站 426 题相同,此题对比原题有改动。:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/convert-binary-search-tree-to-sorted-doubly-linked-list/
class Solution {
Node head, pre;
public Node treeToDoublyList(Node root) {
if(root==null) return null;
dfs(root);
pre.right = head;
head.left =pre;//进行头节点和尾节点的相互指向,这两句的顺序也是可以颠倒的
return head;
}
public void dfs(Node cur){
if(cur==null) return;
dfs(cur.left);
//pre用于记录双向链表中位于cur左侧的节点,即上一次迭代中的cur,当pre==null时,cur左侧没有节点,即此时cur为双向链表中的头节点
if(pre==null) head = cur;
//反之,pre!=null时,cur左侧存在节点pre,需要进行pre.right=cur的操作。
else pre.right = cur;
cur.left = pre;//pre是否为null对这句没有影响,且这句放在上面两句if else之前也是可以的。
pre = cur;//pre指向当前的cur
dfs(cur.right);//全部迭代完成后,pre指向双向链表中的尾节点
}
}
37.序列化二叉树困难
与主站 297 题相同:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/serialize-and-deserialize-binary-tree/
res.append(node.val + ","); 这个点可以优化成 res.append(node.val).append(",");。因为拼接字符串可能增大消耗。力扣层序遍历BFS
38. 字符串的排列
力扣set去重剪枝。回溯模板也可visited[]
39. 数组中出现次数超过一半的数字
与主站 169 题相同:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/majority-element/
本题常见的三种解法:力扣
哈希表统计法: 遍历数组 nums ,用 HashMap 统计各数字的数量,即可找出 众数 。此方法时间和空间复杂度均为 O(N) 。
数组排序法: 将数组 nums 排序,数组中点的元素 一定为众数。
摩尔投票法: 核心理念为 票数正负抵消 。此方法时间和空间复杂度分别为 O(N) 和 O(1),为本题的最佳解法。超过一半的数字等值运算符==优先级要高于赋值运算符+=
假设有一个擂台,有一组人,每个人有编号,相同编号为一组,依次上场,没人时上去的便是擂主(x),若有人,编号相同则继续站着(人数+1),若不同,假设每个人战斗力相同,都同归于尽,则人数-1;那么到最后站着的肯定是人数占绝对优势的那一组啦~
class Solution:
def majorityElement(self, nums: List[int]) -> int:
votes = 0
for num in nums://每一个人都要出来挑战
if votes == 0://擂台上没人 选一个出来当擂主 x就是擂主 votes就是人数
x = num
votes += 1 if num == x else -1//如果是自己人就站着呗 如果不是 就同归于尽
return x























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








