Python数据结构 (Python Data Structures)
Python lists and dictionaries are two data structures in Python used to store data. A Python list is an ordered sequence of objects, whereas dictionaries are unordered. The items in the list can be accessed by an index (based on their position) whereas items in the dictionary can be accessed by keys and not by their position.
Python列表和字典是Python中用于存储数据的两个数据结构。 Python列表是对象的有序序列,而字典是无序的。 列表中的项目可以通过索引(基于它们的位置)来访问,而字典中的项目可以通过键而不是它们的位置来访问。
Let's see how to convert a Python list to a dictionary.
让我们看看如何将Python列表转换成字典。
将Python列表转换为字典的十种不同方法 (Ten different ways to convert a Python list to a dictionary)
- Converting a list of tuples to a dictionary 将元组列表转换为字典
- Converting two lists of the same length to a dictionary 将两个相同长度的列表转换为字典
- Converting two lists of different length to a dictionary 将两个不同长度的列表转换为字典
- Converting a list of alternative key, value items to a dictionary 将备用键,值项列表转换为字典
- Converting a list of dictionaries to a single dictionary 将词典列表转换为单个词典
- Converting a list into a dictionary using enumerate() 使用enumerate()将列表转换成字典
- Converting a list into a dictionary using dictionary comprehension 使用字典理解将列表转换为字典
- Converting a list to a dictionary using dict.fromkeys() 使用dict.fromkeys()将列表转换成字典
- Converting a nested list to a dictionary using dictionary comprehension 使用字典理解将嵌套列表转换为字典
- Converting a list to a dictionary using Counter() 使用Counter()将列表转换为字典
1.将元组列表转换为字典 (1. Converting a List of Tuples to a Dictionary)
The dict() constructor builds dictionaries directly from sequences of key-value pairs.
dict()构造函数直接从键值对序列中构建字典。
-
l1=[(1,'a'),(2,'b'), -
(3,'c'),(4,'d')] -
d1=dict(l1) -
print (d1) -
#Output:{1: 'a', 2: 'b', 3: 'c', 4: 'd'}
2.将两个相同长度的列表转换成字典 (2. Converting Two Lists of the Same Length to a Dictionary)
We can convert two lists of the same length to the dictionary using zip().
我们可以使用以下命令将两个相同长度的列表转换为字典 zip() 。
zip() will return an iterator of tuples. We can convert that zip object to a dictionary using the dict() constructor.
zip()将返回一个元组的迭代器。 我们可以使用以下方式将zip对象转换为字典 dict()构造函数。
压缩() (zip())
Make an iterator that aggregates elements from each of the iterables.
创建一个迭代器,以聚合每个可迭代对象中的元素。
“
zip(*iterables): Returns an iterator of tuples, where the i-th tuple contains the i-th element from each of the argument sequences or iterables. The iterator stops when the shortest input iterable is exhausted. With a single iterable argument, it returns an iterator of 1-tuples. With no arguments, it returns an empty iterator.” — Python documentation“
zip ( *iterables ):返回一个元组的迭代器,其中第i个元组包含每个参数序列或iterables中的第i个元素。 当最短的可迭代输入耗尽时,迭代器停止。 使用单个可迭代参数,它返回1元组的迭代器。 没有参数,它将返回一个空的迭代器。” — Python 文档
Example:
例:
-
l1=[1,2,3,4] -
l2=['a','b','c','d'] -
d1=zip(l1,l2) -
print (d1)#Output:<zip object at 0x01149528> -
#Converting zip object to dict using dict() contructor. -
print (dict(d1)) -
#Output:{1: 'a', 2: 'b', 3: 'c', 4: 'd'}
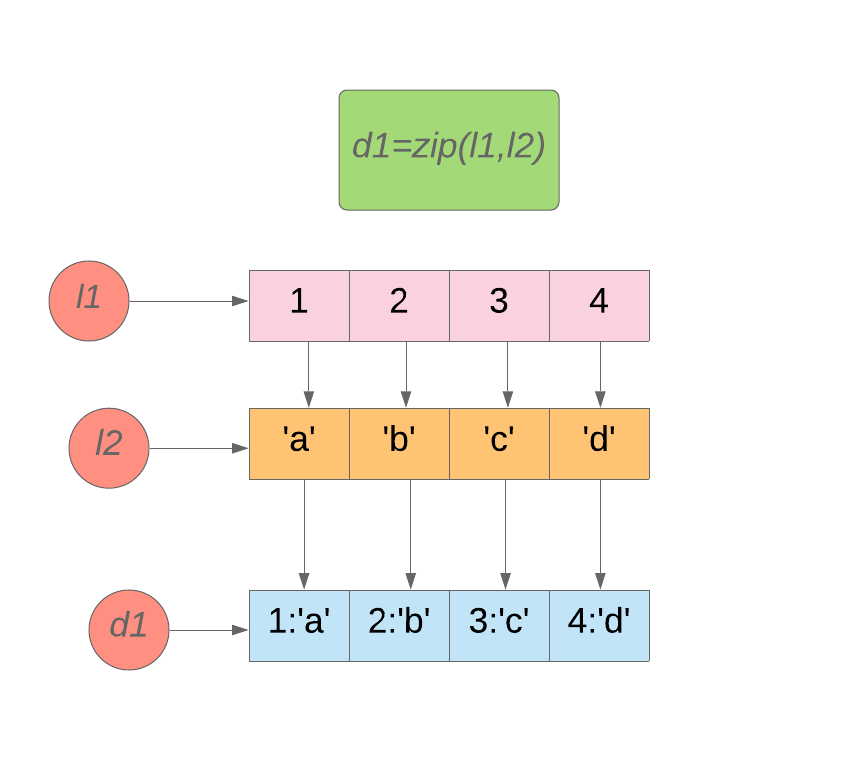
Image source: Author 图片来源:作者
3,将两个不同长度的列表转换成字典 (3.Converting Two Lists of Different Length to a Dictionary)
We can convert two lists of different length to the dictionary using itertools.zip_longest().
我们可以使用itertools.zip_longest()将两个不同长度的列表转换成字典。
As per Python documentation
根据Python文档
“
zip_longest(): Makes an iterator that aggregates elements from each of the iterables. If iterables are of uneven length, missing value is filled with fillvalue. Iteration continues until the longest iterable is exhausted.In zip(),iteration continues until shortest iterable is exhausted.”“
zip_longest():创建一个迭代器,以聚合每个可迭代对象中的元素。 如果可迭代项的长度不均匀,则用填充值填充缺失值。 迭代一直持续到最长的可迭代耗尽为止。在zip()中,迭代一直持续到最短的可迭代耗尽为止。”
itertools.zip_longest(*iterables,fillvalue=None)Using zip(), iteration continues until the shortest iterable is exhausted.
使用zip() ,迭代将持续到最短的可迭代时间 筋疲力尽。
-
l1=[1,2,3,4,5,6,7] -
l2=['a','b','c','d'] -
d1=zip(l1,l2) -
print (d1)#Output:<zip object at 0x01149528> -
#Converting zip object to dict using dict() contructor. -
print (dict(d1)) -
#Output:{1: 'a', 2: 'b', 3: 'c', 4: 'd'}
Using zip_longest(), iteration continues until the longest iterable is exhausted. By default, fillvalue is None.
使用 zip_longest() ,迭代一直持续到 的 最长的迭代时间已耗尽。 默认情况下, fillvalue为None 。
-
from itertools import zip_longest -
l1=[1,2,3,4,5,6,7] -
l2=['a','b','c','d'] -
d1=zip_longest(l1,l2) -
print (d1)#Output:<itertools.zip_longest object at 0x00993C08> -
#Converting zip object to dict using dict() contructor. -
print (dict(d1)) -
#Output:{1: 'a', 2: 'b', 3: 'c', 4: 'd', 5: None, 6: None, 7: None}
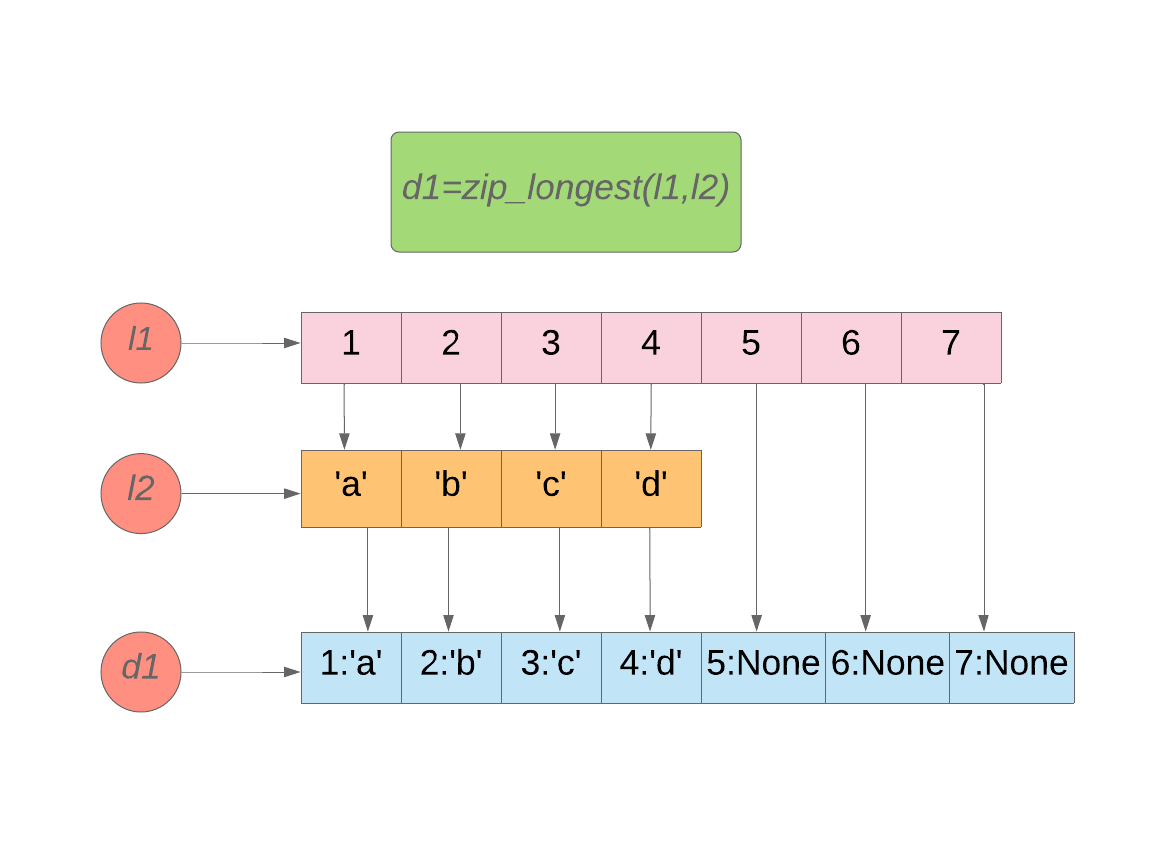
Image by Author 图片作者
fillvalue is mentioned as x.
fillvalue被称为x 。
-
from itertools import zip_longest -
l1=[1,2,3,4,5,6,7] -
l2=['a','b','c','d'] -
d1=zip_longest(l1,l2,fillvalue='x') -
print (d1)#Output:<itertools.zip_longest object at 0x00993C08> -
#Converting zip object to dict using dict() contructor. -
print (dict(d1)) -
#Output:{1: 'a', 2: 'b', 3: 'c', 4: 'd', 5: 'x', 6: 'x', 7: 'x'}
4.将备用键,值项列表转换为字典 (4. Converting a List of Alternative Key, Value Items to a Dictionary)
We can convert a list of alternative keys, values as items to a dictionary using slicing.
我们可以使用切片将替代键列表,值作为项转换为字典。
Slicing returns a new list containing a sequence of items from the list. We can specify a range of indexes.
切片将返回一个新列表,其中包含列表中的一系列项目。 我们可以指定索引范围。
s[i:j:k] — slice of s from i to j with step kWe can create two slice lists. The first list contains keys alone and the next list contains values alone.
我们可以创建两个切片列表。 第一个列表仅包含键,而下一个列表仅包含值。
l1=[1,'a',2,'b',3,'c',4,'d']Create two slice objects from this list.
从此列表中创建两个切片对象。
第一个切片对象将仅包含键 (The first slice object will contain keys alone)
l1[::2]
l1[::2]
start is not mentioned. By default, it will start from the beginning of the list.
start没有提到。 默认情况下,它将从列表的开头开始。
stop is not mentioned. By default, it will stop at the end of the list.
没有提到stop 。 默认情况下,它将停止在列表的末尾。
stop is mentioned as 2.
stop被称为2。
l1[::2] Return a list containing elements from beginning to end using step 2 (alternative elements).
l1[::2]返回一个列表,其中包含使用第2步从头到尾的元素(替代元素)。
[1,2,3,4]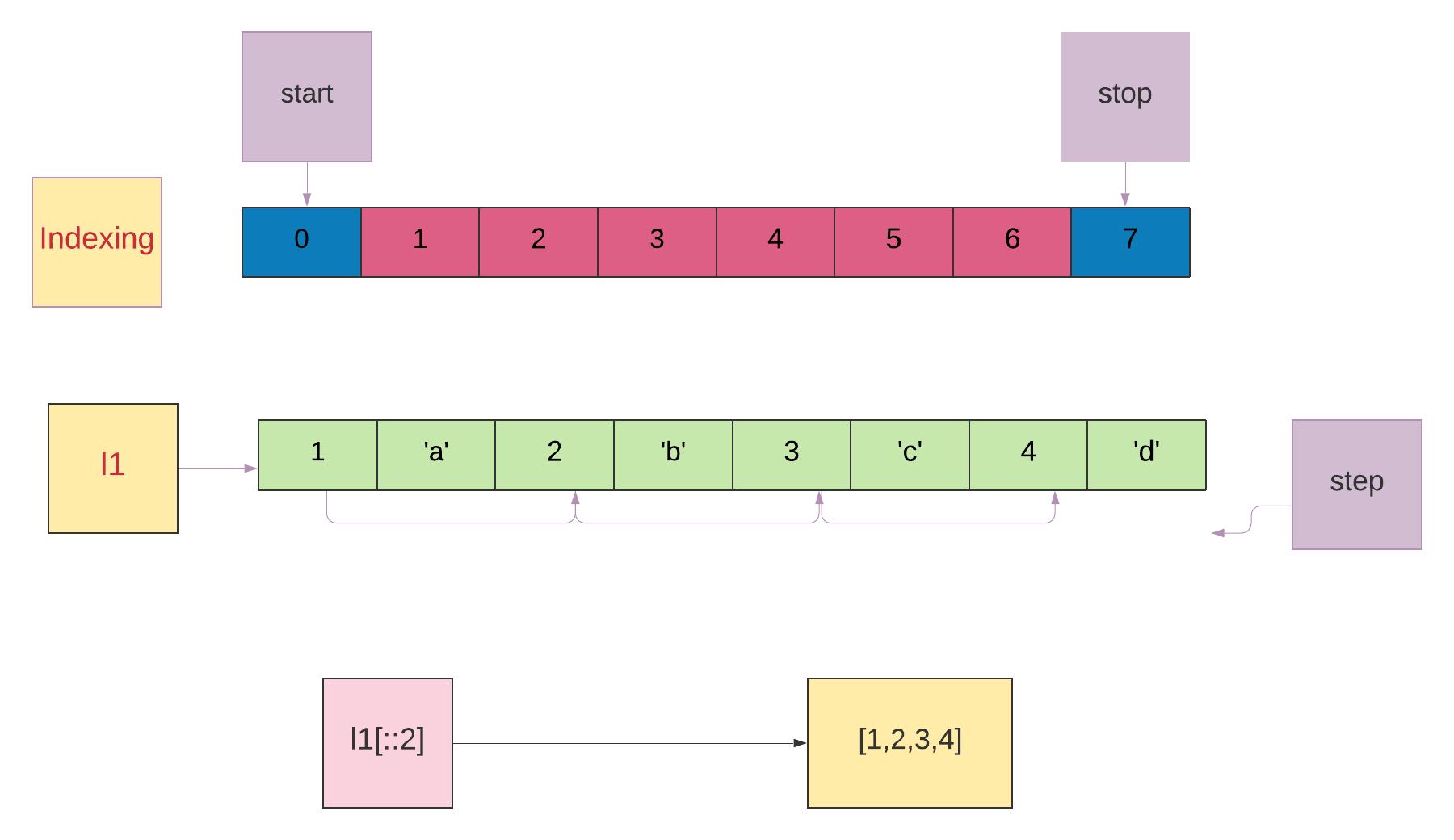
Image source: Author 图片来源:作者
第二个切片对象将仅包含值 (The second slice object will contain values alone)
l1=[1,'a',2,'b',3,'c',4,'d']l1[1::2]
l1[1::2]
start is mentioned as 1. It will start slicing from the first index.
start被提及作为1.将从第一索引开始切片。
stop is not mentioned. It will stop at the end of the list.
没有提到stop 。 它将停止在列表的末尾。
step is mentioned as 2.
step被称为2。
l1[1::2] Return a list containing elements from the first index to the end using step 2 (alternative elements).
l1[1::2 ]使用第2步返回一个列表,该列表包含从第一个索引到末尾的元素(替代元素)。
['a', 'b', 'c', 'd']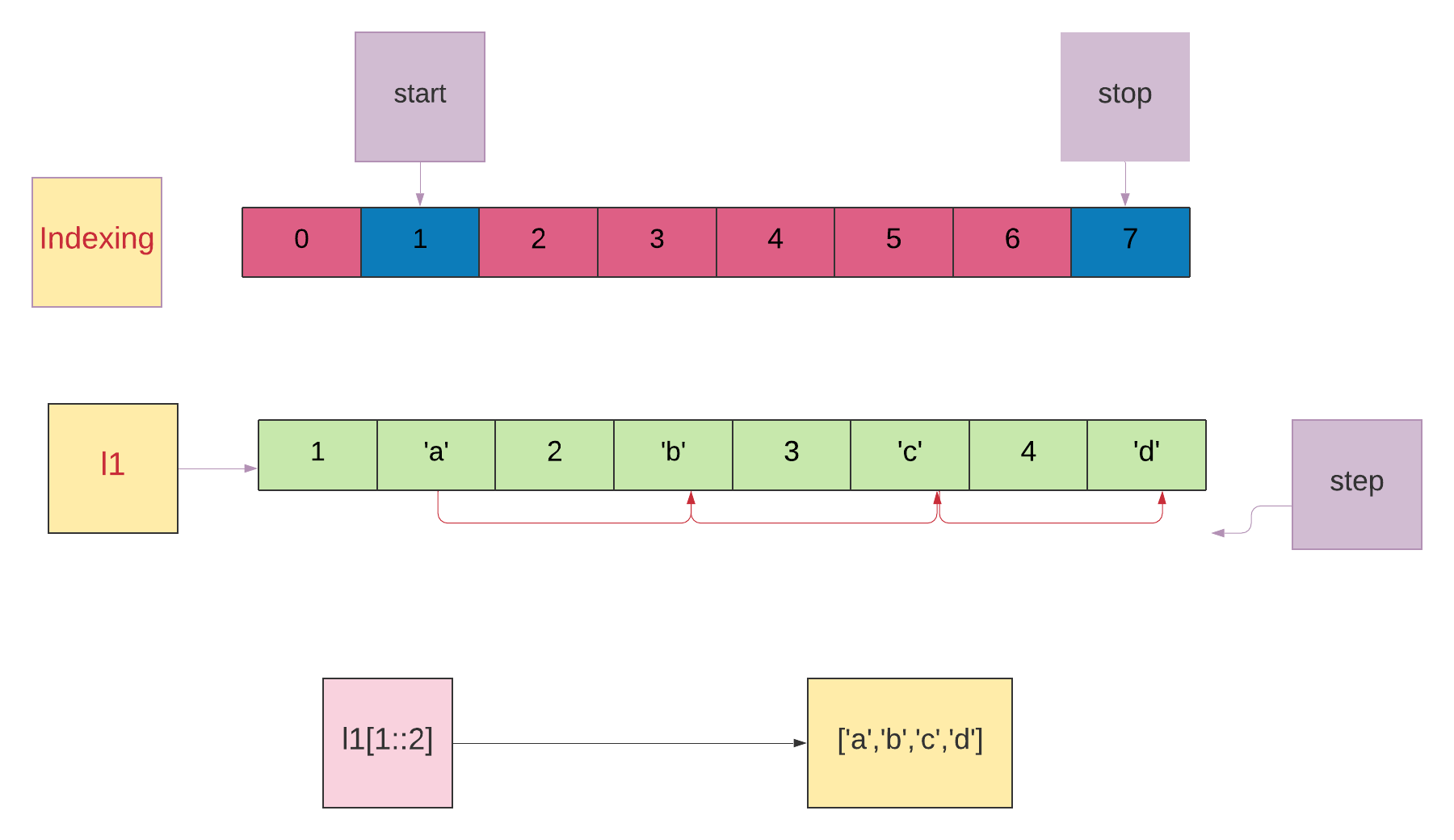
Image Source: Author 图片来源:作者
Now we can merge the two lists using the zip() function.
现在,我们可以使用 zip()函数。
-
l1=[1,'a',2,'b',3,'c',4,'d'] -
#Creating list containing keys alone by slicing -
l2=l1[::2] -
#Creating list containing values alone by slicing -
l3=l1[1::2] -
#merging two lists uisng zip() -
z=zip(l2,l3) -
#Converting zip object to dict using dict() constructor. -
print (dict(z)) -
#Output:{1: 'a', 2: 'b', 3: 'c', 4: 'd'}
5.将词典列表转换为单个词典 (5. Converting a List of Dictionaries to a Single Dictionary)
A list of dictionaries can be converted into a single dictionary by the following ways:
字典列表可以通过以下方式转换为单个字典:
-
dict.update()dict.update() - dictionary comprehension 字典理解
-
Collections.ChainMapCollections.ChainMap
dict.update() (dict.update())
We can convert a list of dictionaries to a single dictionary using dict.update().
我们可以使用dict.update()将字典列表转换为单个字典。
- Create an empty dictionary. 创建一个空字典。
-
Iterate through the list of dictionaries using a
forloop.使用
for循环遍历字典列表。 -
Now update each item (key-value pair) to the empty dictionary using
dict.update().现在,使用
dict.update()将每个项(键值对)更新为空字典。
-
l1=[{1:'a',2:'b'},{3:'c',4:'d'}] -
d1={} -
for i in l1: -
d1.update(i) -
print (d1) -
#Output:{1: 'a', 2: 'b', 3: 'c', 4: 'd'}
字典理解 (Dictionary comprehension)
A dictionary comprehension consists of brackets{} containing two expressions separated with a colon followed by a for clause, then zero or more for or if clauses.
字典推导由括号{}组成,该括号包含两个用冒号分隔的表达式,后跟一个for子句,然后是零个或多个for或if子句。
l1=[{1:'a',2:'b'},{3:'c',4:'d'}]d1={k:v for e in l1 for (k,v) in e.items()}for e in l1 — Return each item in the list {1:’a’,2:’b’}.
for e in l1 —返回列表{1:'a',2:'b'}中的每个项目。
for (k,v) in e.items() — Return the key, value pair in that item. (1,’a’) (2,’b’)
for (k,v) in e.items() —返回该项目中的键,值对。 (1,'a') (2,'b')
k:v — is updated in the dictionary d1
k:v —在字典d1中更新
-
l1=[{1:'a',2:'b'},{3:'c',4:'d'}] -
d1={k:v for e in l1 for (k,v) in e.items()} -
print (d1) -
#Output:{1: 'a', 2: 'b', 3: 'c', 4: 'd'}
Collections.ChainMap (Collections.ChainMap)
By using collections.ChainMap(), we can convert a list of dictionaries to a single dictionary.
通过使用collections.ChainMap() ,我们可以将字典列表转换为单个字典。
As per the Python documentation
根据Python文档
“
ChainMap: A ChainMap groups multiple dictionary or other mappings together to create a single, updateable view.”“
ChainMap: ChainMap将多个字典或其他映射组合在一起,以创建一个可更新的视图。”
The return type will be ChainMap object. We can convert to a dictionary using the dict() constructor.
返回类型将为ChainMap object 。 我们可以使用dict()转换成字典 构造函数。
-
l1=[{1:'a',2:'b'},{3:'c',4:'d'}] -
from collections import ChainMap -
d3=ChainMap(*l1) -
print (d3)#Output:ChainMap({1: 'a', 2: 'b'}, {3: 'c', 4: 'd'}) -
#Converting ChainMap object to dict using dict() constructor. -
print (dict(d3)) -
#Output:{3: 'c', 4: 'd', 1: 'a', 2: 'b'}
6.使用Enumerate()将列表转换为字典 (6. Converting a List to a Dictionary Using Enumerate())
By using enumerate(), we can convert a list into a dictionary with index as key and list item as the value.
通过使用enumerate() ,我们可以将列表转换为字典,索引为键,列表项为值。
enumerate() will return an enumerate object.
enumerate() 将返回一个枚举对象。
We can convert to dict using the dict() constructor.
我们可以使用dict()构造函数转换为dict。
As per the Python documentation:
根据Python文档 :
“
enumerate(iterable, start=0): Returns an enumerate object. iterable must be a sequence, an iterator, or some other object which supports iteration. The__next__()method of the iterator returned byenumerate()returns a tuple containing a count (from start which defaults to 0) and the values obtained from iterating over iterable.“
enumerate( iterable , start=0 ):返回一个枚举对象。 可迭代必须是一个序列, 我 terator,或支持迭代一些其它物体。 由enumerate()返回的迭代器的__next__()方法返回一个元组,该元组包含一个计数(从起始位置开始,默认为0)以及通过对iterable进行迭代而获得的值。
-
l1=['a','b','c','d'] -
d1=dict(enumerate(l1)) -
print (d1)#Output:{0: 'a', 1: 'b', 2: 'c', 3: 'd'}
7.使用字典理解将列表转换成字典 (7. Converting List Into a Dictionary Using Dictionary Comprehension)
By using dictionary comprehension, we can convert a list of keys to a dictionary having the same value.
通过使用字典理解,我们可以将键列表转换为具有相同值的字典。
d1={k:"a" for k in l1}It will iterate through the list and change its item as a key (k), and value will be a for all keys.
它将遍历列表并将其项更改为键( k ),并且所有键的值均为a 。
-
l1=[1,2,3,4] -
d1={k:"a" for k in l1} -
print (d1) -
#Output:{1: 'a', 2: 'a', 3: 'a', 4: 'a'}
8.使用dict.fromkeys()将列表转换成字典 (8. Converting a List to a Dictionary Using dict.fromkeys())
dict.from keys() will accept a list of keys, which is converted to dictionary keys, and a value, which is to be assigned.
dict.from keys()将接受一个键列表,该列表将转换为字典键,以及一个值,该值将被分配。
The same value will be assigned to all keys.
相同的值将分配给所有键。
-
l1=['red','blue','orange'] -
d1=dict.fromkeys(l1,"colors") -
print (d1) -
#Output:{'red': 'colors', 'blue': 'colors', 'orange': 'colors'}
9.使用字典理解将嵌套列表转换为字典 (9. Converting a Nested List to a Dictionary Using Dictionary Comprehension)
We can convert a nested list to a dictionary by using dictionary comprehension.
通过使用字典理解,我们可以将嵌套列表转换为字典。
l1 = [[1,2],[3,4],[5,[6,7]]]d1={x[0]:x[1] for x in l1}
l1 = [[1,2],[3,4],[5,[6,7]]]d1={x[0]:x[1] for x in l1}
It will iterate through the list.
它将遍历列表。
It will take the item at index 0 as key and index 1 as value.
它将把物品放在 索引0 作为键,索引1作为值。
-
l1 = [[1,2],[3,4],[5,[6,7]]] -
d1={x[0]:x[1] for x in l1} -
print(d1)#Output:{1: 2, 3: 4, 5: [6, 7]}
10.使用Counter()将列表转换为字典 (10. Converting a List to a Dictionary Using Counter())
“
Counter: Counter is a dict subclass for counting hashable objects. It is a collection where elements are stored as dictionary keys and their counts are stored as dictionary values. Counts are allowed to be any integer value including zero or negative counts.” — Python documentation“
Counter: Counter是用于计算可哈希对象的dict子类。 它是一个集合,其中元素存储为字典键,其计数存储为字典值。 计数可以是任何整数值,包括零或负计数。” — Python 文档
collections.Counter(iterable-or-mapping)Counter() will convert list items to keys and their frequencies to values.
Counter() 将列表项转换为键,并将其频率转换为值。
-
from collections import Counter -
c1=Counter(['c','b','a','b','c','a','b']) -
#key are elements and corresponding values are their frequencies -
print (c1)#Output:Counter({'b': 3, 'c': 2, 'a': 2}) -
print (dict(c1))#Output:{'c': 2, 'b': 3, 'a': 2}





















 1万+
1万+











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








