前言:
在好多面试上 面试官都会问到这个问题,为什么是这样? 本篇文章就带大家探索一下,如何实现这一操作。
例一
Integer a=128;
Integer b=128;
System.out.println(a==b);
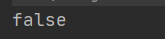
输出结果: 不相等
Integer c=127;
Integer d=127;
System.out.println(c==d);
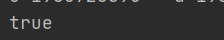
c和d 变量输出 就是相等,这是为什么那 128就不相等,127就相等,我们来看看源码实现
二、源码查看
public static Integer valueOf(int i) {
if (i >= IntegerCache.low && i <= IntegerCache.high)
return IntegerCache.cache[i + (-IntegerCache.low)];
return new Integer(i);
}
private static class IntegerCache {
static final int low = -128;
static final int high;
static final Integer cache[];
static {
// high value may be configured by property
int h = 127;
String integerCacheHighPropValue =
sun.misc.VM.getSavedProperty("java.lang.Integer.IntegerCache.high");
if (integerCacheHighPropValue != null) {
try {
int i = parseInt(integerCacheHighPropValue);
i = Math.max(i, 127);
// Maximum array size is Integer.MAX_VALUE
h = Math.min(i, Integer.MAX_VALUE - (-low) -1);
} catch( NumberFormatException nfe) {
// If the property cannot be parsed into an int, ignore it.
}
}
high = h;
cache = new Integer[(high - low) + 1];
int j = low;
for(int k = 0; k < cache.length; k++)
cache[k] = new Integer(j++);
// range [-128, 127] must be interned (JLS7 5.1.7)
assert IntegerCache.high >= 127;
}
IntegerCache 注意看 是一个静态内部类, 它的常量low=-128 下面还有一个static静态块, h赋值是127 。
当jvm启动时静态类和静态块会优先加载,我就先不说类的加载顺序了,会把这些数值存在 命名为cache[] 数组中,加载到了常量池中
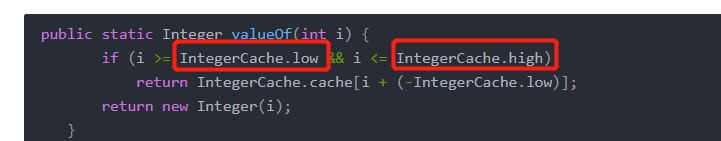
IntegerCache.low 初始化值是-128
IntegerCache.high初始化值是 127
那么当我赋值 Integer a=128 的时候, a大于-128 但是不小于127 , 所以走 new Integer, 是个新对象
我再赋值一个 Integer b=128 进来也是这样的流程,也会new Integer 这时用== 他们两个对象地址都是new的 是个全新的, 所以是不相等。
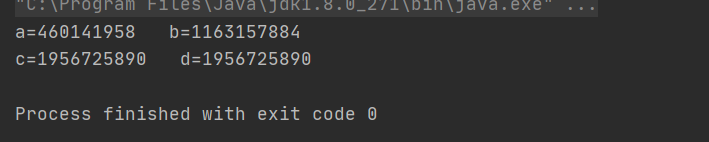
所以Integer c=127 和Integer d=127 取得都是同一个对象的地址。因为127存在常量池中
使用System.identityHashCode() 这个方法会输出改对象的地址。
Integer a=128;
Integer b=128;
System.out.println("a="+System.identityHashCode(b)+""+"b="+System.identityHashCode(a));
Integer c=127;
Integer d=127;
System.out.println("c="+System.identityHashCode(c)+" "+"d="+System.identityHashCode(d));
例二
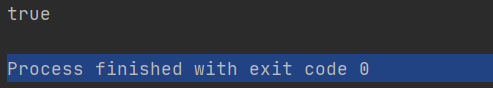
System.out.println(Integer.valueOf("127").equals(Integer.valueOf("127")));
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
if (obj instanceof Integer) {
return value == ((Integer)obj).intValue();
}
return false;
}





















 2870
2870











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








