一,Collection和Map
练习1:
• 键盘录入学生信息,保存到集合中。
o 循环录入的方式,1:表示继续录入,0:表示结束录入。
o 定义学生类,属性为姓名,年龄,使用学生对象保存录入数据。
o 使用ArrayList集合,保存学生对象,录入结束后,用foreach遍历集合。
• 代码实现,效果如图所示:

public class StudentTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
ArrayList stuList = new ArrayList();
for (;;) {
System.out.println("选择(录入 1 ;结束 0)");
int x = scanner.nextInt();//根据x的值,判断是否需要继续循环
if (x == 1) {
System.out.println("姓名");
String name = scanner.next();
System.out.println("年龄");
int age = scanner.nextInt();
Student stu = new Student(age, name);
stuList.add(stu);
} else if (x == 0) {
break;
} else {
System.out.println("输入有误,请重新输入");
}
}
for (Object stu : stuList) {
System.out.println(stu);
}
}
}
练习2:
• 随机生成30个数,范围2-100,获取其中的质数。
• 代码实现,效果如图所示:
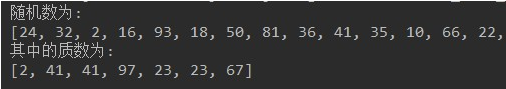
写法一:
public class PrimeNumberPrintTest1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList numberList = new ArrayList();
int num = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 30; i++) {
//随机数random*(b-a+1)+a
num = (int)(Math.random() * (100-2+1) ) + 2;
if(!numberList.contains(num)){
numberList.add(num);
}else{
i--;
}
}
System.out.println(numberList);
ArrayList primeList = new ArrayList();//用于存储所有的质数
int j;
boolean flag;
for (int i = 0; i < numberList.size(); i++) {
flag = false;
int number = (int) numberList.get(i);
for (j = 2; j <= Math.sqrt(number); j++) {
if (number % j == 0){
flag = true;
break;
}
}
if (!flag){
primeList.add(number);
}
}
System.out.println("当前随机数中的质数有:");
for(Object obj : primeList){
System.out.println(obj);
}
}
}
写法二:
public class PrimeNumberPrintTest2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List numberList = generateRandomNumber(30, 2, 100);
System.out.println(numberList);
List primeList = getPrimeNumber(numberList);
System.out.println("当前随机数中的质数有:");
System.out.println(primeList);
}
/**
* 获取30个随机数,范围为2-100
*
* @Description
* @author shkstart
* @date 2020年3月16日上午9:34:37
* @param size
* @param startNumber
* @param endNumber
* @return
*/
private static List generateRandomNumber(int size, int startNumber, int endNumber) {
ArrayList numberList = new ArrayList();
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
int num = (int) (Math.random() * (endNumber - startNumber + 1)) + startNumber;
if (!numberList.contains(num)) {
numberList.add(num);
} else {
i--;
}
}
return numberList;
}
/**
* 获取指定List中所有数值中的质数
* @Description
* @author shkstart
* @date 2020年3月16日上午9:37:08
* @param numberList
* @return
*/
private static List getPrimeNumber(List numberList) {
ArrayList primeList = new ArrayList();// 用于存储所有的质数
for (int i = 0; i < numberList.size(); i++) {
boolean flag = false;
int number = (int) numberList.get(i);
for (int j = 2; j <= Math.sqrt(number); j++) {
if (number % j == 0) {
flag = true;
break;
}
}
if (!flag) {
primeList.add(number);
}
}
return primeList;
}
}
二、复习
-
字符串相关的类:String\StringBuffer\StringBuilder (重点)
-
比较器:Comparable \ Comparator (可以实现java中的对象比较大小、排序) (重点)
-
日期时间的API
- jdk 8之前的API:java.util.Date (子类:java.sql.Date) 、Calendar、SimpleSDateFormat(格式化、解析)
- jdk8中API:Instant、LocalDate\LocalTime\ LocalDateTime、DateTimeFormater
-
其他的常用类:BigInteger、BigDecimal
-
Collection\List\Set\Map存储数据的特点
-
Collection中的常用方法(掌握)
- 遍历时,使用迭代器(Iterator)
-
List
- List中的常用方法: 增、删、改、查、插、长度、遍历
- 三个实现类的对比—>面试题
- ArrayList、LinkedList的源码分析
三、List的源码分析
3.1 ArrayList的源码分析
3.1 jdk7版本:
* ArrayList list = new ArrayList();//初始化底层的elementDate的Object[]数组,长度为10.
* list.add(123);//elementDate[0] = new Integer(123);
* ...
* list.add("AA");//一旦添加的数据的个数超出了底层数组的长度10,需要考虑扩容。
* 默认容量扩容扩容为原来的1.5倍,同时将旧数组中的数据都复制到新的数组中。
*
源码情况:
/**
* Constructs an empty list with an initial capacity of ten.
*/
public ArrayList() {
this(10);
}
#######################
/**
* Constructs an empty list with the specified initial capacity.
*
* @param initialCapacity the initial capacity of the list
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if the specified initial capacity
* is negative
*/
public ArrayList(int initialCapacity) {
super();
if (initialCapacity < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal Capacity: "+
initialCapacity);
this.elementData = new Object[initialCapacity];
}
#######################
public boolean add(E e) {
ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1); // Increments modCount!!
elementData[size++] = e;
return true;
}
在添加数据之前,需要先判断底层数组的容量是否够:ensureCapacityInternal()
#######################
private void ensureCapacityInternal(int minCapacity) {
modCount++;
// overflow-conscious code
if (minCapacity - elementData.length > 0)
grow(minCapacity); //满足条件的情况,底层进行扩容
}
#######################
private void grow(int minCapacity) {
// overflow-conscious code
int oldCapacity = elementData.length;
int newCapacity = oldCapacity + (oldCapacity >> 1);//默认扩容比例:1.5倍
//特殊情况的扩容比例:
if (newCapacity - minCapacity < 0)
newCapacity = minCapacity;
if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0)
newCapacity = hugeCapacity(minCapacity);
//创建新长度的数组,并将原有数组中的数据copy到新的数组中。
elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity);
}
* 3.2 jdk8版本:
* ArrayList list = new ArrayList();//初始化底层elementData的Object[]数组为{}
* list.add(123);//此时底层创建长度为10的elementData数组,并将new Integer(123)存放到角标0的索引位置。
* 。。。
* list.add("AA");//一旦添加的数据的个数超出了底层数组的长度10,需要考虑扩容。
* 默认容量扩容扩容为原来的1.5倍,同时将旧数组中的数据都复制到新的数组中。
源码:
/**
* Constructs an empty list with an initial capacity of ten.
*/
public ArrayList() {
this.elementData = DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA;
}
#######################
private static final Object[] DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {};
#######################
public boolean add(E e) {
ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1); // Increments modCount!!
elementData[size++] = e;
return true;
}
#######################
private void ensureCapacityInternal(int minCapacity) {
//如果是首次调用add(),则此时的minCapacity赋值为10
if (elementData == DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA) {
minCapacity = Math.max(DEFAULT_CAPACITY, minCapacity);
}
//如果是首次添加,调用此方法,将原有的{}替换为长度为10的Object[]数组
ensureExplicitCapacity(minCapacity);
}
#######################
private void ensureExplicitCapacity(int minCapacity) {
modCount++;
// overflow-conscious code
if (minCapacity - elementData.length > 0)
grow(minCapacity);
}
#######################
private void grow(int minCapacity) {
// overflow-conscious code
int oldCapacity = elementData.length;
int newCapacity = oldCapacity + (oldCapacity >> 1);
if (newCapacity - minCapacity < 0)
newCapacity = minCapacity;
if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0)
newCapacity = hugeCapacity(minCapacity);
// minCapacity is usually close to size, so this is a win:
elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity);
}
* 3.3 说明:
* jdk7中ArrayList底层的数组的创建类似于单例模式中的饿汉式,jdk8中ArrayList底层的数组的创建类似于单例模式中的懒汉式
*
3.2 Vector的源码分析
* Vector v = new Vector();
* v.add(123);
* 。。。
* > jdk7和jdk8中在创建对象时,底层的操作相同,都是创建长度为10的Object[]。
* > 当底层容量不足时,默认扩容为原来的2倍
源码:
public Vector() {
this(10);
}
public Vector(int initialCapacity) {
this(initialCapacity, 0);
}
public Vector(int initialCapacity, int capacityIncrement) {
super();
if (initialCapacity < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal Capacity: "+
initialCapacity);
this.elementData = new Object[initialCapacity];
this.capacityIncrement = capacityIncrement;
}
private void grow(int minCapacity) {
// overflow-conscious code
int oldCapacity = elementData.length;
int newCapacity = oldCapacity + ((capacityIncrement > 0) ?
capacityIncrement : oldCapacity);
if (newCapacity - minCapacity < 0)
newCapacity = minCapacity;
if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0)
newCapacity = hugeCapacity(minCapacity);
elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity);
}
3.3 LinkecList的源码分析
* LinkedList list = new LinkedList();
* list.add(123);
* ....
*
* 底层的Node为:记录了当前元素的前一个元素和后一个元素。证明:LinkedList中是双向链表
* private static class Node<E> {
E item;
Node<E> next;
Node<E> prev;
Node(Node<E> prev, E element, Node<E> next) {
this.item = element;
this.next = next;
this.prev = prev;//前向指针的产生
}
}
*
* LinkedList在添加数据时,元素封装在Node对象中,并指明其前一个和后一个元素。
* LinkedList不存在添加时,考虑扩容的问题。因为底层不是使用的数组,在内存中多个元素也不是连续存放的。
源码:
/**
* Constructs an empty list.
*/
public LinkedList() {
}
#########################
public boolean add(E e) {
linkLast(e);
return true;
}
#########################
transient Node<E> first;
transient Node<E> last;
void linkLast(E e) {
final Node<E> l = last;
final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(l, e, null);
last = newNode;
if (l == null) //返回true,表示是首次添加
first = newNode;
else //表示不是首次添加
l.next = newNode;//后向指针的产生
size++;
modCount++;
}
#########################
private static class Node<E> {
E item;
Node<E> next;
Node<E> prev;
Node(Node<E> prev, E element, Node<E> next) {
this.item = element;
this.next = next;
this.prev = prev;//前向指针的产生
}
}
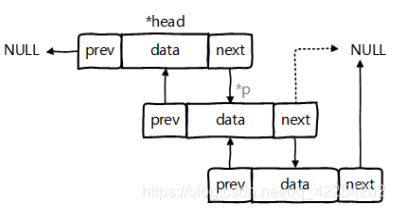
3.4 结论
* 小结
* 1. 建议开发中,如果基本确定底层数组的容量,建议使用带参数的构造器
* ArrayList list = new ArrayList(int initialCapacity);//new Object[initialCapacity];
* 避免底层不断的扩容和复制操作
* 2. 对于数组来说,查找操作的复杂度是O(1),插入或删除操作的复杂度是O(n)
* 对于链表来说,查找操作的复杂度是O(n),插入或删除操作的复杂度是O(1)
*
* 开发中,如果很少执行插入或删除操作,建议使用ArrayList
* 如果频繁的使用插入或删除操作,建议使用LinkedList
四、Set的使用
4.1 主要实现类和方法
- 主要实现类就是:HashSet
- 常用方法:Set接口中声明的方法都是Collection接口声明过的。HashSet能使用的就是Collection中定义的方法。
@Test
public void test1(){
Set set = new HashSet();
set.add(223);
set.add(new String("AA"));
set.add("CC");
set.add(223);
set.add(new String("AA"));
set.add(new Person("Tom",12));
set.add(new Person("Tom",12));
set.add(null);
for(Object obj : set){
System.out.println(obj);
}
}
4.2 Set的特性:无序性、不可重复性
① 无序性:不等同于随机性!元素在底层储存的位置不是像数组一样是依次紧密排列的,而是参考其hashCode值决定的存储位置。理解为无序性
② 不可重复性:根据对象的equals()进行判断。如果返回true,则添加失败。保证了不可重复性。
4.3 向HashSet中添加数据的过程
如何将元素添加到HashSet中的呢?
* 前提:HashSet底层也是使用数组+链表+(jdk8:红黑树)存储
* ① 将元素e1添加到HashSet中,首先调用e1所在类的hashCode(),获取e1对象的哈希值。
* ② 此哈希值,经过某种算法以后,获取其在HashSet底层数组中的存放位置。
* ③ 如果此位置上,没有其他任何元素,则e1添加成功 --->情况1
* 如果此位置上,已经存在某个或某几个元素e2,则继续判断。
* ④ 比较e1和e2的哈希值,如果两个哈希值不相同。则e1添加成功。 --->情况2
* 比较e1和e2的哈希值,如果两个哈希值相同,则调用e1所在类的equals()方法
* ⑤ equals()方法返回false,则e1添加成功。 --->情况3
* equals()方法返回true,则e1添加失败。
*
* 情况1:将e1直接保存在数组的指定位置
* 情况2、情况3:此时e1与现有索引位置上的元素,以链表的方式进行保存。
* > jdk7:新的元素e1方法到数组中,指向原有的元素
* > jdk8:已有的元素的末尾指向新的元素e1.
* 总结:"七上八下"
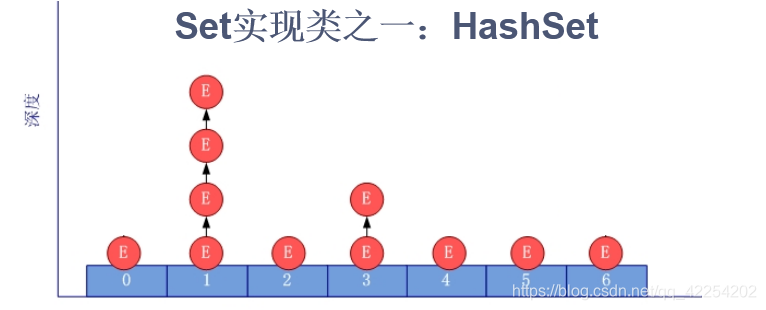
4.4 向HashSet中添加的元素所在类的要求
1. 针对于HashSet或者LinkedHashSet来说,如果多个对象需要存储到上述两个Set中时,为了保证不可重复性,
* 必须要求对象所属的类要重写hashCode()和equals()
2. 重写hashCode()和equals()要保证一致性!相等的对象必须具有相等的散列码
4.5 Set的不同实现类的对比
|-----Collection:存储一个一个的数据
* |-----Set:存储无序的、不可重复的数据: 高中的集合
* |-----HashSet:是Set的主要实现类;线程不安全的;可以存储null值
|-----LinkedHashSet:是HashSet的子类;在添加数据之外,还通过一对指针记录先后添加 的顺序,使得遍历Set元素时,较HashSet效率更高。
|-----TreeSet:可以按照添加的元素的指定的属性的大小进行遍历;底层使用的是红黑树(排序二 叉树的一种)
4.6 LinkedHashSet的测试 (了解)
@Test
public void test2(){
Set set = new LinkedHashSet();
set.add(223);
set.add(new String("AA"));
set.add("CC");
set.add(223);
set.add(new String("AA"));
set.add(new Person("Tom",12));
set.add(new Person("Tom",12));
set.add(null);
for(Object obj : set){
System.out.println(obj);
}
}
对应的图示:
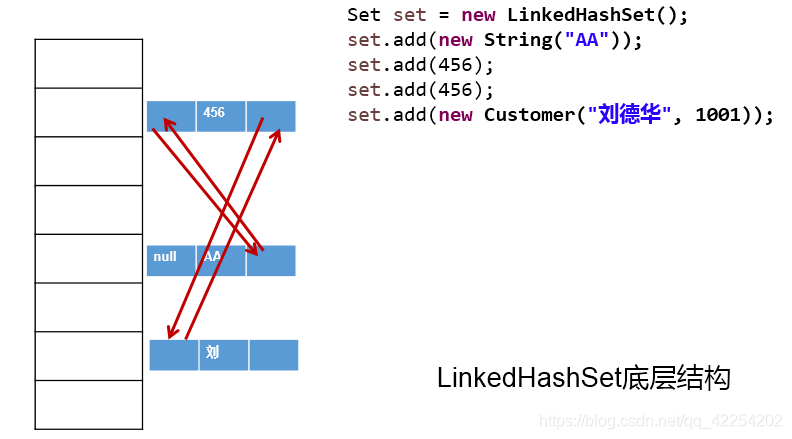
4.7 TreeSet添加数据的情况 (了解)
//1. TreeSet可以按照添加的元素的指定的属性的大小进行遍历;
// 排序的方式有:自然排序,定制排序
//2. TreeSet底层使用的是红黑树(排序二叉树的一种)
//3. 要求:向TreeSet中添加的元素必须是同一个类型的对象。
//4. 说明:TreeSet中不能存放相同的元素。判断的标准不再是元素所在类的hashCode()和equals()了。而是按照自然
// 排序或定制排序中重写的compareTo()或compare()进行比较。
-
自然排序
举例1:
@Test
public void test1(){
TreeSet set = new TreeSet();
set.add("CC");
set.add("MM");
set.add("GG");
set.add("TT");
set.add("JJ");
set.add("KK");
// set.add(123);//报ClassCastException
Iterator iterator = set.iterator();
while(iterator.hasNext()){
System.out.println(iterator.next());
}
}
举例2:
@Test
public void test2(){
TreeSet set = new TreeSet();
Person p1 = new Person("Tom",12);
Person p2 = new Person("Jim",32);
Person p3 = new Person("Jerry",26);
Person p4 = new Person("Mike",43);
Person p5 = new Person("Lily",26);
set.add(p1);
set.add(p2);
set.add(p3);
set.add(p4);
set.add(p5);
Iterator iterator = set.iterator();
while(iterator.hasNext()){
System.out.println(iterator.next());
}
}
其中,Person类定义如下:
public class Person implements Comparable{
private String name;
private int age;
public Person() {
super();
}
public Person(String name, int age) {
super();
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Person [name=" + name + ", age=" + age + "]";
}
/*
@Override
public int hashCode() { //return age + name.hashCode();
final int prime = 31;
int result = 1;
result = prime * result + age;
result = prime * result + ((name == null) ? 0 : name.hashCode());
return result;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
System.out.println("Person equals....");
if (this == obj)
return true;
if (obj == null)
return false;
if (getClass() != obj.getClass())
return false;
Person other = (Person) obj;
if (age != other.age)
return false;
if (name == null) {
if (other.name != null)
return false;
} else if (!name.equals(other.name))
return false;
return true;
}
*/
//先按照年龄从小到大排列,再按照姓名从小到大排
@Override
public int compareTo(Object o) {
if(o instanceof Person){
Person p = (Person)o;
int value = this.age - p.age;
if(value != 0){
return value;
}else{
return this.name.compareTo(p.name);
}
}
throw new RuntimeException("输入的类型不匹配");
}
}
- 定制排序
@Test
public void test3(){
Comparator com = new Comparator(){
@Override
public int compare(Object o1, Object o2) {//o1,o2应该为Person的实例
if(o1 instanceof Person && o2 instanceof Person){
Person p1 = (Person)o1;
Person p2 = (Person)o2;
return -p1.getName().compareTo(p2.getName());
}
return 0;
}
};
TreeSet set = new TreeSet(com);
Person p1 = new Person("Tom",12);
Person p2 = new Person("Jim",32);
Person p3 = new Person("Jerry",26);
Person p4 = new Person("Mike",43);
Person p5 = new Person("Lily",26);
set.add(p1);
set.add(p2);
set.add(p3);
set.add(p4);
set.add(p5);
Iterator iterator = set.iterator();
while(iterator.hasNext()){
System.out.println(iterator.next());
}
}
4.8 课后练习
练习1:
HashSet set = new HashSet();
Person p1 = new Person(1001,"AA");
Person p2 = new Person(1002,"BB");
set.add(p1);
set.add(p2);
p1.name = "CC";
set.remove(p1);
System.out.println(set);
set.add(new Person(1001,"CC"));
System.out.println(set);
set.add(new Person(1001,"AA"));
System.out.println(set);
其中Person类中重写了hashCode()和equal()方法
练习2:
练习:在List内去除重复数字值,要求尽量简单
答案:
public static List duplicateList(List list) {
HashSet set = new HashSet();
set.addAll(list);
return new ArrayList(set);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
List list = new ArrayList();
list.add(new Integer(1));
list.add(new Integer(2));
list.add(new Integer(2));
list.add(new Integer(4));
list.add(new Integer(4));
List list2 = duplicateList(list);
for (Object integer : list2) {
System.out.println(integer);
}
}
练习3:
1. 定义一个Employee类。
该类包含:private成员变量name,age,birthday,其中 birthday 为 MyDate 类的对象;
并为每一个属性定义 getter, setter 方法;
并重写 toString 方法输出 name, age, birthday
MyDate类包含:
private成员变量year,month,day;并为每一个属性定义 getter, setter 方法;
创建该类的 5 个对象,并把这些对象放入 TreeSet 集合中(下一章:TreeSet 需使用泛型来定义)
分别按以下两种方式对集合中的元素进行排序,并遍历输出:
1). 使Employee 实现 Comparable 接口,并按 name 排序
2). 创建 TreeSet 时传入 Comparator对象,按生日日期的先后排序。
五、Map的使用
5.1 Map的架构
|-----Map:存储一对一对的数据(key-value):高中的函数。 y = f(x) (x1,y1),(x2,y2)
* |-----HashMap:主要实现类;线程不安全的,效率高;存储null的key和value
* |-----LinkedHashMap:是HashMap的子类,可以按照添加key-value的顺序实现遍历。
* 底层在HashMap结构的基础上,给前后添加的key-value额外添加了一对指针,记录添加的先后顺序。
* |-----TreeMap:可以按照key-value中的key的大小实现排序遍历。底层使用红黑树实现的
* |-----Hashtable:古老实现类;线程安全的,效率低;不可以存储null的key或value
* |-----Properties:是Hashtable的子类,key和value都是String类型,常用来处理属性文件
*
5.2 HashMap中元素的特点
* Map中的key彼此不可重复、无序 ,使用HashSet存储 ---> key所在的类要重写hashCode()和equals()
* Map中的value无序、可以重复的,使用Collection存储 ---> value所在的类重写equals()
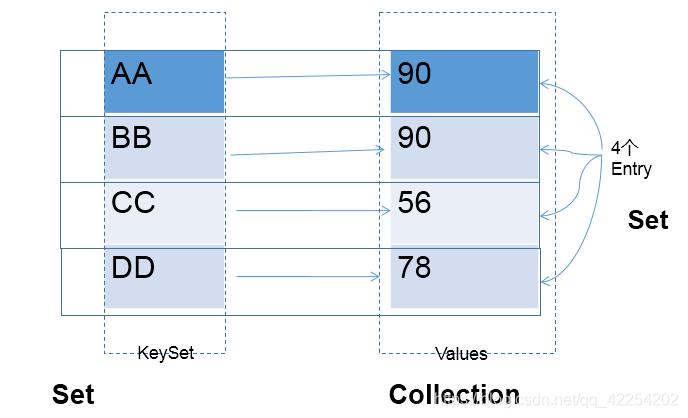
* Map中一个key-value对构成了一个Entry
* Map中的Entry是此次不可重复、无序,使用HashSet存储
对应的图示:
5.3 HashMap的底层实现原理
-
原理的描述
3.1 jdk7中的实现过程: * HashMap map = new HashMap();//底层创建长度为16的Entry数组table * 。。。 * map.put(key1,value1); * * 。。。 * * 1. 当添加key1-vulue1时,首先通过key1所在类的hashCode()方法,计算key1的哈希值 * 2. 此哈希值经过某种算法以后,确定其在table数组中的存放位置:i * 3. 如果table[i]位置为空,则key1-value1添加成功 --->情况1 * 如果table[i]位置不为空,则比较key1与table[i]位置现有元素key2-value2进行对比 * 4.比较key1和key2的哈希值,如果哈希值不相同,则key1-value1添加成功 --->情况2 * 比较key1和key2的哈希值,如果哈希值相同,调用key1所在类的equals(),将key2作为参数传入equals() * 5. 如果equals()返回false,则key1-value1添加成功 --->情况3 * 如果equals()返回true,则用value1替换原有的value2 * * 情况1:将e1直接保存在数组的指定位置 * 情况2、情况3:此时e1与现有索引位置上的元素,以链表的方式进行保存。 * * 3.2 jdk8相较于jdk7的不同: * ① new HashMap():底层并没有创建一个长度为16的数组 * ② 当首次调用put()时,底层才创建长度为16的数组 * ③ jdk8中底层的数组是Node[],而非Entry[] * ④ jdk7:新的元素方法到数组中,指向原有的元素 * jdk8:已有的元素的末尾指向新的元素. * ⑤ 当某一个索引位置上的元素数操作8且数组table的长度超过64时,此索引位置上的所有元素要从链表结构改为红黑树结构 -
源码的显示
- jdk7中:初始化底层数组的源码:HashMap map = new HashMap()
static final int DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY = 16;//默认数组的容量
static final float DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR = 0.75f;//默认的加载因子
transient Entry<K,V>[] table;//保存Map添加的数据
public HashMap() {
this(DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY, DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR);
}
public HashMap(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor) {
if (initialCapacity < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal initial capacity: " +
initialCapacity);
if (initialCapacity > MAXIMUM_CAPACITY)
initialCapacity = MAXIMUM_CAPACITY;
if (loadFactor <= 0 || Float.isNaN(loadFactor))
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal load factor: " +
loadFactor);
// Find a power of 2 >= initialCapacity
int capacity = 1;
while (capacity < initialCapacity) //此循环确定底层数组的长度
capacity <<= 1;
this.loadFactor = loadFactor;
threshold = (int)Math.min(capacity * loadFactor, MAXIMUM_CAPACITY + 1);
table = new Entry[capacity];//确定了底层数组在默认初始化时,长度为16
useAltHashing = sun.misc.VM.isBooted() &&
(capacity >= Holder.ALTERNATIVE_HASHING_THRESHOLD);
init();
}
Entry定义如下:
static class Entry<K,V> implements Map.Entry<K,V> {
final K key;
V value;
Entry<K,V> next;
int hash;
/**
* Creates new entry.
*/
Entry(int h, K k, V v, Entry<K,V> n) {
value = v;
next = n;
key = k;
hash = h;
}
}
-
put操作源码
loadFactor); // Find a power of 2 >= initialCapacity int capacity = 1; while (capacity < initialCapacity) //此循环确定底层数组的长度 capacity <<= 1; this.loadFactor = loadFactor; threshold = (int)Math.min(capacity * loadFactor, MAXIMUM_CAPACITY + 1); table = new Entry[capacity];//确定了底层数组在默认初始化时,长度为16 useAltHashing = sun.misc.VM.isBooted() && (capacity >= Holder.ALTERNATIVE_HASHING_THRESHOLD); init();}
Entry定义如下:
static class Entry<K,V> implements Map.Entry<K,V> {
final K key;
V value;
Entry<K,V> next;
int hash;
/**
* Creates new entry.
*/
Entry(int h, K k, V v, Entry<K,V> n) {
value = v;
next = n;
key = k;
hash = h;
}
}
- put操作源码





















 1662
1662











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








