文章目录
对于排序以及优先队列回调函数的探究
1. sort的cmp参数
sort函数的原型为
template<class _RanIt,
class _Pr> inline
void sort(const _RanIt _First, const _RanIt _Last, _Pr _Pred)
{ // order [_First, _Last), using _Pred
_Adl_verify_range(_First, _Last);
const auto _UFirst = _Get_unwrapped(_First);
const auto _ULast = _Get_unwrapped(_Last);
_Sort_unchecked(_UFirst, _ULast, _ULast - _UFirst, _Pass_fn(_Pred));
}
sort函数cmp参数的使用
vector<int> v{ 1,5,6,9,3,2 };
auto cmp = [](const int& a, const int& b) {
return a < b;
};
sort(v.begin(), v.end(), cmp);
sort函数cmp的比较规则
还是对于上述的代码
vector<int> v{ 1,5,6,9,3,2};
auto cmp = [](const int& a, const int& b) {
return a < b;
};
sort(v.begin(), v.end(), cmp);
for (int e : v) {
cout << e << " ";
}
// 结果为:
// 1 2 3 5 6 9
- 而当cmp函数为
return a > b时,输出为9 6 5 3 2 1; - 可见当cmp函数中为小于号时,为从小到大排序,为大于号时,为从大到小排序;
- 至于其他的排序规则,比如按照绝对值、平方等等,原理都是类似的;当参数a和b相比时,a相对于b的排序规则(大小等等),就是整个序列的排序规则
做一个检验,想让绝对值小的排在前面
vector<int> v{ -1,5,-6,9,-3,2};
auto cmp = [](const int& a, const int& b) {
return abs(a) < abs(b);
};
sort(v.begin(), v.end(), cmp);
for (int e : v) {
cout << e << " ";
}
// 结果为:
// -1 2 -3 5 -6 9
这里再顺带插一嘴C++sort函数原理:先使用快排,当分割的次数(递归层数)过多时,采用堆排序;若分割次数很少,则采用插入排序即可。
2. priority_queue的cmp模板参数
priority_queue的模板原型
// CLASS TEMPLATE priority_queue
template<class _Ty,
class _Container = vector<_Ty>,
class _Pr = less<typename _Container::value_type> >
class priority_queue
{ // priority queue implemented with a _Container
public:
typedef _Container container_type;
typedef _Pr value_compare;
typedef typename _Container::value_type value_type;
/*
...
*/
};
priority_queue模板的使用
using P = pair<string, int>;
struct cmp{
bool operator()(const P& p1, const P& p2) {
if(p1.second == p2.second) return p1.first > p2.first;
return p1.second < p2.second;
}
};
priority_queue<P, vector<P>, cmp> q;
// 或者
auto cmp = [](const P& p1, const P& p2){
if(p1.second == p2.second) return p1.first > p2.first;
return p1.second < p2.second;
};
priority_queue<P, vector<P>, decltype(cmp)> q(cmp);
priority_queue中cmp的比较规则
若熟悉优先队列的原理,不难想到,优先队列的排序或者比较不像sort一样(前后互换位置),而是节点的上浮下沉。所以类似于sort中cmp的比较规则:当cmp的参数a和b相比时,a相对于b的排序规则的节点会下沉,例如:
vector<int> v{ 5, 6, 9, 3, 8, 2 };
auto cmp = [](const int& a, const int& b) {
return a < b;
};
priority_queue<int, vector<int>, decltype(cmp)> q(v.begin(), v.end(), cmp);
while (!q.empty()) {
cout << q.top() << " ";
q.pop();
}
// 结果为:
// 9 8 6 5 3 2
可以看出,cmp函数中为a < b,即值小的节点会下沉,所以整个优先队列是一个大顶堆
priority_queue的练习题
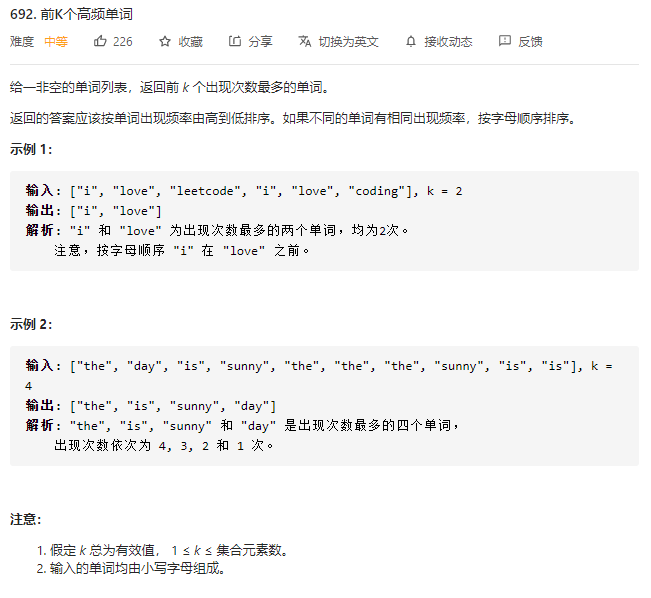
-
解题思路 – 1
- 题目要求频率高的词在前面,相同词频的,字典序小的在前面
- 若使用优先队列来做,很容易想到,应该对词频建立最大堆,对字典序建立最小堆
-
代码
class Solution {
public:
using P = pair<string, int>;
struct cmp{
bool operator()(const P& p1, const P& p2) {
// 字典序最小堆
if(p1.second == p2.second) return p1.first > p2.first;
// 词频最大堆
return p1.second < p2.second;
}
};
vector<string> topKFrequent(vector<string>& words, int k) {
// 使用 map 来统计词频
map<string, int> mp;
for(string& word : words){
mp[word]++;
}
// 将所有的 pair压入队列
priority_queue<P, vector<P>, cmp> q{mp.begin(), mp.end()};
vector<string> ret;
// 取前 k 个高频词
while(k){
ret.push_back(q.top().first);
q.pop();
--k;
}
return ret;
}
};
当前代码的空间复杂度为:O(N);时间复杂度为:O(NlogN) 【实际是要小于该结果的,应该为O(log(N!))】
-
解题思路 – 2
- 上述代码由于使用了最大堆(词频),需要维护所有压入队列的元素,时间复杂度可能偏高;故我们也可以使用 最小堆(词频),只需要维护前K个元素,复杂度降低
-
代码
class Solution {
public:
using P = pair<string, int>;
struct cmp{
bool operator()(const P& p1, const P& p2) {
// 字典序最大堆
if(p1.second == p2.second) return p1.first < p2.first;
// 词频最小堆
return p1.second > p2.second;
}
};
vector<string> topKFrequent(vector<string>& words, int k) {
// 使用 map 统计词频
map<string, int> mp;
for(string& word : words){
mp[word]++;
}
priority_queue<P, vector<P>, cmp> q;
// 所有元素压入队列
for(const auto& e : mp){
q.push(e);
// 但只维护前 K 个元素,因为堆顶元素词频小且字典序大
if(q.size() > k) q.pop();
}
vector<string> ret;
while(!q.empty()){
ret.push_back(q.top().first);
q.pop();
}
// 需要将结果反转
reverse(ret.begin(), ret.end());
return ret;
}
};
当前代码的空间复杂度:O(N),时间复杂度:O(NlogK)【实际也要小于该结果】























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








