前言
配置中心已经成为越来越多公司必备的基础设施,大部分配置中心都支持配置管理(配置项crud、变更历史版本、权限管理)和对应用内配置实时生效的功能,使得开发人员从原始手写繁重的配置中解放出来。
本文将重点讨论apollo在spring中是如何实现实时生效、以及spring environment是如何管理所有的配置。
一、apollo扩展点入口
apollo使用起来非常简单,以spring boot架构使用apollo举例,你只需要在启动类上加上注解@EnableApolloConfig,项目内的@Value("${xx.xx}")即可生效。
@SpringBootApplication()
@EnableApolloConfig(
value = {
"application",
"config1",
"config2",
})
public class BootApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(BootApplication.class, args);
}
}
或者同在配置文件中加入相关配置,这将通过spring boot 提供的自动化装载spi的机制接入。
apollo.bootstrap.enabled = true
pollo.bootstrap.namespaces = application、config1、config2
好了,我们看看注解@EnableApolloConfig有什么。
@Import(ApolloConfigRegistrar.class)
public @interface EnableApolloConfig {
String[] value() default {ConfigConsts.NAMESPACE_APPLICATION};
int order() default Ordered.LOWEST_PRECEDENCE;
}
不管是通过spring boot提供@import的作为统一扩展点入口还是spring boot 提供的spi机制,统一扩展类入口均为ApolloConfigRegistrar类。
再来看看ApolloConfigRegistrar中的关键部分。
@Override
public void registerBeanDefinitions(AnnotationMetadata importingClassMetadata, BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
//解析@EnableApolloConfig注解
AnnotationAttributes attributes = AnnotationAttributes
.fromMap(importingClassMetadata.getAnnotationAttributes(EnableApolloConfig.class.getName()));
//拿到需要加载配置的命名空间
String[] namespaces = attributes.getStringArray("value");
int order = attributes.getNumber("order");
//加入静态统一集合仓库
PropertySourcesProcessor.addNamespaces(Lists.newArrayList(namespaces), order);
//设置配置
Map<String, Object> propertySourcesPlaceholderPropertyValues = new HashMap<>();
//设置当存在多个后置处理器的时候,指定优先级。比如,其他处理器依赖apollo的配置,那么apollo的优先级一定要比其高。
propertySourcesPlaceholderPropertyValues.put("order", 0);
//解析到不可解析的占位符,跳过,从下一个占位符开始重新解析。默认是false,那样解析到错误占位符的格式将会报错。
propertySourcesPlaceholderPropertyValues.put("ignoreUnresolvablePlaceholders", true);
//加入spring boot 属性配置解析器。spring boot默认自动装载也会加入该类,这里提前加入,应该是可以提前设置上边的两个属性。
BeanRegistrationUtil.registerBeanDefinitionIfNotExists(registry, PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer.class.getName(),
PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer.class, propertySourcesPlaceholderPropertyValues);
//扩展点1 初始化apollo配置、接入spring environment、初始化apollo配置变化监听器。
BeanRegistrationUtil.registerBeanDefinitionIfNotExists(registry, PropertySourcesProcessor.class.getName(),
PropertySourcesProcessor.class);
//扩展点2 提供对@ApolloConfig @ApolloConfigChangeListener 支持
BeanRegistrationUtil.registerBeanDefinitionIfNotExists(registry, ApolloAnnotationProcessor.class.getName(),
ApolloAnnotationProcessor.class);
//扩展点3 提供对@Value动态生效能力 针对实例bean
BeanRegistrationUtil.registerBeanDefinitionIfNotExists(registry, SpringValueProcessor.class.getName(),
SpringValueProcessor.class);
//扩展点4 提供对@Value动态生效能力 针对bean定义
BeanRegistrationUtil.registerBeanDefinitionIfNotExists(registry, SpringValueDefinitionProcessor.class.getName(),
SpringValueDefinitionProcessor.class);
//扩展点5 提供对@ApolloJsonValue 支持
BeanRegistrationUtil.registerBeanDefinitionIfNotExists(registry, ApolloJsonValueProcessor.class.getName(),
ApolloJsonValueProcessor.class);
}
| 扩展类 | 扩展功能 | spring 扩展点 |
|---|---|---|
| PropertySourcesProcessor | 初始化apollo配置 、接入spring environment 、初始化apollo配置变化监听器 | BeanFactoryPostProcessor |
| ApolloAnnotationProcessor | 提供对@ApolloConfig @ApolloConfigChangeListener 支持 | BeanPostProcessor |
| SpringValueProcessor | 提供对@Value动态生效能力 针对实例bean | BeanPostProcessor、BeanFactoryPostProcessor |
| SpringValueDefinitionProcessor | 提供对@Value动态生效能力 针对bean定义 | BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor |
| ApolloJsonValueProcessor | 提供对@ApolloJsonValue 支持 | BeanPostProcessor |
综上所述,apollo基于spring提供的扩展点来嵌入自己的能力。主要为BeanFactoryPostProcessor、BeanPostProcessor这两个扩展点。因不是本文中点,不详细阐述,只需要知道,BeanFactoryPostProcessor、BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor在生成所有beandefinition之后调用,而BeanPostProcessor在通过beandefinition实例化bean的过程中调用即可。
二、spring environment
为更好了解apollo扩展类具体实现,我们首先要知道spring是如何解析@Value。
解析@Value具体靠AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor类实现,因不是本文重点,这里简单说一下,在bean实例化之后需要组装属性,该扩展类会扫描@Value注解,找到注解上的Spel占位符,通过解析占位符,拿到真正的key,最终会去environment中取到value。
重点是environment,所有的配置都存在environment当中,那environment到底是什么呢?
The Environment interface is an abstraction integrated in the container that models two key aspects of the application environment:
profilesandproperties.
以上是spring文档中的原话。spring即为环境,也就是上下文,程序的运行依赖上下文,它主要集成了两个方面,profiles和properties。
profiles
spring 允许向多环境定制不同的bean和配置文件,然后通过spring.profiles.active来激活。
profiles多环境定制可以通过以下方式进行编写:
1、 编码方式
@Configuration
public class AppConfig {
@Bean("dataSource")
@Profile("development")
public DataSource standaloneDataSource() {
return new EmbeddedDatabaseBuilder()
.setType(EmbeddedDatabaseType.HSQL)
.addScript("classpath:com/bank/config/sql/schema.sql")
.addScript("classpath:com/bank/config/sql/test-data.sql")
.build();
}
@Bean("dataSource")
@Profile("production")
public DataSource jndiDataSource() throws Exception {
Context ctx = new InitialContext();
return (DataSource) ctx.lookup("java:comp/env/jdbc/datasource");
}
}
2、 配置文件方式

profiles激活环境可以通过以下方式进行指定:
- 代码
- vm参数
- 配置文件
ctx.getEnvironment().setActiveProfiles(“profile1”, “profile2”);
-Dspring.profiles.active=“profile1,profile2”
spring.profiles.active=“profile1,profile2”
properties
properties就是我们熟悉的配置文件,来源不限于
- jvm 系统属性 (-d、命令行参数)
- jvm 系统环境变量(操作系统环境变量)
- 本地文件(application.properties/yaml)
- 配置中心(apollo、nacos)
总的来说,environment 集成了profiles和properties两个概念,完成了对多环境、多来源配置的管理。
好了,让我们来看看spring environment 是如何实现profiles和properties的
profiles 在spring 中的实现
@Conditional(ProfileCondition.class)
public @interface Profile {
String[] value();
}
@profiles是靠@Conditional注解来实现的。
具体看一下org.springframework.context.annotation.ProfileCondition#matches方法。
@Override
public boolean matches(ConditionContext context, AnnotatedTypeMetadata metadata) {
MultiValueMap<String, Object> attrs = metadata.getAllAnnotationAttributes(Profile.class.getName());
if (attrs != null) {
for (Object value : attrs.get("value")) {
//关键方法,会和激活好的环境做比对,如果指定的环境满足激活的环境,那么注入。
if (context.getEnvironment().acceptsProfiles((String[]) value)) {
return true;
}
}
//表示跳过该bean的注入
return false;
}
return true;
}
可以看到,只有当指定的环境满足激活的环境,那么该bean将会被注入。
@Conditional实现不在本文的讨论的范围之内,有兴趣的同学可以去看下这个方法。
org.springframework.context.annotation.ConfigurationClassBeanDefinitionReader.TrackedConditionEvaluator#shouldSkip
properties 在spring 中的实现
properties为方便获取所有属性来源的配置,引入了PropertySource概念。PropertySource就是一个配置来源的抽象,一个PropertySource表示一个配置来源。而StandardEnvironment类中只持有List<PropertySource<?>> propertySourceList,即所有的配置来源都在environment中了。
你可以想象每一个PropertySource就是一个map,而这个map里面具体是什么配置,取决于你往这个map里面塞了什么。
简单看几个PropertySource实现,以下为简写。
jvm 系统属性
public class SystemPropertySources extends PropertySource<String> {
private Map source ;
public void init(){
this.source = (Map) System.getProperties()
}
@Nullable
public Object getProperty(String name){
return this.source.get(name);
}
}
jvm 环境变量
public class SystemPropertySources extends PropertySource<String> {
private Map source ;
public void init(){
this.source = return (Map) System.getenv();
}
@Nullable
public Object getProperty(String name){
return this.source.get(name);
}
}
读取application.xxx构建PropertySource
因代码流程比较多就不全贴了,spring会读取本地application.xxx的配置文件然后构建一个PropertySource加入到environment中,被统一上下文管理(默认行为)。值得注意的是,spring在构建本地application.xxxPropertySource的时候,会根据应用激活的profiles环境,为application-xxx.xxx也构建PropertySource。
org.springframework.boot.context.config.ConfigFileApplicationListener.Loader#loadForFileExtension
private void loadForFileExtension(PropertySourceLoader loader, String prefix,
String fileExtension, Profile profile,
DocumentFilterFactory filterFactory, DocumentConsumer consumer) {
DocumentFilter defaultFilter = filterFactory.getDocumentFilter(null);
DocumentFilter profileFilter = filterFactory.getDocumentFilter(profile);
if (profile != null) {
String profileSpecificFile = prefix + "-" + profile + fileExtension;
//解析application-xxx.xxx
//defaultFilter处理application-xxx.xxx中可能有指定了新的spring.profile.active、spring.profile.include
load(loader, profileSpecificFile, profile, defaultFilter, consumer);
load(loader, profileSpecificFile, profile, profileFilter, consumer);
//在处理过程当中解析到了新的spring.profile.active、spring.profile.include
//在当前文件前缀循环处理
for (Profile processedProfile : this.processedProfiles) {
if (processedProfile != null) {
String previouslyLoaded = prefix + "-" + processedProfile
+ fileExtension;
load(loader, previouslyLoaded, profile, profileFilter, consumer);
}
}
}
// 默认会在最后处理application.xxx配置文件(默认行为)
load(loader, prefix + fileExtension, profile, profileFilter, consumer);
}
StandardEnvironment
StandardEnvironment 为spring 默认实现。
好了,让我们看一下构建好的environment,看到有profile激活的环境,还有多配置来源PropertySource,除了刚刚介绍的,还有对servletconfig和servletContext配置的处理。
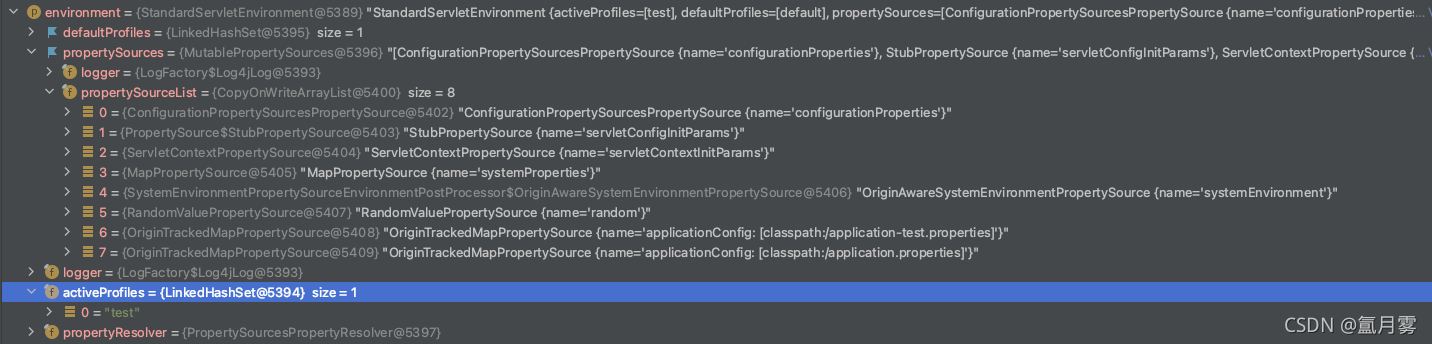
最关键的来了,那么environment如何通过key去PropertySource集合拿到相应value呢?
protected <T> T getProperty(String key, Class<T> targetValueType, boolean resolveNestedPlaceholders) {
if (this.propertySources != null) {
for (PropertySource<?> propertySource : this.propertySources) {
//循环去每一个propertySource中寻找值
Object value = propertySource.getProperty(key);
//找到值之后,中断循环,立马返回值。
if (value != null) {
//判断是否解决嵌套占位符 比如 spring.xx = ${xxx.xx}
if (resolveNestedPlaceholders && value instanceof String) {
value = resolveNestedPlaceholders((String) value);
}
//是否有必要转换值
return convertValueIfNecessary(value, targetValueType);
}
}
}
return null;
}
答案是遍历所有的PropertySource,从第一个元素开始找,找到即结束。也就是说当多配置来源,含有相同key,取第一个,前者覆盖后者.
三 apollo扩展类具体实现
最后,在看看apollo的扩展类是如何实现和spring environment交互的呢?
PropertySourcesProcessor
扩展类方法入口为postProcessBeanFactory,所有的bean还未开始实例化前调用。
@Override
public void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException {
//初始化PropertySources
initializePropertySources();
//初始化配置项更新监听器
initializeAutoUpdatePropertiesFeature(beanFactory);
}
//根据namespace初始化PropertySource,并叫给spring管理
private void initializePropertySources() {
//组合式PropertySource 类似于List<PropertySource> 把所有的PropertySource聚合成一个整体
CompositePropertySource composite = new CompositePropertySource(PropertySourcesConstants.APOLLO_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME);
//排序
ImmutableSortedSet<Integer> orders = ImmutableSortedSet.copyOf(NAMESPACE_NAMES.keySet());
Iterator<Integer> iterator = orders.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
int order = iterator.next();
//循环拿到所有
for (String namespace : NAMESPACE_NAMES.get(order)) {
//和apollo做交互
Config config = ConfigService.getConfig(namespace);
//加入到组合式PropertySource中
composite.addPropertySource(configPropertySourceFactory.getConfigPropertySource(namespace, config));
}
}
//清理仓库 上面已经将NAMESPACE_NAMES中namespace转换成了PropertySource
NAMESPACE_NAMES.clear();
//将所有转换成PropertySource的namespace,交给spring管理。
environment.getPropertySources().addFirst(composite);
}
private void initializeAutoUpdatePropertiesFeature(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
//初始化统一监听类
AutoUpdateConfigChangeListener autoUpdateConfigChangeListener = new AutoUpdateConfigChangeListener(
environment, beanFactory);
//获取所有初始化好的namespace
List<ConfigPropertySource> configPropertySources = configPropertySourceFactory.getAllConfigPropertySources();
for (ConfigPropertySource configPropertySource : configPropertySources) {
//把统一监听类加入到所有初始化好的namespace,监听所有namespace的kv变化。
configPropertySource.addChangeListener(autoUpdateConfigChangeListener);
}
}
可以看到,一共做了三件事情,1、将所有配置的nameSpace通过ConfigService.getConfig(namespace)和apollo建立关系,通过config内部的map构建PropertySource,将所有namespace的PropertySource聚合成一个大的PropertySource(内部其实就是PropertySource集合)。2、将聚合好的PropertySource交给spring管理,到这一步,已经实现了@Value("${xxx.xxx}")从apollo中拿值了 3、给所有namespace添加监听类AutoUpdateConfigChangeListener,监听器原理也是利用apollo官方提供的Config.addChangeListener Api。
好,继续,看下类AutoUpdateConfigChangeListener
public void onChange(ConfigChangeEvent changeEvent) {
//提取发生变化的key
Set<String> keys = changeEvent.changedKeys();
if (CollectionUtils.isEmpty(keys)) {
return;
}
for (String key : keys) {
// 1. 根据key从springValueRegistry仓库中获取相应的SpringValue信息
Collection<SpringValue> targetValues = springValueRegistry.get(beanFactory, key);
if (targetValues == null || targetValues.isEmpty()) {
continue;
}
// 2. SpringValue中包含bean实例、反射字段对象,直接把值设置回去就好了。
for (SpringValue val : targetValues) {
updateSpringValue(val);
}
e }
}
通过apollo提供监听api,可以拿到所有的变化的kv,遍历所有变化的kv,通过key从springValueRegistry中取出所有的SpringValue,再调用updateSpringValue方法。
springValueRegistry比较简单,里面会记录所有SpringValue,类似一个SpringValue仓库,全局唯一,记录所有的SpringValue。
public class SpringValueRegistry {
private static final long CLEAN_INTERVAL_IN_SECONDS = 5;
//这行是重点
private final Map<BeanFactory, Multimap<String, SpringValue>> registry = Maps.newConcurrentMap();
}
而SpringValue里面究竟有什么呢?
public class SpringValue {
private MethodParameter methodParameter;
private Field field;
private WeakReference<Object> beanRef;
private String beanName;
private String key;
private String placeholder;
private Class<?> targetType;
private Type genericType;
private boolean isJson;
}
最后再来看看updateSpringValue方法。
private void injectField(Object newVal) throws IllegalAccessException {
Object bean = beanRef.get();
if (bean == null) {
return;
}
boolean accessible = field.isAccessible();
field.setAccessible(true);
field.set(bean, newVal);
field.setAccessible(accessible);
}
好家伙,原来实时生效是通过apollo监听api再拿到提前解析好的bean实例,和相应key的字段反射进行设置的。
那是什么时候放进来的呢?
SpringValueProcessor闪亮登场。
SpringValueProcessor
SpringValueProcessor继承ApolloProcessor,会在bean的初始化过程中调用,可以看到,会解析bean的每一个字段和方法。
public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName)
throws BeansException {
Class clazz = bean.getClass();
for (Field field : findAllField(clazz)) {
//处理bean的每一个字段
processField(bean, beanName, field);
}
for (Method method : findAllMethod(clazz)) {
//处理bean的每一个方法
processMethod(bean, beanName, method);
}
return bean;
}
看下子类SpringValueProcessor,具体是如何解析字段的吧。
@Override
protected void processField(Object bean, String beanName, Field field) {
// register @Value on field
Value value = field.getAnnotation(Value.class);
if (value == null) {
return;
}
Set<String> keys = placeholderHelper.extractPlaceholderKeys(value.value());
if (keys.isEmpty()) {
return;
}
for (String key : keys) {
SpringValue springValue = new SpringValue(key, value.value(), bean, beanName, field, false);
//将解析好的结果放入springValueRegistry
springValueRegistry.register(beanFactory, key, springValue);
}
}
结果不必多说了吧,SpringValueProcessor在bean初始化的时候,解析bean并提取@Value的字段信息,然后放入SpringValueRegistry。
继续看看相关性比较强的SpringValueDefinitionProcessor
SpringValueDefinitionProcessor
private void processBeanPropertyValues(Object bean, String beanName) {
Collection<SpringValueDefinition> propertySpringValues = beanName2SpringValueDefinitions
.get(beanName);
if (propertySpringValues == null || propertySpringValues.isEmpty()) {
return;
}
for (SpringValueDefinition definition : propertySpringValues) {
PropertyDescriptor pd = BeanUtils
.getPropertyDescriptor(bean.getClass(), definition.getPropertyName());
Method method = pd.getWriteMethod();
if (method == null) {
continue;
}
SpringValue springValue = new SpringValue(definition.getKey(), definition.getPlaceholder(),
bean, beanName, method, false);
springValueRegistry.register(beanFactory, definition.getKey(), springValue);
}
}
关键部分如上,SpringValueDefinitionProcessor会把相关beanDefinition中的字段也加入到springValueRegistry。
也就是说,当我修改一个key,apollo不光会修改bean对象,连相应的beanDefinition也会被修改。
apollo这样做,也不难理解,因为bean对象可能会被清理掉,比如说这个bean是prototype的,该bean 的重新生成依赖beanDefinition,所以,key被修改,相应的beanDefinition也应该被修改。
ApolloAnnotationProcessor
@Override
protected void processField(Object bean, String beanName, Field field) {
ApolloConfig annotation = AnnotationUtils.getAnnotation(field, ApolloConfig.class);
if (annotation == null) {
return;
}
String namespace = annotation.value();
//从apollo获取config
Config config = ConfigService.getConfig(namespace);
ReflectionUtils.makeAccessible(field);
ReflectionUtils.setField(field, bean, config);
}
一样的套路,不一样的配方,可以看到@ApolloConfig的实际原理,就是bean初始化过程中,解析到@ApolloConfig,把Config通过反射设置进去。
@Override
protected void processMethod(final Object bean, String beanName, final Method method) {
ApolloConfigChangeListener annotation = AnnotationUtils
.findAnnotation(method, ApolloConfigChangeListener.class);
if (annotation == null) {
return;
}
Class<?>[] parameterTypes = method.getParameterTypes();
ReflectionUtils.makeAccessible(method);
String[] namespaces = annotation.value();
String[] annotatedInterestedKeys = annotation.interestedKeys();
String[] annotatedInterestedKeyPrefixes = annotation.interestedKeyPrefixes();
ConfigChangeListener configChangeListener = new ConfigChangeListener() {
@Override
public void onChange(ConfigChangeEvent changeEvent) {
//反射调用@ApolloConfigChangeListener描述的方法
ReflectionUtils.invokeMethod(method, bean, changeEvent);
}
};
Set<String> interestedKeys = annotatedInterestedKeys.length > 0 ? Sets.newHashSet(annotatedInterestedKeys) : null;
Set<String> interestedKeyPrefixes = annotatedInterestedKeyPrefixes.length > 0 ? Sets.newHashSet(annotatedInterestedKeyPrefixes) : null;
for (String namespace : namespaces) {
Config config = ConfigService.getConfig(namespace);
if (interestedKeys == null && interestedKeyPrefixes == null) {
config.addChangeListener(configChangeListener);
} else {
config.addChangeListener(configChangeListener, interestedKeys, interestedKeyPrefixes);
}
}
}
@ApolloConfigChangeListener的实现也是依赖于apollo提供的config.addChangeListener方法,一旦该key对应namespace发生变化,会反射调用@ApolloConfigChangeListener描述的方法。
ApolloJsonValueProcessor
@Override
protected void processField(Object bean, String beanName, Field field) {
ApolloJsonValue apolloJsonValue = AnnotationUtils.getAnnotation(field, ApolloJsonValue.class);
if (apolloJsonValue == null) {
return;
}
String placeholder = apolloJsonValue.value();
//解析占位符
Object propertyValue = placeholderHelper
.resolvePropertyValue(beanFactory, beanName, placeholder);
// 只支持String
if (!(propertyValue instanceof String)) {
return;
}
boolean accessible = field.isAccessible();
field.setAccessible(true);
//关键点:解析json
ReflectionUtils
.setField(field, bean, parseJsonValue((String)propertyValue, field.getGenericType()));
field.setAccessible(accessible);
//autoUpdateInjectedSpringProperties 默认为true 也纳入实时生效springValueRegistry仓库内
if (configUtil.isAutoUpdateInjectedSpringPropertiesEnabled()) {
Set<String> keys = placeholderHelper.extractPlaceholderKeys(placeholder);
for (String key : keys) {
SpringValue springValue = new SpringValue(key, placeholder, bean, beanName, field, true);
springValueRegistry.register(beanFactory, key, springValue);
}
}
}
提供对@ApolloJsonValue支持,也就是通过拿到具体的value之后,可能是json格式,多了一步解析json的过程。最后该bean也被加入到springValueRegistry中,也就是说,被@ApolloJsonValue修饰的字段也支持实时生效。
总结
稍微总结一下整个流程,首先apollo把所有的namespace对应的config构造成PropertySource加入到spring evironment,这样@Value就已经支持从apollo获取配置了。而实时生效,apollo会在bean的初始化过程中,拿到key和bean的关系,并统一保存。一旦key变化,通过这个关系,可以找到这个bean,把相应value设置进去就完事了。

























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








