朴素版Dijkstra算法(
):适合于无负权边的稠密图,采用贪心思想
算法流程(使用邻接矩阵存边):一共进行次循环
,每次循环找出未确定最短距离的节点中到源点距离最短的节点,将该点存入集合(存已确定最短距离的点的集合)。并用该点更新其它点到源点的距离
。
AcWing 849. Dijkstra求最短路 I
给定一个 个点
条边的有向图,图中可能存在重边和自环,所有边权均为正值。
请你求出号点到
号点的最短距离,如果无法从
号点走到
号点,则输出
。
代码(Java)
import java.util.*;
class Main {
static int N = 510;
static int[][] g = new int[N][N];
static boolean[] st = new boolean[N];
static int[] dist = new int[N];
static int INF = (int)1e9;
static int n,m;
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
n = sc.nextInt();
m = sc.nextInt();
for(int i = 0;i < N;i++) {
Arrays.fill(g[i],INF);
}
while(m-- > 0) {
int a = sc.nextInt(),b = sc.nextInt(),c = sc.nextInt();
g[a][b] = Math.min(g[a][b],c);
}
dijkstra();
System.out.println(dist[n] == INF ? -1 : dist[n]);
}
static void dijkstra() {
Arrays.fill(dist,INF);
dist[1] = 0;
for(int i = 0;i < n;i++) {
int t = -1;
for(int j = 1;j <= n;j++) {
if(!st[j] && (t == -1 || dist[t] > dist[j])) {
t = j;
}
}
if(t == -1) continue;
st[t] = true;
for(int j = 1;j <= n;j++) {
dist[j] = Math.min(dist[j],dist[t] + g[t][j]);
}
}
}
}堆优化版Dijkstra算法(
):适合于无负权边的稀疏图,小根堆优化
算法流程(使用邻接表存图):使用小跟堆存节点以及节点到源点的距离,那么在朴素版Dijkstra算法中寻找未确定最短距离的节点中到源点距离最短的节点的时间复杂度就优化到,再利用该节点更新其它节点到源点的最短距离。
题目同上,只是边和节点数量级都在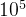 。
。
代码(Java)
import java.util.*;
class Main {
static int N = 150010;
static int[] h = new int[N];
static int[] ne = new int[N];
static int[] v = new int[N];
static int[] w = new int[N];
static int idx = 0;
static int INF = (int)1e9;
static int[] dist = new int[N];
static boolean[] st = new boolean[N];
static int n,m;
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
n = sc.nextInt();
m = sc.nextInt();
Arrays.fill(h,-1);
while(m-- > 0) {
int x = sc.nextInt(),y = sc.nextInt(),z = sc.nextInt();
add(x,y,z);
}
dijkstra();
System.out.println(dist[n] == INF ? -1 : dist[n]);
}
static void add(int a,int b,int c) {
v[idx] = b;
w[idx] = c;
ne[idx] = h[a];
h[a] = idx++;
}
static void dijkstra() {
Arrays.fill(dist,INF);
dist[1] = 0;
PriorityQueue<int[]> q = new PriorityQueue<int[]>(new Comparator<int[]>() {
public int compare(int[] a,int[] b) {
return a[0] - b[0];
}
});
q.offer(new int[]{0,1});
while(q.size() > 0) {
int[] x = q.poll();
int src = x[1],di = x[0];
if(st[src]) continue;
for(int i = h[src];i != -1;i = ne[i]) {
int tar = v[i];
if(dist[tar] > di + w[i]) {
dist[tar] = dist[src] + w[i];
q.offer(new int[]{dist[tar],tar});
}
}
st[src] = true;
}
}
}Bellman-Ford算法
:适合于有负权边且有边数限制的场景
算法流程(使用二维矩阵来存,第一维是边,第二维是边的信息:起始点,终止点,边权):两层循环,第一层循环是经过的边数,第二次循环是所有边,利用边来更新最短距离。
AcWing 853. 有边数限制的最短路
给定一个个点
条边的有向图,图中可能存在重边和自环, 边权可能为负数。
请你求出从号点到
号点的最多经过
条边的最短距离,如果无法从
号点走到
号点,输出
impossible。
注意:图中可能 存在负权回路 。
代码(Java)
import java.util.*;
class Main {
static int N = 510;
static int M = 10010;
static int[] dist = new int[N];
static int[][] edge = new int[M][3];
static int[] backup = new int[N];
static int n,m,k;
static int INF = (int)1e9;
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
n = sc.nextInt();
m = sc.nextInt();
k = sc.nextInt();
for(int i = 1;i <= m;i++) {
edge[i][0] = sc.nextInt();
edge[i][1] = sc.nextInt();
edge[i][2] = sc.nextInt();
}
bellman_ford();
System.out.println(dist[n] > INF/2 ? "impossible" : dist[n]);
}
public static void bellman_ford() {
Arrays.fill(dist,INF);
dist[1] = 0;
while(k-- > 0) {
backup = Arrays.copyOf(dist,n+1);
for(int i = 1;i <= m;i++) {
int src = edge[i][0],tar = edge[i][1],w = edge[i][2];
backup[tar] = Math.min(backup[tar],dist[src] + w);
}
dist = Arrays.copyOf(backup,n+1);
}
}
}注意:每次循环边数时,需要有个备份数组,以防止此次的数据更新后面的距离(串联效应)
spfa算法(正常
,最坏情况
):适合于大多数情况,极端情况会被卡常,宽搜
算法流程(使用邻接表存图): 优化bellman-ford算法之处在于不会每次循环所有的边,而只遍历那些对距离产生影响的边。
AcWing 851. spfa求最短路
给定一个个点
条边的有向图,图中可能存在重边和自环, 边权可能为负数。
请你求出号点到
号点的最短距离,如果无法从
号点走到
号点,则输出
impossible。
数据保证不存在负权回路。
代码(Java)
import java.util.*;
class Main {
static int N = 100010;
static int[] h = new int[N];
static int[] w = new int[N];
static int[] v = new int[N];
static int[] ne = new int[N];
static int idx = 0;
static int[] dist = new int[N];
static boolean[] st = new boolean[N];
static int INF = (int)1e9;
static int n,m;
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
n = sc.nextInt();
m = sc.nextInt();
Arrays.fill(h,-1);
while(m-- > 0) {
int a = sc.nextInt(),b = sc.nextInt(),c = sc.nextInt();
add(a,b,c);
}
spfa();
System.out.println(dist[n] > INF/2 ? "impossible" : dist[n]);
}
public static void add(int a,int b,int c) {
v[idx] = b;
w[idx] = c;
ne[idx] = h[a];
h[a] = idx++;
}
public static void spfa() {
Arrays.fill(dist,INF);
dist[1] = 0;
Queue<Integer> q = new LinkedList<>();
q.offer(1);
st[1] = true;
while(q.size() > 0) {
int x = q.poll();
st[x] = false;
for(int i = h[x];i != -1;i = ne[i]) {
int y = v[i];
if(dist[y] > dist[x] + w[i]) {
dist[y] = dist[x] + w[i];
if(!st[y]) {
q.offer(y);
st[y] = true;
}
}
}
}
}
} 使用spfa还能用于判断图中是否有负环,就是当求解最短距离时,如果最短距离能够更新次及以上的话,而我们知道图中两个点之间如果连通的话,最多只会经过
个边,那么由抽屉原理可以知道网络中一定存在负环。判断是否有负环只需要在spfa算法上增加一个cnt数组,记录最短距离经过的边数。
AcWing 852. spfa判断负环
给定一个个点
条边的有向图,图中可能存在重边和自环, 边权可能为负数。
请你判断图中是否存在负权回路。
代码(Java)
import java.util.*;
class Main {
static int N = 2010;
static int M = 10010;
static int[] h = new int[N];
static int[] ne = new int[M];
static int[] w = new int[M];
static int[] v = new int[M];
static int idx = 0;
static int[] dist = new int[N];
static int[] cnt = new int[N];
static boolean[] st = new boolean[N];
static int INF = (int)1e9;
static int n,m;
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
n = sc.nextInt();
m = sc.nextInt();
Arrays.fill(h,-1);
while(m-- > 0) {
int a = sc.nextInt(), b = sc.nextInt(),c = sc.nextInt();
add(a,b,c);
}
System.out.println(spfa());
}
public static void add(int a,int b,int c) {
w[idx] = c;
v[idx] = b;
ne[idx] = h[a];
h[a] = idx++;
}
public static String spfa() {
Arrays.fill(dist,INF); //距离不初始化也有解
dist[1] = 0;
Queue<Integer> q = new LinkedList<>();
for(int i = 1;i <= n;i++) {
q.offer(i);
st[i] = true;
}
while(q.size() > 0) {
int x = q.poll();
st[x] = false;
for(int i = h[x];i != -1;i = ne[i]) {
int y = v[i];
if(dist[y] > dist[x] + w[i]) {
dist[y] = dist[x] + w[i];
cnt[y] = cnt[x] + 1;
if(cnt[y] >= n) {
return "Yes";
}
if(!st[y]) {
q.offer(y);
}
}
}
}
return "No";
}
}floyd算法
:计算网络中任两点之间的距离,动态规划
算法流程(使用邻接矩阵存图): 状态表示表示节点
之间只经过
的最短距离。状态转移
。优化一维空间
AcWing 854. Floyd求最短路
给定一个个点
条边的有向图,图中可能存在重边和自环,边权可能为负数。
再给定个询问,每个询问包含两个整数
和
,表示查询从点
到点
的最短距离,如果路径不存在,则输出
impossible。
数据保证图中不存在负权回路。
import java.util.*;
class Main {
static int N = 210;
static int M = 20010;
static int[][] d = new int[N][N];
static int n,m,q;
static int INF = (int)1e9;
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
n = sc.nextInt();
m = sc.nextInt();
q = sc.nextInt();
for(int i = 0;i < N;i++) {
Arrays.fill(d[i],INF);
}
for(int i = 0;i < N;i++) {
d[i][i] = 0;
}
while(m-- > 0) {
int a = sc.nextInt(),b = sc.nextInt(),c= sc.nextInt();
d[a][b] = Math.min(d[a][b],c);
}
floyd();
while(q-- > 0) {
int a = sc.nextInt(), b = sc.nextInt();
System.out.println(d[a][b] > INF/2 ? "impossible" : d[a][b]);
}
}
public static void floyd() {
for(int k = 1;k <= n;k++) {
for(int i = 1;i <= n;i++) {
for(int j = 1;j <= n;j++) {
d[i][j] = Math.min(d[i][j],d[i][k] + d[k][j]);
}
}
}
}
}





















 1375
1375

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








