认识异常过滤器-以及简单的示例
什么是异常过滤器
一定要养成看文档的习惯,文档
下面是官方的说法。
Nest内置了一个异常层,负责处理应用程序中所有未处理的异常。当应用程序代码未处理异常时,该层会捕获异常,然后自动发送适当的用户友好响应。
之前我们的课程中有看到404的异常,其实就是nest本身帮我们做了处理,而nest也支持我们自己对异常进行处理。
在开始前,我们先把之前中间件的引入注释掉。

生成一个 Exception filter
请出我们的老朋友 nest g

一样的,我们在apps/demo/src下生成
nest g f custom-error

import { ArgumentsHost, Catch, ExceptionFilter } from '@nestjs/common';
@Catch()
export class CustomErrorFilter<T> implements ExceptionFilter {
catch(exception: T, host: ArgumentsHost) {}
}
引入
有多种引入方式
Module内引入
Module引入和中间件不同,我们可以简单了解下providers,我直接百度翻译:提供者是Nest的核心概念。许多基本的Nest类,如服务、存储库、工厂和助手,都可以被视为提供者。提供者背后的关键思想是,它可以作为依赖项注入,允许对象之间形成各种关系。“连接”这些对象的责任主要由Nest运行时系统处理。
可以理解为,module是人,controller是核心,其他构件如service,拦截器,守卫等等一起构成了人的运行。所以我们可以在module中把它当个provide,而且nest也内置了这些的名称


import { MiddlewareConsumer, Module, NestModule } from '@nestjs/common';
import { Demo2Service } from './demo2.service';
import { Demo2Controller } from './demo2.controller';
import { ResponseMiddleware } from '../response/response.middleware';
import { LoggerMiddleware } from '../logger/logger.middleware';
import { APP_FILTER } from '@nestjs/core';
import { CustomErrorFilter } from '../custom-error/custom-error.filter';
@Module({
controllers: [Demo2Controller],
providers: [Demo2Service,{
provide:APP_FILTER,
useClass:CustomErrorFilter
}],
})
export class Demo2Module implements NestModule {
configure(consumer: MiddlewareConsumer) {
consumer
.apply( LoggerMiddleware,ResponseMiddleware)
.forRoutes(Demo2Controller);
}
}
为某个controller引入

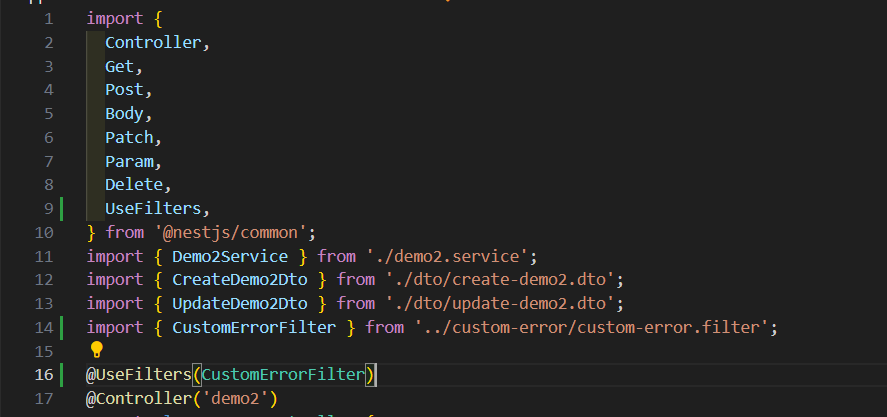

整个应用引入

app.useGlobalFilters(new CustomErrorFilter())
这里其实还可以为构造器传递参数,不过你要在异常过滤器中完善构造函数。
编写逻辑
这里我们使用hello2这个get请求来做测试。
注释掉其它地方对filter的引入,保留整个应用的引入。
由于我们把中间件注释掉了,所以这里没有data,code,message那些包裹。

import { ArgumentsHost, Catch, ExceptionFilter } from '@nestjs/common';
@Catch()
export class CustomErrorFilter<T> implements ExceptionFilter {
catch(exception: T, host: ArgumentsHost) {}
}
目前我们的代码是这样。我们修改下demo2.controller.ts中的hello2
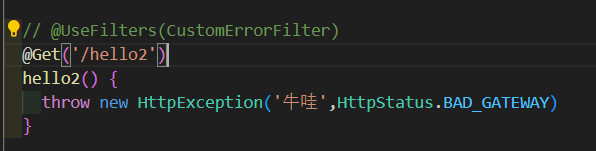
拦截所有异常
过滤器代码如下,此时所有的异常都会经过这里的处理。目前我们正常返回了。此时调用请求,localhost:3000/demo2/hello2
@Catch()
export class CustomErrorFilter<T> implements ExceptionFilter {
catch(exception: T, host: ArgumentsHost) {
const ctx = host.switchToHttp();
const response = ctx.getResponse<Response>();
const request = ctx.getRequest<Request>();
console.error(exception)
// console.log(response)
response.json()
}
}

换个异常呢
import { BadGatewayException } from '@nestjs/common';
throw new BadGatewayException('真牛')

这里是拦截了所有的异常进行处理。那么如何返回异常响应呢。
这里先把 exception 类型改成any,我们把response的status改成异常的status如果没有就用BAD_REQUEST(400)。
@Catch()
export class CustomErrorFilter<T> implements ExceptionFilter {
catch(exception: any, host: ArgumentsHost) {
const ctx = host.switchToHttp();
const response = ctx.getResponse<any>();
const request = ctx.getRequest<Request>();
const status = Number(exception.status || HttpStatus.BAD_REQUEST);
response.status(status).json({
code:status,
message:exception.message || '请求异常'
})
}
}
会返回下面响应。

对Error呢
@Get('/hello2')
hello2() {
// return '嗨,哥们,喝多了啊。';
throw new Error('真牛')
// throw new HttpException('牛哇',HttpStatus.BAD_GATEWAY)
}
@Catch()
export class CustomErrorFilter<T> implements ExceptionFilter {
catch(exception: HttpException, host: ArgumentsHost) {
const ctx = host.switchToHttp();
const response = ctx.getResponse<any>();
const request = ctx.getRequest<Request>();
const status = 400
response.status(status).json({
code:status,
message:exception.message || '请求异常',
isCatch:true
})
}
}
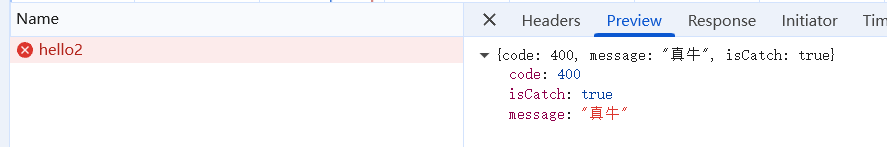
拦截单个异常
上面我们对所以异常进行了拦截,无论是HttpException还是Error都可以拦截,那如果只对某个请求进行拦截呢。如HttpException。
只需要在Catch中填入你想要的异常即可。
import { ArgumentsHost, Catch, ExceptionFilter, HttpException } from '@nestjs/common';
@Catch(HttpException)
export class CustomErrorFilter<T> implements ExceptionFilter {
catch(exception: HttpException, host: ArgumentsHost) {
const ctx = host.switchToHttp();
const response = ctx.getResponse<any>();
const request = ctx.getRequest<Request>();
const status = exception.getStatus()
response.status(status).json({
code:status,
message:exception.message || '请求异常'
})
}
}
这个时候我们再抛出Error
@Get('/hello2')
hello2() {
// return '嗨,哥们,喝多了啊。';
throw new Error('真牛')
// throw new HttpException('牛哇',HttpStatus.BAD_GATEWAY)
}
哎!发现并没有走我们的拦截器,而是走了nest自己处理的。

改为抛出http异常
@Get('/hello2')
hello2() {
// return '嗨,哥们,喝多了啊。';
// throw new Error('真牛')
throw new HttpException('牛哇',HttpStatus.BAD_GATEWAY)
}

是不是很Nice
拦截自定义异常
可以拦截异常,那么如果我们不想把一些业务异常当作真的错误,可以自定义一套异常处理。
我们自定义了一套异常处理逻辑,自定义异常类 CustomException ,Catch过滤 CustomException 。所有的响应都是200。只是额外返回了业务逻辑错误code.
import { ArgumentsHost, Catch, ExceptionFilter, HttpException, HttpExceptionOptions } from '@nestjs/common';
export enum BusinessErrorStatus {
BE_DRUNK = 50001
}
const BusinessErrorStatusTxt: { [key: number]: string } = {
[BusinessErrorStatus.BE_DRUNK]: "喝醉了,进行不了业务了"
}
export class CustomException extends HttpException {
code: BusinessErrorStatus;
constructor(code: BusinessErrorStatus, options?: HttpExceptionOptions) {
const message = BusinessErrorStatusTxt[code]
super(message, 200, options)
this.code = code
}
}
@Catch(CustomException)
export class CustomErrorFilter<T> implements ExceptionFilter {
catch(exception: CustomException, host: ArgumentsHost) {
const ctx = host.switchToHttp();
const response = ctx.getResponse<any>();
const request = ctx.getRequest<Request>();
const status = exception.getStatus()
const code = exception.code;
response.status(status).json({
code: code,
message: exception.message || '请求异常',
isCatch: true
})
}
}
来试一下吧.
在demo2.controller.ts中修改hello2
@Get('/hello2')
hello2() {
throw new CustomException(BusinessErrorStatus.BE_DRUNK)
}

思考
我们的自定义异常是继承了http异常,那我们此时还能捕获到http异常吗?
我们改下hello2 尝试一下。
@Get('/hello2')
hello2() {
throw new HttpException('牛哇', HttpStatus.BAD_GATEWAY)
}
并没有。因为你捕获的是儿子(后代),爹可没儿子的基因。
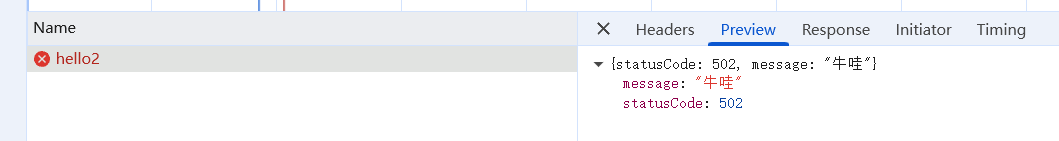
那如果我们抛出的是自定义异常,捕获的是http异常呢

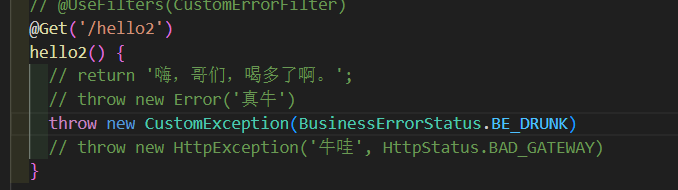

又能捕获了,为什么啊,简单来说就是,他儿带着爹的基因啊。
还有一些异常,我们自己可以知道,但是没必要抛出的,如数据库异常,其他异常等等,都可以做对应的处理,或者拦截所有异常,自己返回异常逻辑。


























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










